解题思路
先考虑最简单的「暴力遍历」,即枚举出所有情况,并从中选择最大利润。设数组 prices 的长度为 $n$ ,由于只能先买入后卖出,因此第 1 天买可在未来 $n - 1$ 天卖出,第 2 天买可在未来 $n - 2$ 天卖出……以此类推,共有 $(n - 1) + (n - 2) + \cdots + 0 = \frac{n (n - 1)}{2}$ 种情况,时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ 。考虑到题目给定的长度范围 $1 \leq prices.length \leq 10^5$ ,需要思考更优解法。
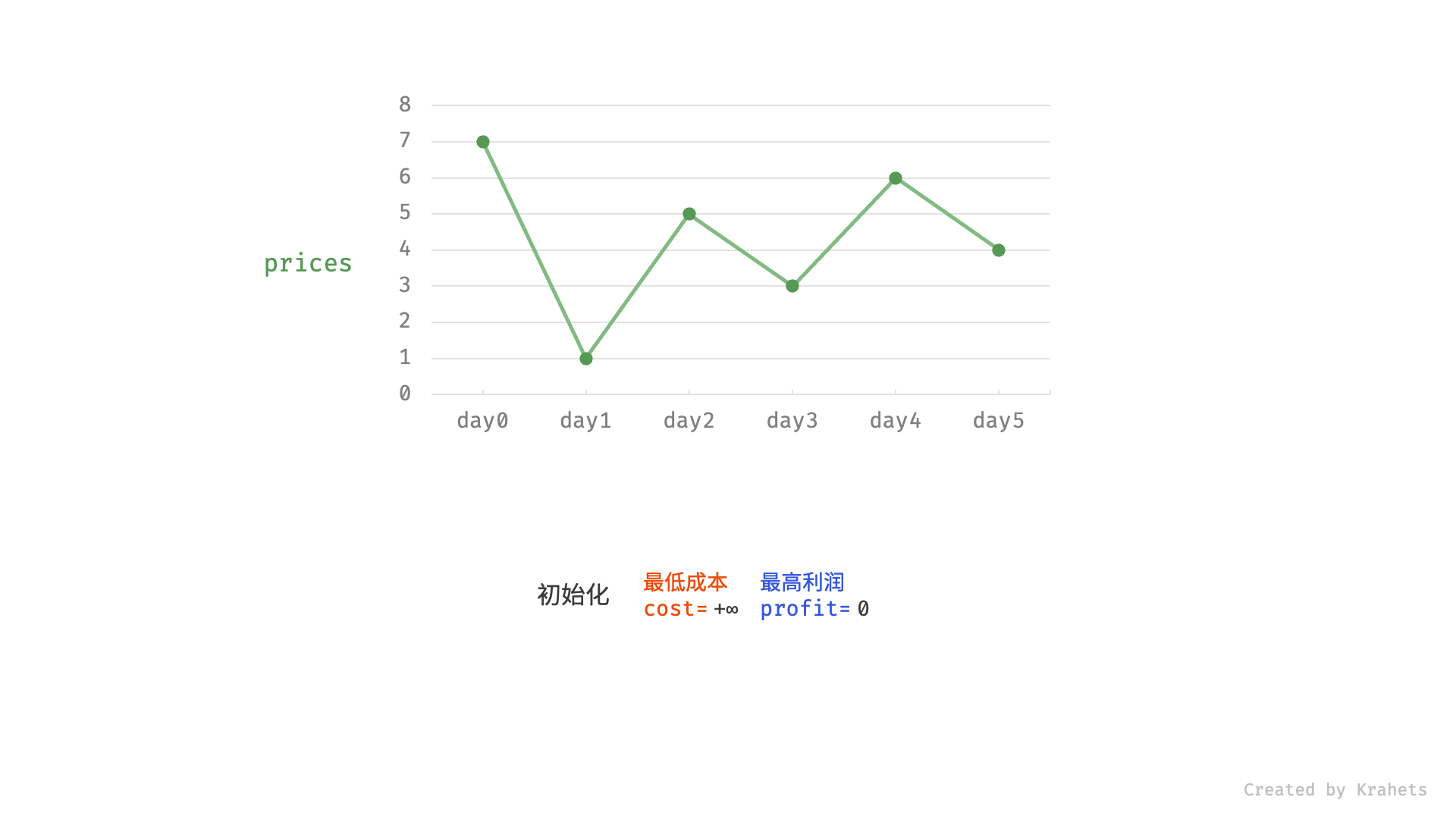