解题思路:
长度为 $N$ 的字符串共有 $\frac{(1 + N)N}{2}$ 个子字符串(复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ ),判断长度为 $N$ 的字符串是否有重复字符的复杂度为 $O(N)$ ,因此本题使用暴力法解决的复杂度为 $O(N^3)$ 。
本题有滑动窗口和动态规划两种解法。
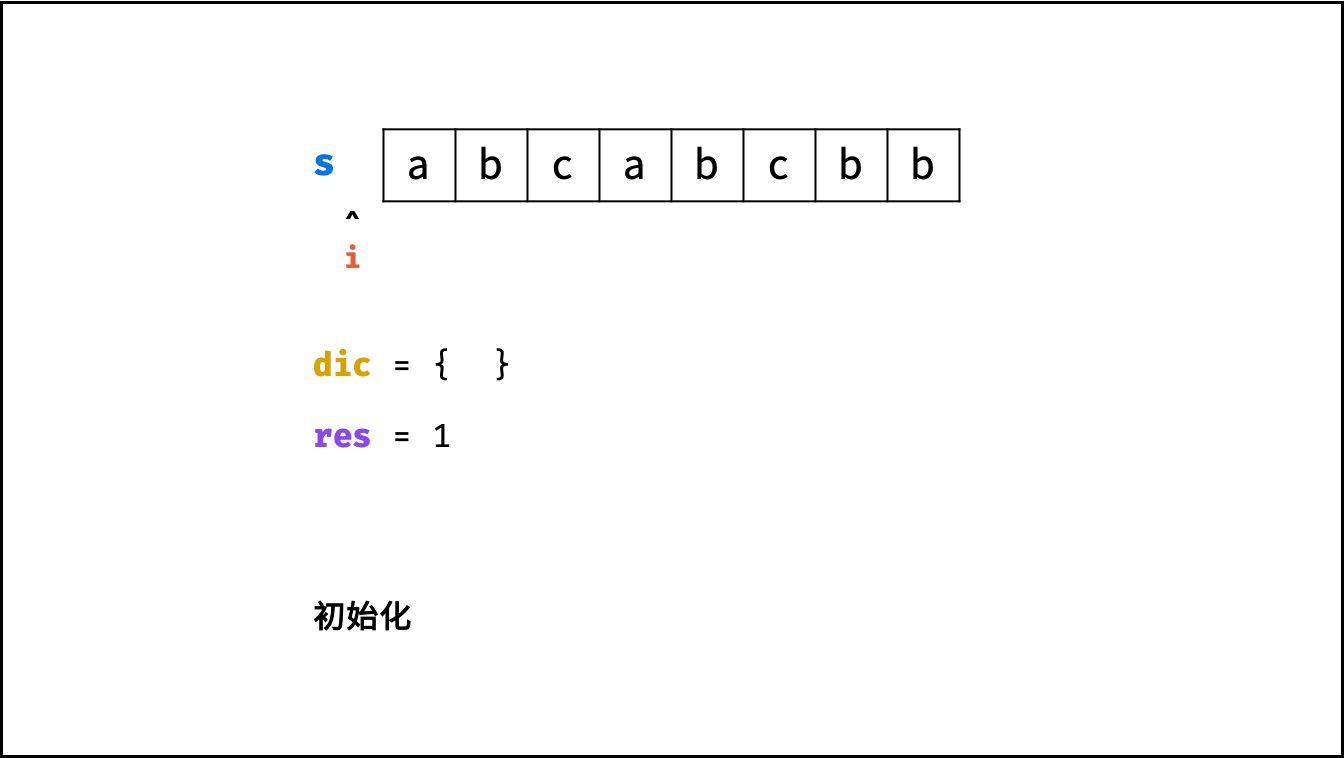
方法一:滑动窗口 + 哈希表
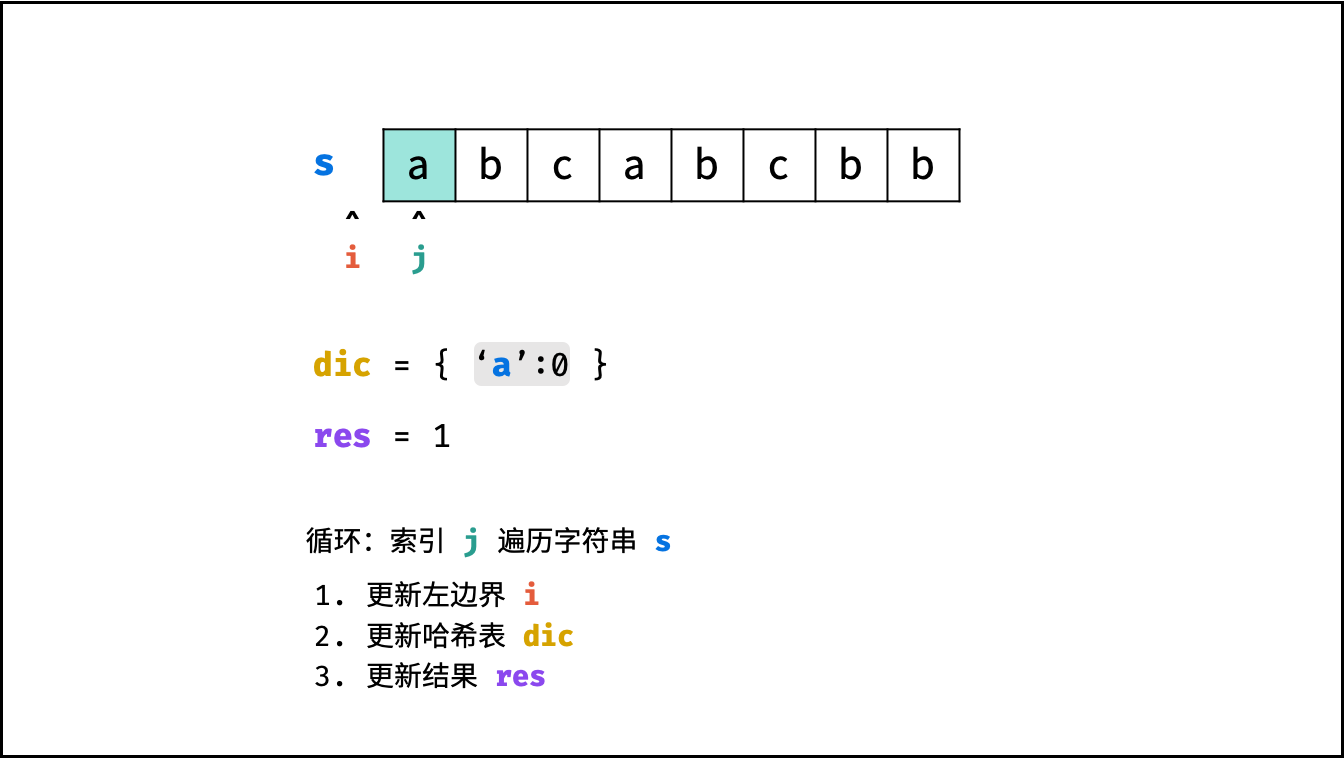
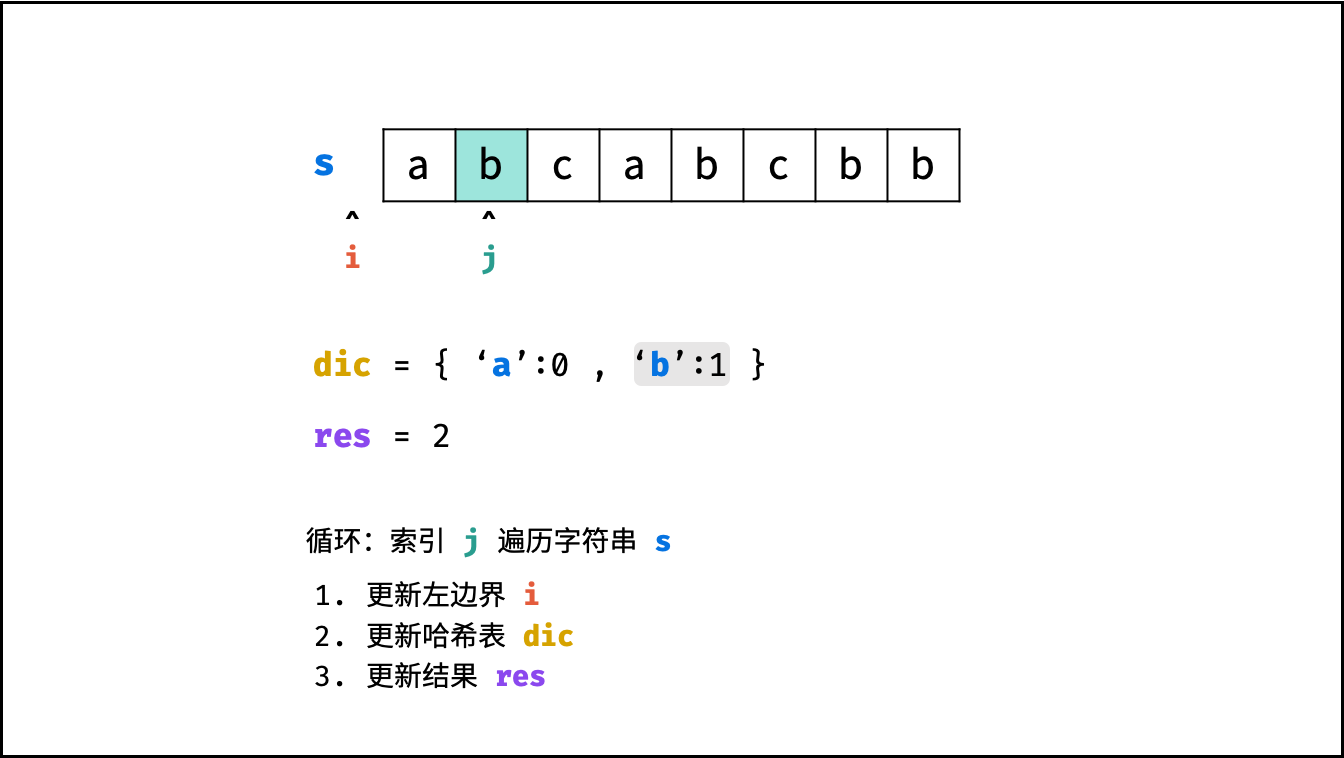
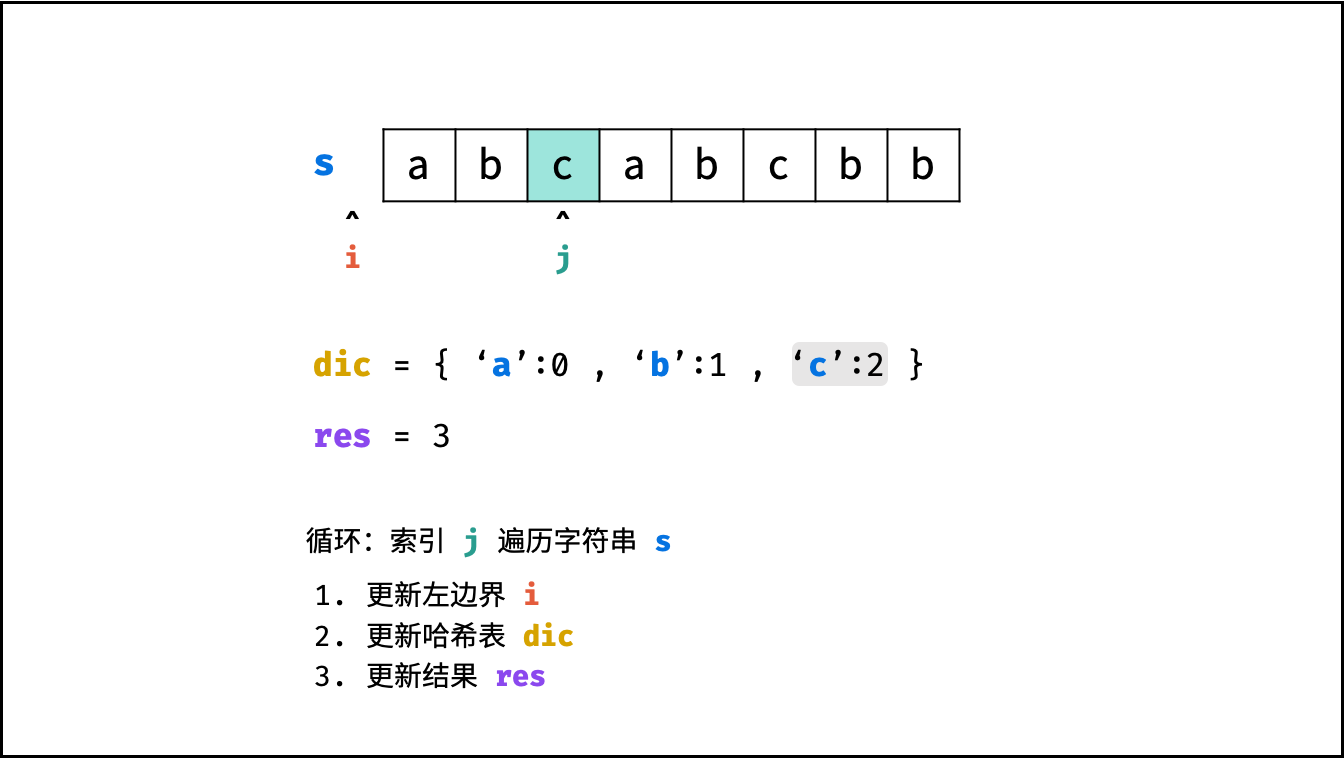
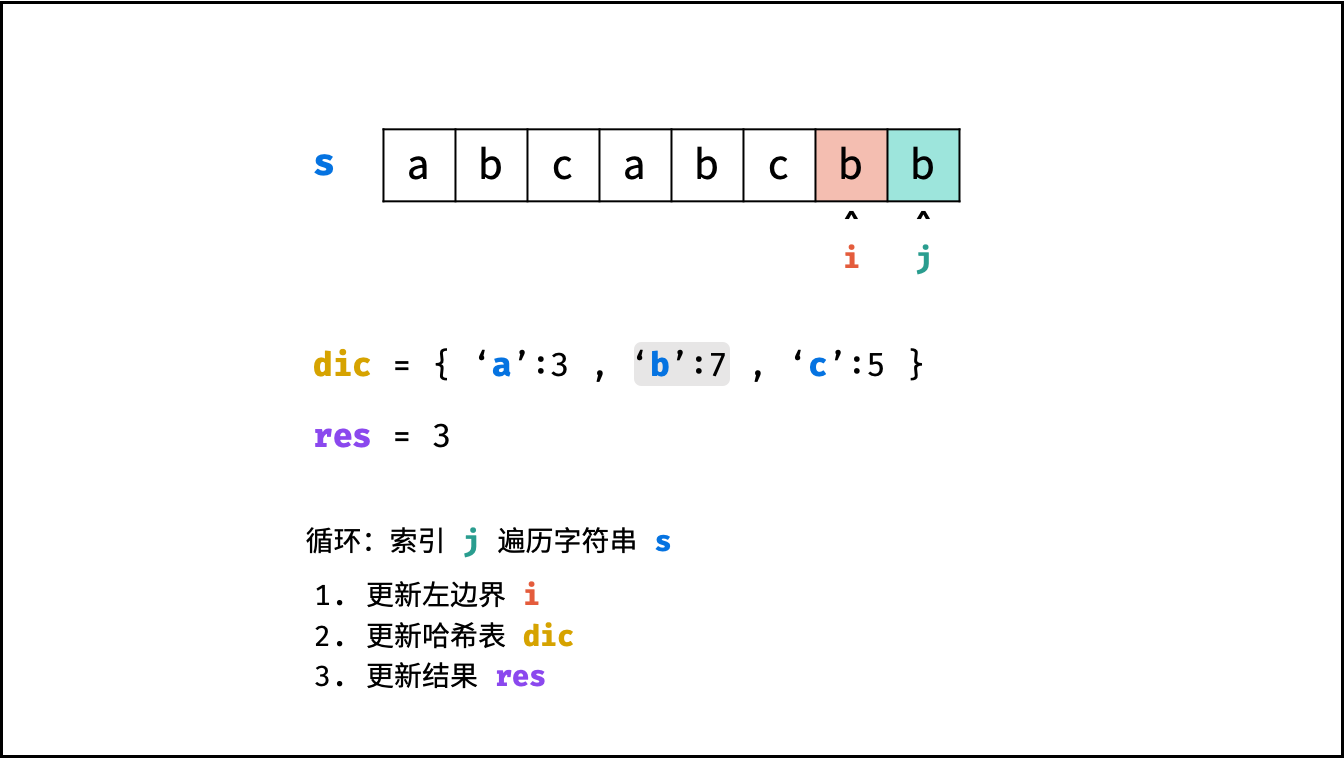
哈希表 $dic$ 统计: 指针 $j$ 遍历字符 $s$ ,哈希表统计字符 $s[j]$ 最后一次出现的索引 。
更新左指针 $i$ : 根据上轮左指针 $i$ 和 $dic[s[j]]$ ,每轮更新左边界 $i$ ,保证区间 $[i + 1, j]$ 内无重复字符且最大。
$$ i = \max(dic[s[j]], i) $$
