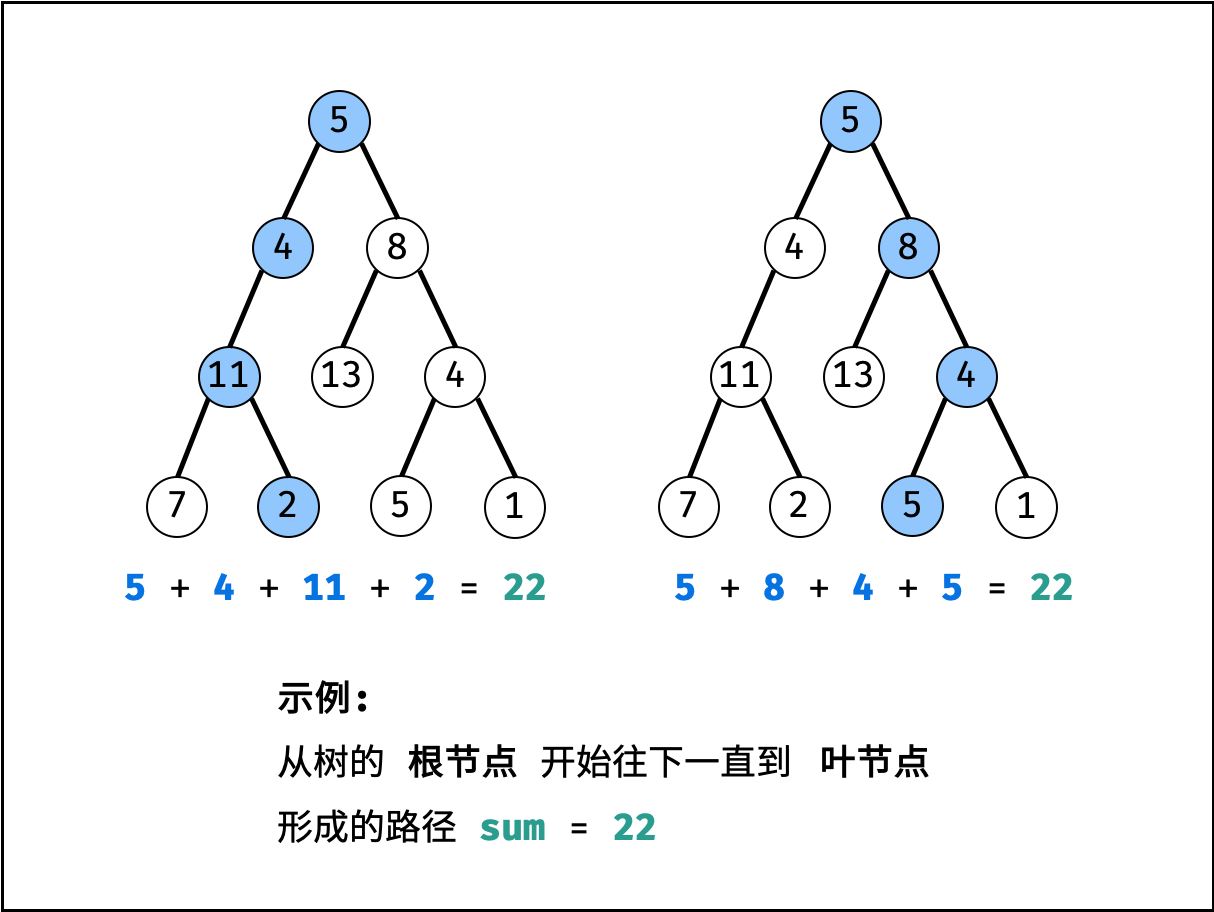
解题思路:
本题是典型的回溯问题,解法包含先序遍历 + 路径记录两部分:
- 先序遍历: 按照 “根、左、右” 的顺序,遍历树的所有节点。
- 路径记录: 在先序遍历中,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径。当路径满足 (1) 根节点到叶节点形成的路径 且 (2) 各节点值的和等于目标值
targetSum时,将此路径加入结果列表。
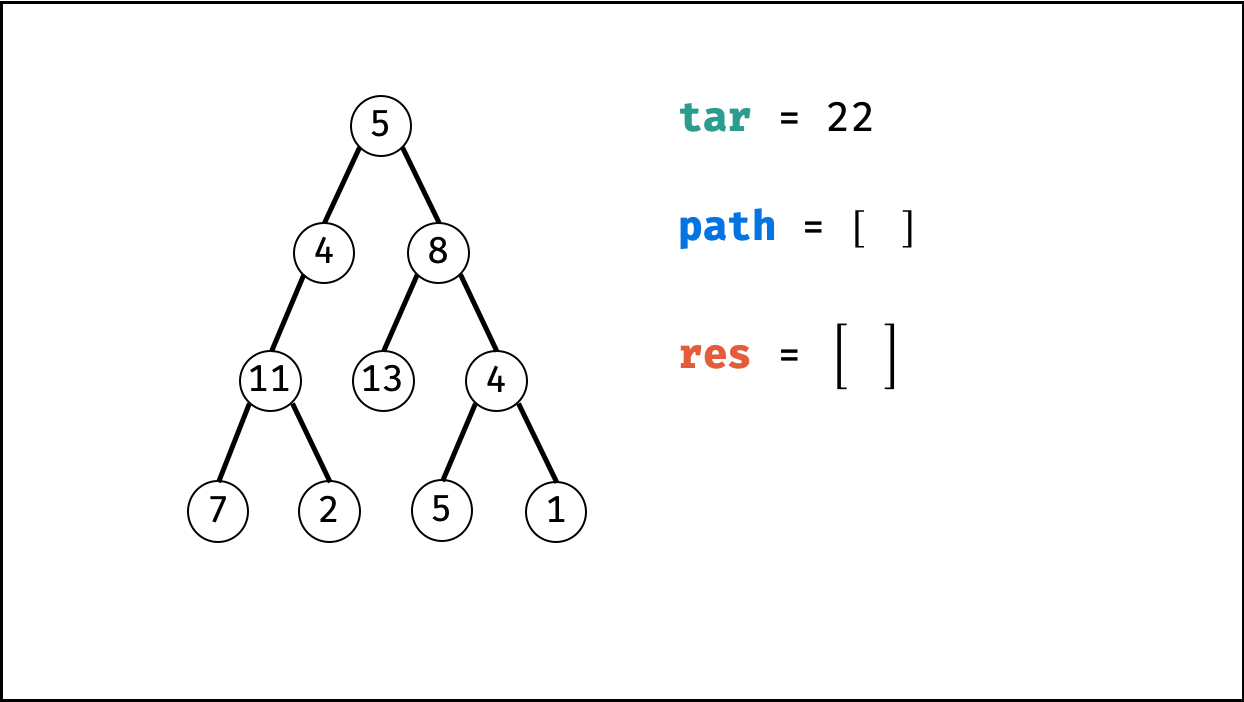
算法流程:
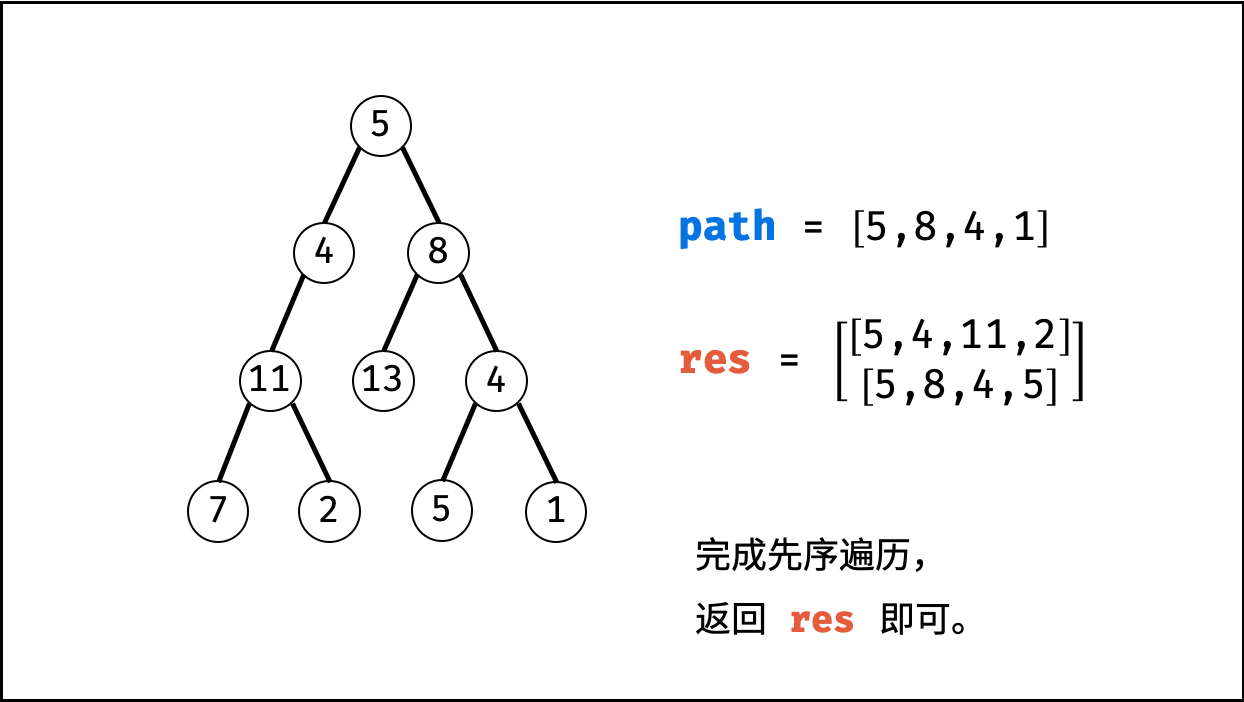