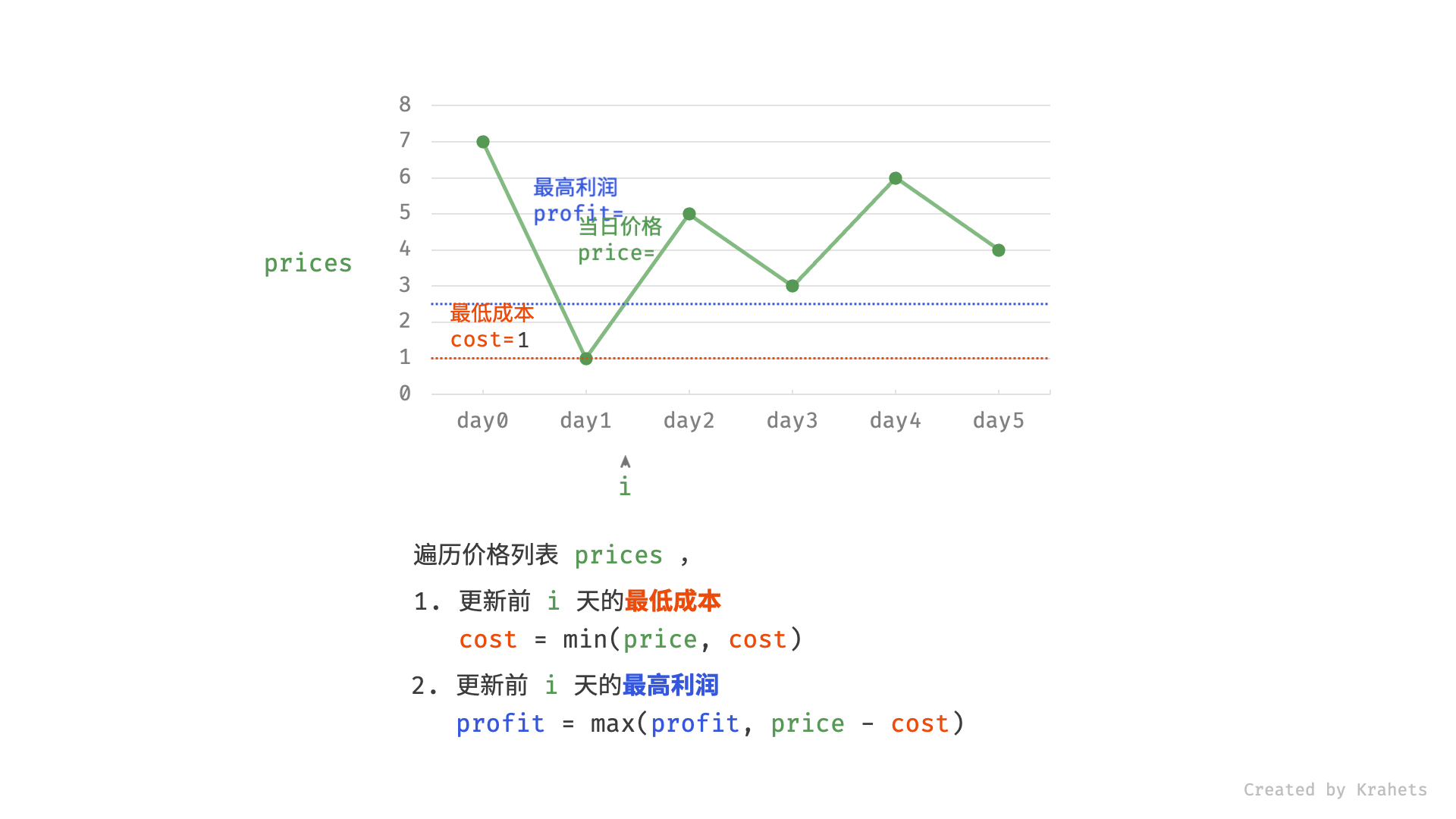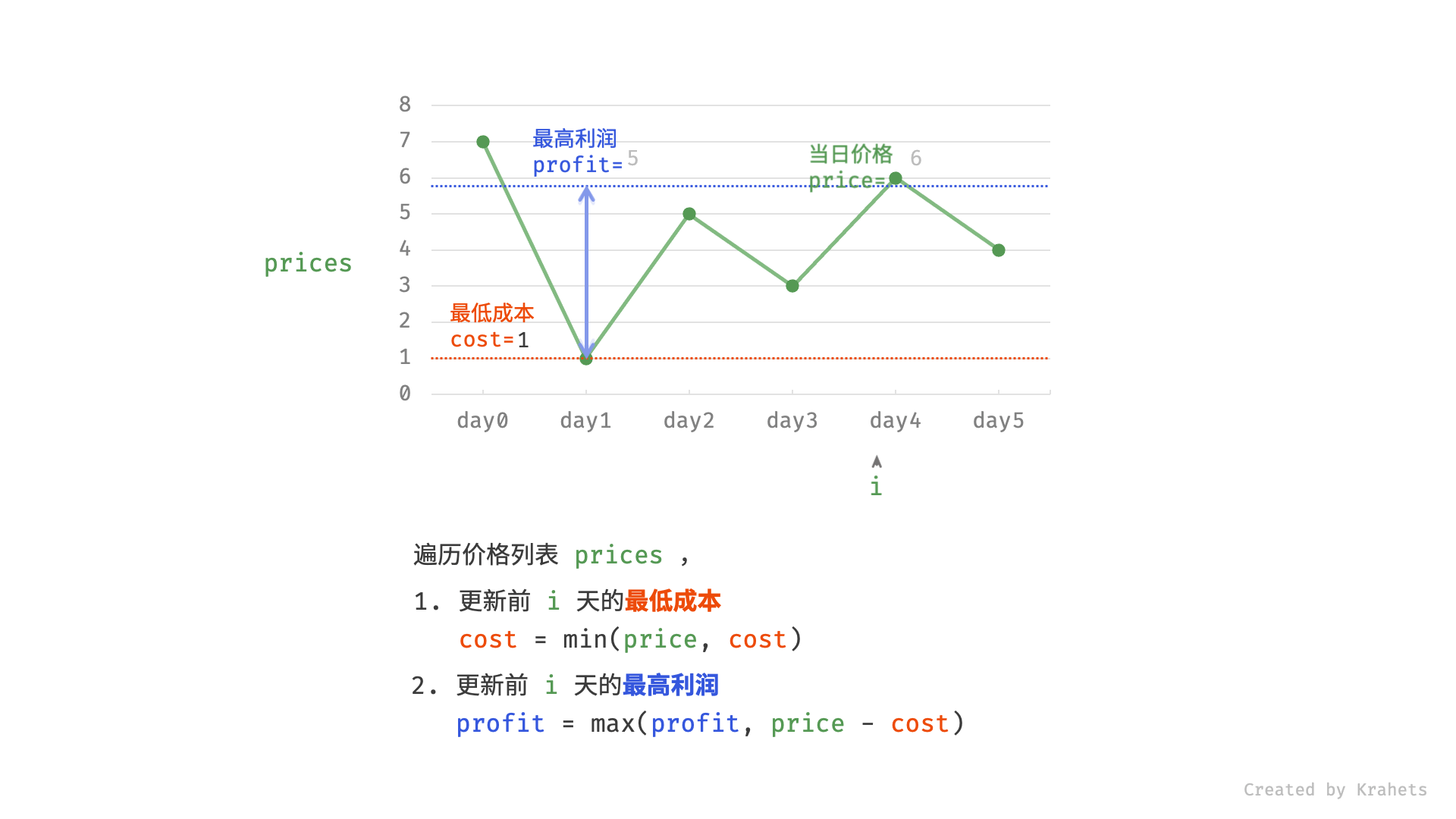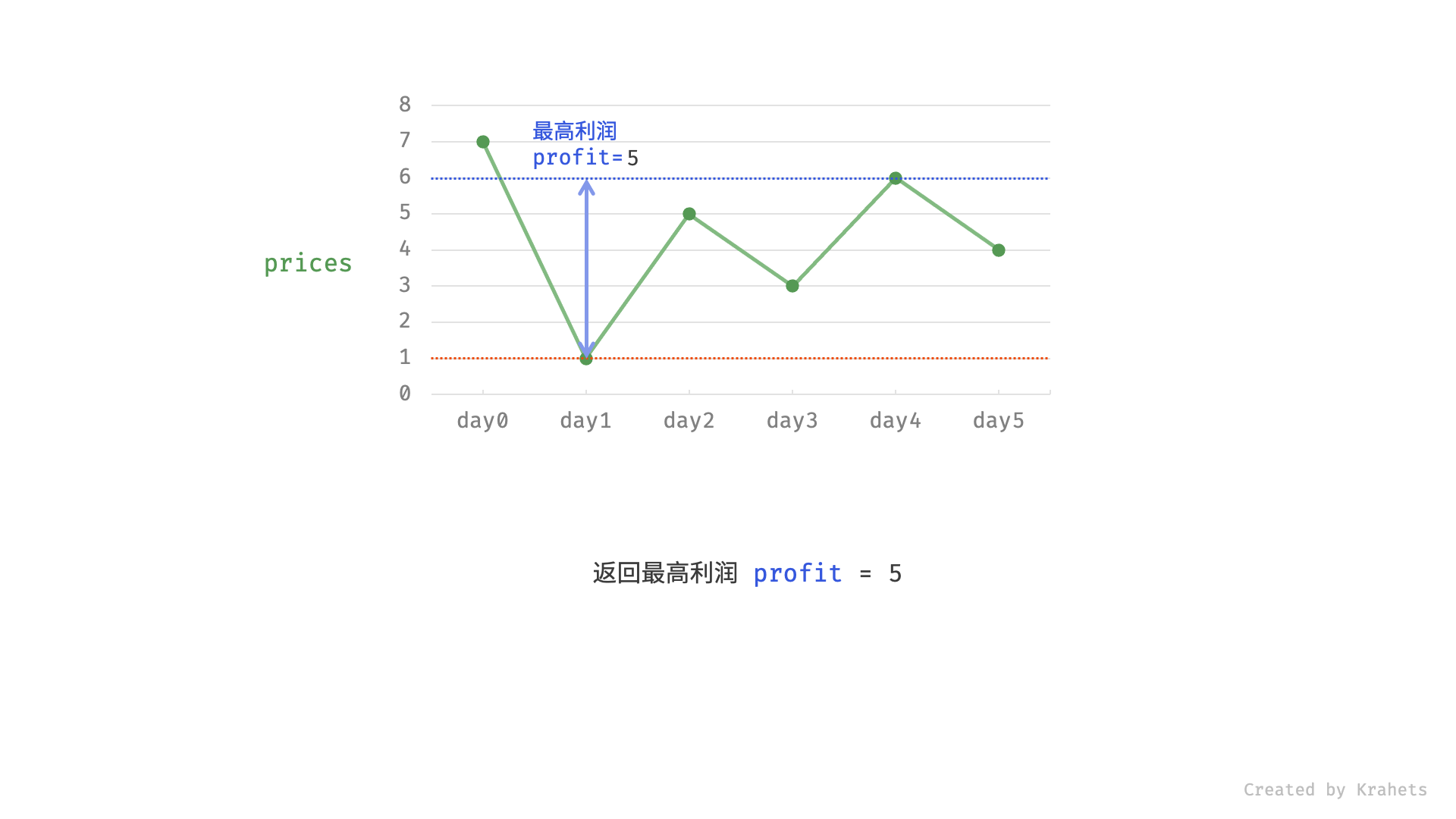