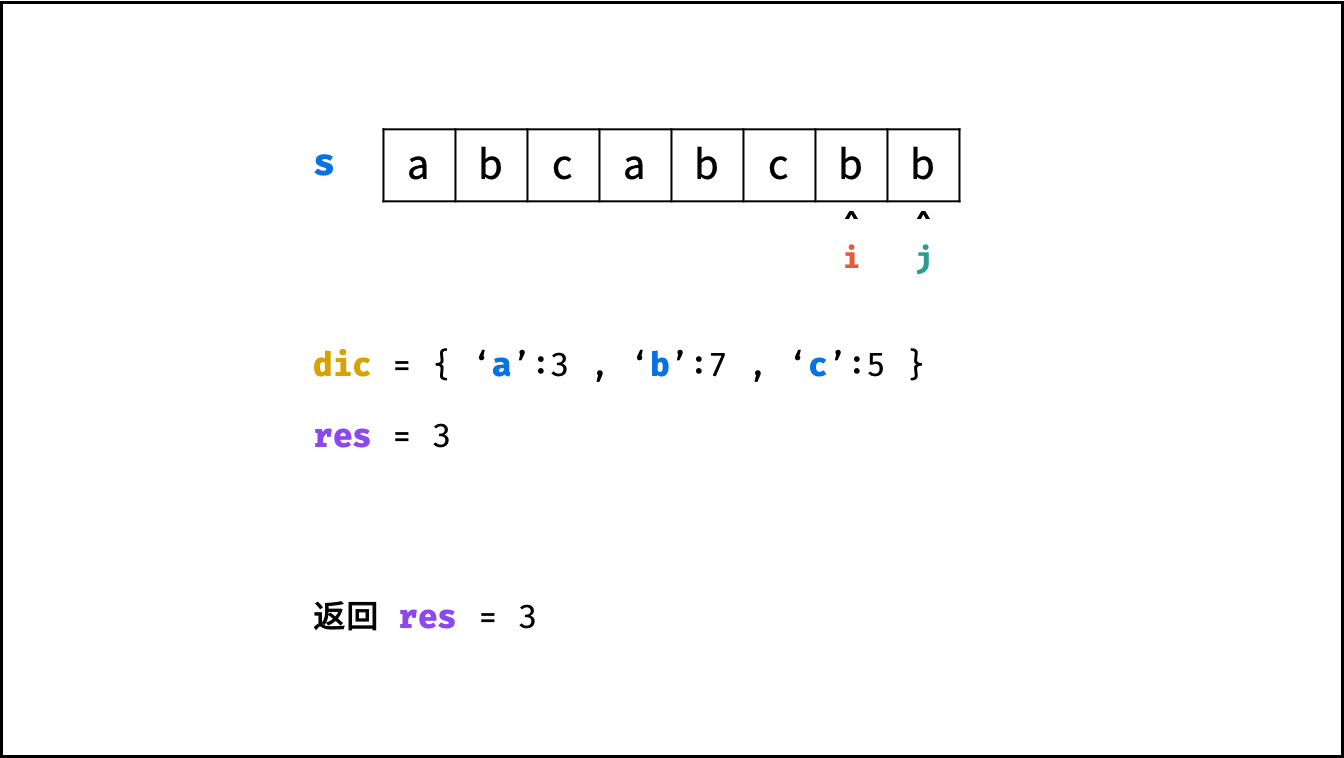
更新结果 $res$ : 取上轮 $res$ 和本轮双指针区间 $[i + 1,j]$ 的宽度(即 $j - i$ )中的最大值。
$$ res = \max(res, j - i) $$
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,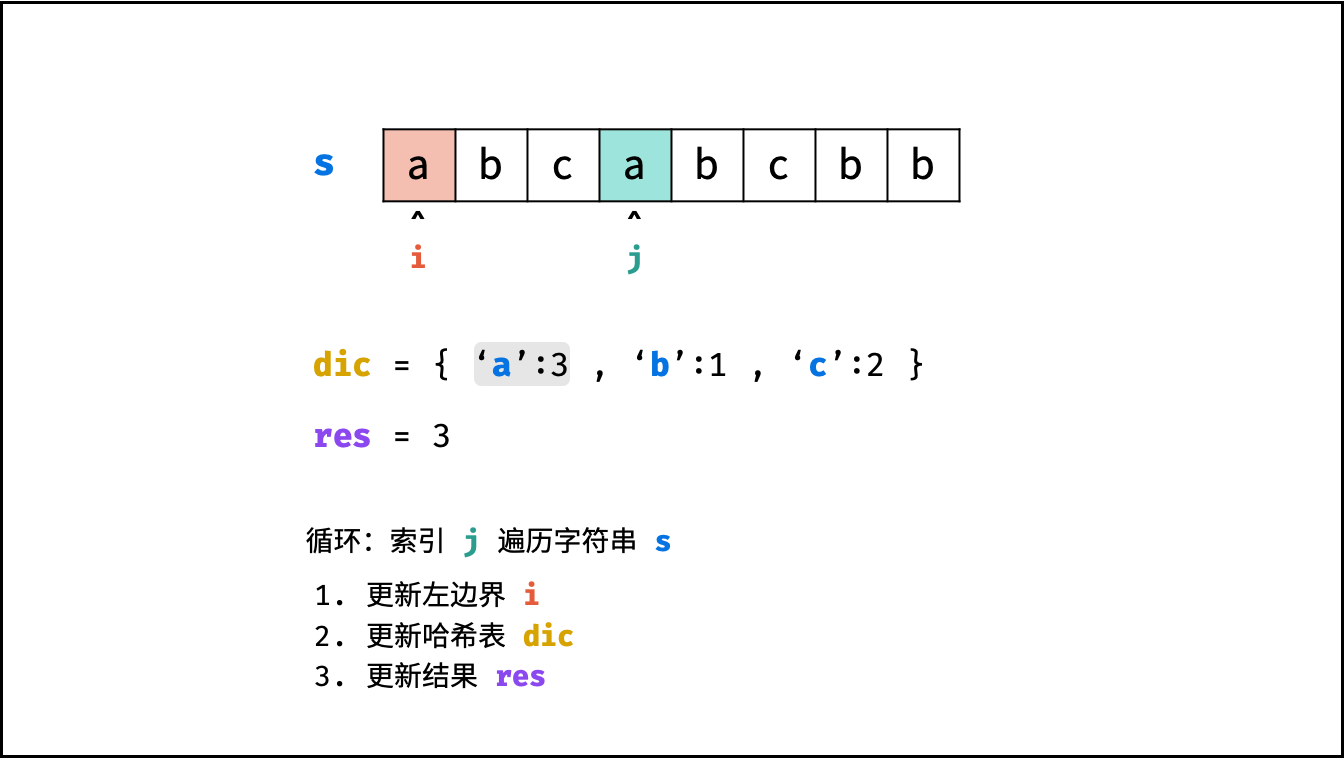 ,
,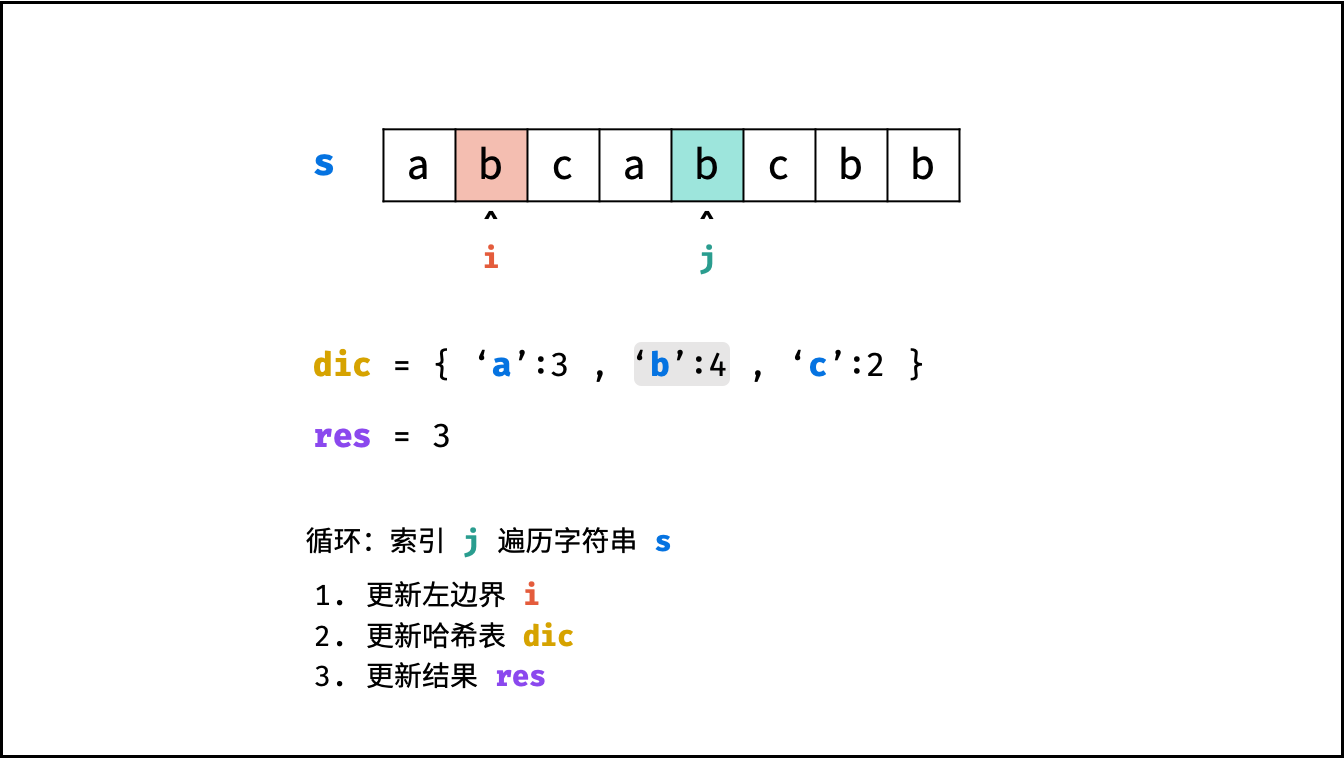 ,
,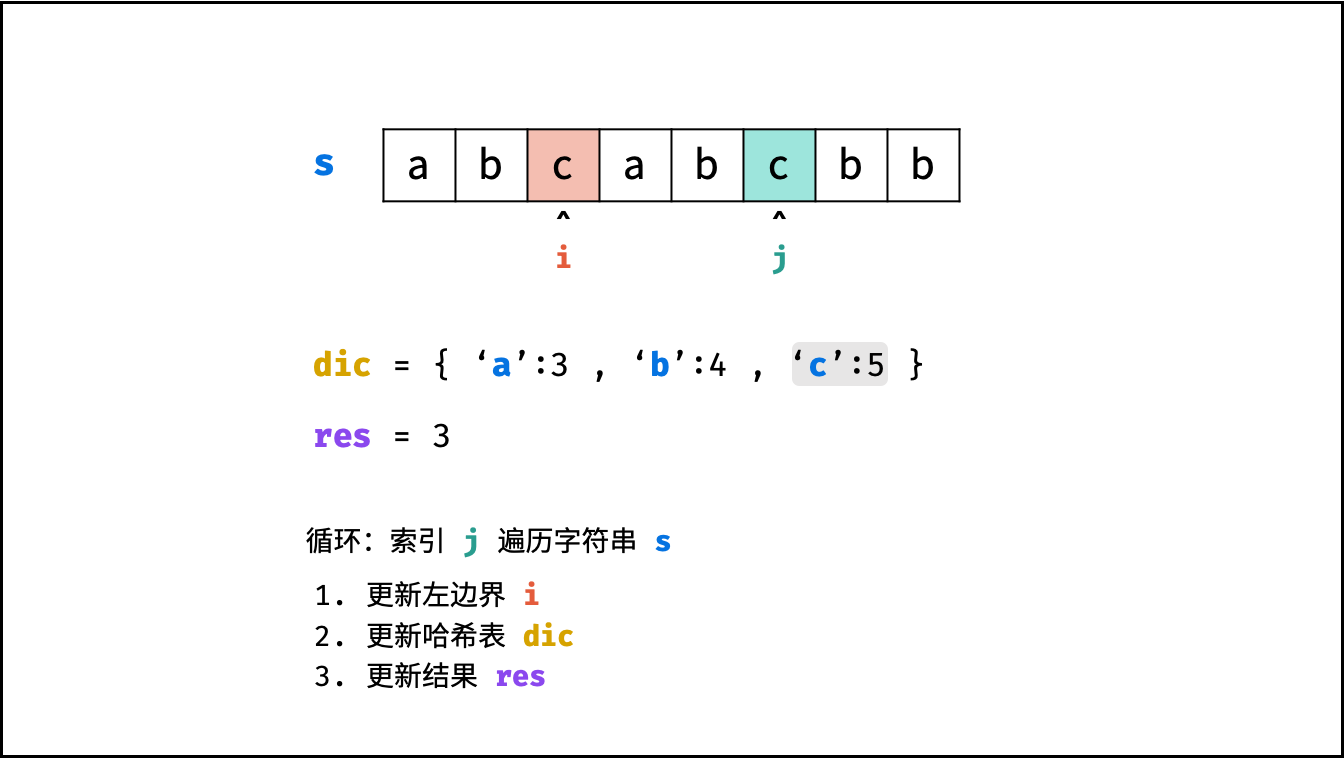 ,
,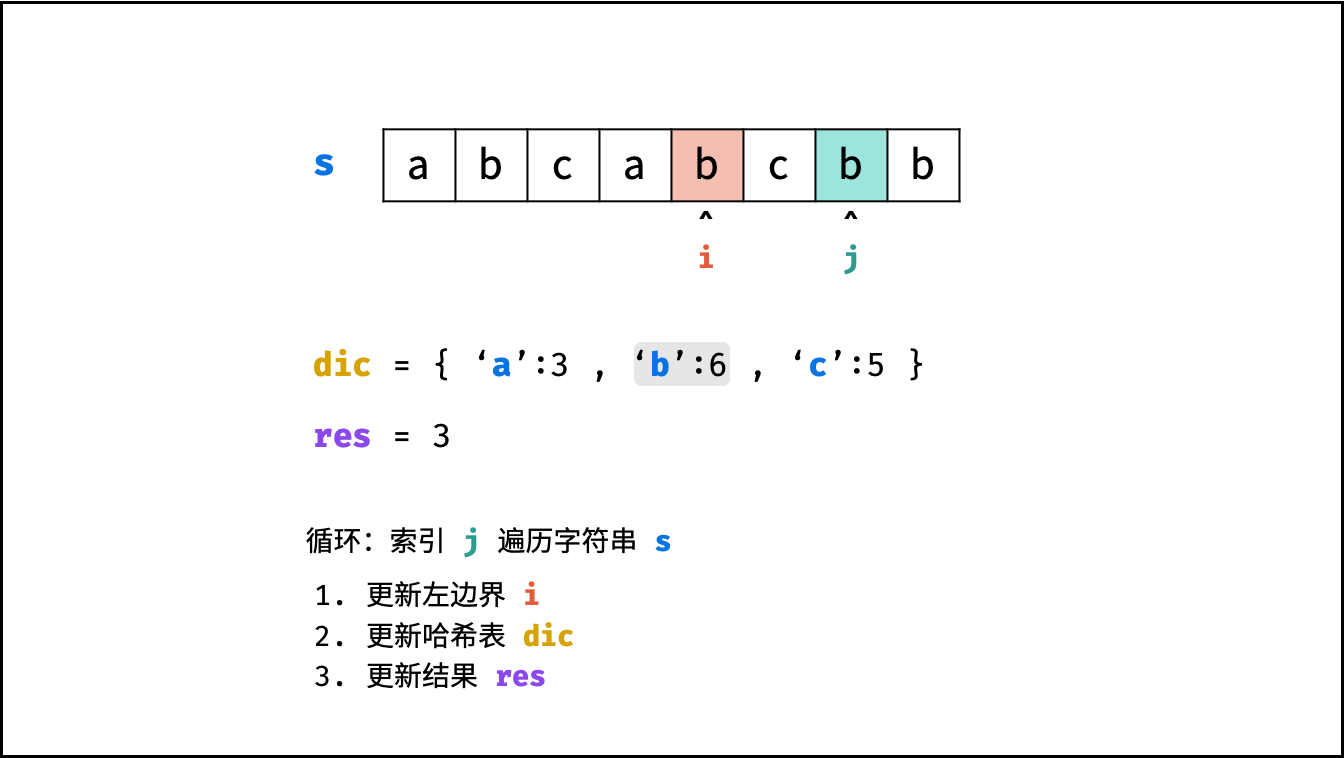 ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
dic, res, i = {}, 0, -1
for j in range(len(s)):
if s[j] in dic:
i = max(dic[s[j]], i) # 更新左指针 i
dic[s[j]] = j # 哈希表记录
res = max(res, j - i) # 更新结果
return resclass Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
