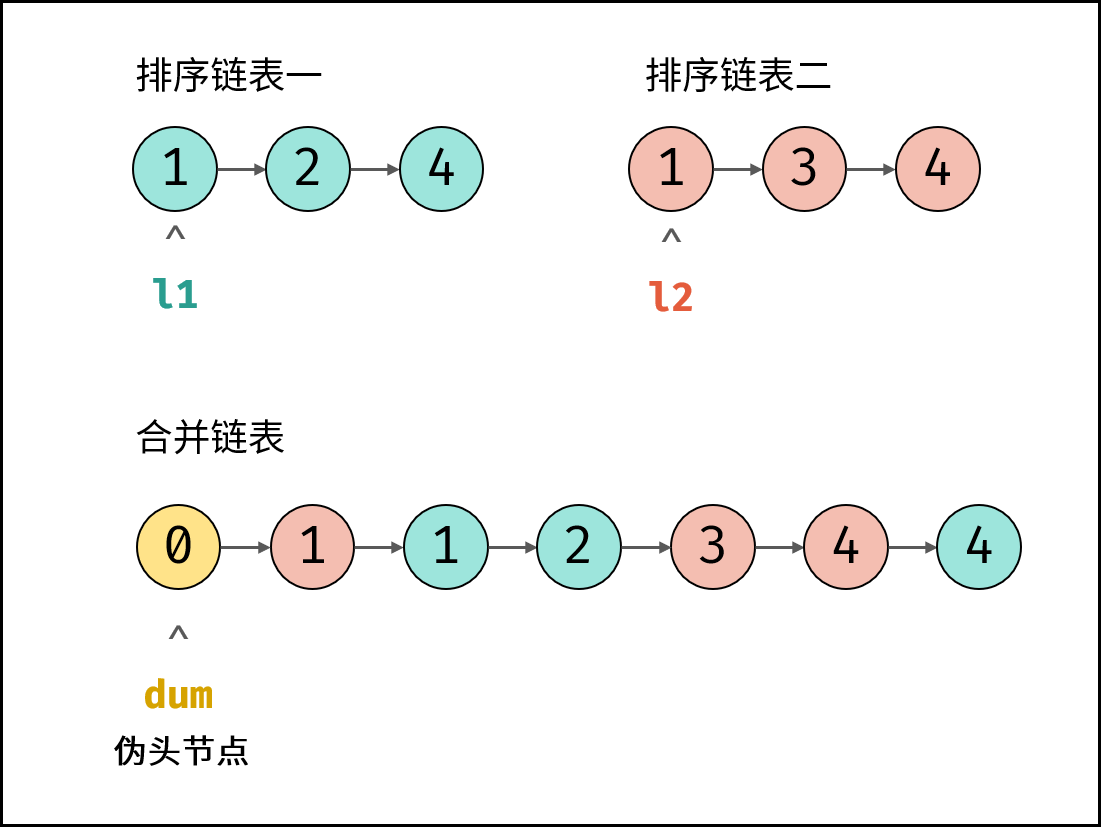
解题思路:
根据题目描述, 链表 $l_1$ , $l_2$ 是 递增 的,因此容易想到使用双指针 $l_1$ 和 $l_2$ 遍历两链表,根据 $l_1.val$ 和 $l_2.val$ 的大小关系确定节点添加顺序,两节点指针交替前进,直至遍历完毕。
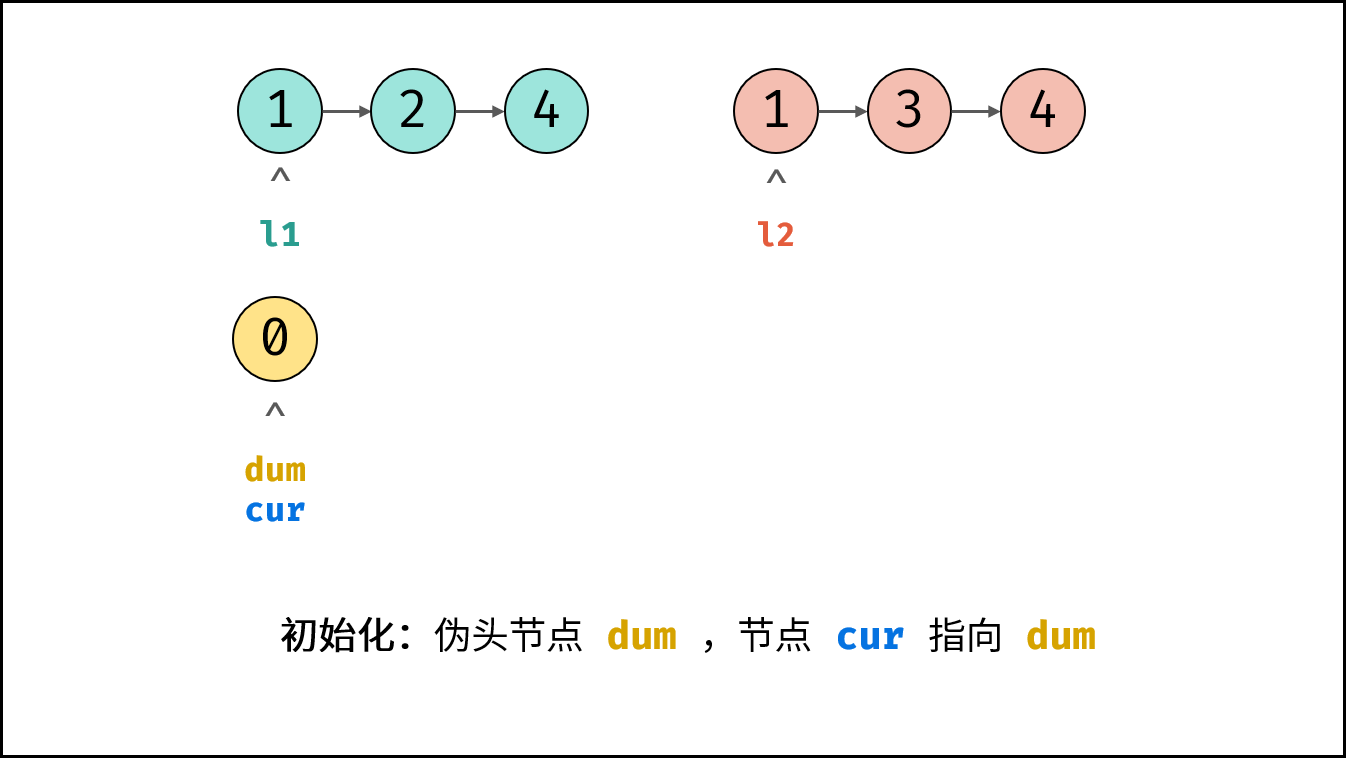
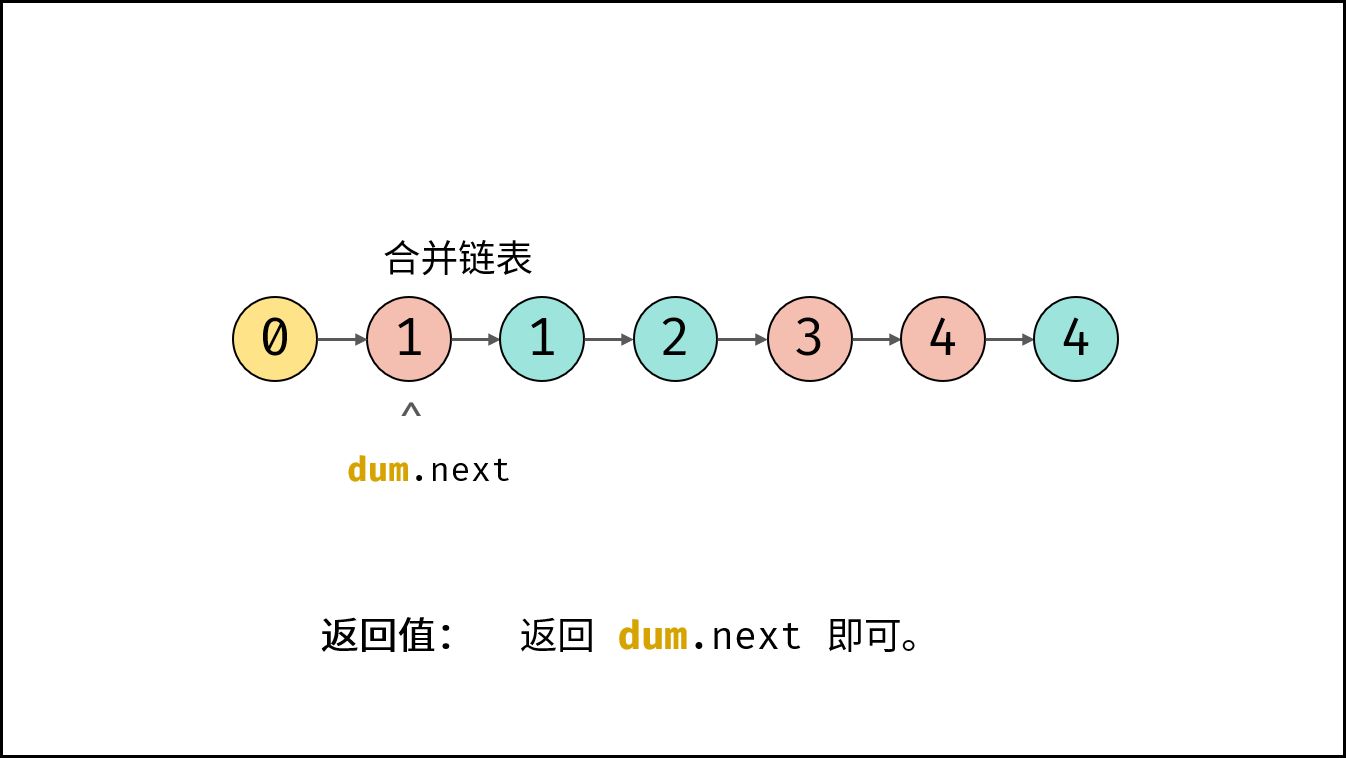
引入伪头节点: 由于初始状态合并链表中无节点,因此循环第一轮时无法将节点添加到合并链表中。解决方案:初始化一个辅助节点 $dum$ 作为合并链表的伪头节点,将各节点添加至 $dum$ 之后。