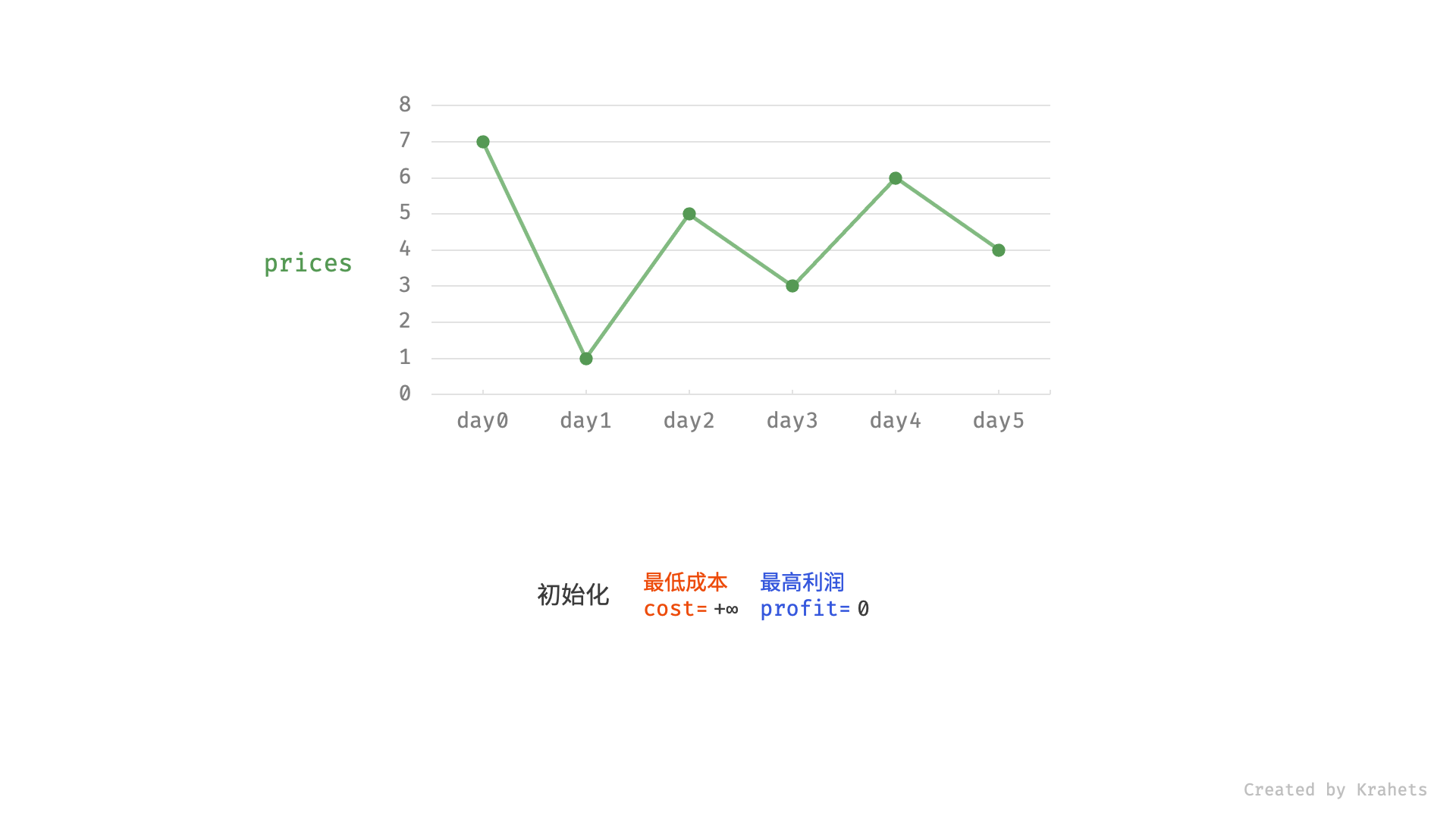
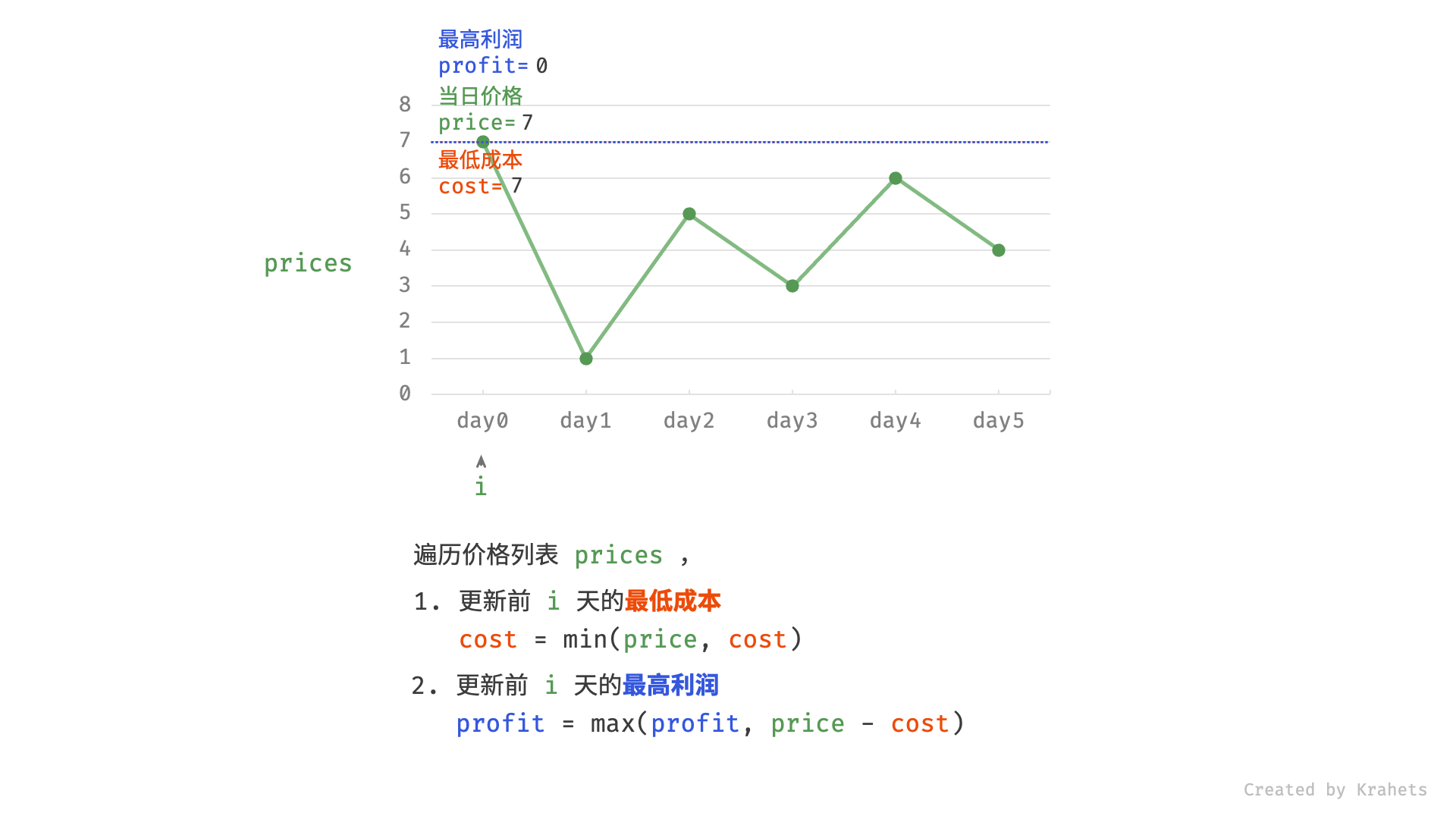