函数 pathSum(root, targetSum) :
- 初始化: 结果列表
res,路径列表path。 - 返回值: 返回
res即可。
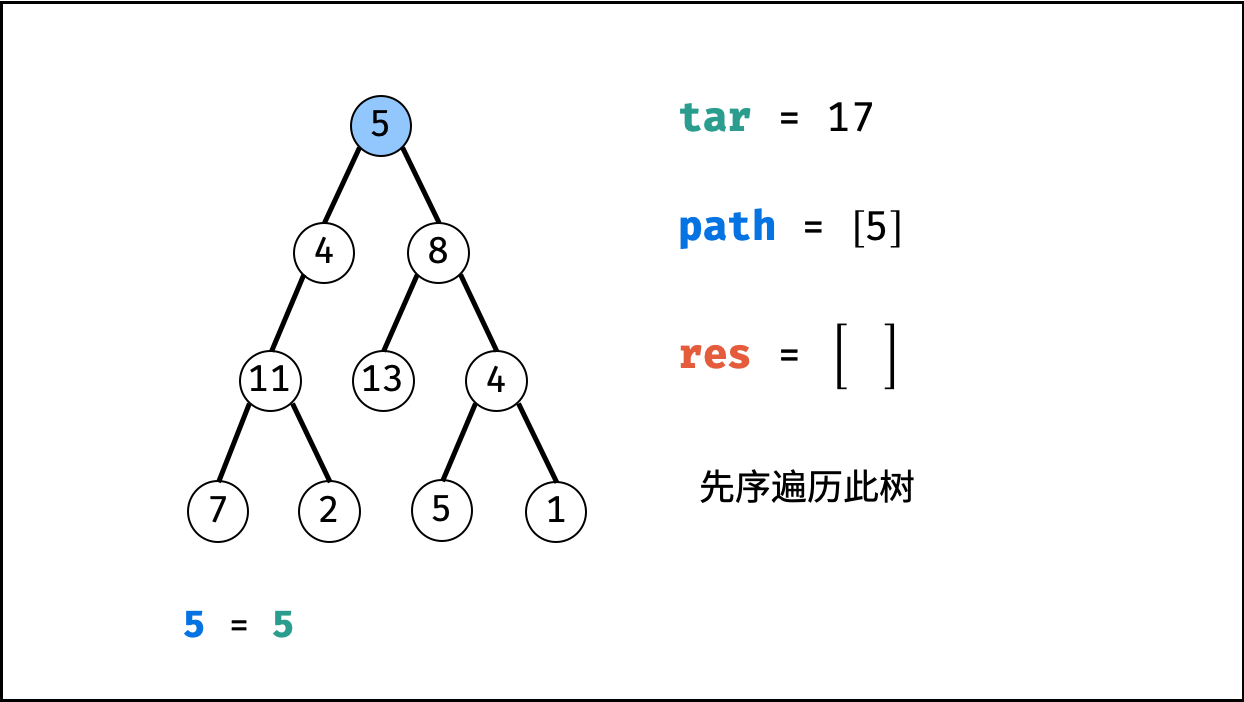
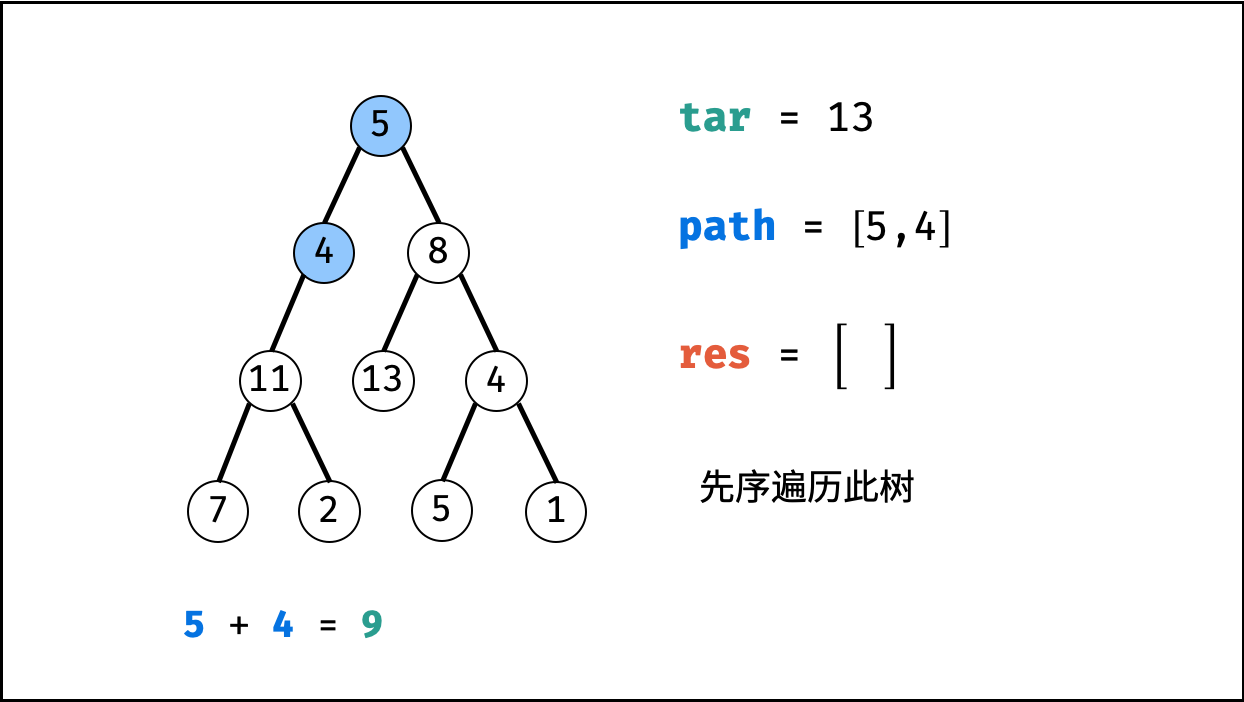
函数 recur(root, tar) :
- 递推参数: 当前节点
root,当前目标值tar。 - 终止条件: 若节点
root为空,则直接返回。 - 递推工作:
- 路径更新: 将当前节点值
root.val加入路径path。 - 目标值更新:
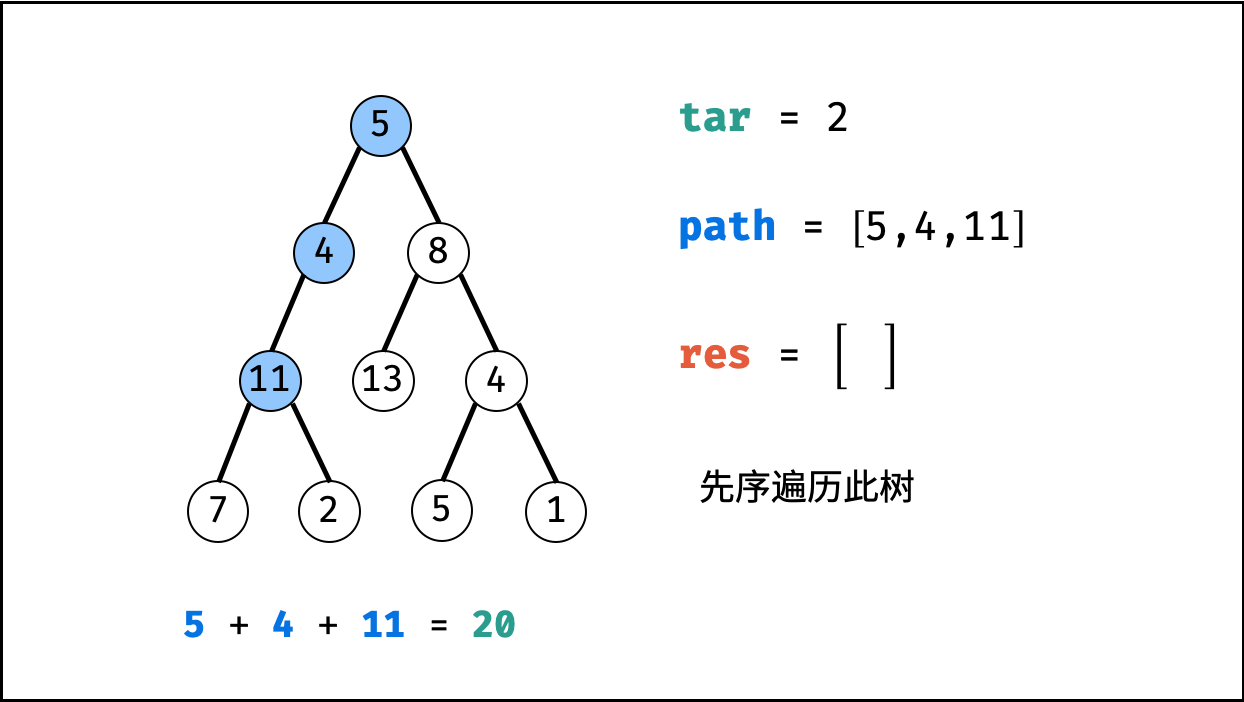
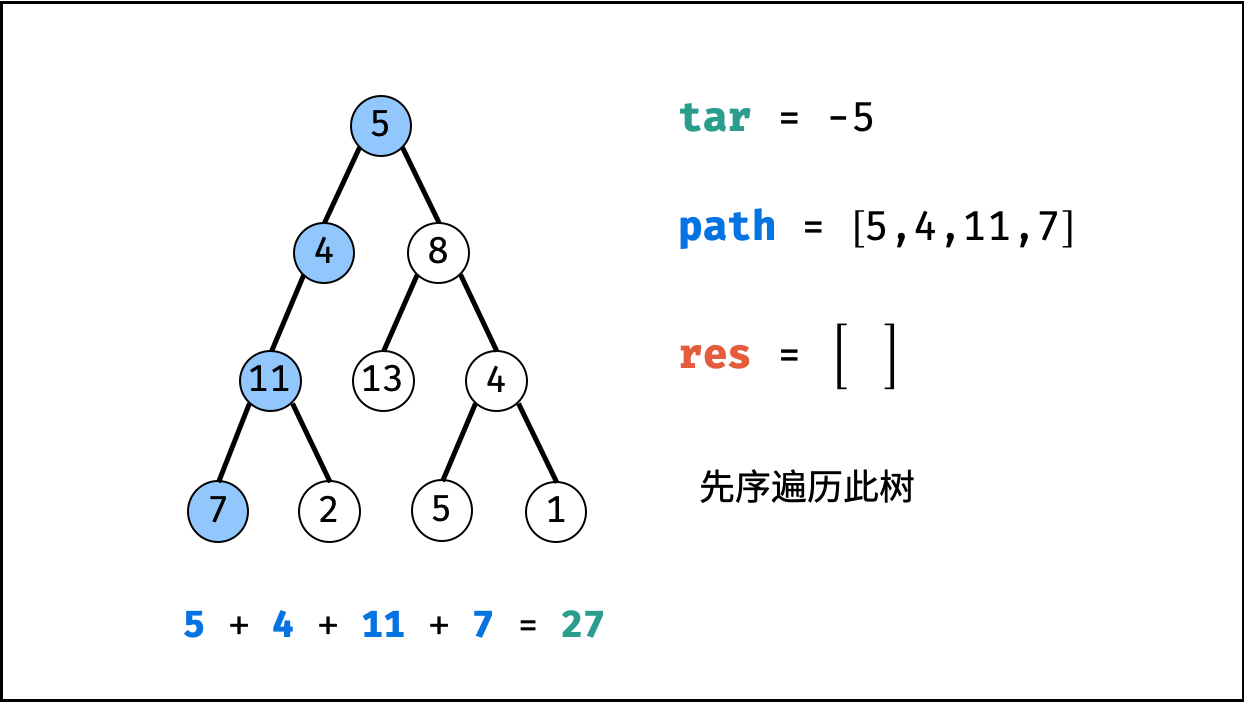