int i = -1, res = 0, len = s.length();
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (dic.containsKey(s.charAt(j)))
i = Math.max(i, dic.get(s.charAt(j))); // 更新左指针 i
dic.put(s.charAt(j), j); // 哈希表记录
res = Math.max(res, j - i); // 更新结果
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> dic;
int i = -1, res = 0, len = s.size();
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (dic.find(s[j]) != dic.end())
i = max(i, dic.find(s[j])->second); // 更新左指针
dic[s[j]] = j; // 哈希表记录
res = max(res, j - i); // 更新结果
}
return res;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为字符串长度,动态规划需遍历计算 $dp$ 列表。
- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 字符的 ASCII 码范围为 $0$ ~ $127$ ,哈希表 $dic$ 最多使用 $O(128) = O(1)$ 大小的额外空间。
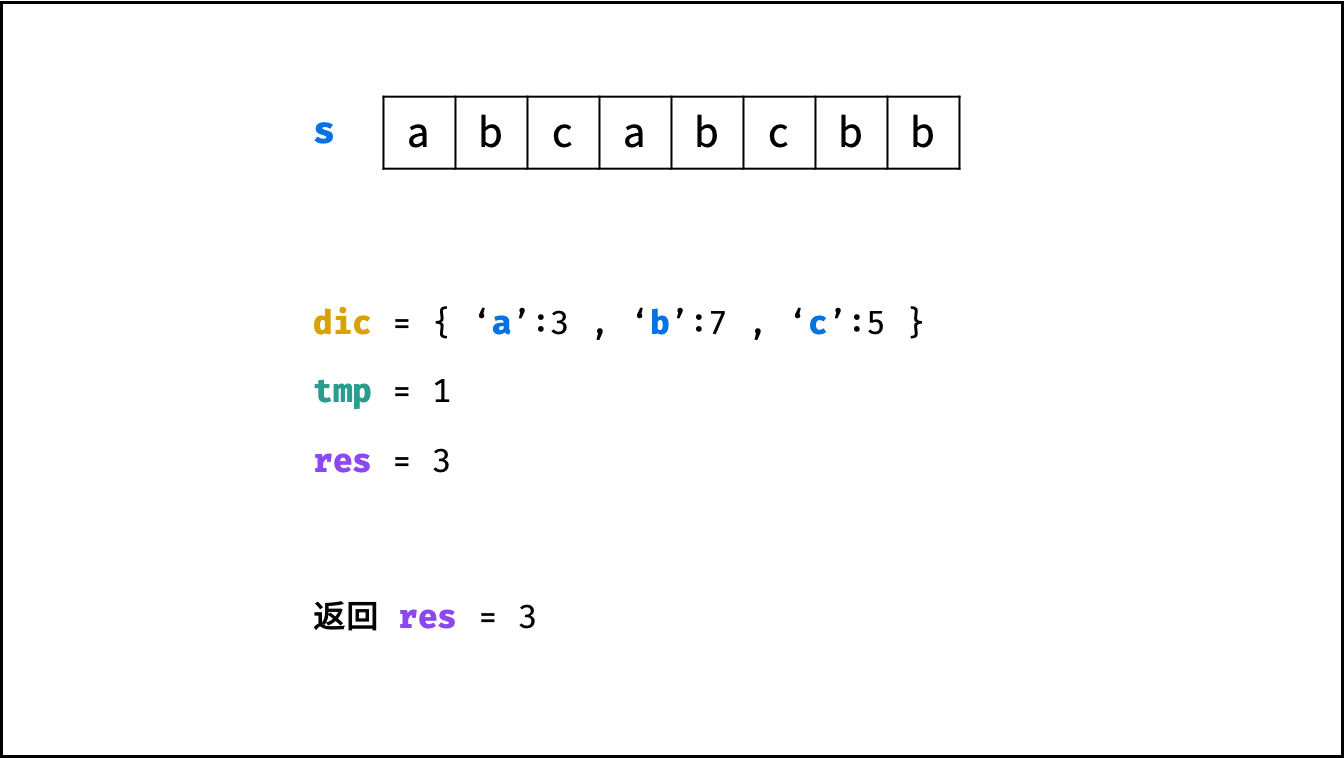
方法二:动态规划 + 哈希表
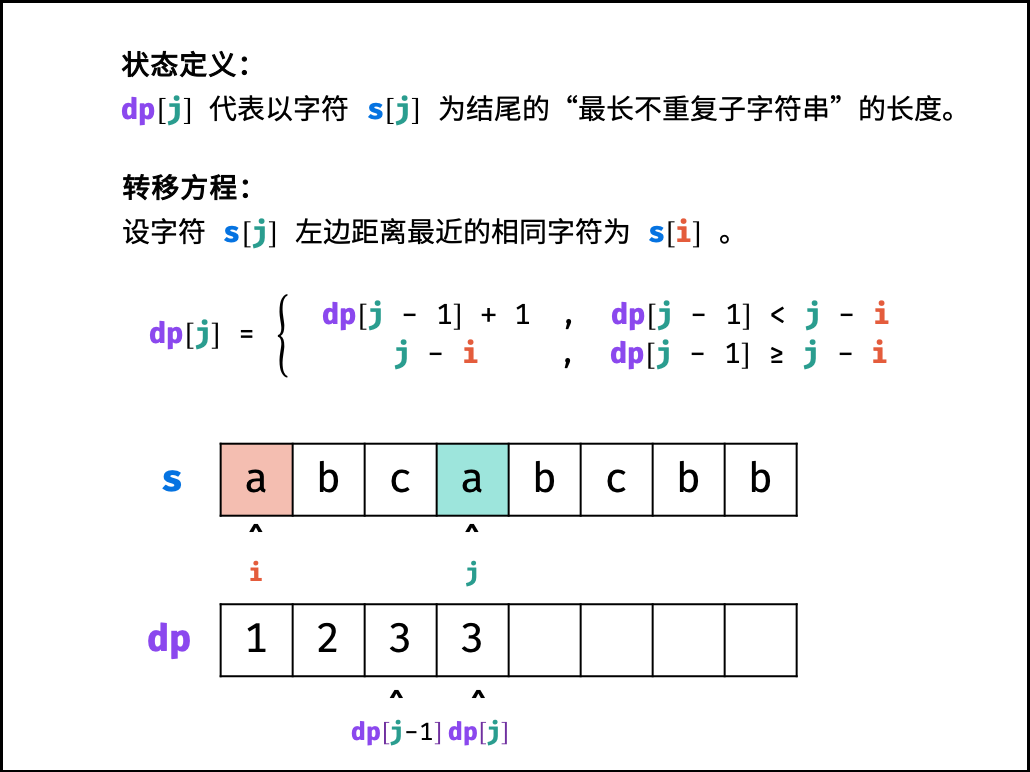
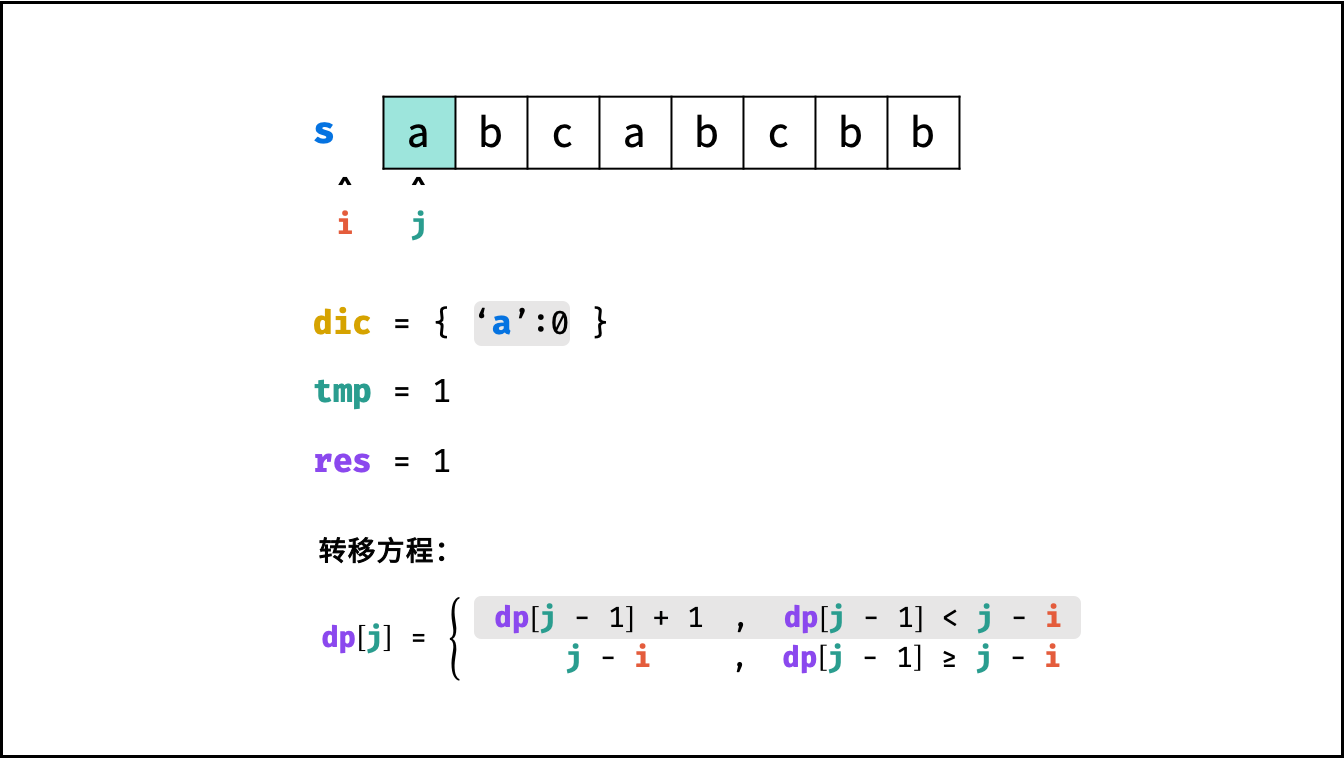
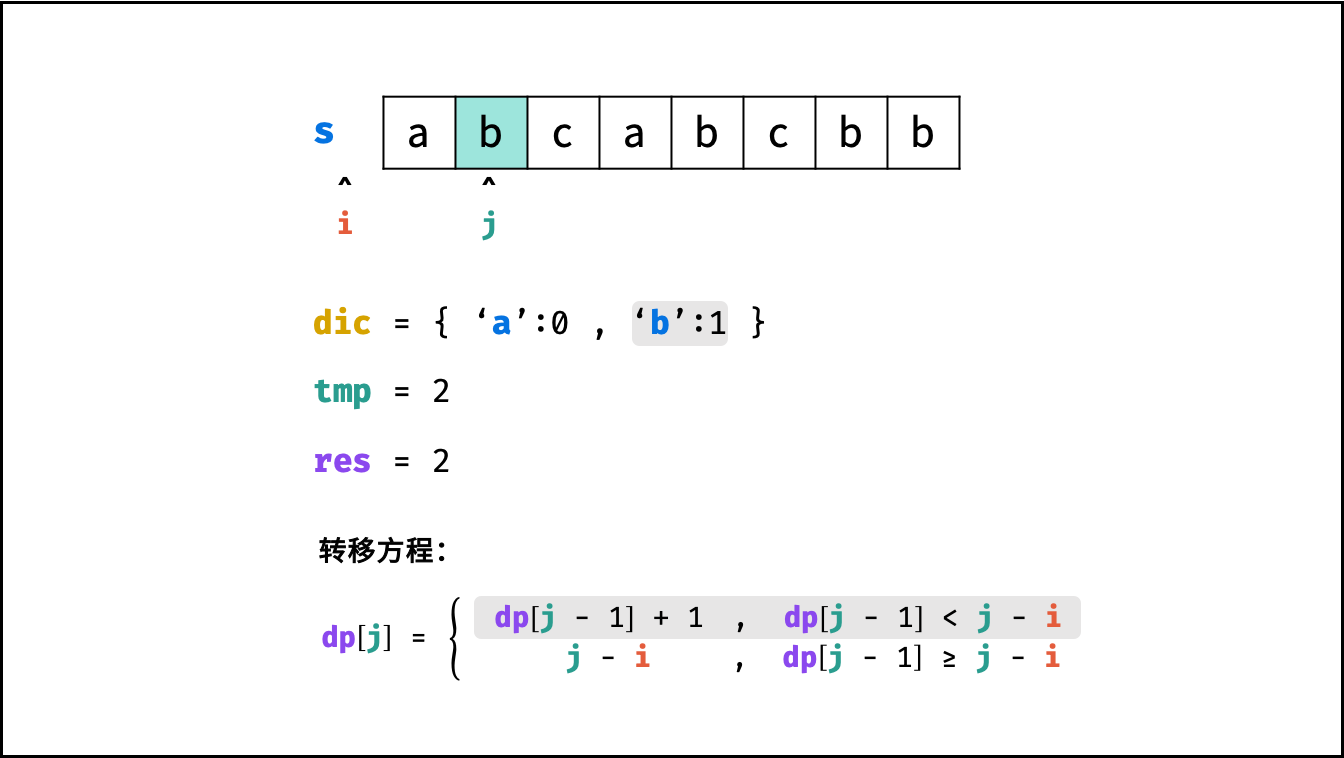
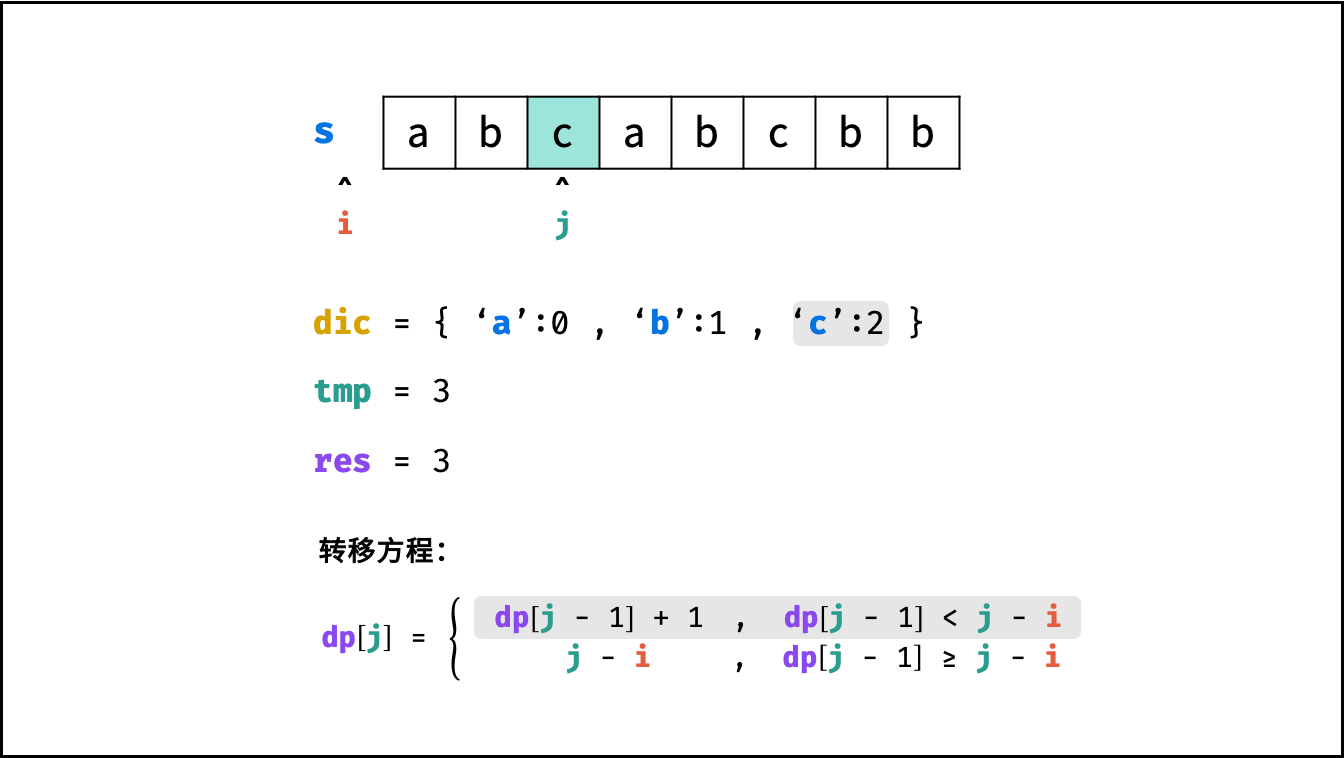
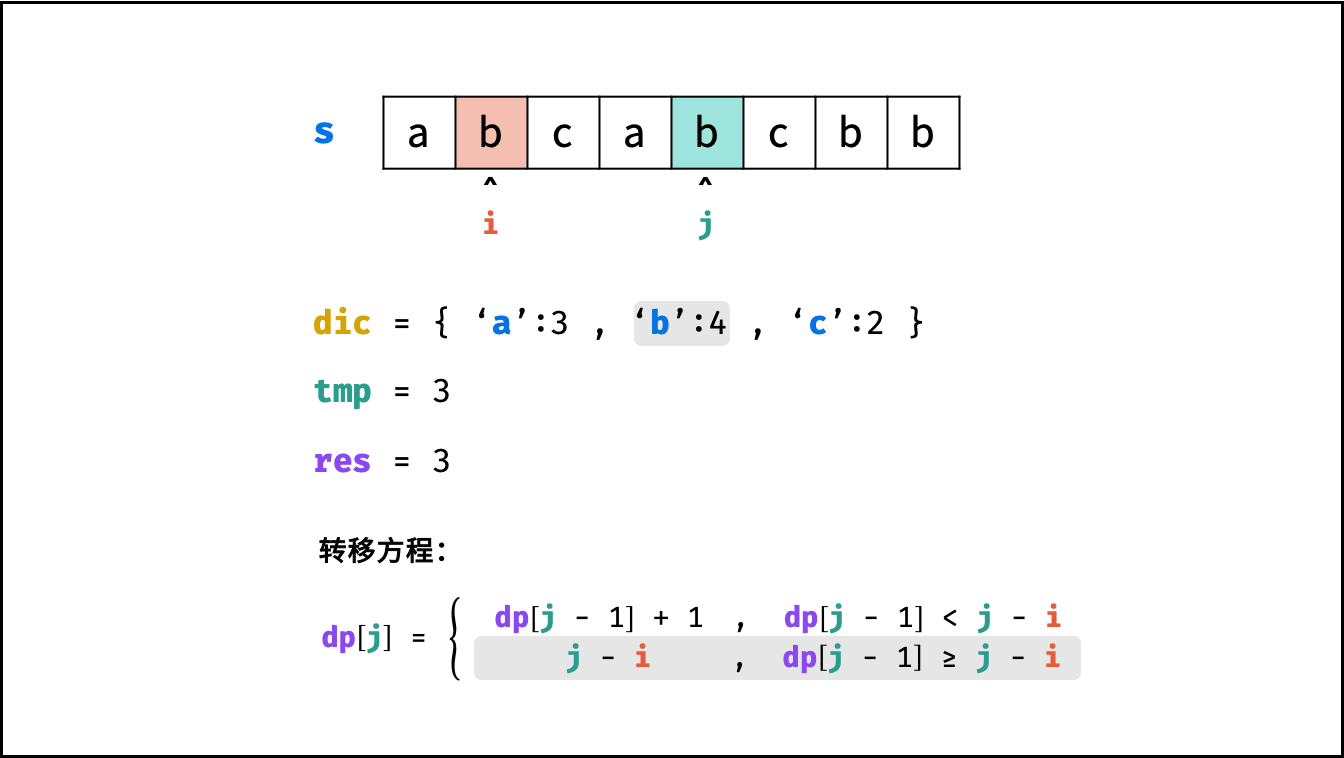
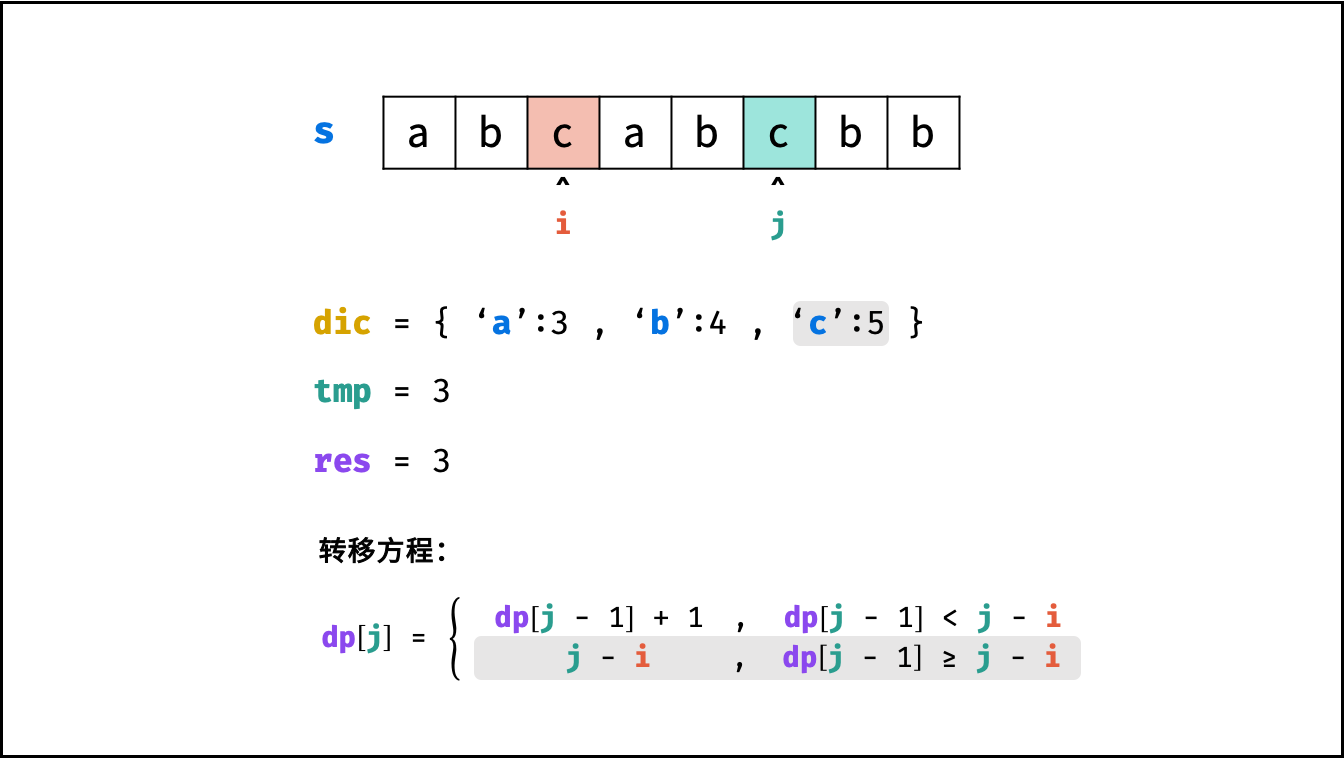
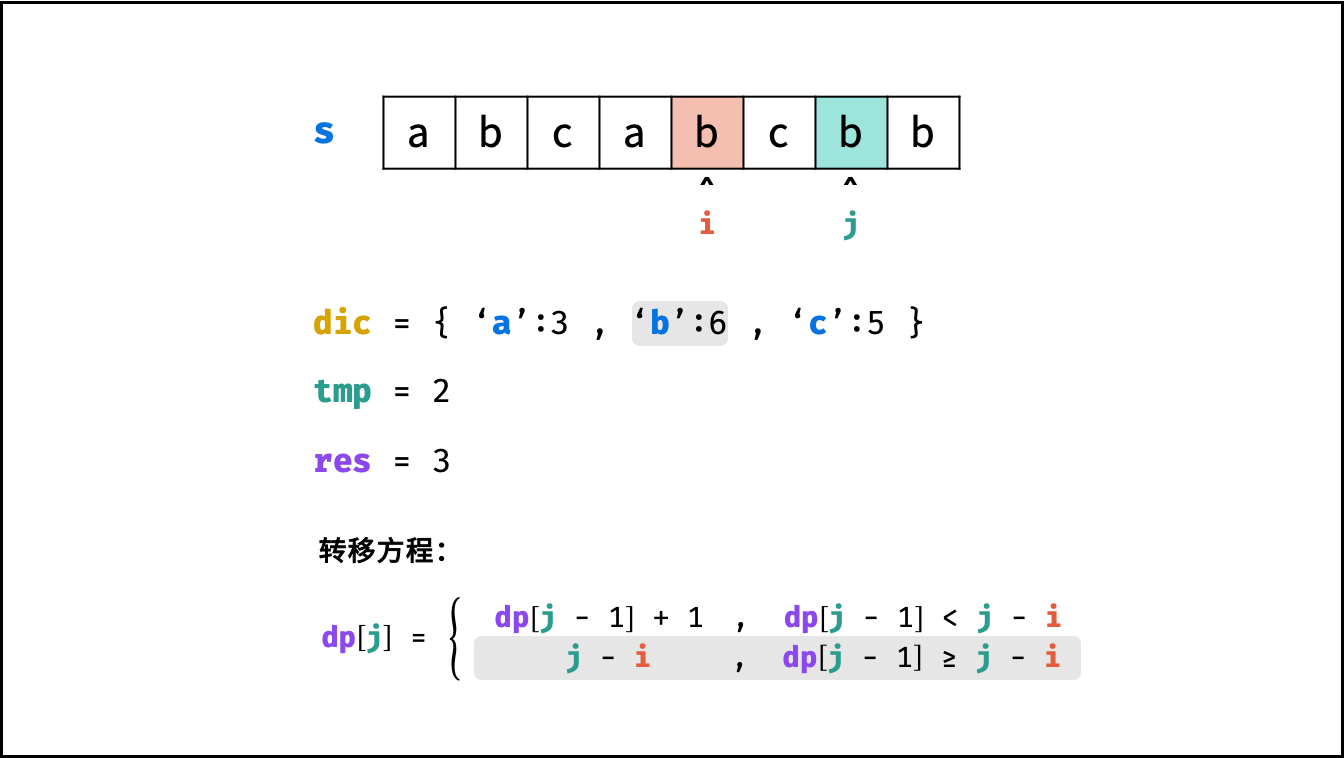
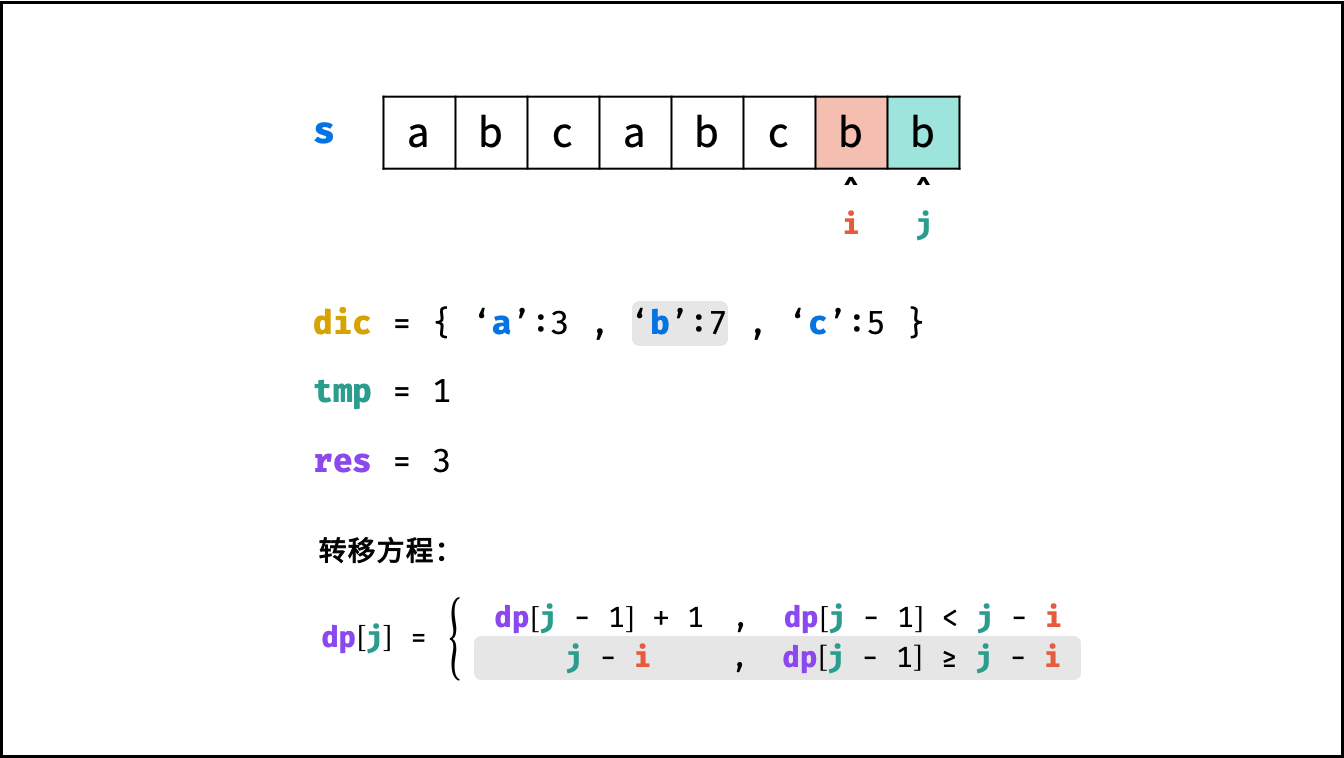
状态定义: 设动态规划列表 $dp$ ,$dp[j]$ 代表以字符 $s[j]$ 为结尾的 “最长不重复子字符串” 的长度。