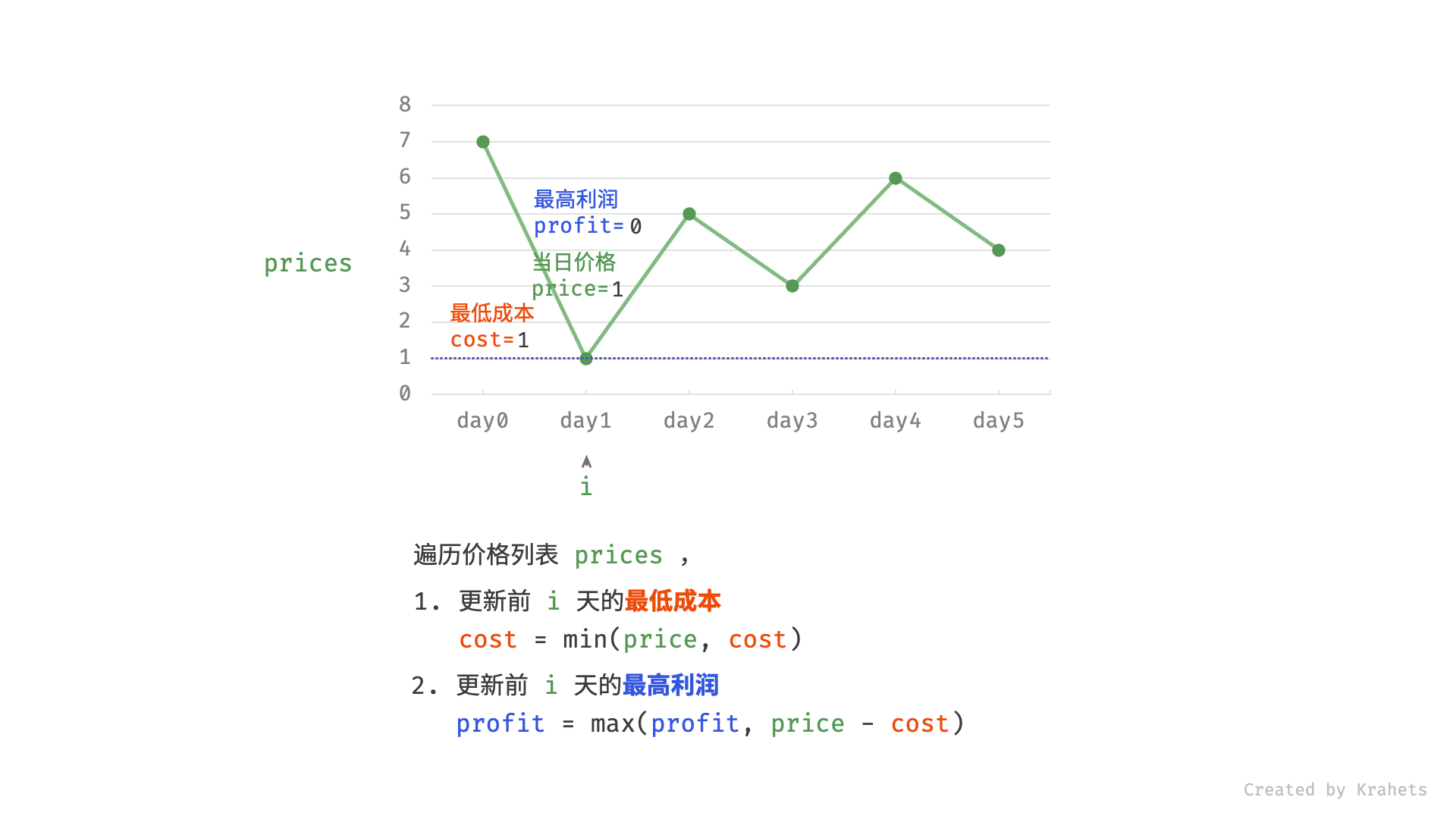
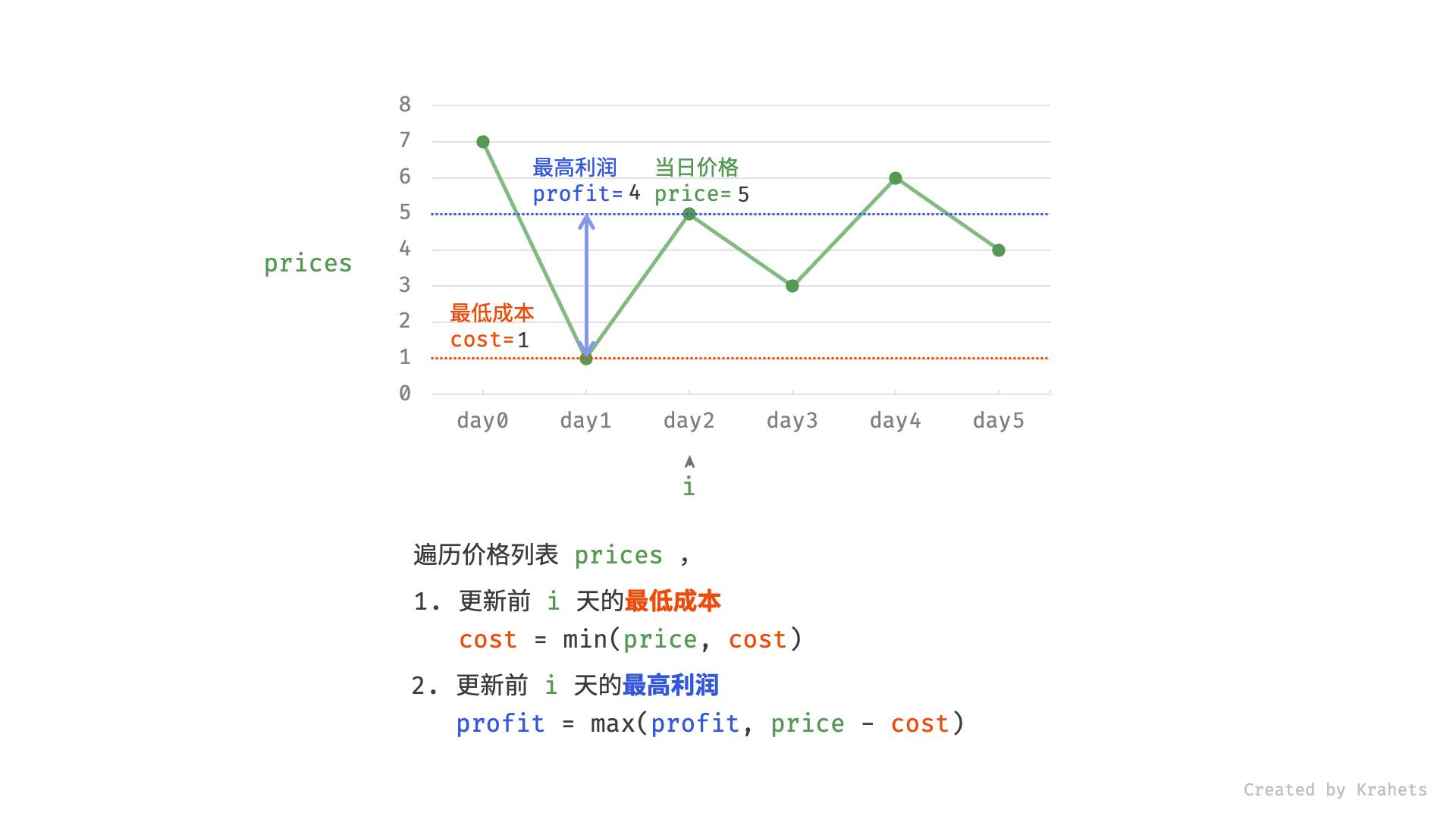