算法流程:
- 初始化: 伪头节点 $dum$ ,节点 $cur$ 指向 $dum$ 。
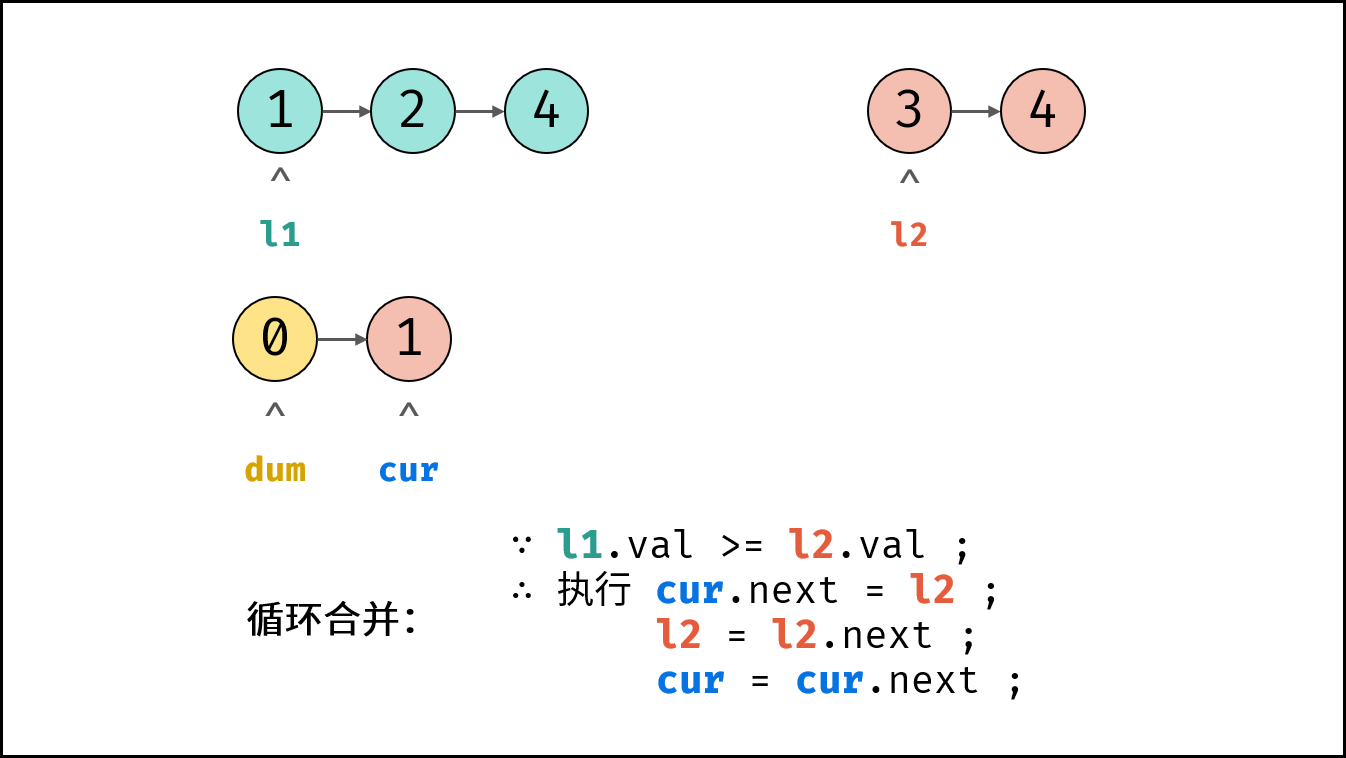
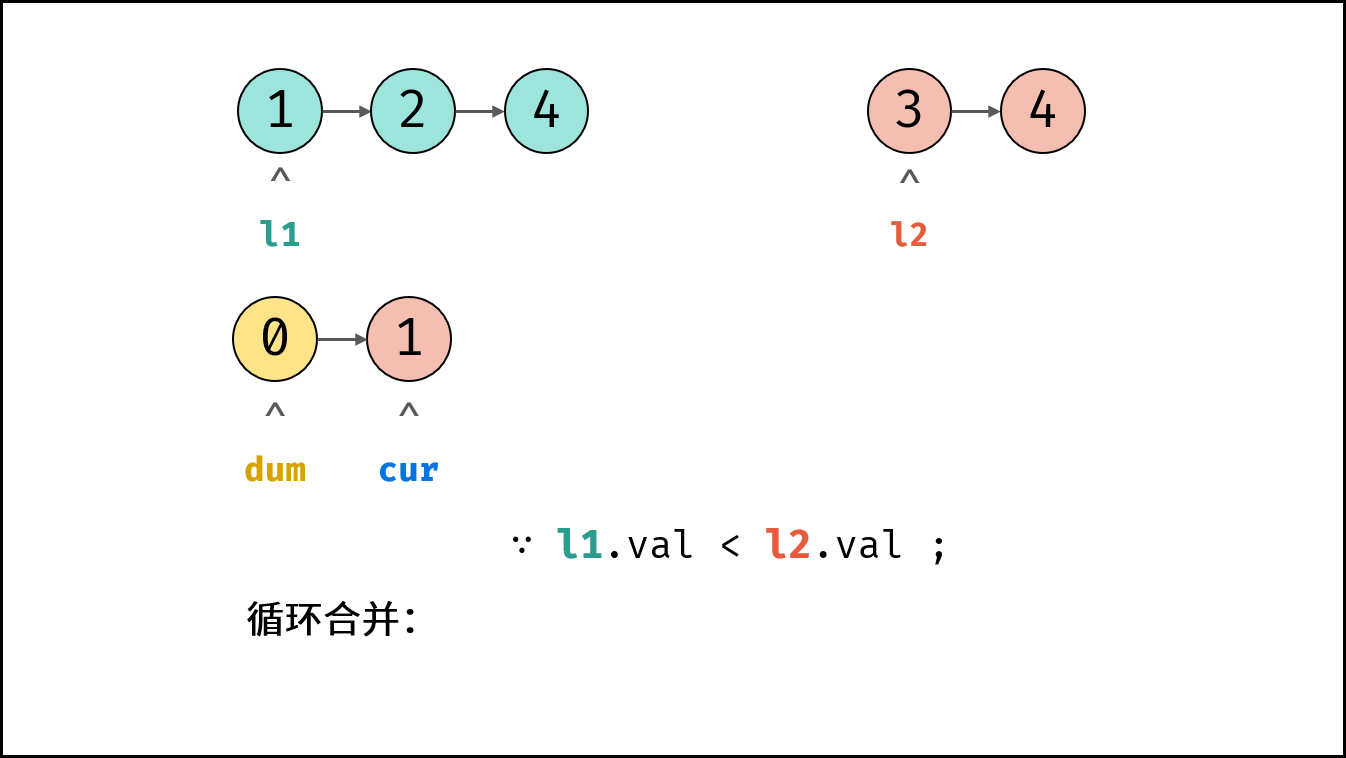
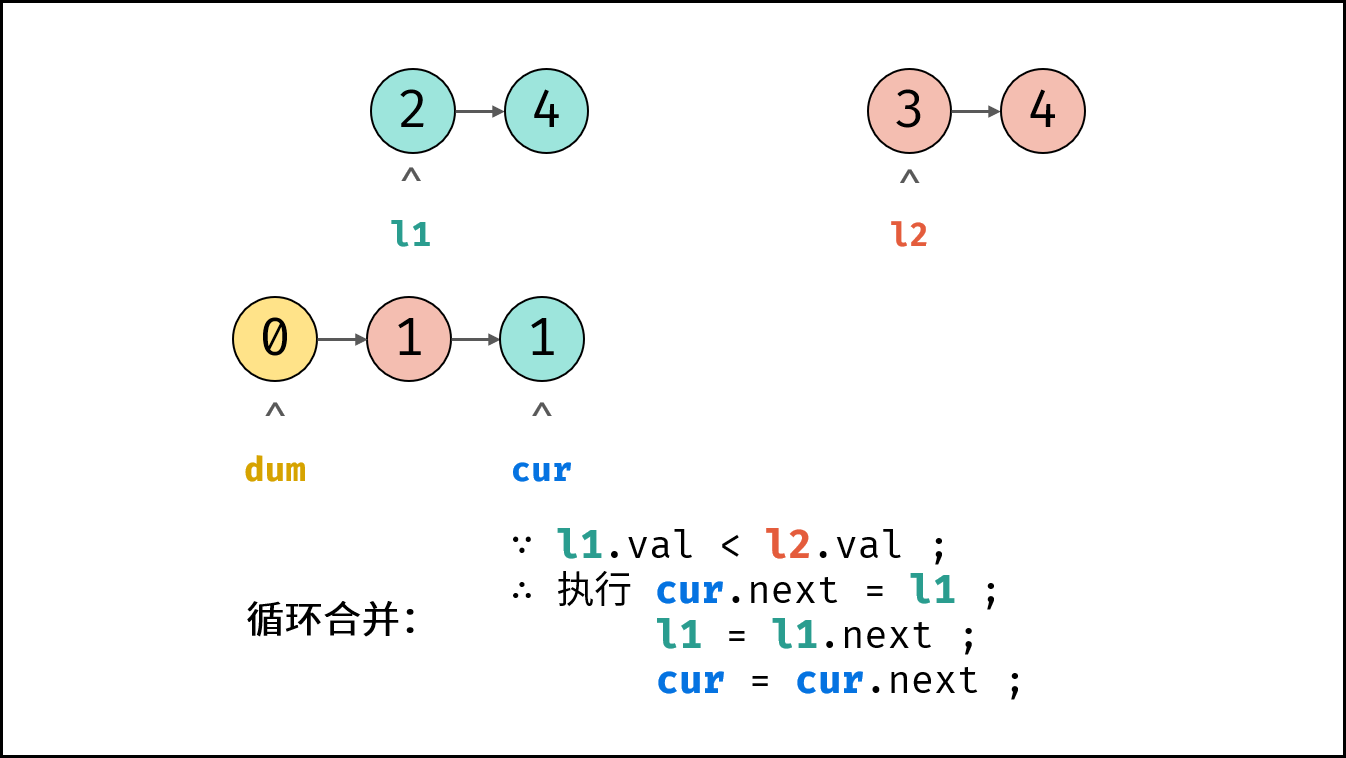
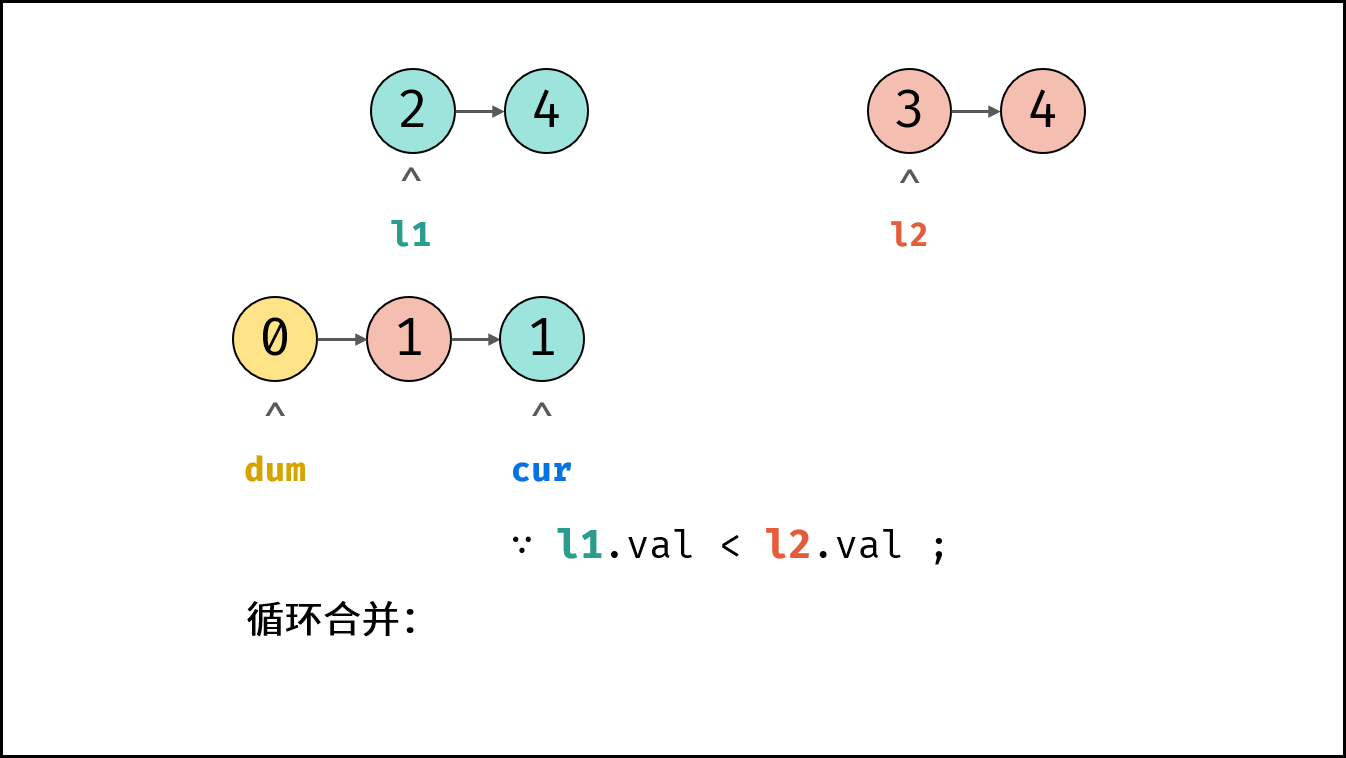
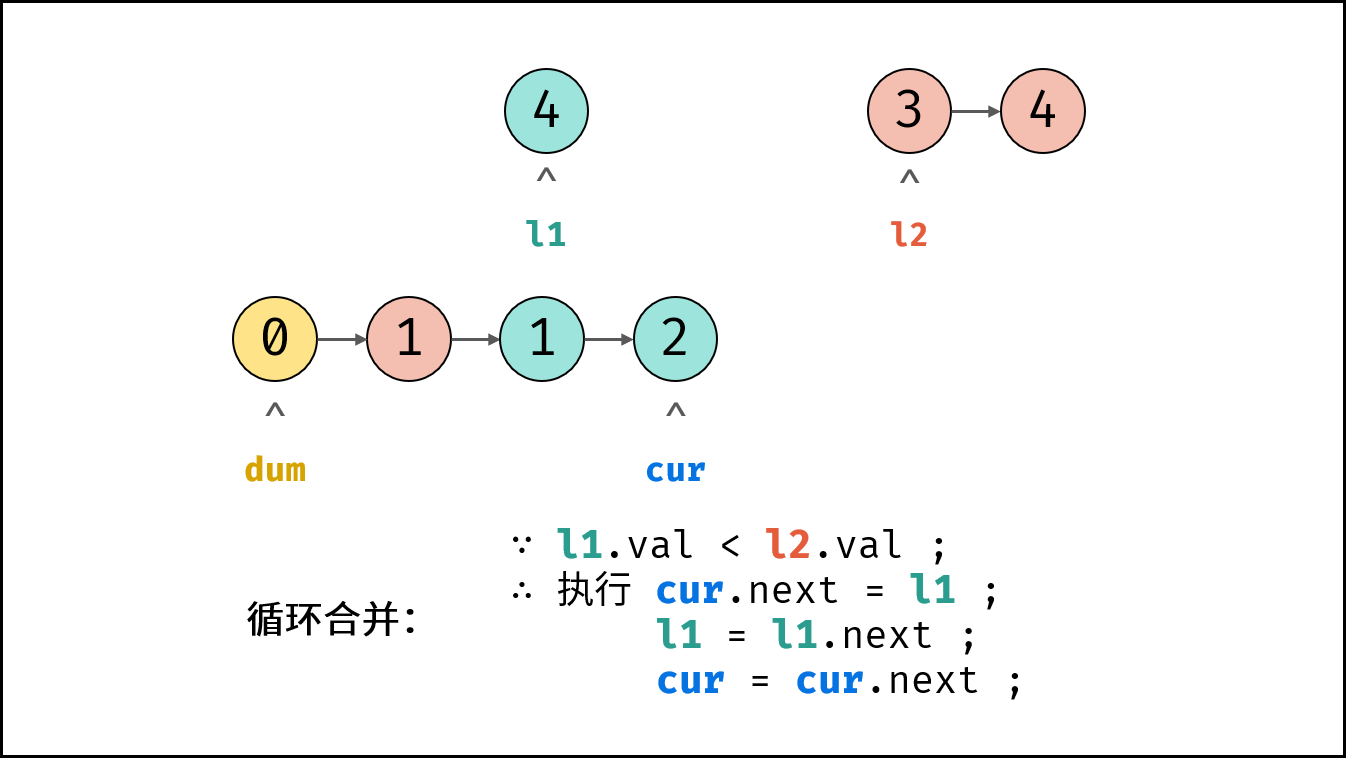
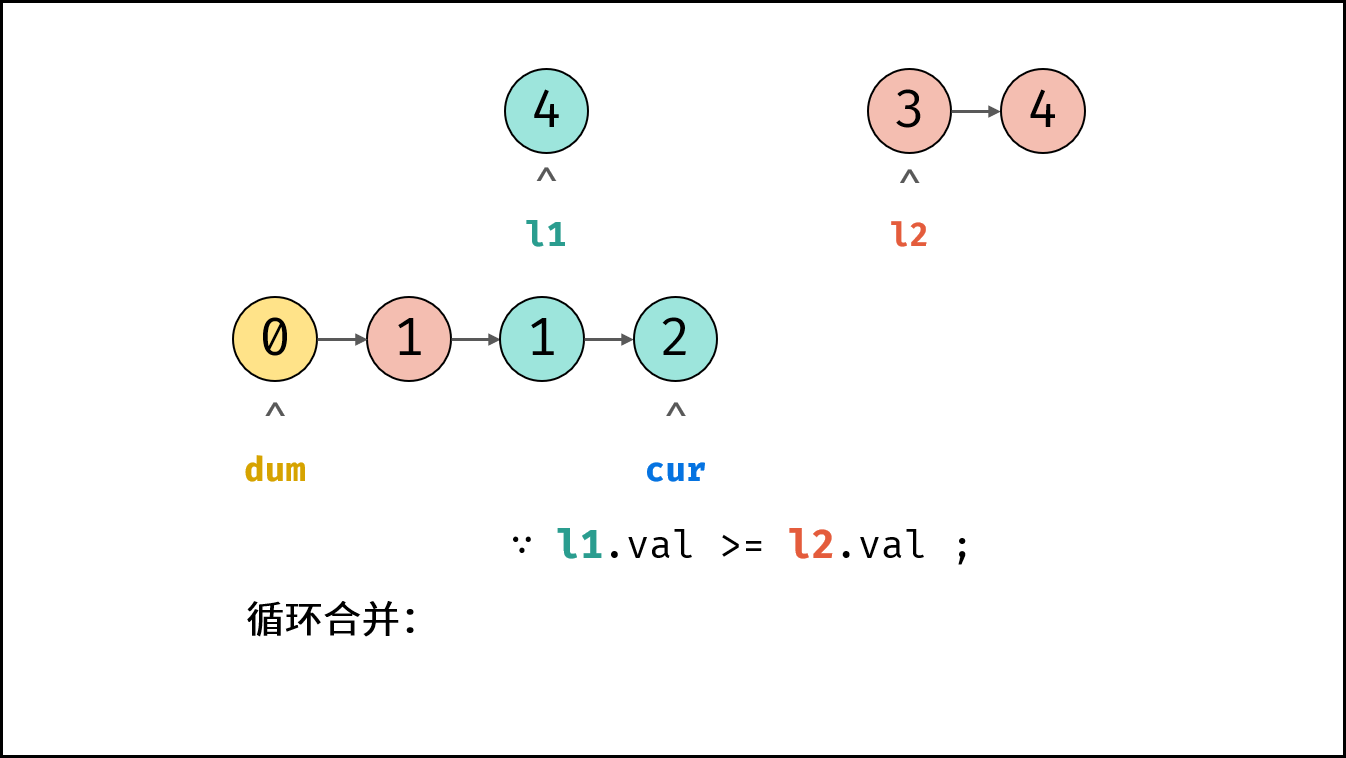