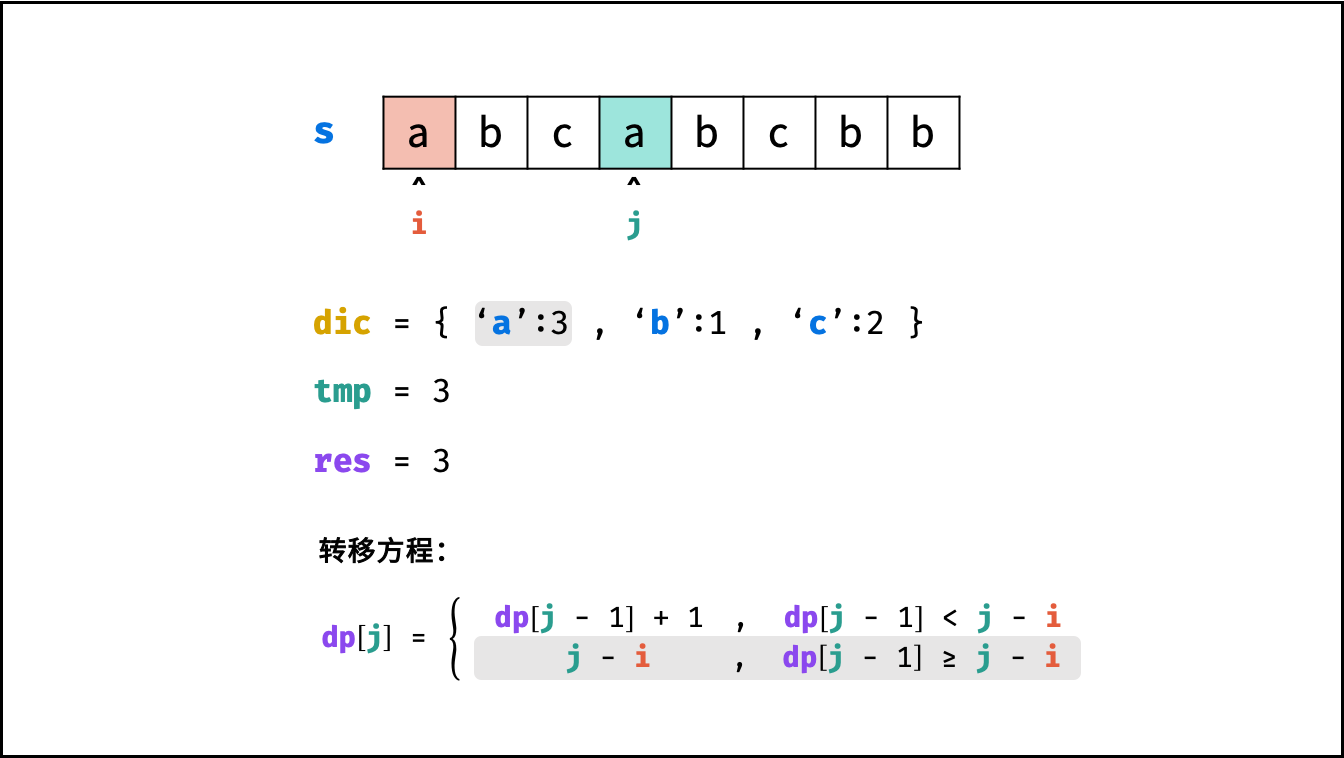
转移方程: 固定右边界 $j$ ,设字符 $s[j]$ 左边距离最近的相同字符为 $s[i]$ ,即 $s[i] = s[j]$ 。
- 当 $i < 0$ ,即 $s[j]$ 左边无相同字符,则 $dp[j] = dp[j-1] + 1$ 。
- 当 $dp[j - 1] < j - i$ ,说明字符 $s[i]$ 在子字符串 $dp[j-1]$ 区间之外 ,则 $dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1$ 。
- 当 $dp[j - 1] \geq j - i$ ,说明字符 $s[i]$ 在子字符串 $dp[j-1]$ 区间之中 ,则 $dp[j]$ 的左边界由 $s[i]$ 决定,即 $dp[j] = j - i$ 。
当 $i < 0$ 时,由于 $dp[j - 1] \leq j$ 恒成立,因而 $dp[j - 1] < j - i$ 恒成立,因此分支
1.和2.可被合并。
$$ dp[j] = \begin{cases} dp[j - 1] + 1 & , dp[j-1] < j - i \ j - i & , dp[j-1] \geq j - i \end{cases} $$
