解题思路:
如下图所示,题目要求实现链表所有「值 $< x$ 节点」出现在「值 $\geq x$ 节点」前面。
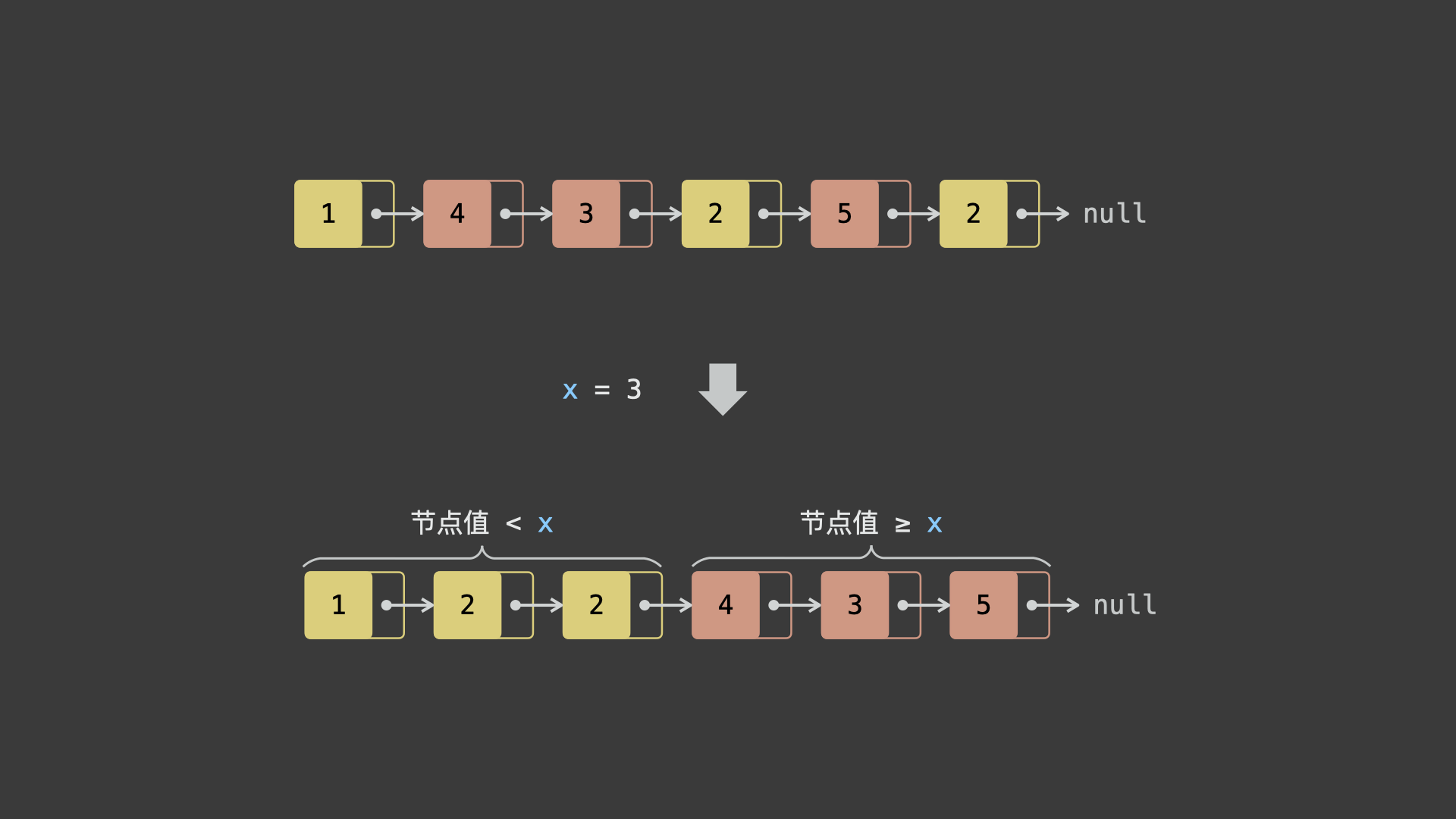
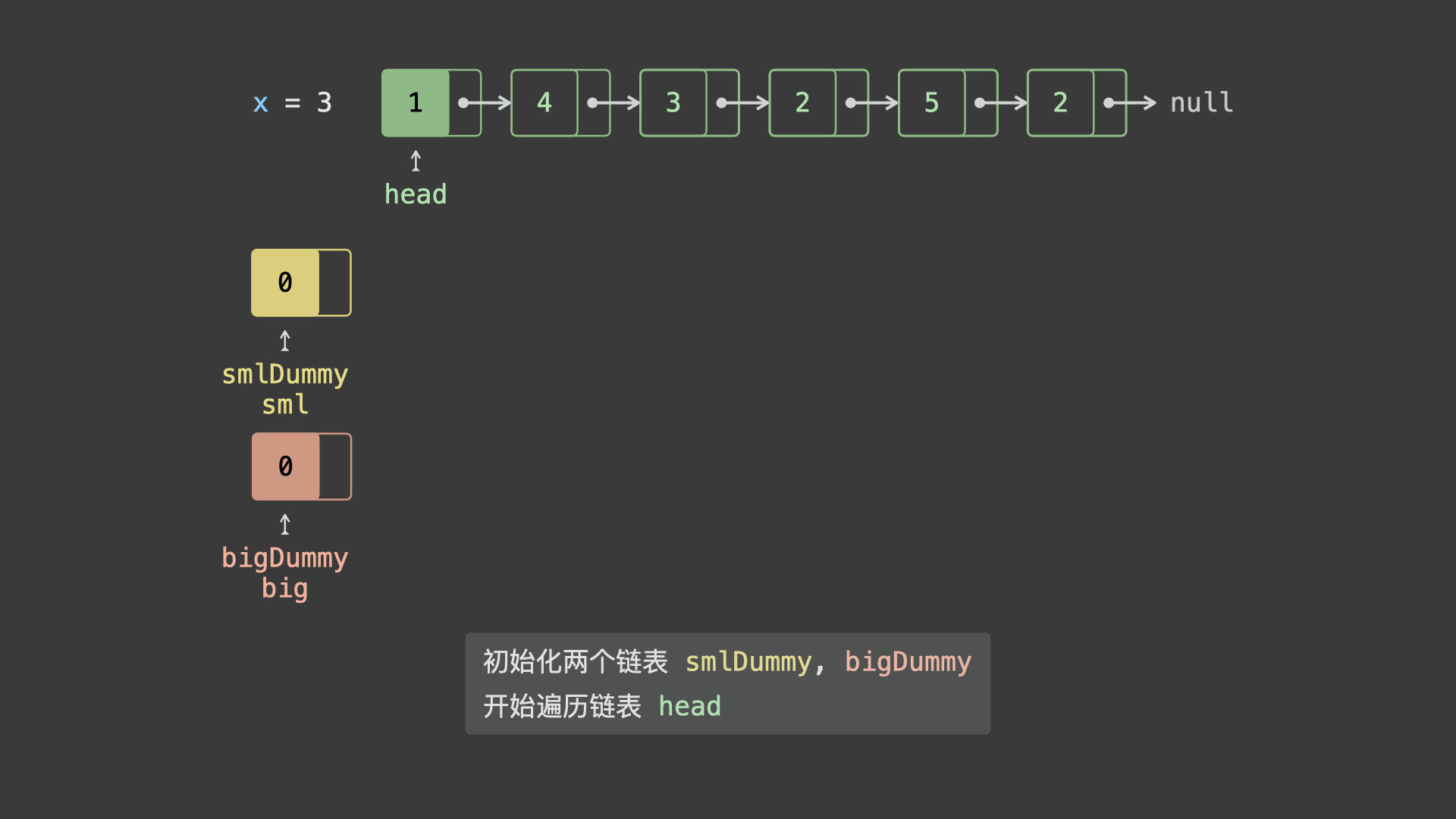
根据题意,考虑通过「新建两个链表」实现原链表分割,算法流程为:
- 新建两个链表
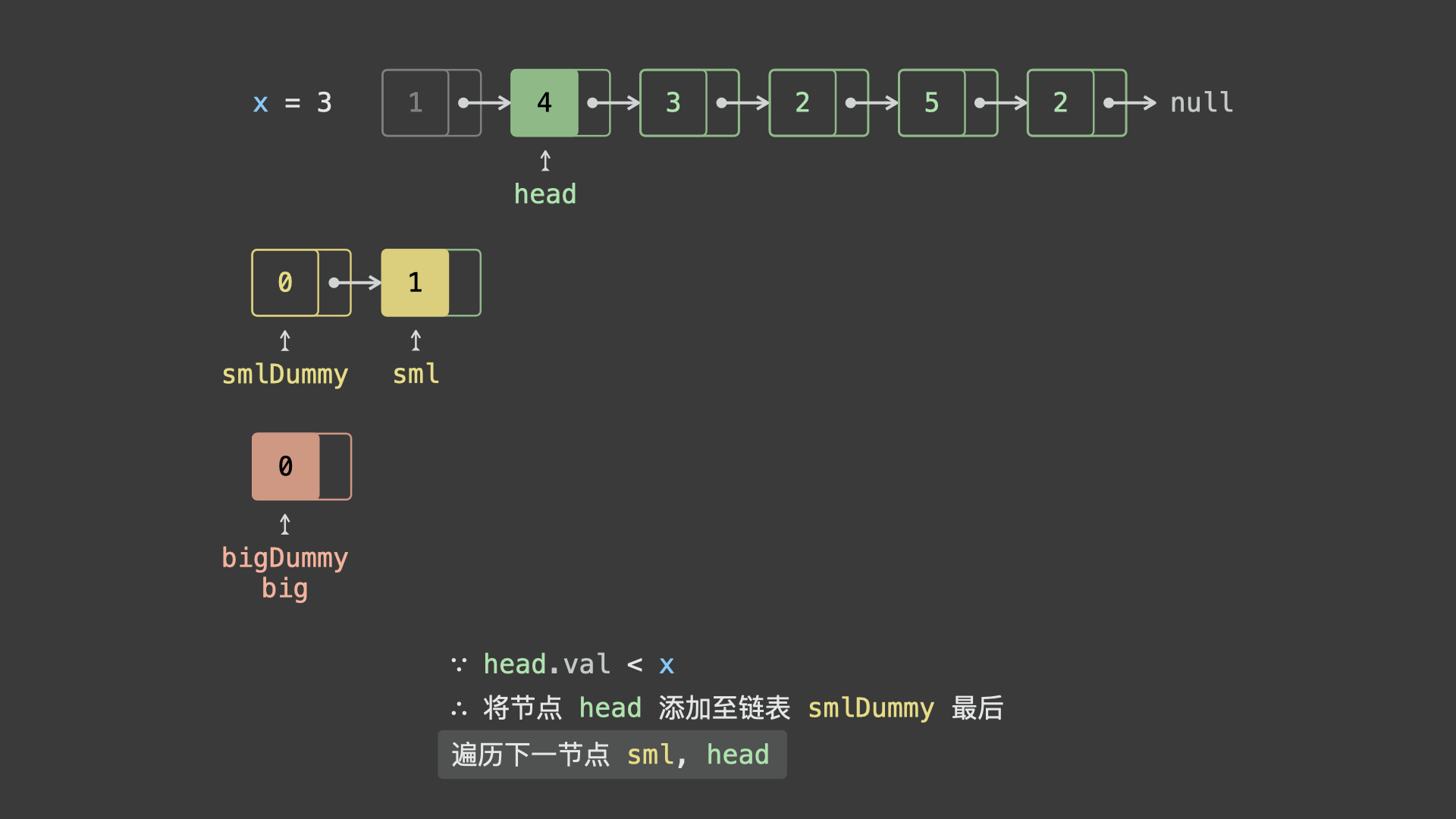
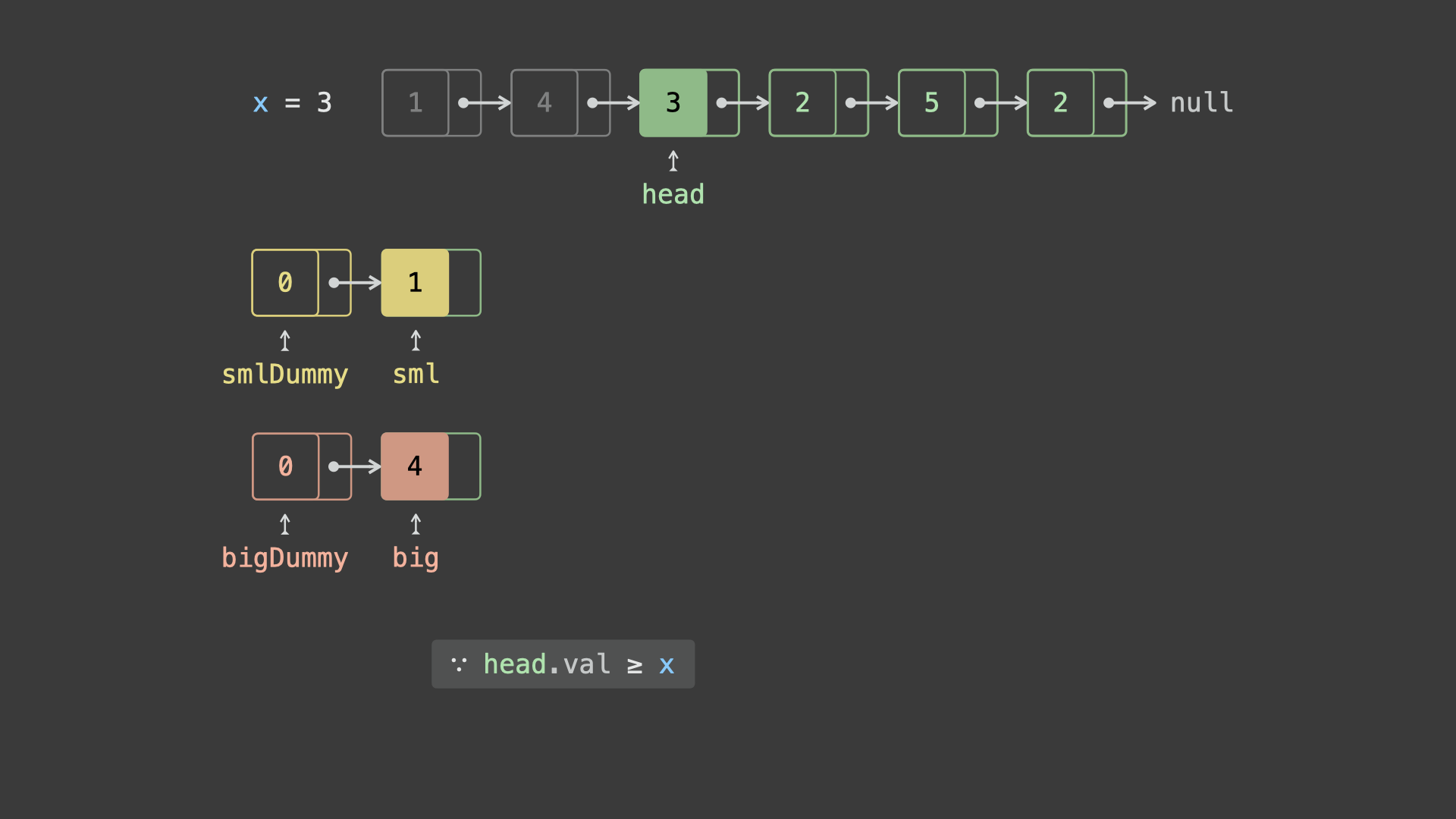
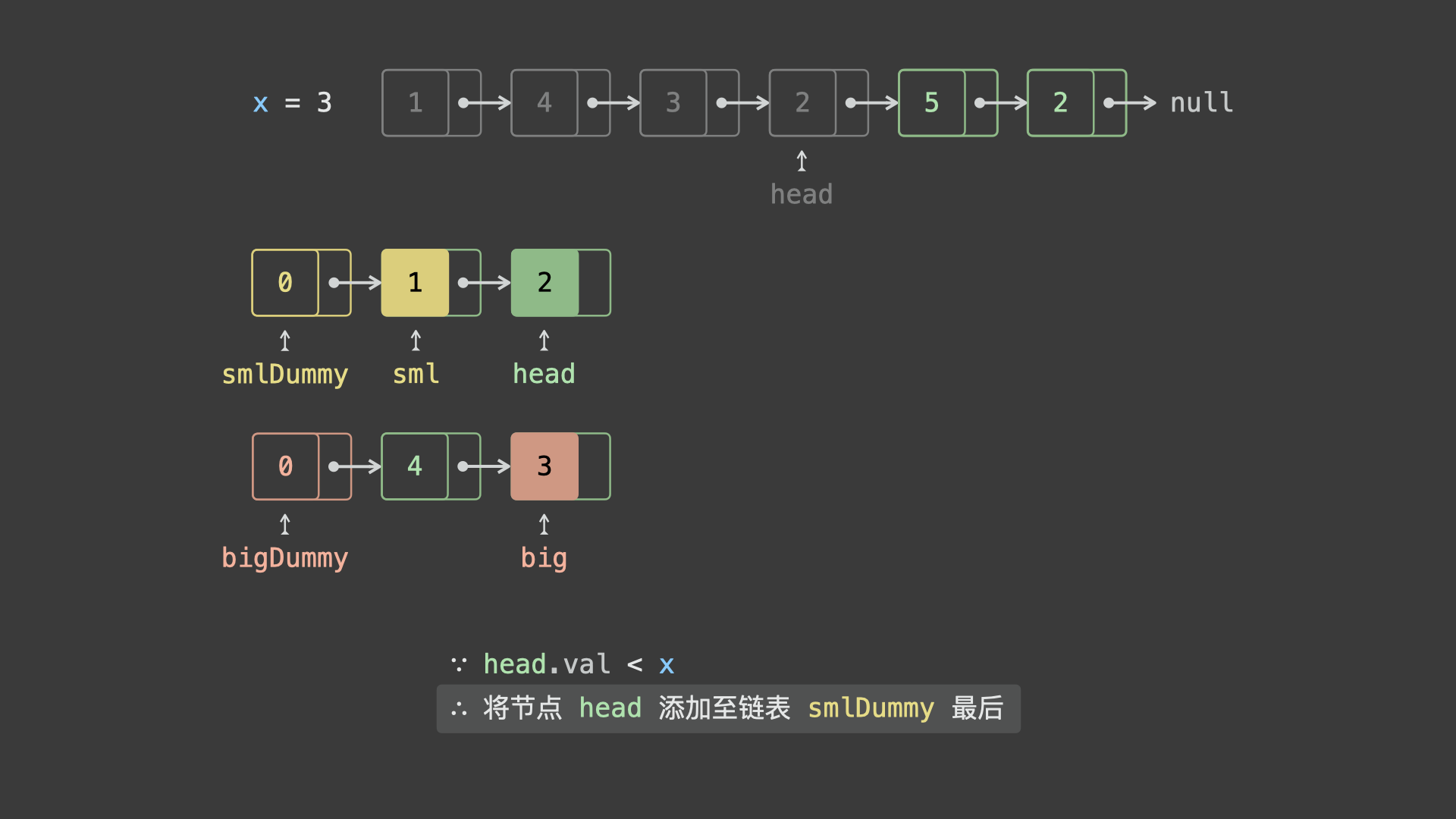
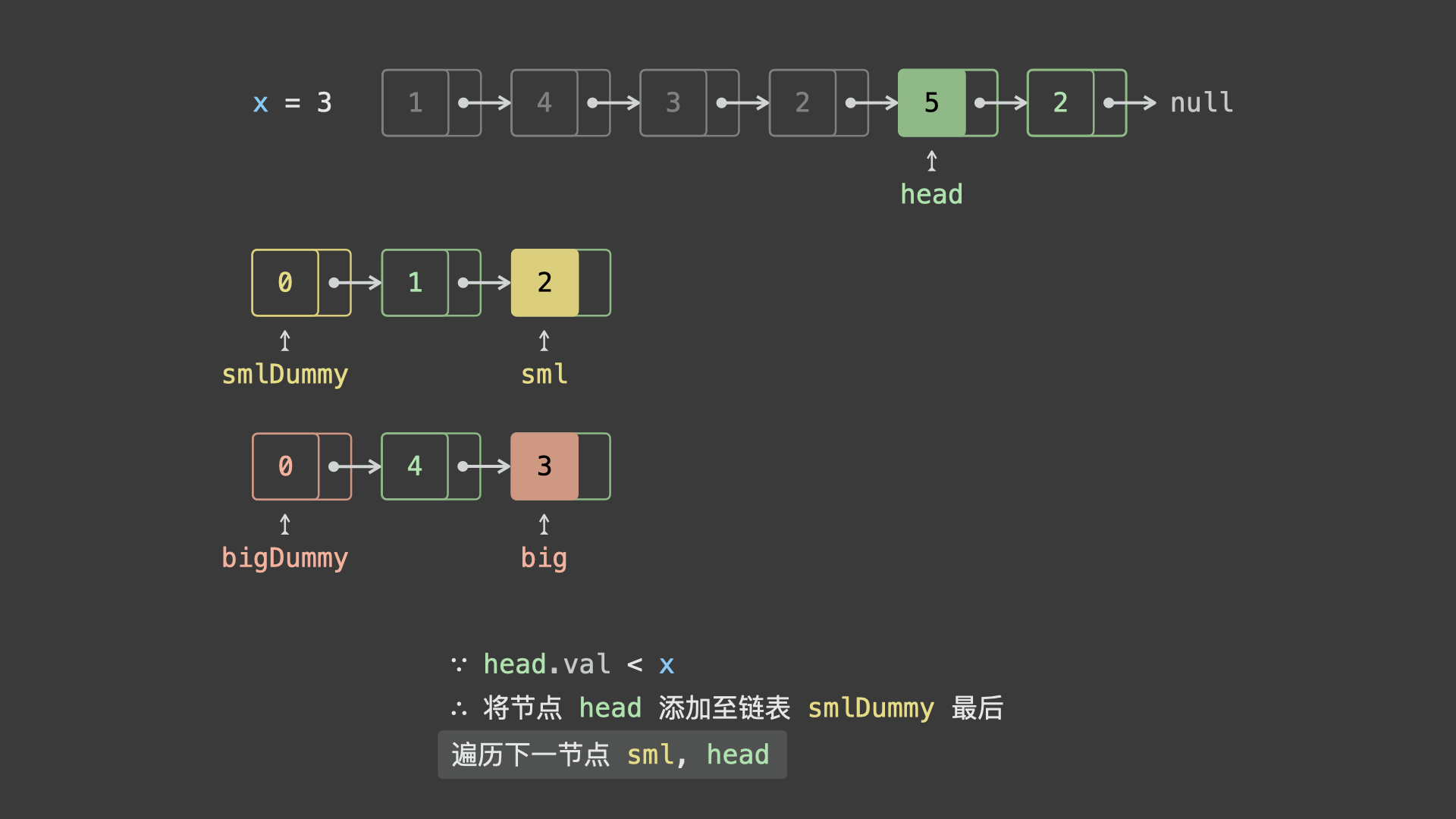
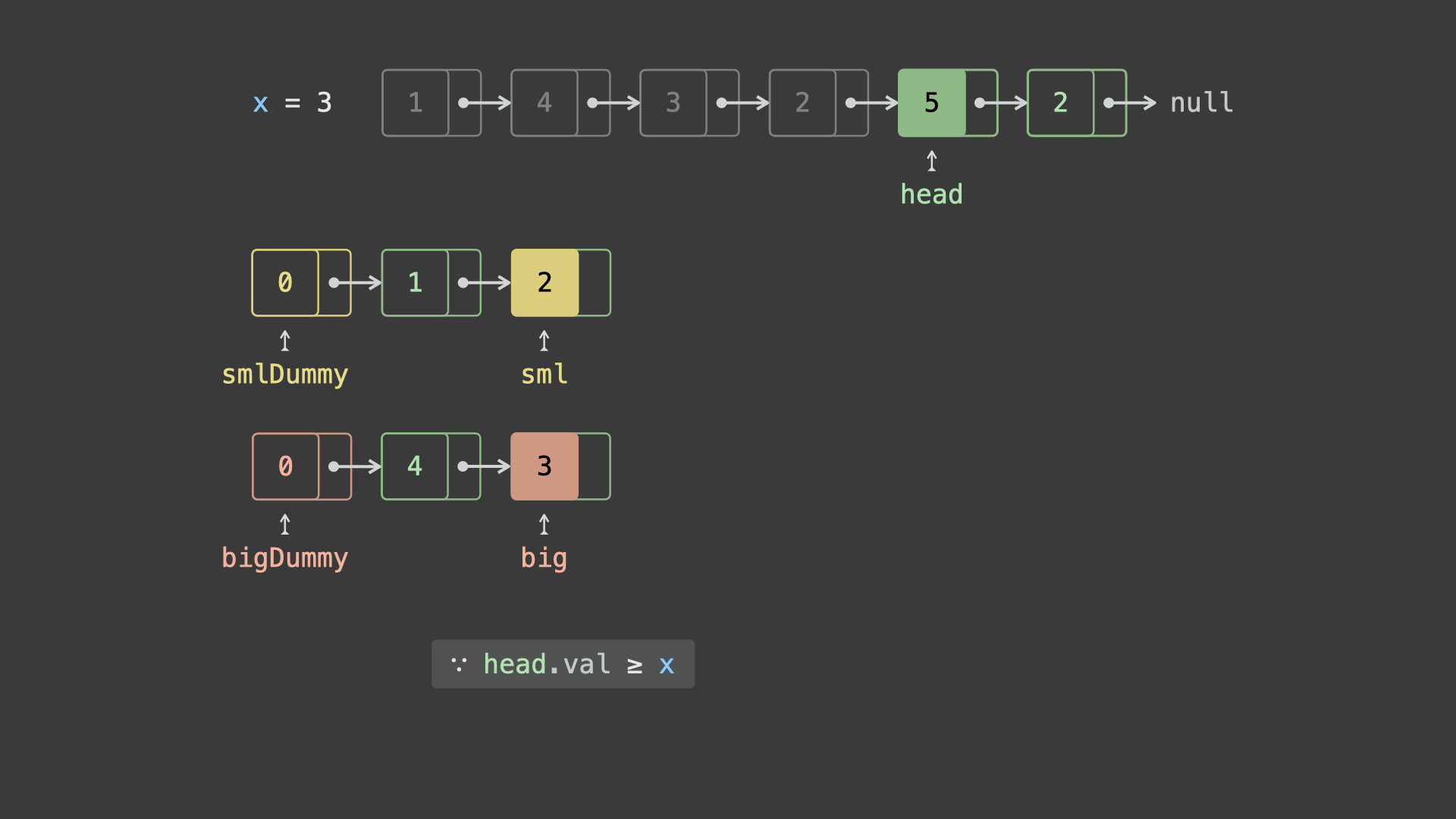
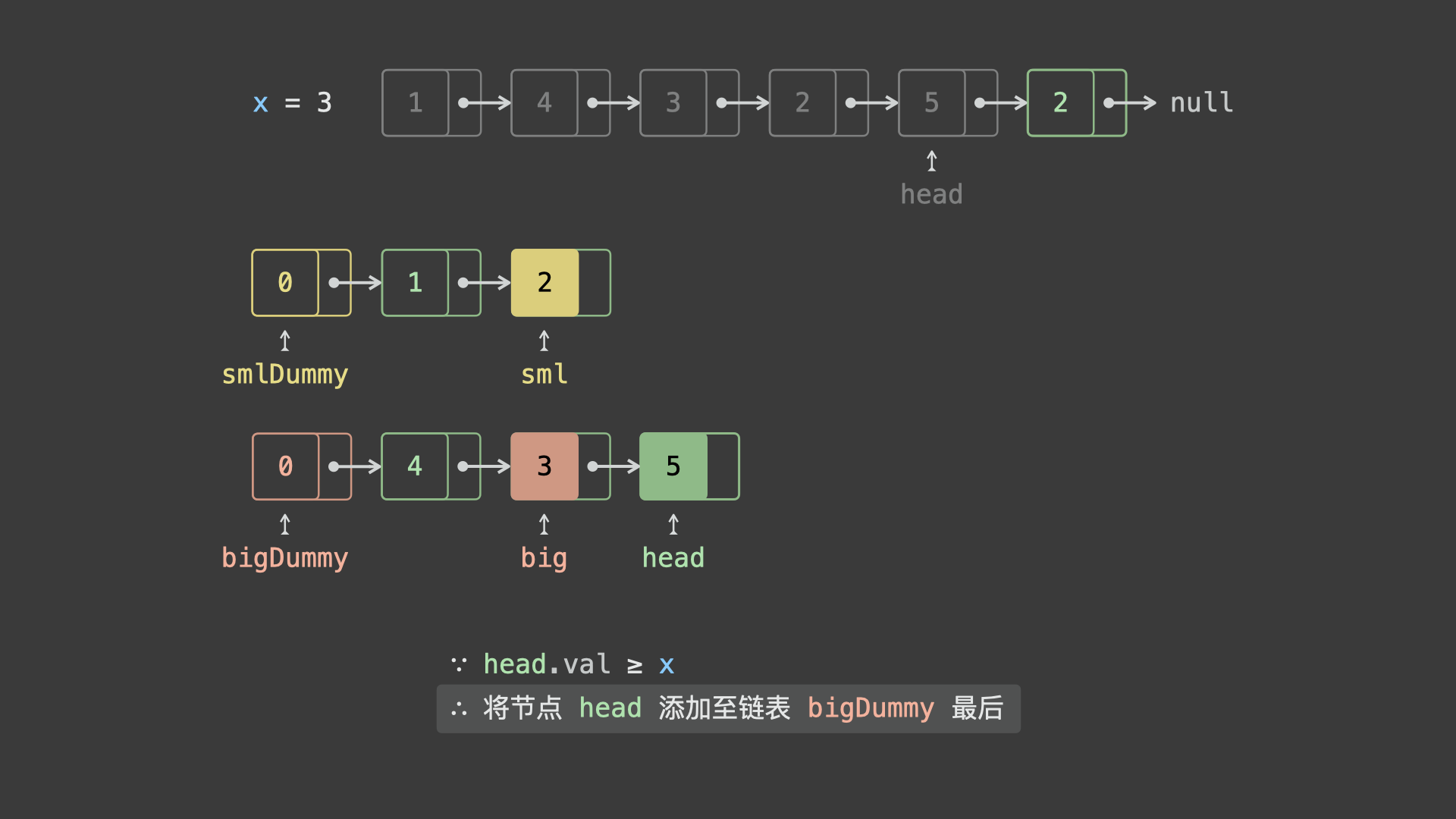
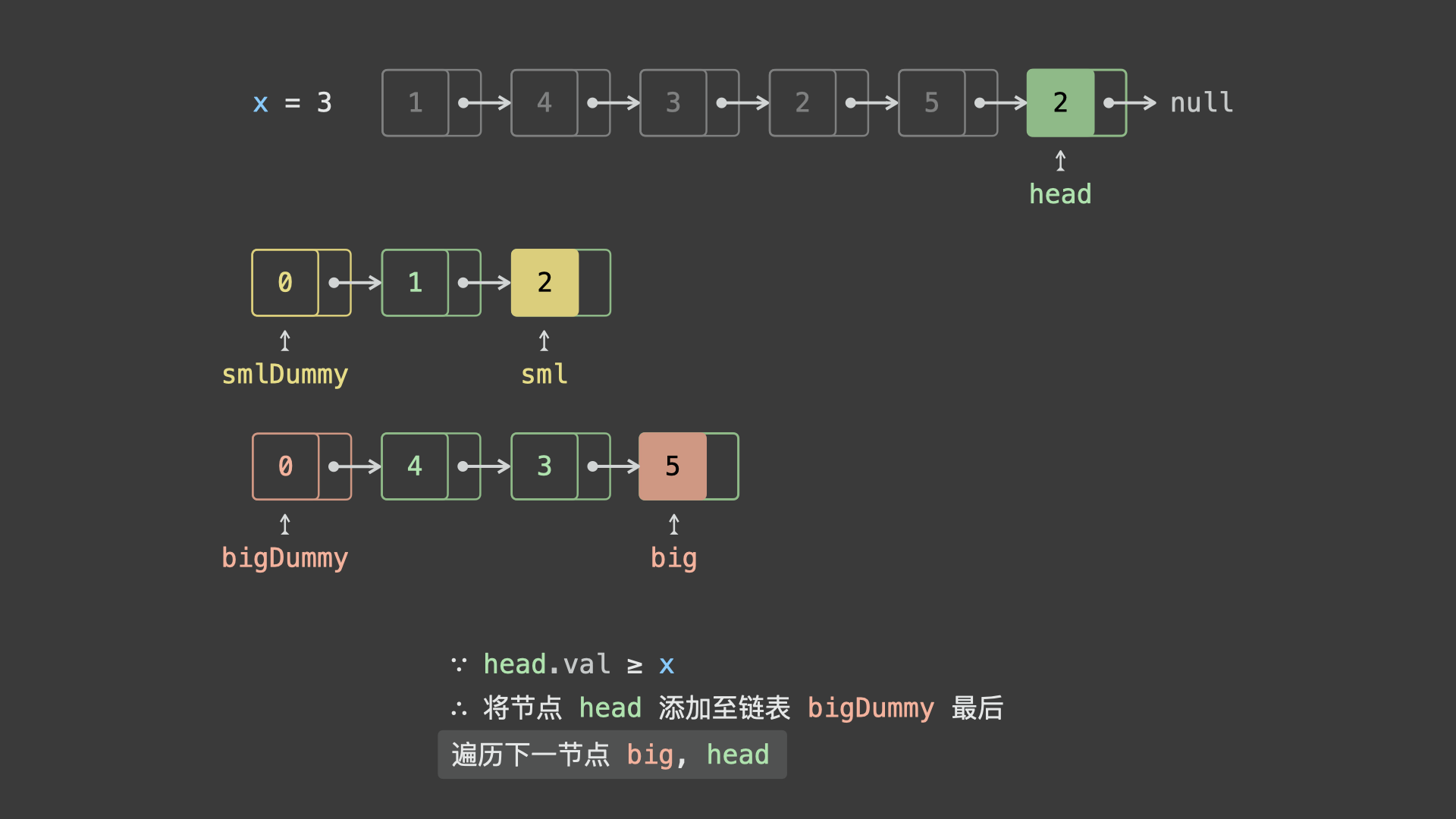
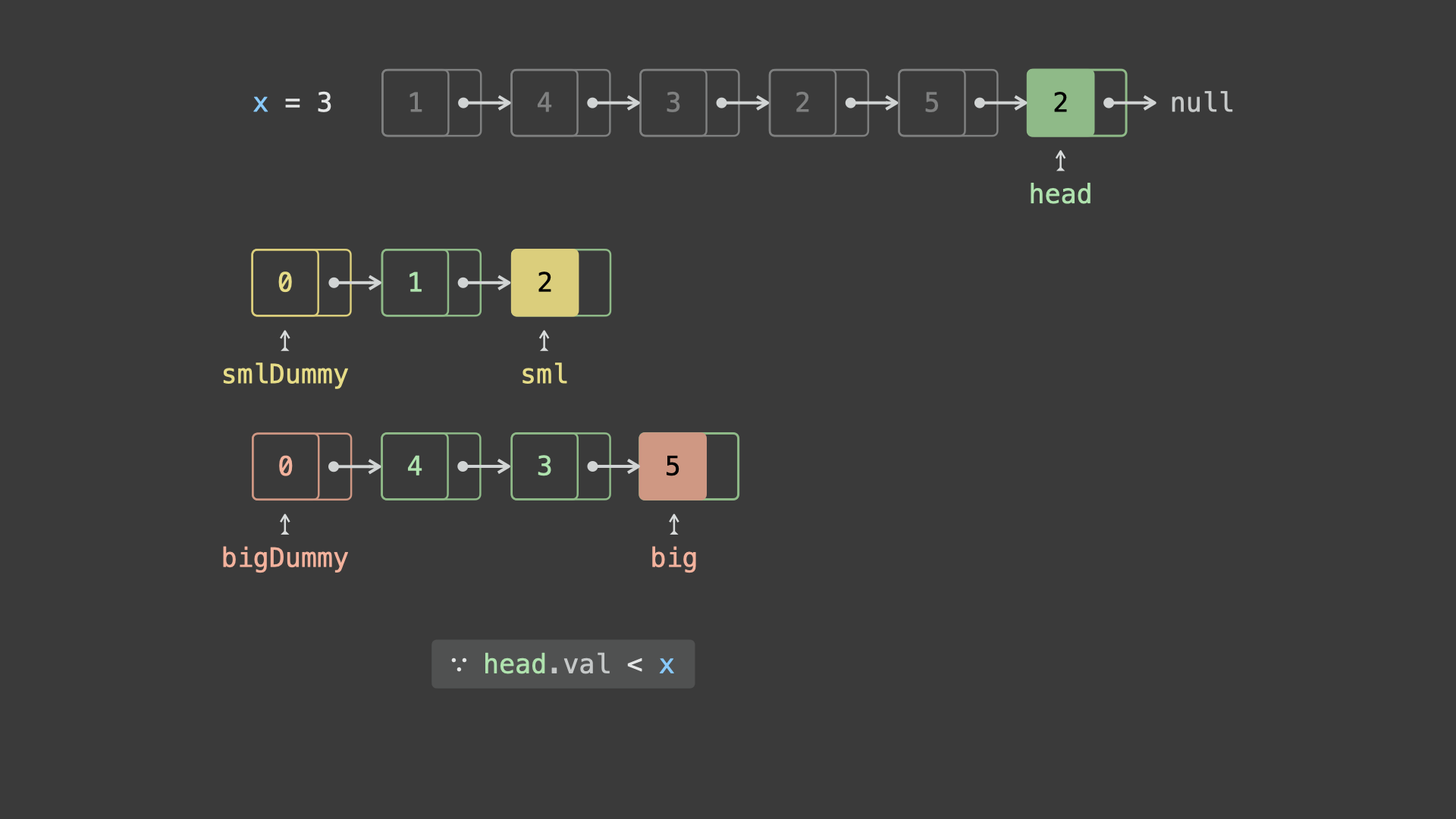