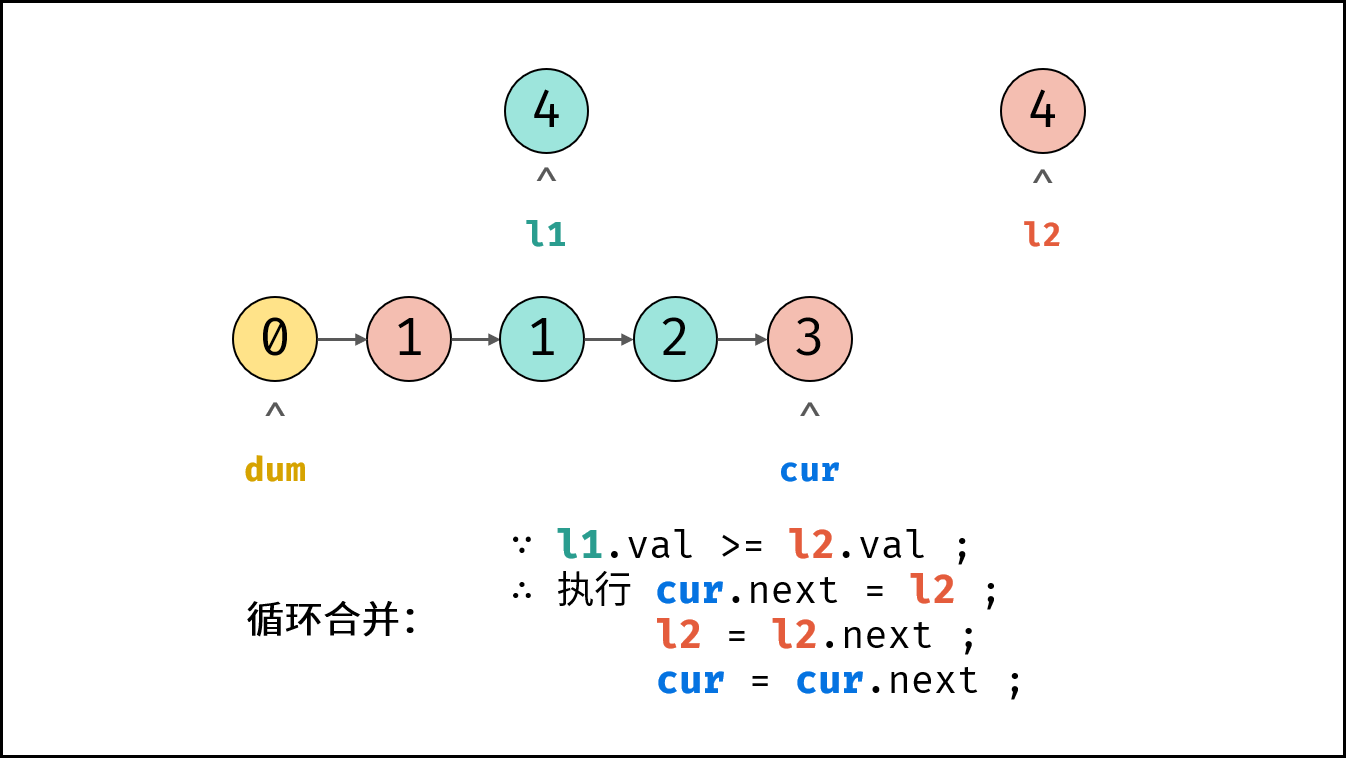
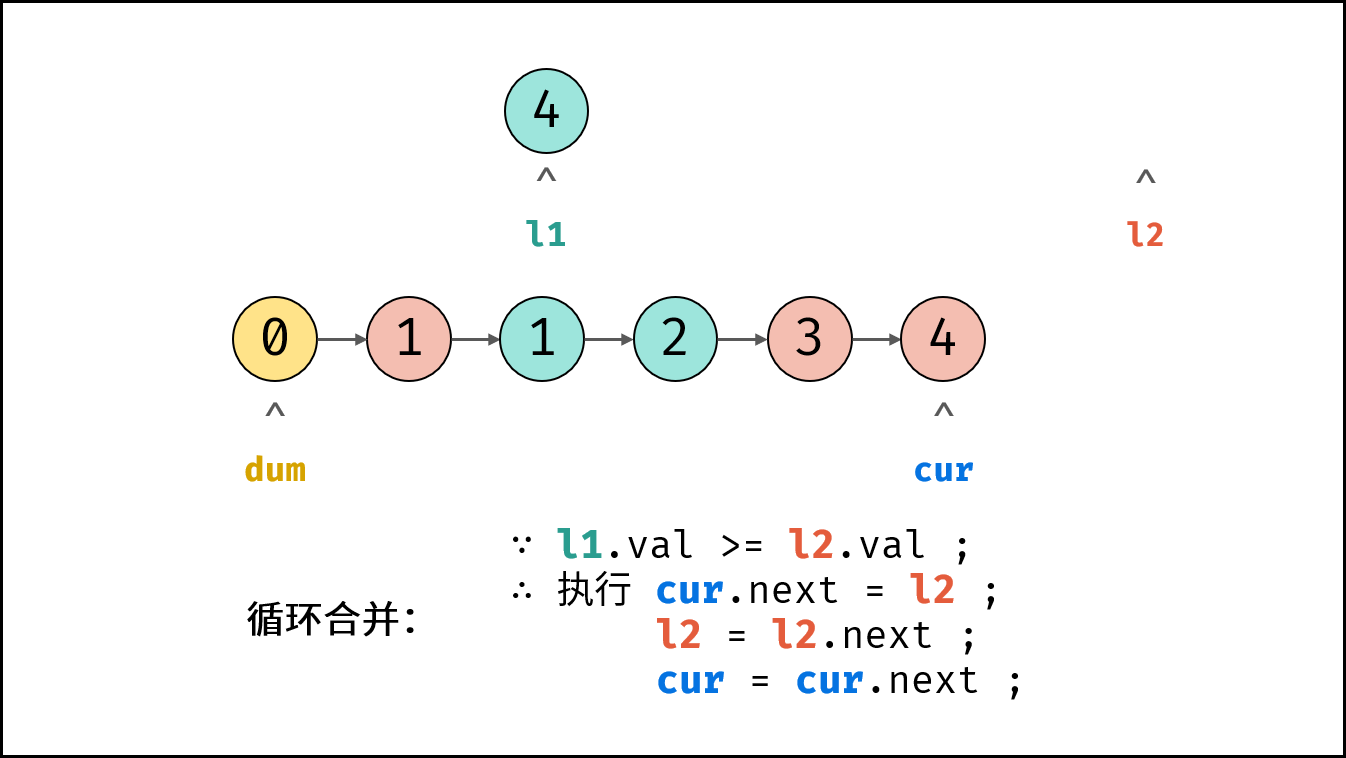
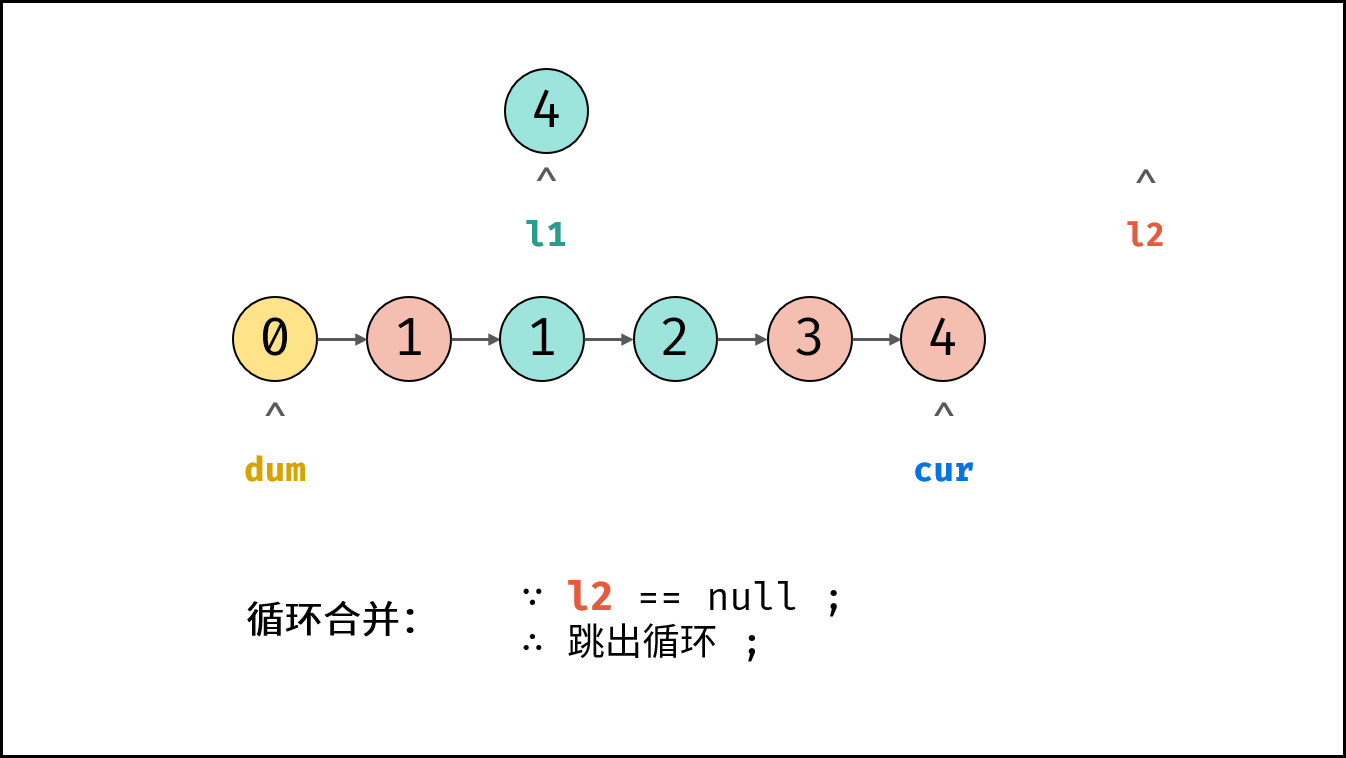
- 循环合并: 当 $l_1$ 或 $l_2$ 为空时跳出。
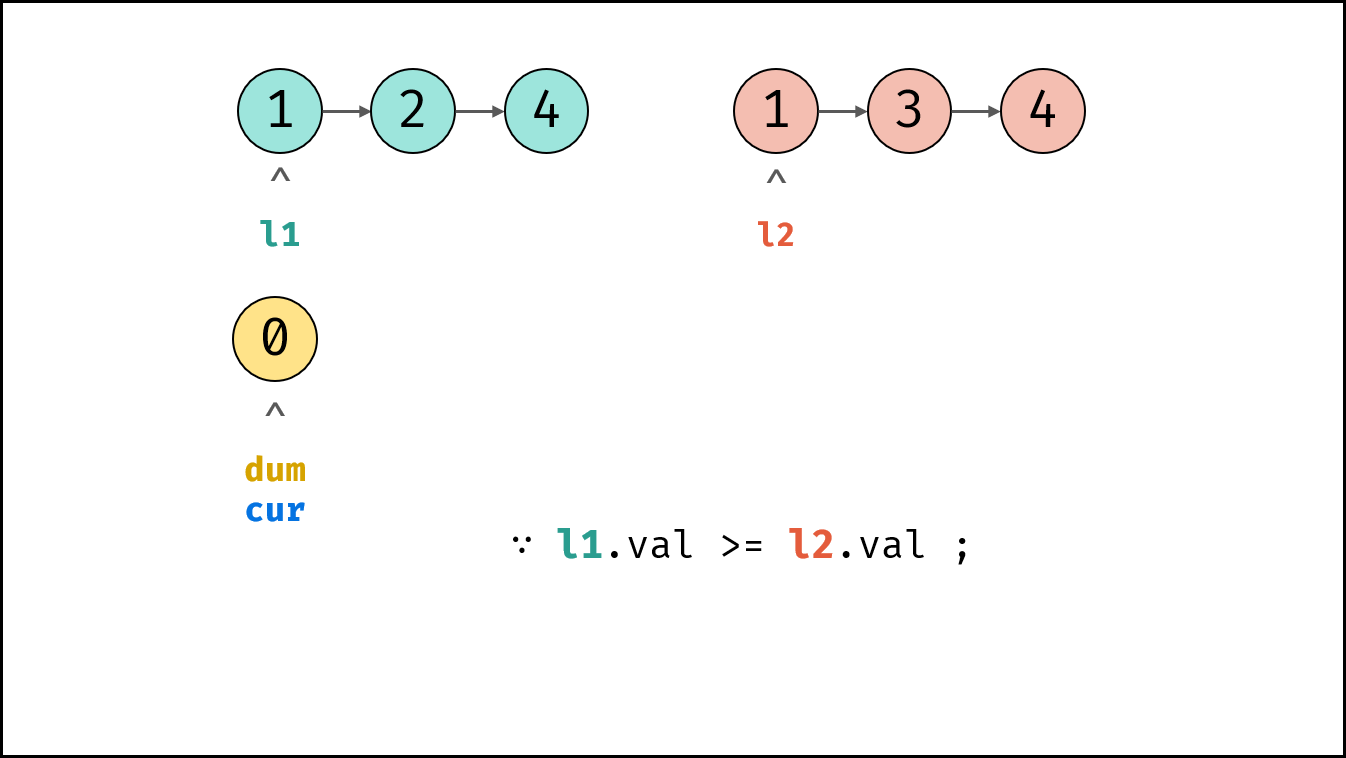
- 当 $l_1.val < l_2.val$ 时: $cur$ 的后继节点指定为 $l_1$ ,并 $l_1$ 向前走一步。
- 当 $l_1.val \geq l_2.val$ 时: $cur$ 的后继节点指定为 $l_2$ ,并 $l_2$ 向前走一步 。