- 返回值: $\max(dp)$ ,即全局的 “最长不重复子字符串” 的长度。
状态压缩:
- 由于返回值是取 $dp$ 列表最大值,因此可借助变量 $tmp$ 存储 $dp[j]$ ,变量 $res$ 每轮更新最大值即可。
- 此优化可节省 $dp$ 列表使用的 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间。
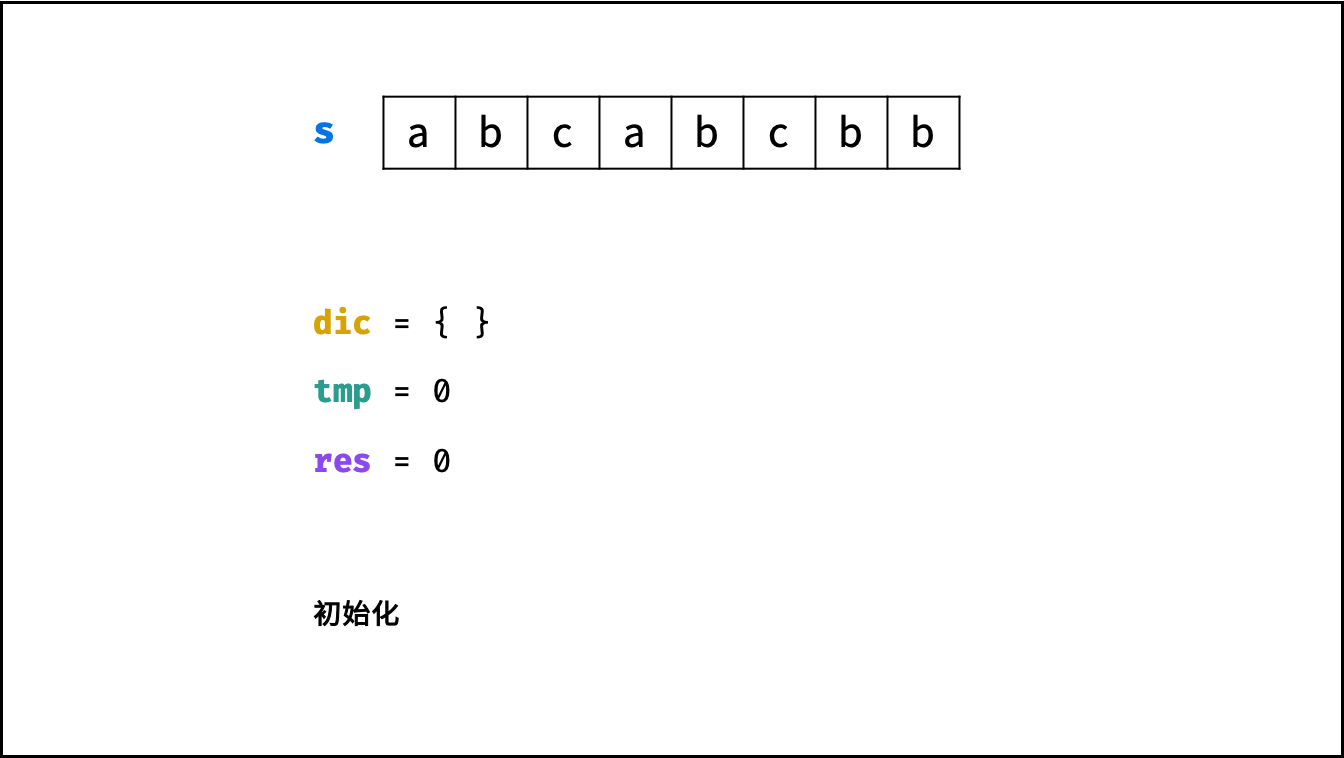
哈希表记录:
观察转移方程,可知关键问题:每轮遍历字符 $s[j]$ 时,如何计算索引 $i$ ?
- 哈希表统计: 遍历字符串 $s$ 时,使用哈希表(记为 $dic$ )统计 各字符最后一次出现的索引位置 。
- 左边界 $i$ 获取方式: 遍历到 $s[j]$ 时,可通过访问哈希表 $dic[s[j]]$ 获取最近的相同字符的索引 $i$ 。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python 的 get(key, default) 方法和 Java 的 getOrDefault(key, default) ,代表当哈希表包含键 key 时返回对应 value ,不包含时返回默认值 default 。