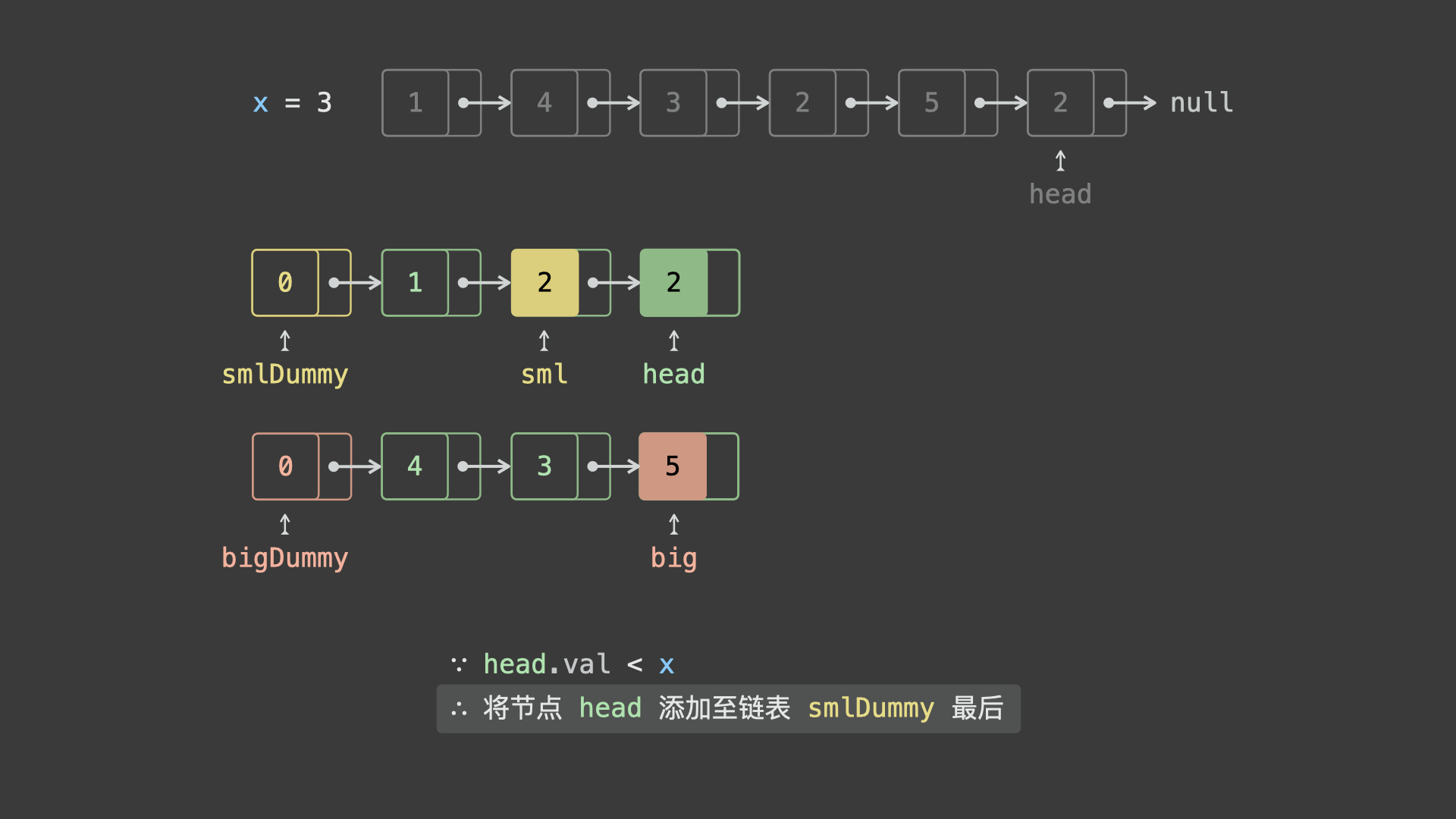
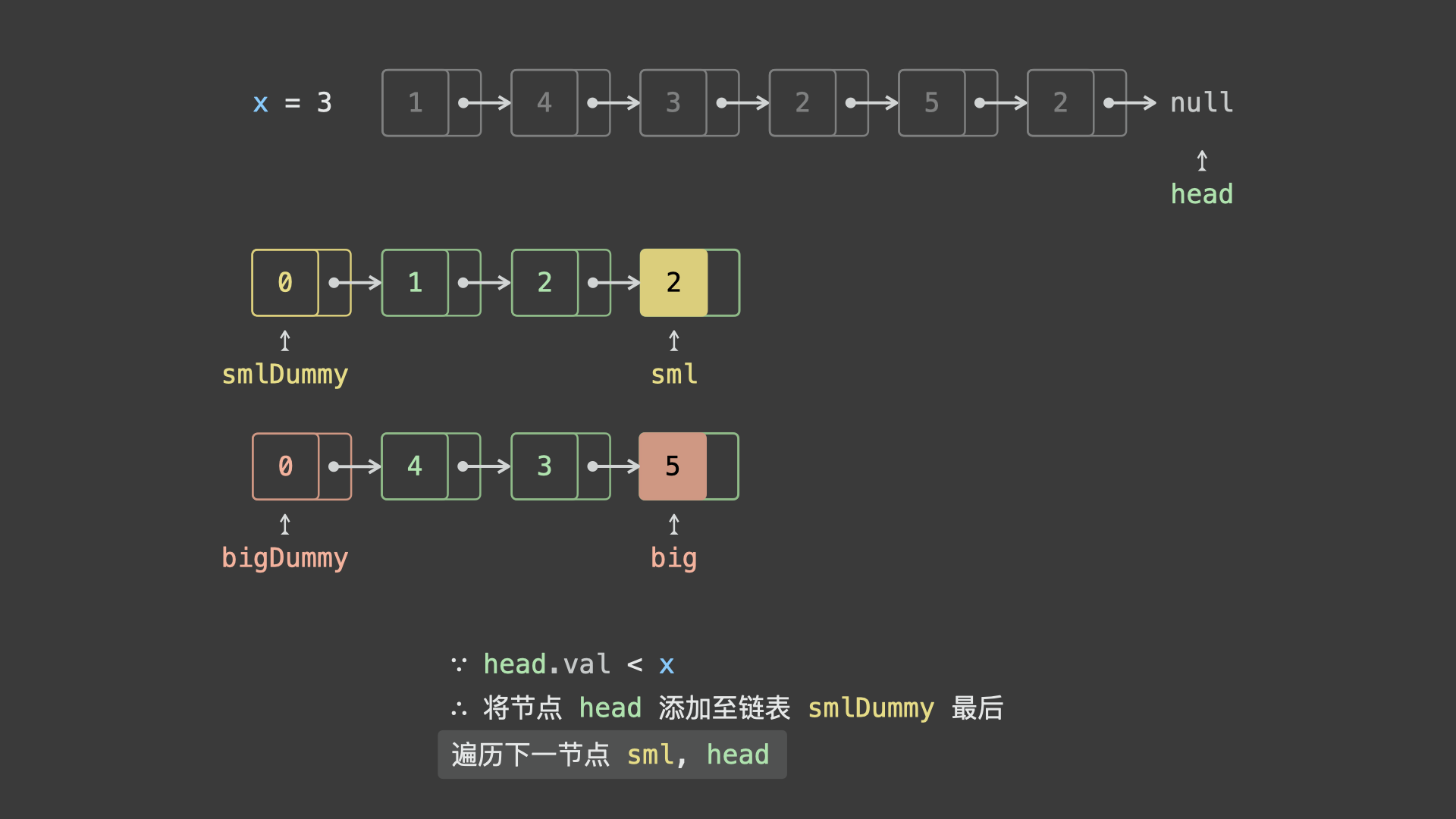
sml_dummy,big_dummy,分别用于添加所有「节点值 $< x$ 」、「节点值 $\geq x$ 」的节点。 - 遍历链表
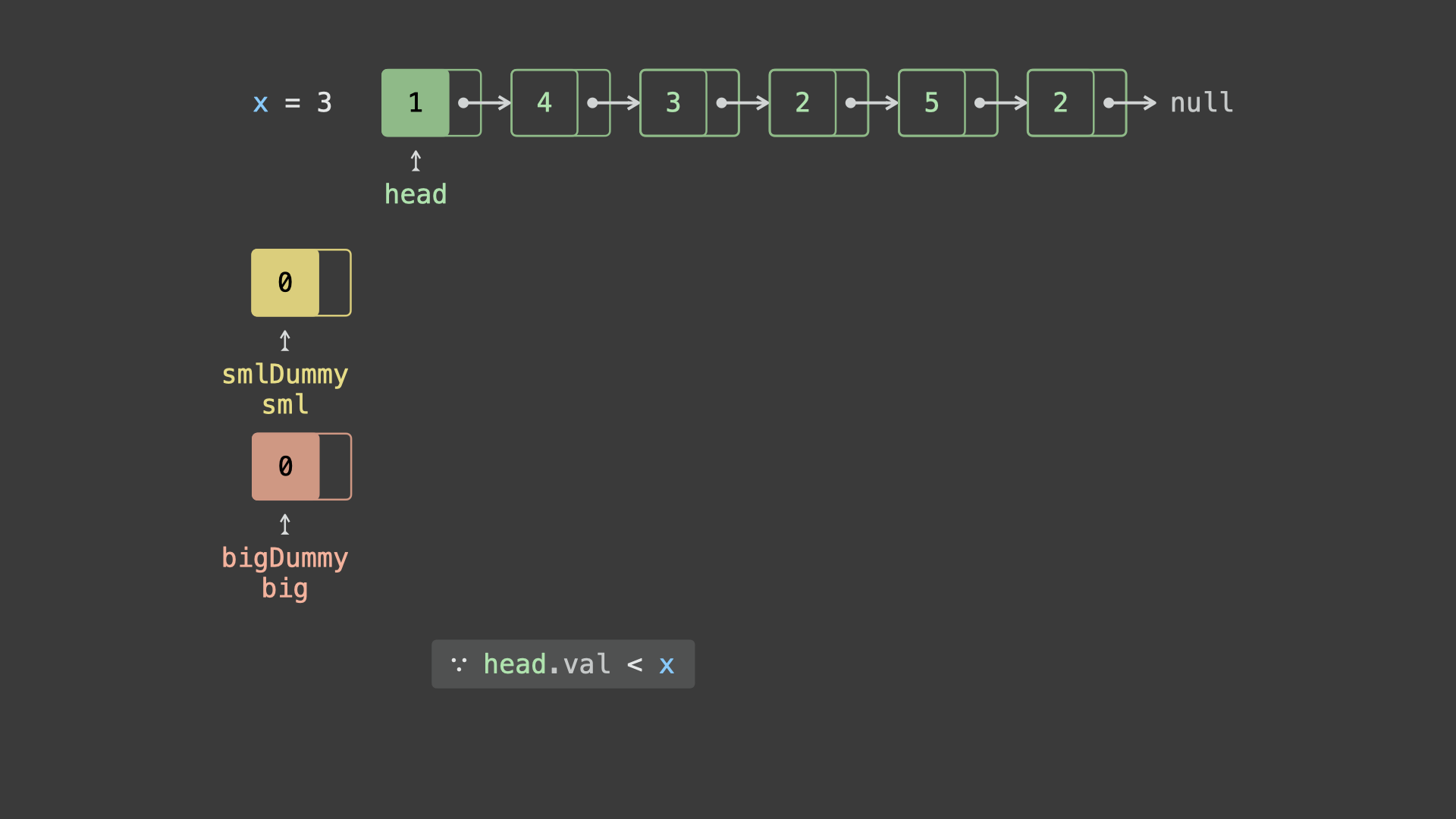
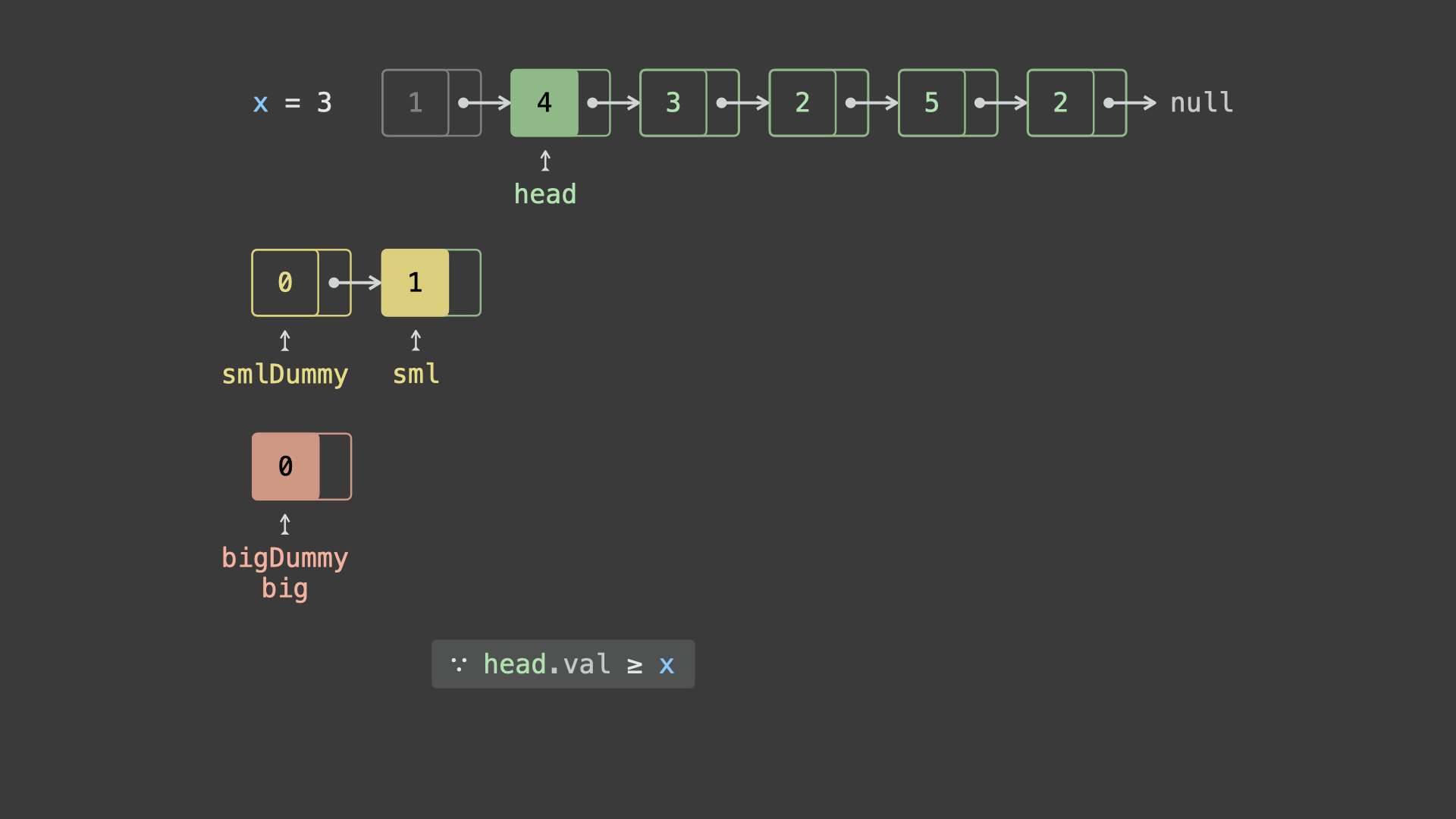
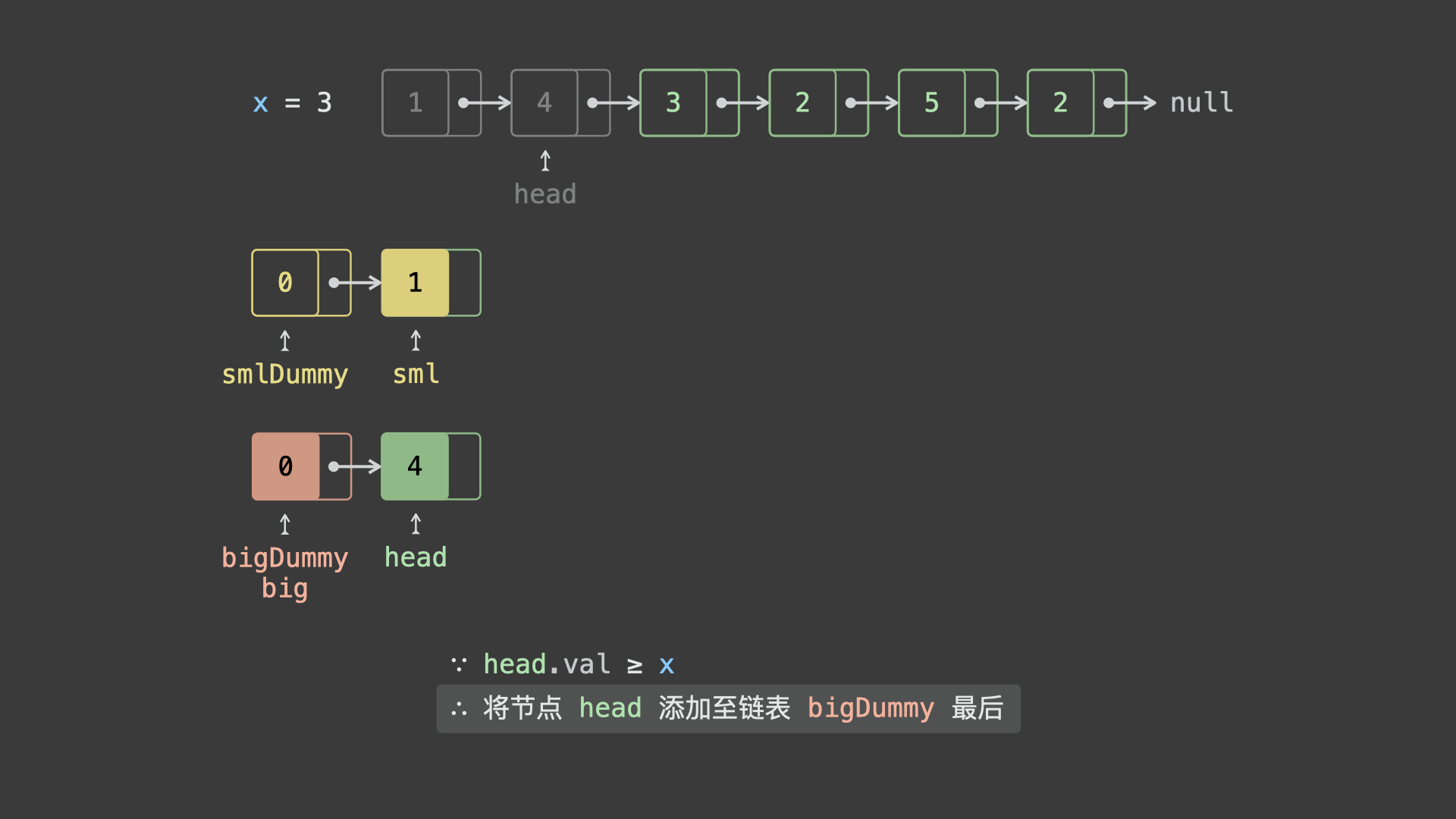
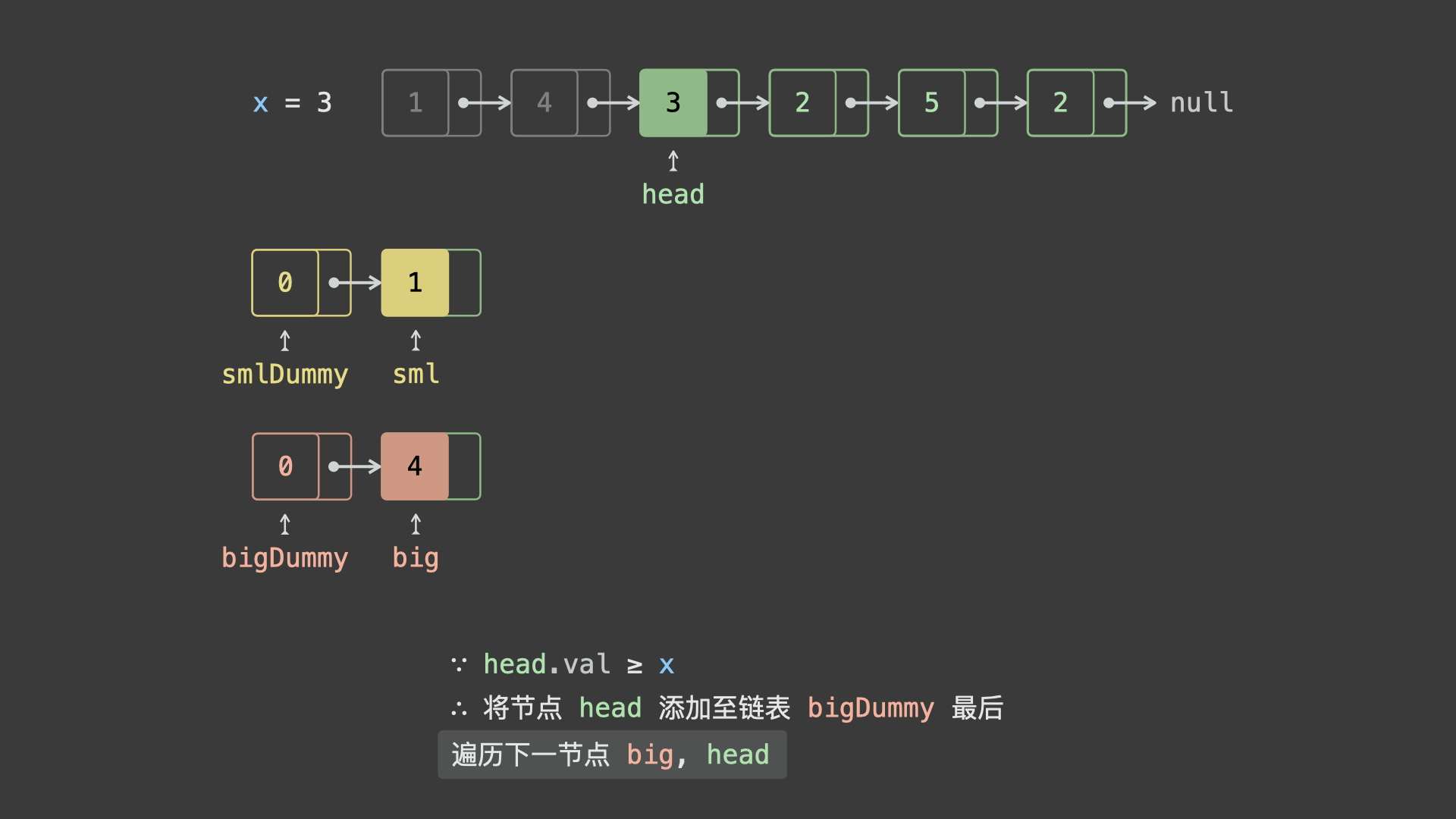
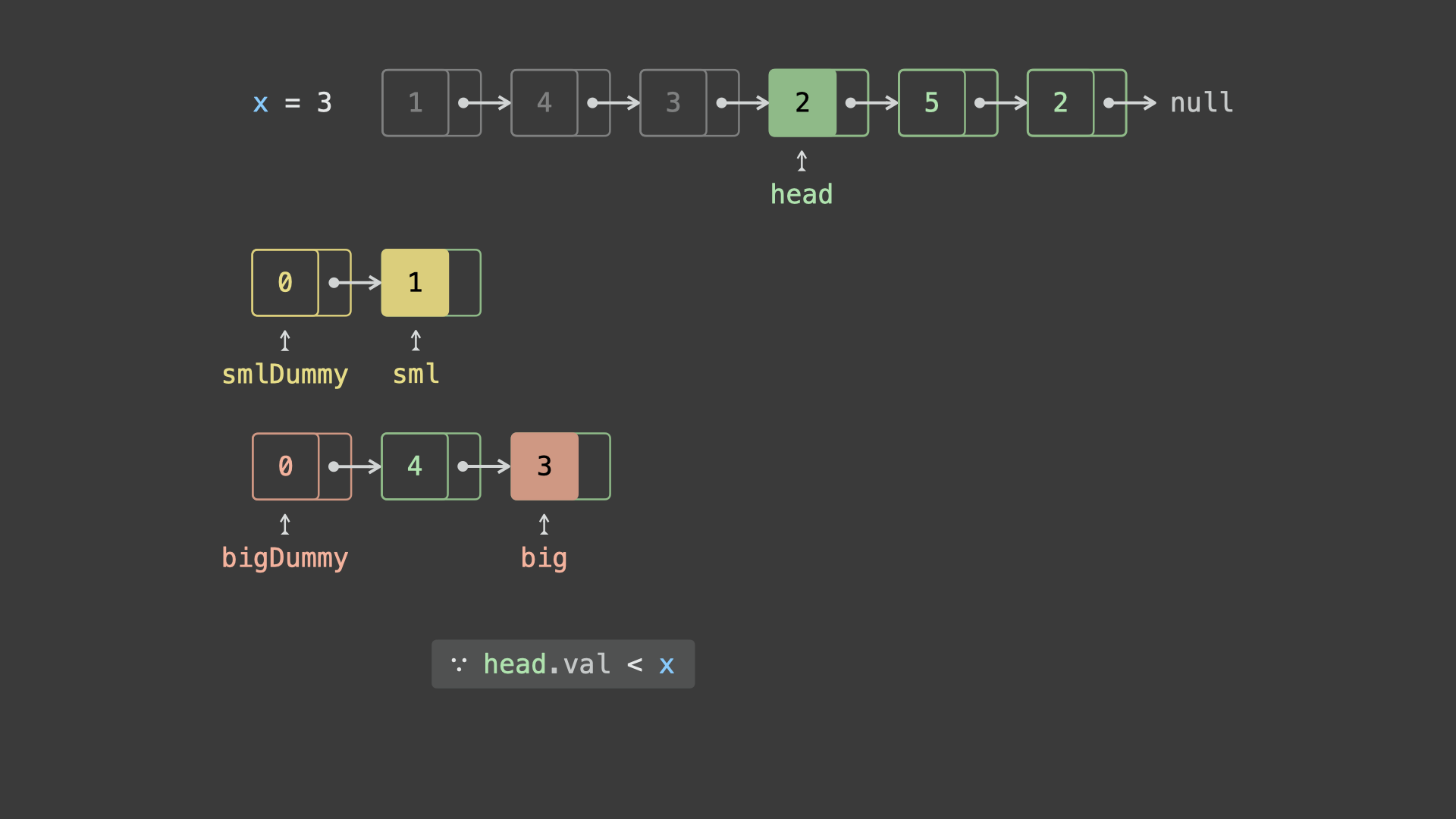
head并依次比较各节点值head.val和 $x$ 的大小:- 若
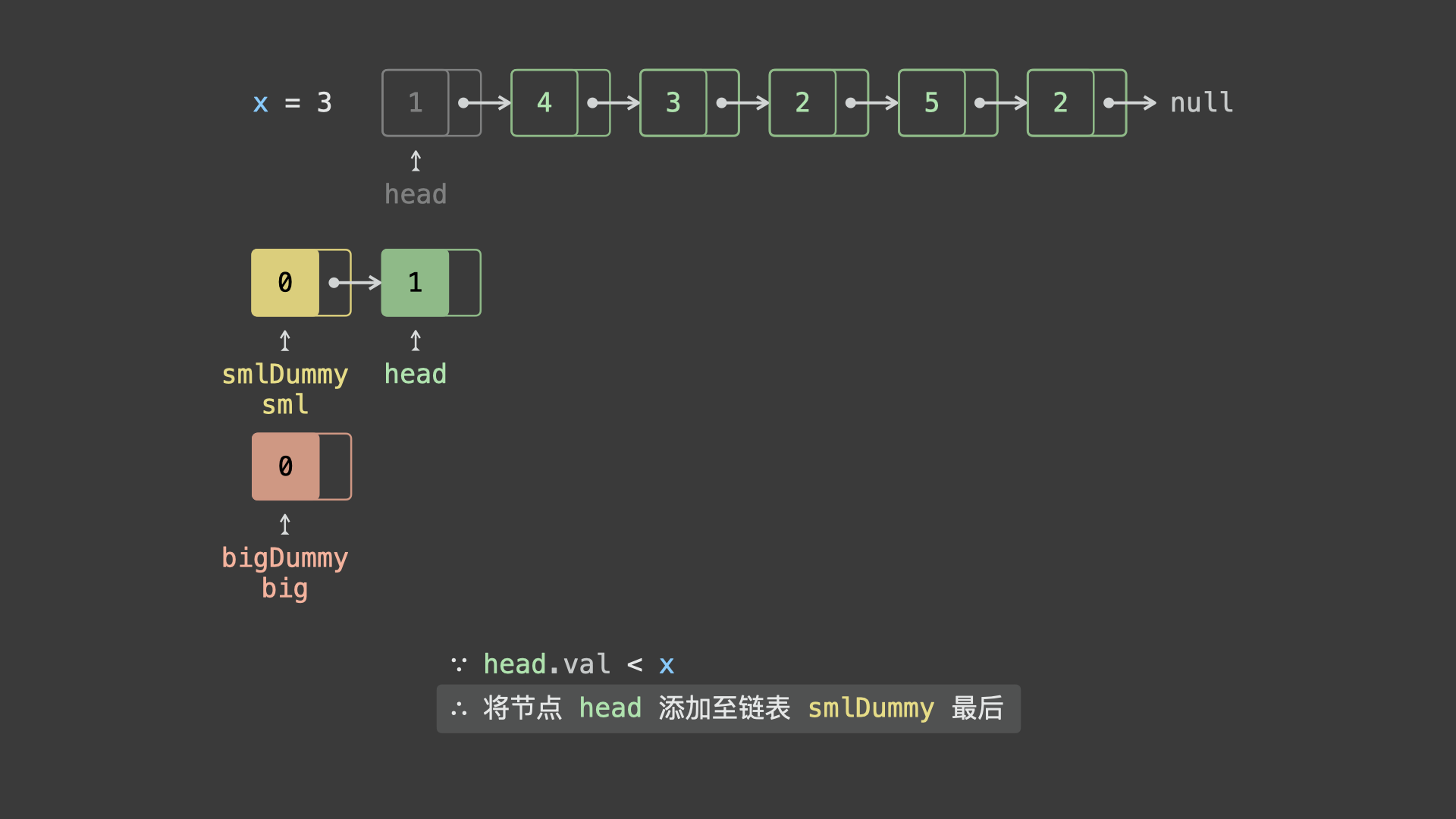
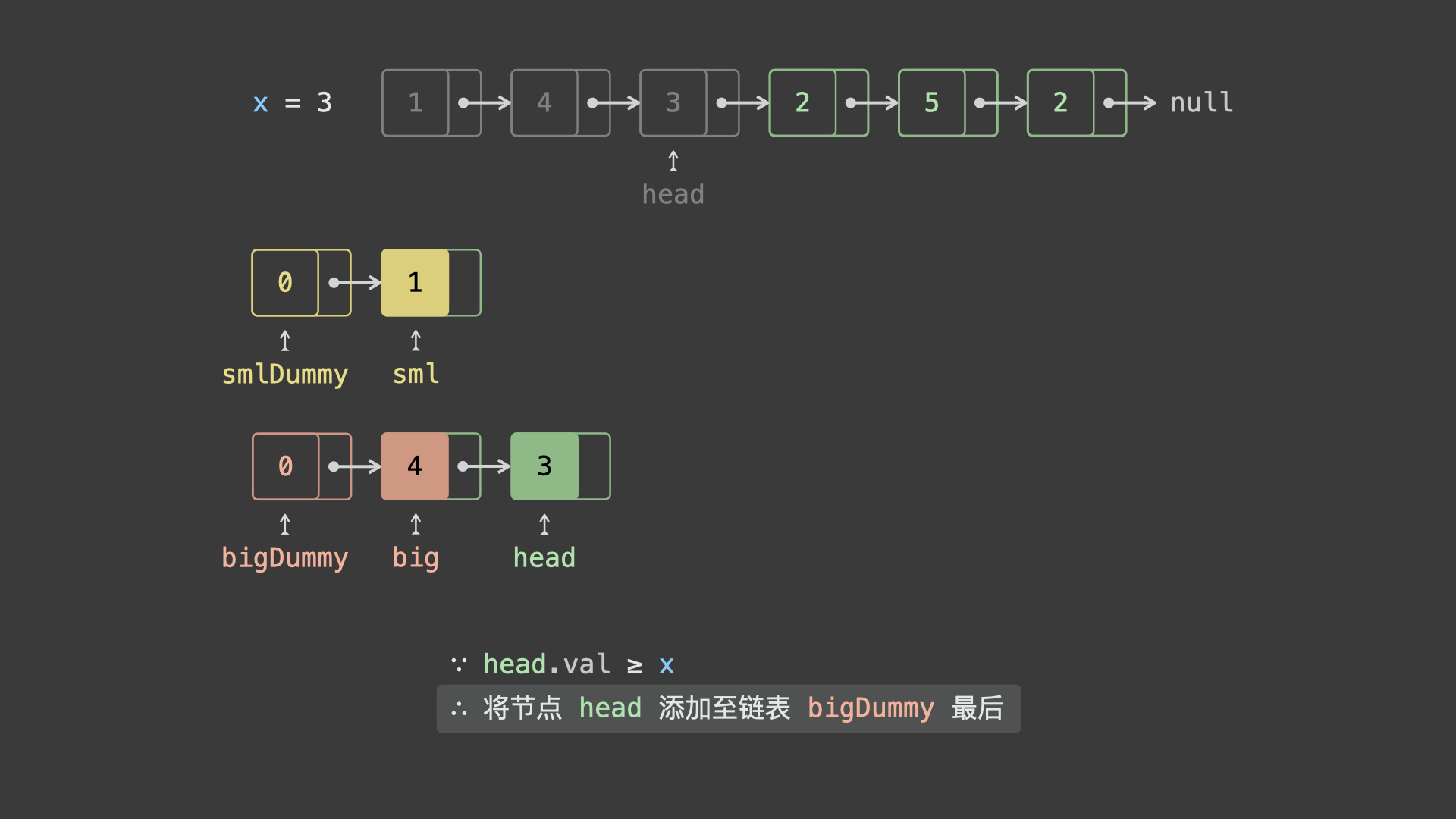