- 节点 $cur$ 向前走一步,即 $cur = cur.next$ 。
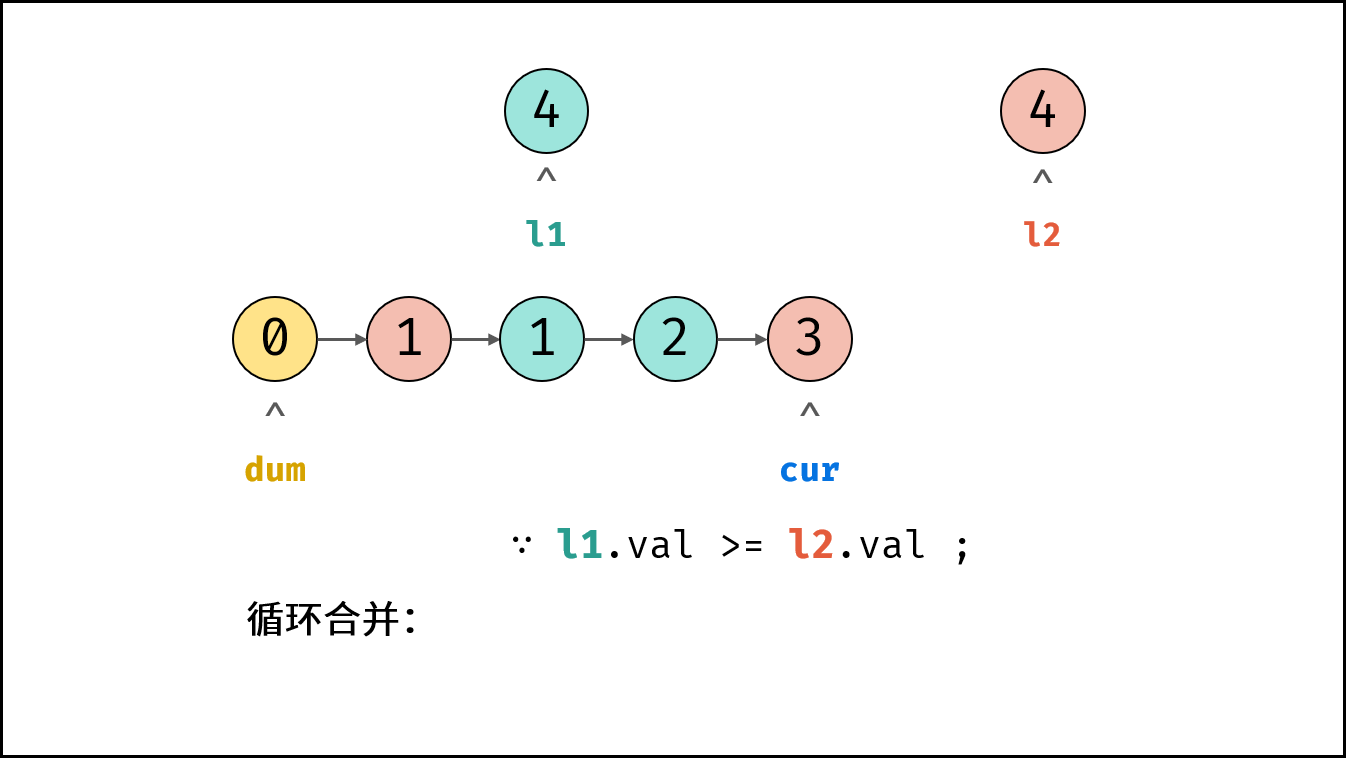
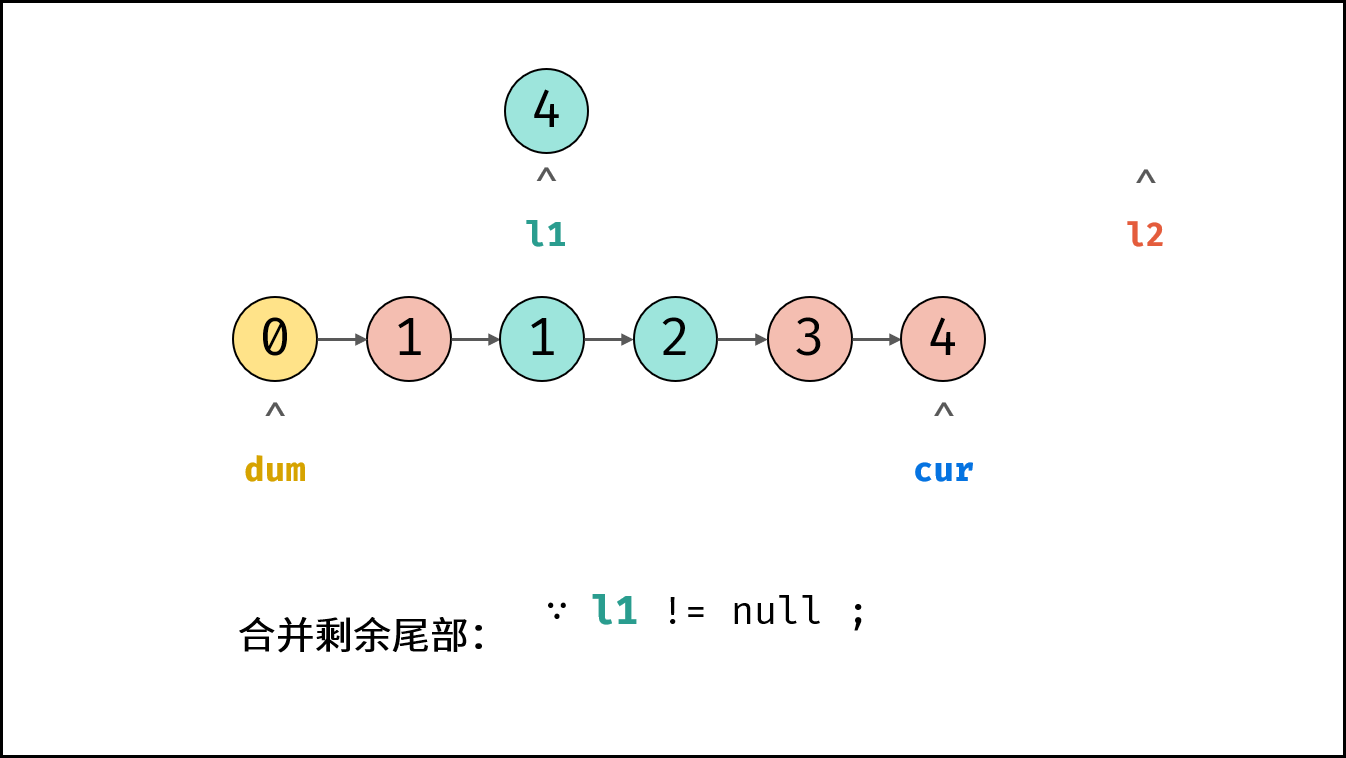
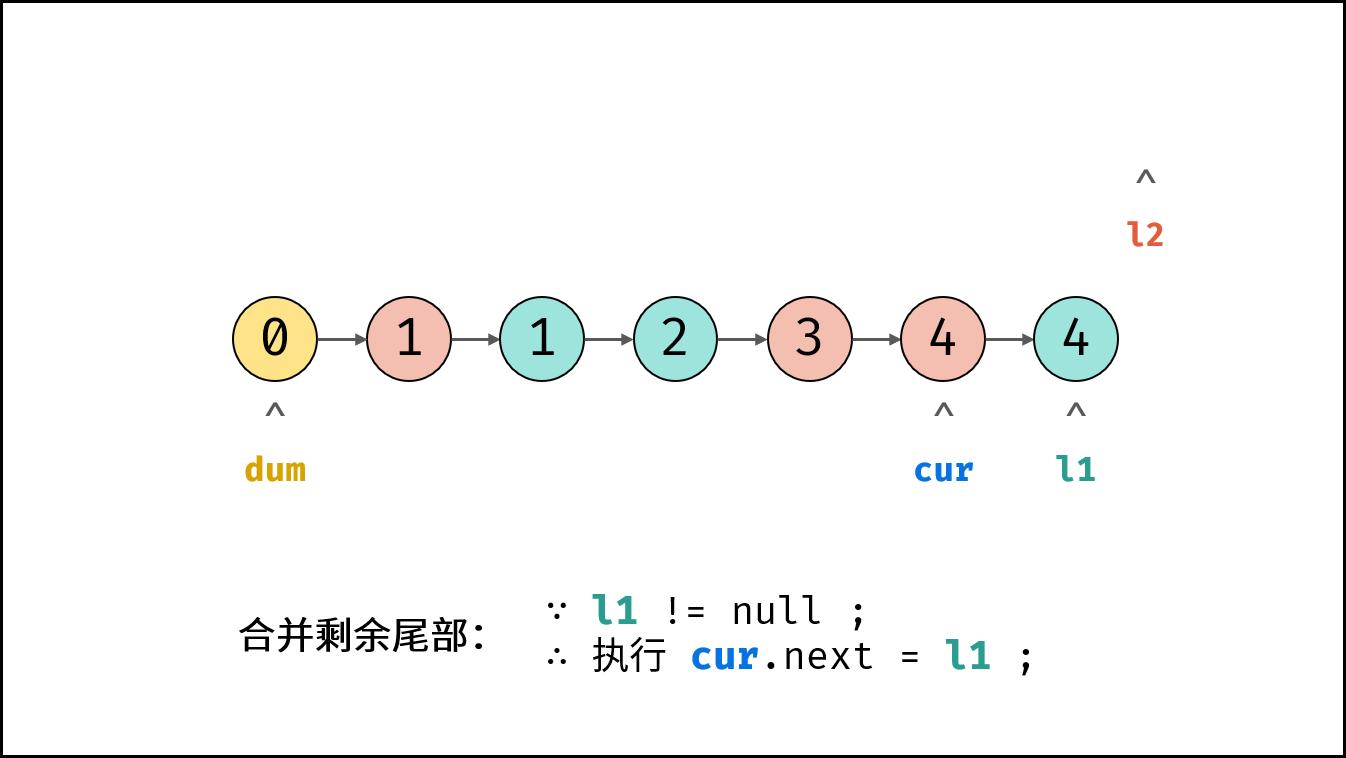
- 合并剩余尾部: 跳出时有两种情况,即 $l_1$ 为空 或 $l_2$ 为空。
- 若 $l_1 \ne null$ : 将 $l_1$ 添加至节点 $cur$ 之后。
- 否则: 将 $l_2$ 添加至节点 $cur$ 之后。
- 返回值: 合并链表在伪头节点 $dum$ 之后,因此返回 $dum.next$ 即可。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python 三元表达式写法 A if x else B ,代表当 $x = True$ 时执行 $A$ ,否则执行 $B$ 。
Python
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
cur = dum = ListNode(0)
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val < list2.val:
cur.next, list1 = list1, list1.next
else:
cur.next, list2 = list2, list2.next
cur = cur.next
cur.next = list1 if list1 else list2
return dum.nextJava
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dum = new ListNode(0), cur = dum;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else {
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = list1 != null ? list1 : list2;
return dum.next;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dum = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dum;
while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr) {
if (list1->val < list2->val) {
cur->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else {
cur->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = list1 != nullptr ? list1 : list2;
return dum->next;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(M+N)$ : $M, N$ 分别为链表 $l_1$, $l_2$ 的长度,合并操作需遍历两链表。
- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 节点引用 $dum$ , $cur$ 使用常数大小的额外空间。