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
dic = {}
res = tmp = 0
for j in range(len(s)):
i = dic.get(s[j], -1) # 获取索引 i
dic[s[j]] = j # 更新哈希表
tmp = tmp + 1 if tmp < j - i else j - i # dp[j - 1] -> dp[j]
res = max(res, tmp) # max(dp[j - 1], dp[j])
return resclass Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0, tmp = 0, len = s.length();
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
int i = dic.getOrDefault(s.charAt(j), -1); // 获取索引 i
dic.put(s.charAt(j), j); // 更新哈希表
tmp = tmp < j - i ? tmp + 1 : j - i; // dp[j - 1] -> dp[j]
res = Math.max(res, tmp); // max(dp[j - 1], dp[j])
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> dic;
int res = 0, tmp = 0, len = s.size(), i;
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (dic.find(s[j]) == dic.end()) i = - 1;
else i = dic.find(s[j])->second; // 获取索引 i
dic[s[j]] = j; // 更新哈希表
tmp = tmp < j - i ? tmp + 1 : j - i; // dp[j - 1] -> dp[j]
res = max(res, tmp); // max(dp[j - 1], dp[j])
}
return res;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为字符串长度,动态规划需遍历计算 $dp$ 列表。
- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 字符的 ASCII 码范围为 $0$ ~ $127$ ,哈希表 $dic$ 最多使用 $O(128) = O(1)$ 大小的额外空间。