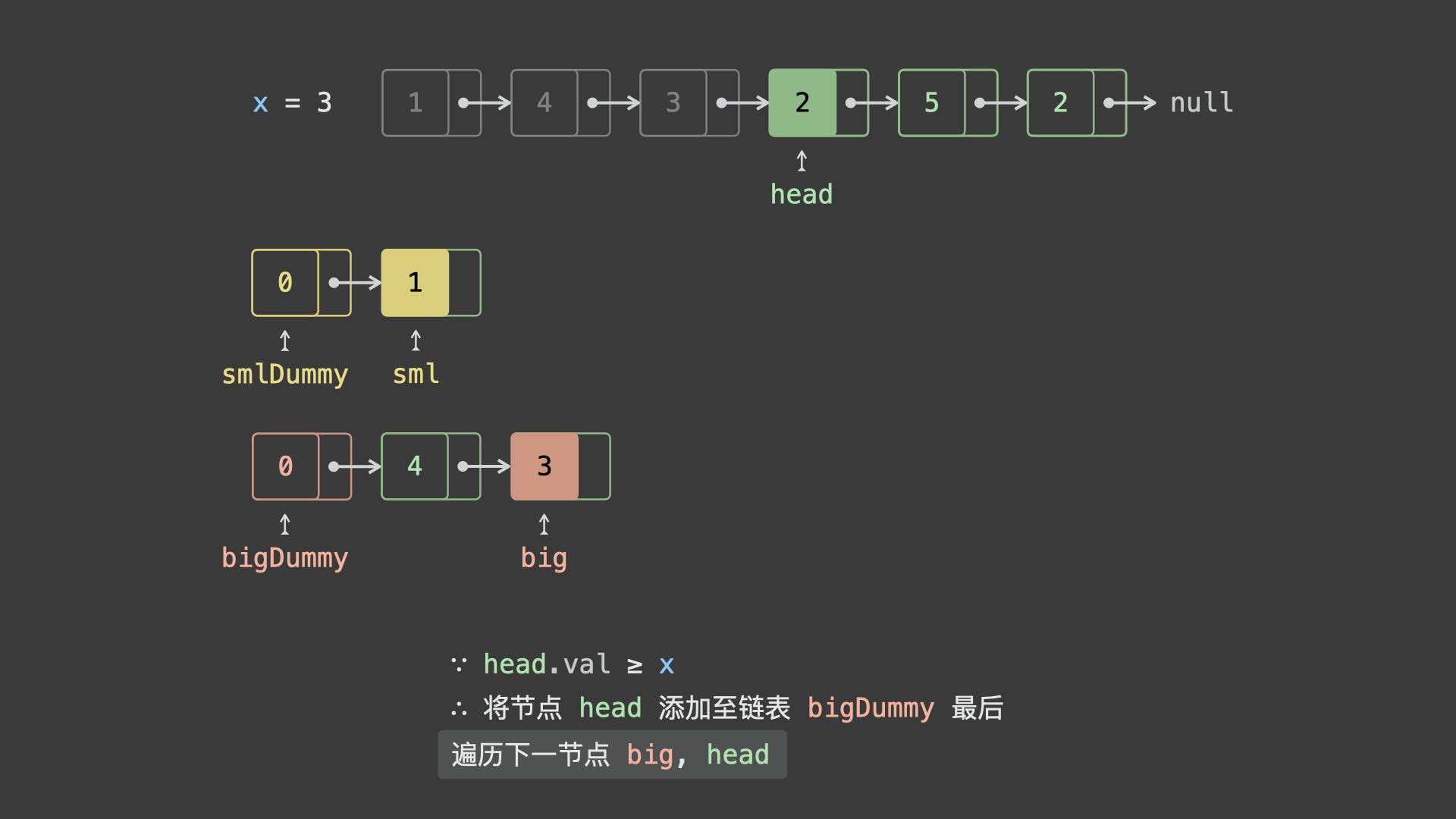
head.val < x,则将节点head添加至链表sml_dummy最后面; - 若
head.val >= x,则将节点head添加至链表big_dummy最后面;
- 若
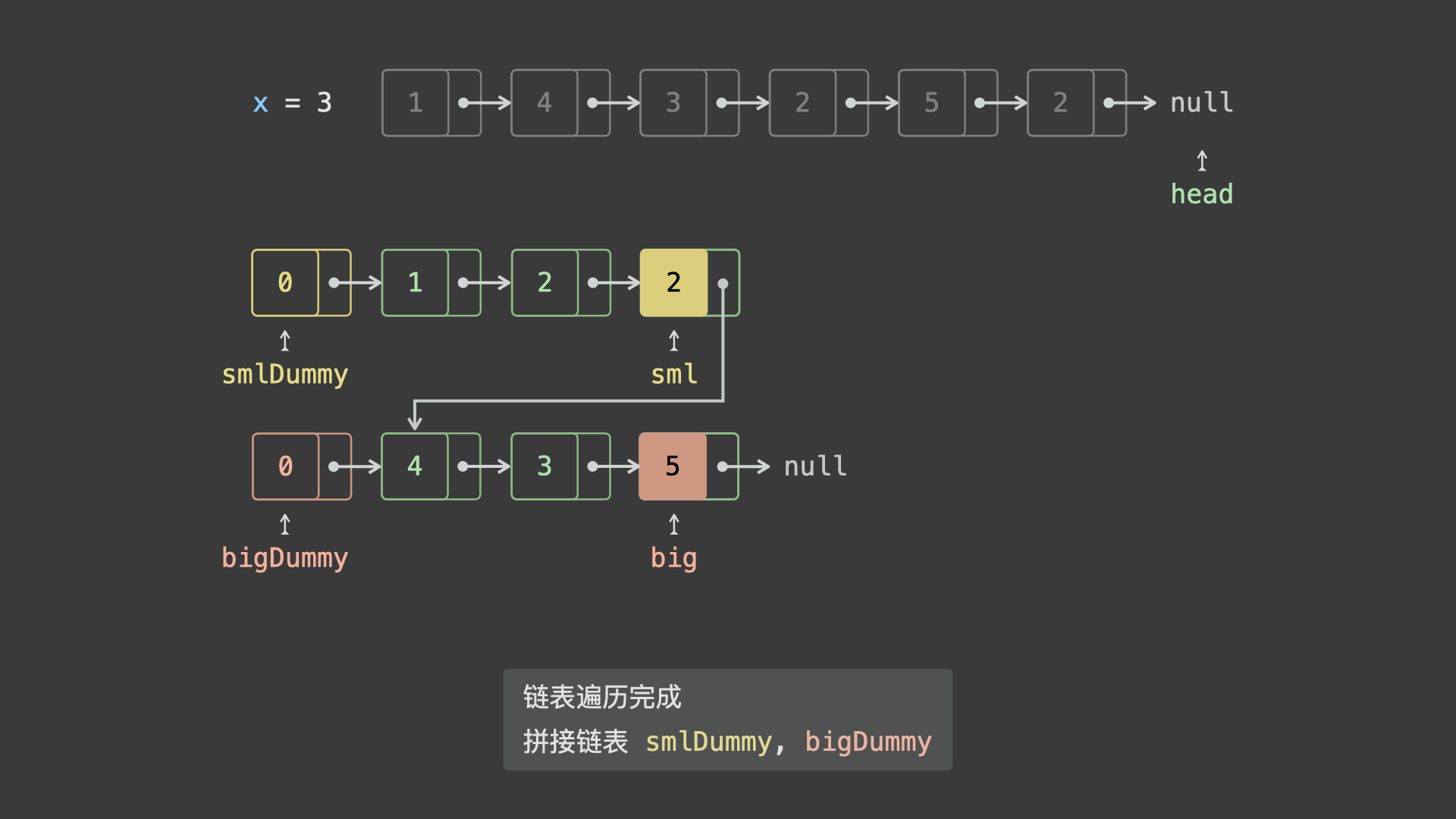
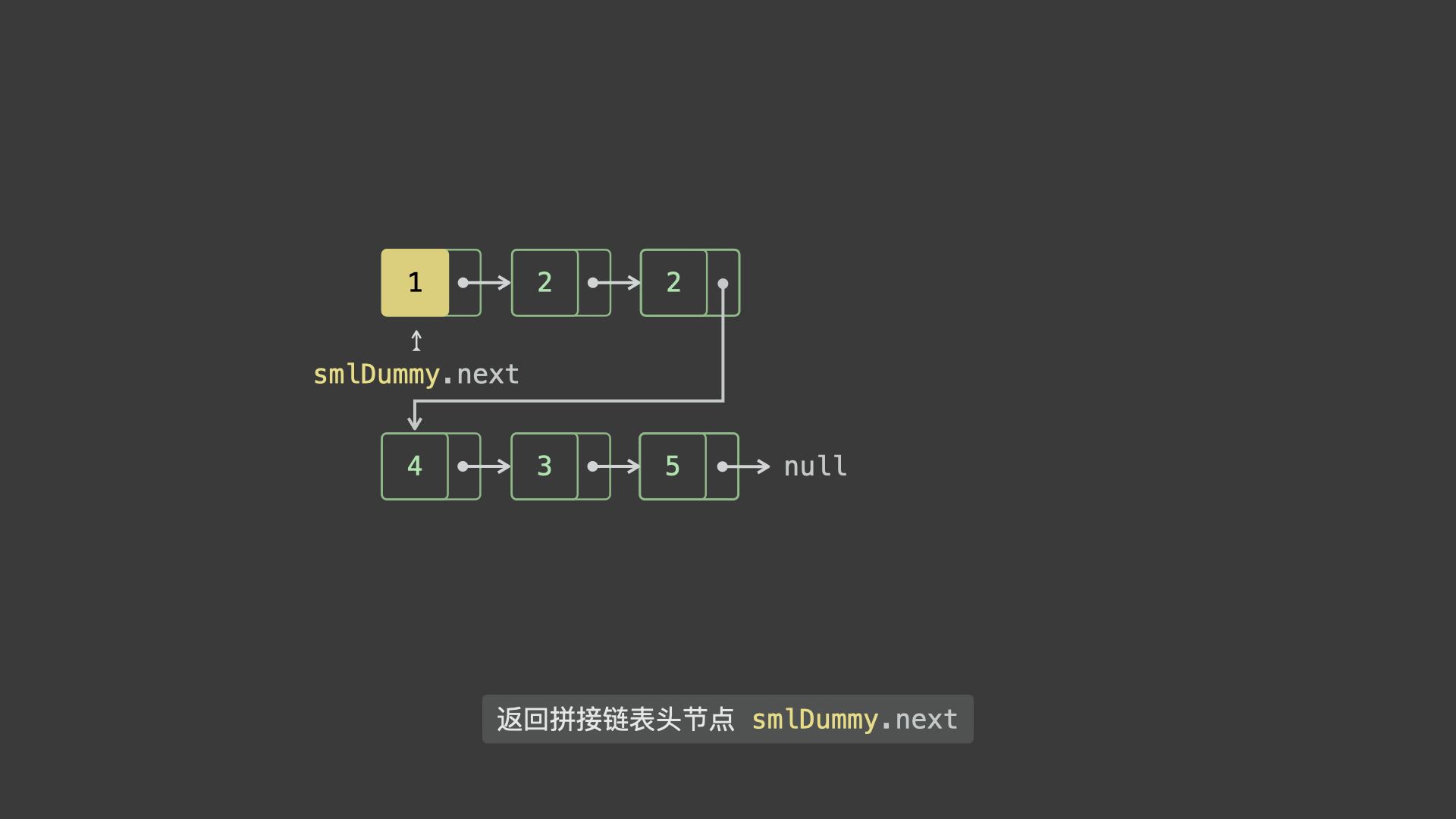
- 遍历完成后,拼接
sml_dummy和big_dummy链表。 - 最终返回头节点
sml_dummy.next即可。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
后三个 Tab 为「代码注释解析」。
Python
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
sml_dummy, big_dummy = ListNode(0), ListNode(0)
sml, big = sml_dummy, big_dummy
while head:
if head.val < x:
sml.next = head
sml = sml.next
else:
big.next = head
big = big.next
head = head.next
sml.next = big_dummy.next
big.next = None
return sml_dummy.nextJava
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode smlDummy = new ListNode(0), bigDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode sml = smlDummy, big = bigDummy;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
sml.next = head;
sml = sml.next;
} else {
big.next = head;
big = big.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
sml.next = bigDummy.next;
big.next = null;
return smlDummy.next;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
ListNode *smlDummy = new ListNode(0), *bigDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *sml = smlDummy, *big = bigDummy;
while (head != nullptr) {
if (head->val < x) {
sml->next = head;
sml = sml->next;
} else {
big->next = head;
big = big->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
sml->next = bigDummy->next;
big->next = nullptr;
return smlDummy->next;
}
};Python
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 新建两个链表
sml_dummy, big_dummy = ListNode(0), ListNode(0)
# 遍历链表
sml, big = sml_dummy, big_dummy
while head:
# 将 < x 的节点加入 sml 节点后
if head.val < x:
sml.next = head
sml = sml.next
# 将 >= x 的节点加入 big 节点后
else:
big.next = head
big = big.next
head = head.next
# 拼接两链表
sml.next = big_dummy.next
big.next = None
return sml_dummy.nextJava
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
// 新建两个链表
ListNode smlDummy = new ListNode(0), bigDummy = new ListNode(0);
// 遍历链表
ListNode sml = smlDummy, big = bigDummy;
while (head != null) {
// 将 < x 的节点加入 sml 节点后
if (head.val < x) {
sml.next = head;
sml = sml.next;
// 将 >= x 的节点加入 big 节点后
} else {
big.next = head;
big = big.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
// 拼接两链表
sml.next = bigDummy.next;
big.next = null;
return smlDummy.next;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
// 新建两个链表
ListNode *smlDummy = new ListNode(0), *bigDummy = new ListNode(0);
// 遍历链表
ListNode *sml = smlDummy, *big = bigDummy;
while (head != nullptr) {
// 将 < x 的节点加入 sml 节点后
if (head->val < x) {
sml->next = head;
sml = sml->next;
// 将 >= x 的节点加入 big 节点后
} else {
big->next = head;
big = big->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
// 拼接两链表
sml->next = bigDummy->next;
big->next = nullptr;
return smlDummy->next;
}
};复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为链表长度;遍历链表使用线性时间。
空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 假头节点使用常数大小的额外空间。