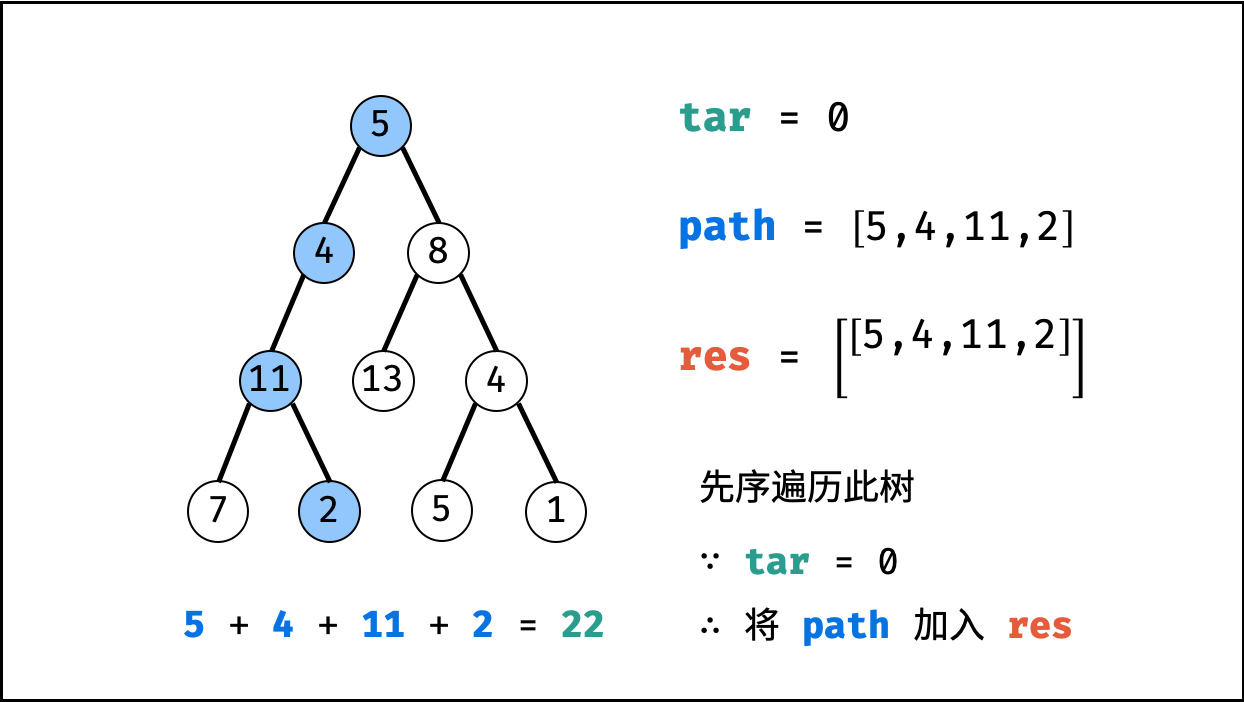
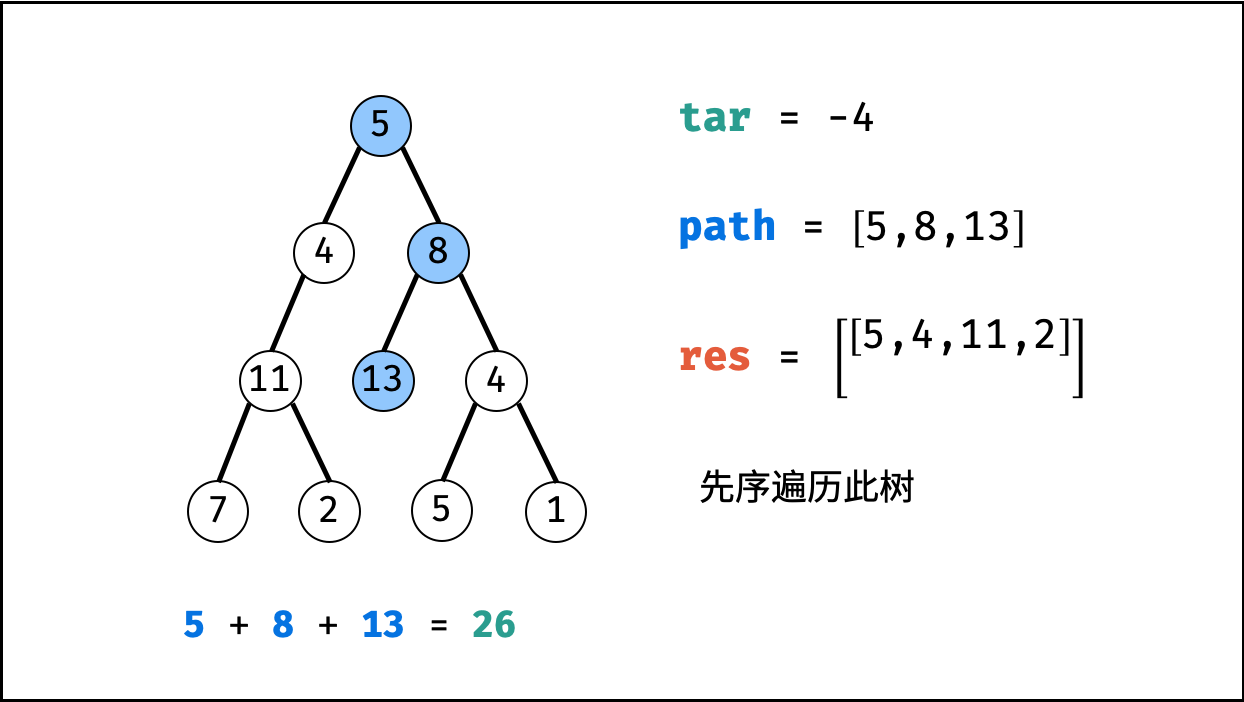
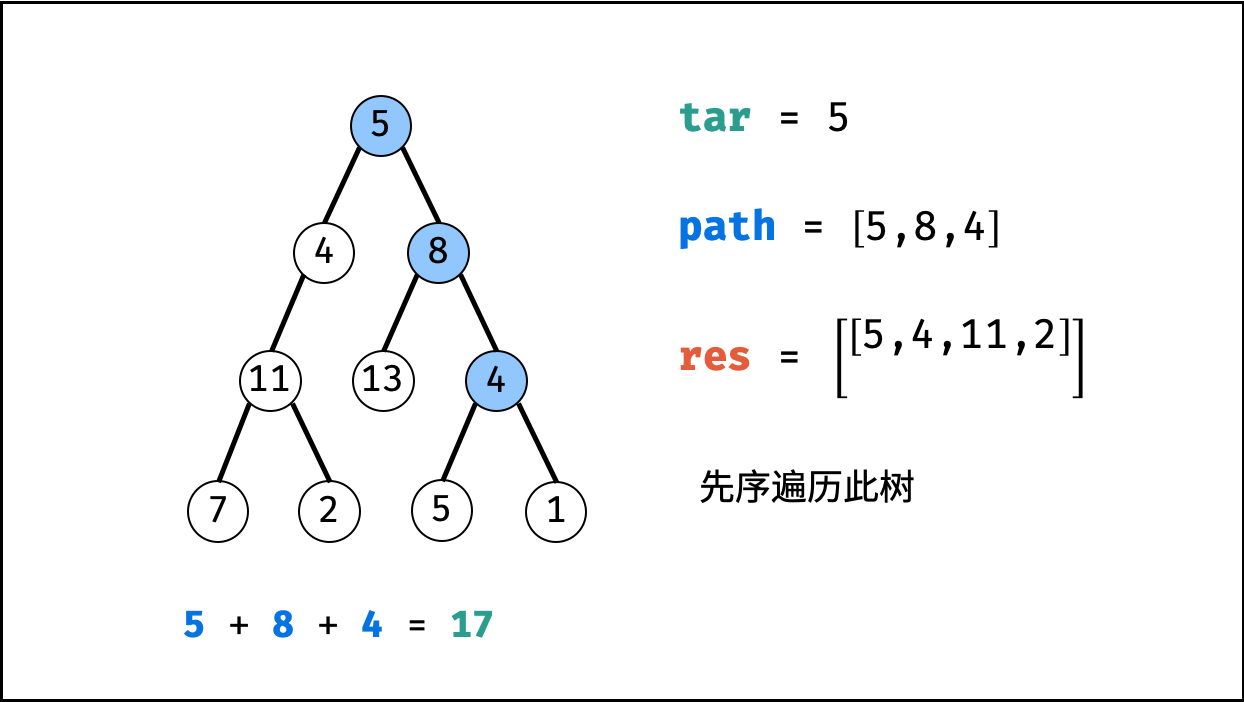
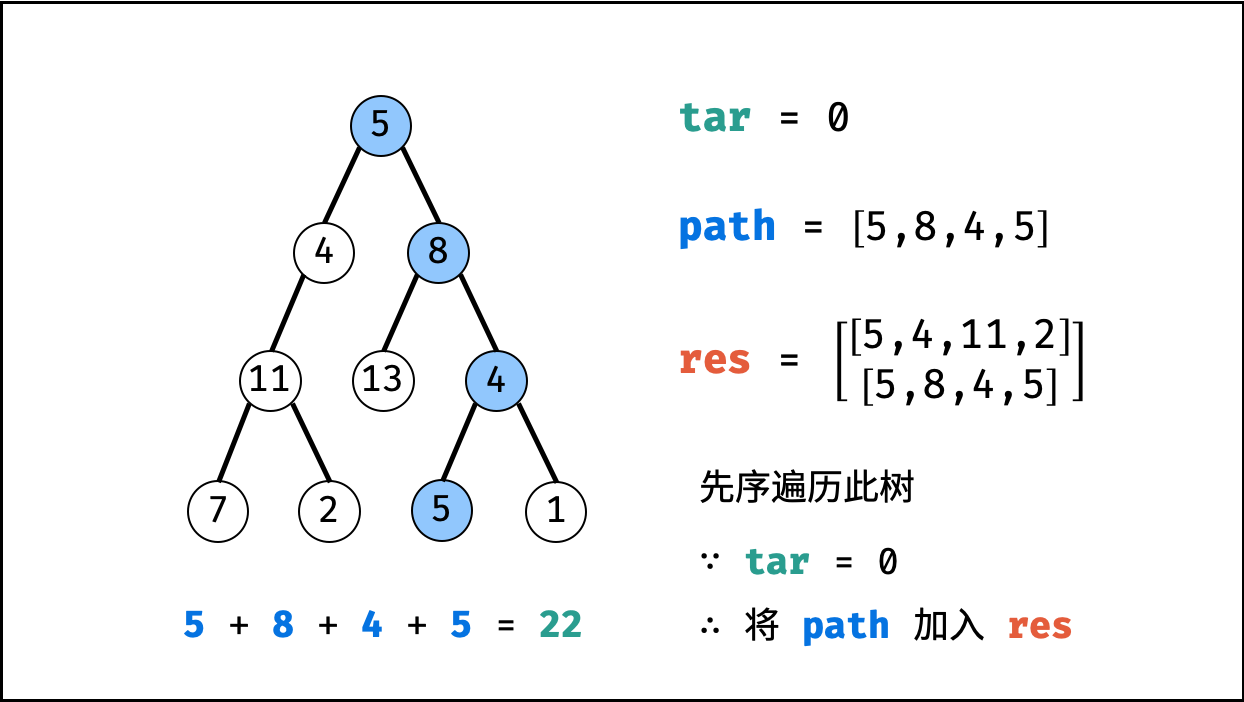
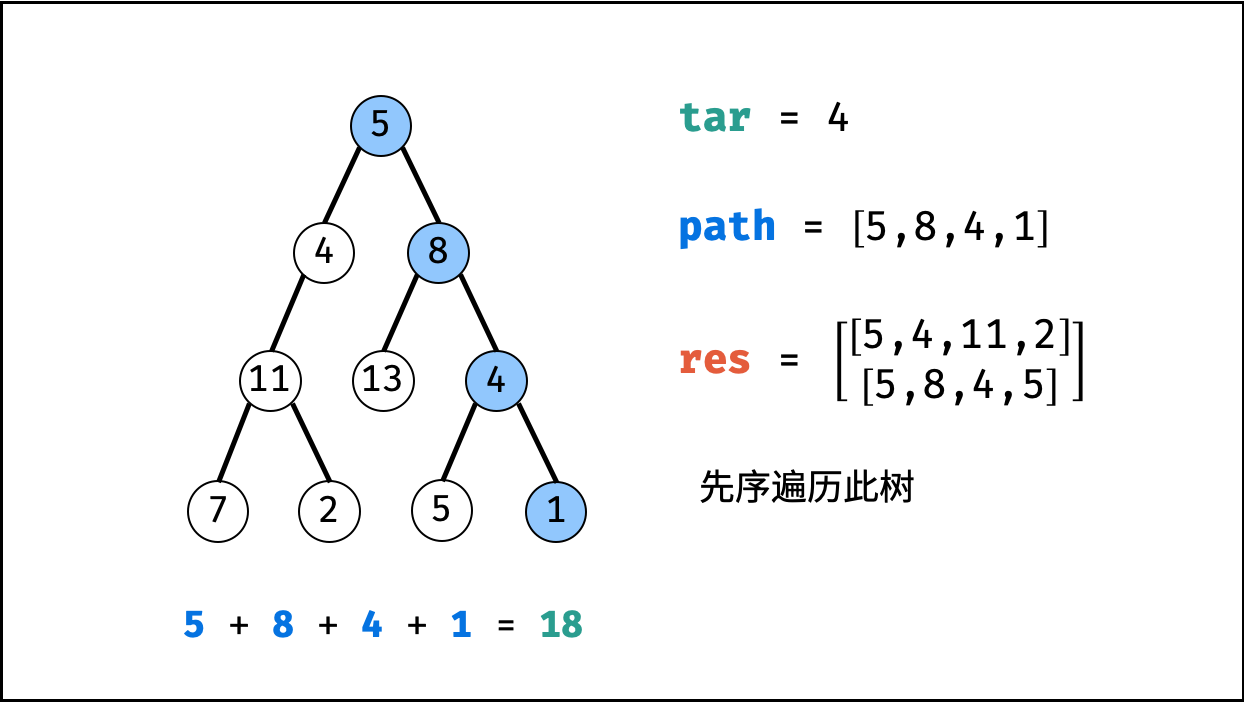
tar = tar - root.val(即目标值tar从targetSum减至 $0$ )。 - 路径记录: 当 (1)
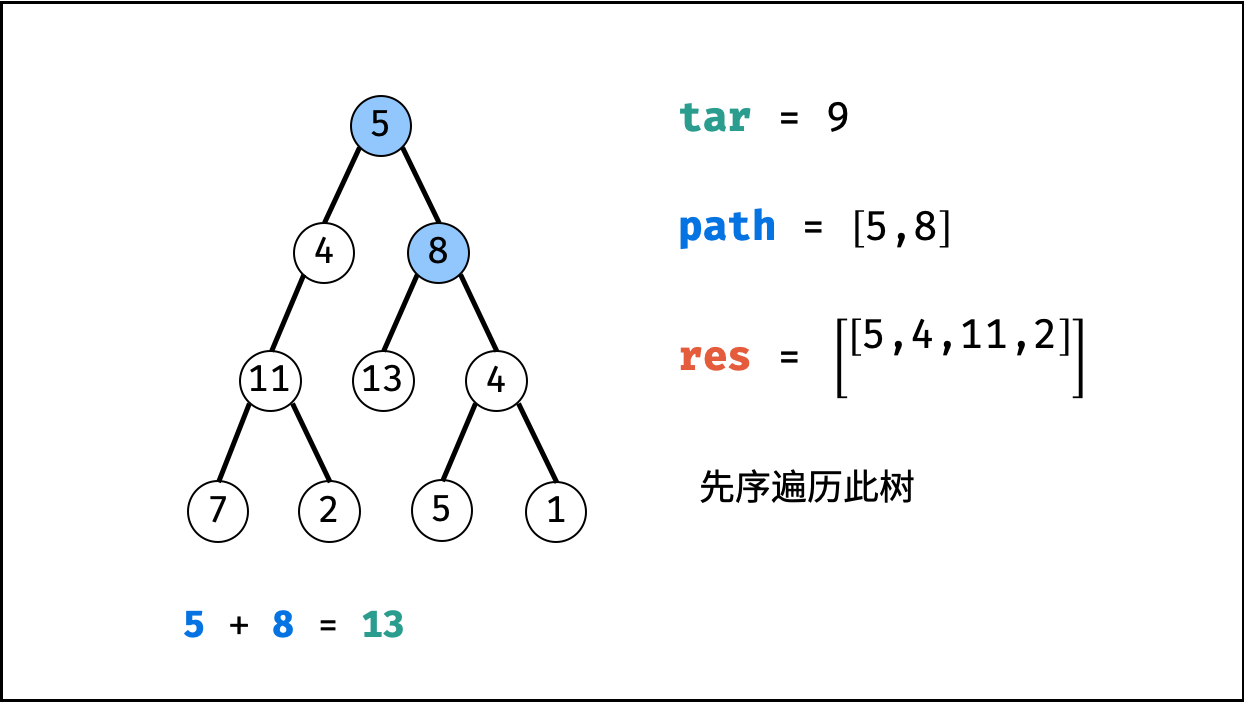
root为叶节点 且 (2) 路径和等于目标值 ,则将此路径path加入res。 - 先序遍历: 递归左 / 右子节点。
- 路径恢复: 向上回溯前,需要将当前节点从路径
path中删除,即执行path.pop()。
- 路径更新: 将当前节点值
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
以 Python 语言为例,记录路径时若直接执行 res.append(path) ,则是将此 path 对象加入了 res ;后续 path 改变时, res 中的 path 对象也会随之改变,因此无法实现结果记录。正确做法为:
- Python:
res.append(list(path))。 - Java:
res.add(new LinkedList(path))。 - C++:
res.push_back(path)。
三者的原理都是避免直接添加 path 对象,而是拷贝了一个 path 对象并加入到 res 。
Python
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res, path = [], []
def recur(root, tar):
if not root: return
path.append(root.val)
tar -= root.val
if tar == 0 and not root.left and not root.right:
res.append(list(path))
recur(root.left, tar)
recur(root.right, tar)
path.pop()
recur(root, targetSum)
return resJava
class Solution {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
recur(root, targetSum);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode root, int tar) {
if (root == null) return;
path.add(root.val);
tar -= root.val;
if (tar == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null)
res.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
recur(root.left, tar);
recur(root.right, tar);
path.removeLast();
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
recur(root, targetSum);
return res;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void recur(TreeNode* root, int tar) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
tar -= root->val;
if (tar == 0 && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
res.push_back(path);
recur(root->left, tar);
recur(root->right, tar);
path.pop_back();
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : $N$ 为二叉树的节点数,先序遍历需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下,即树退化为链表时,
path存储所有树节点,使用 $O(N)$ 额外空间。