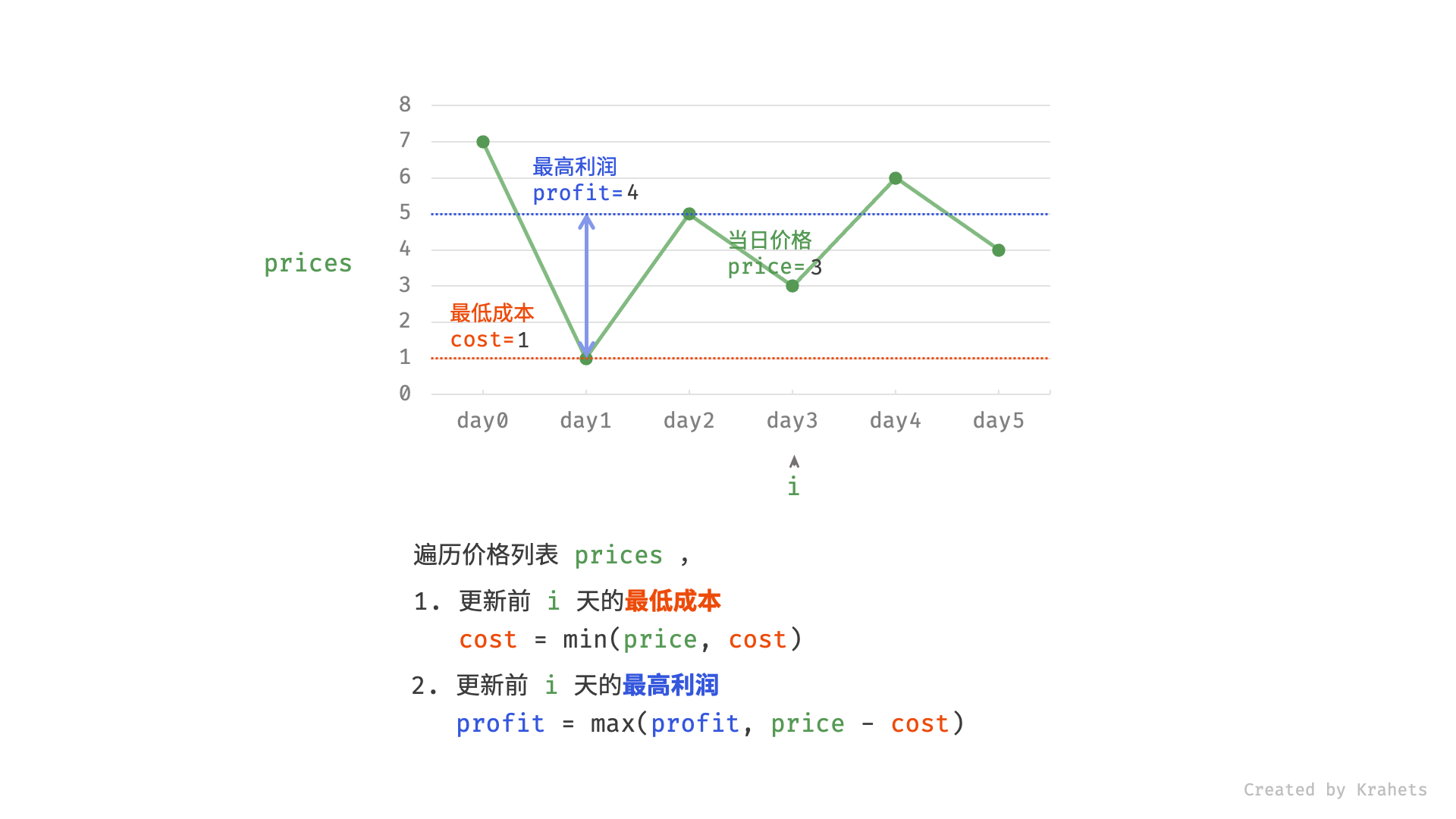
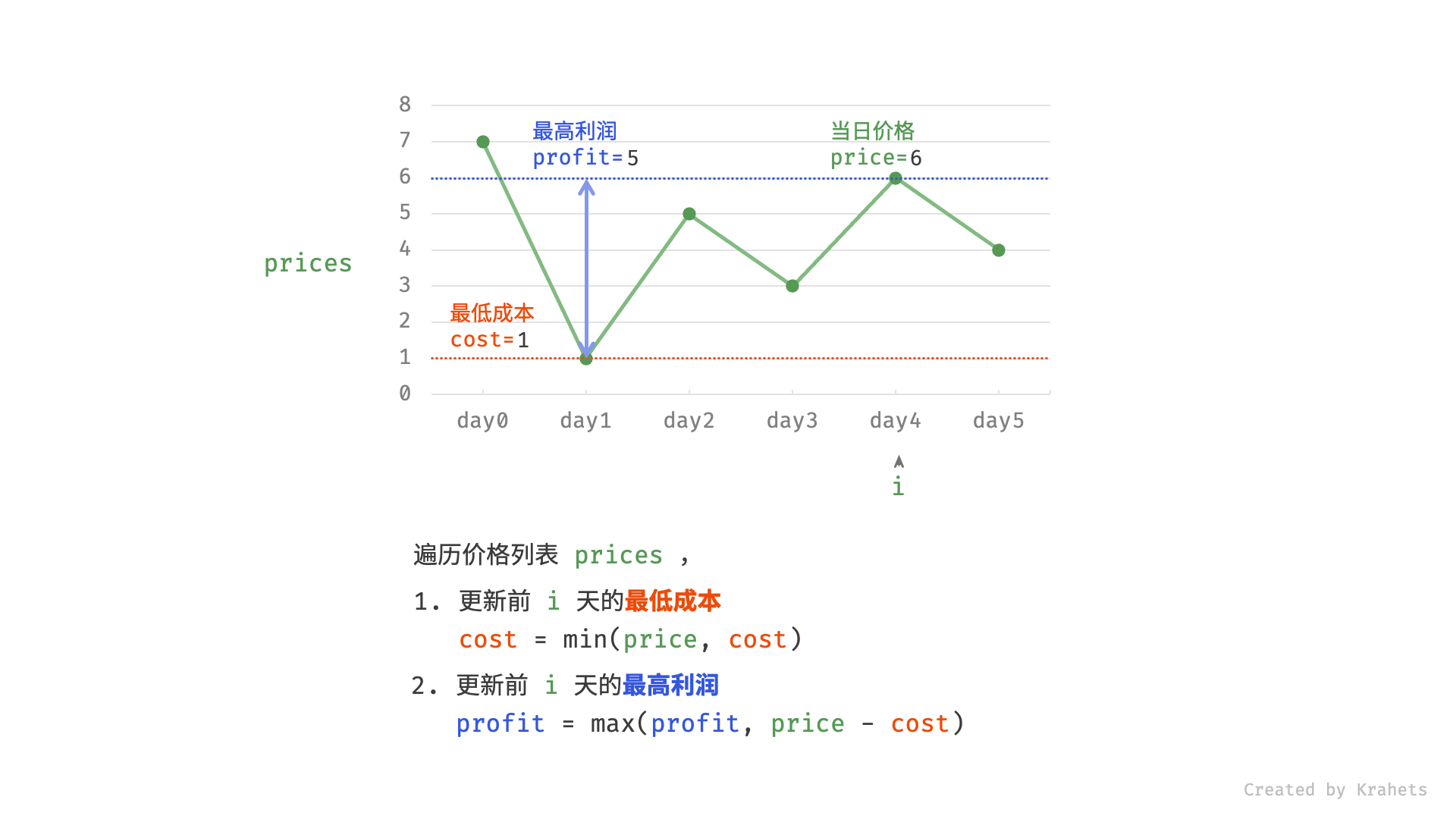
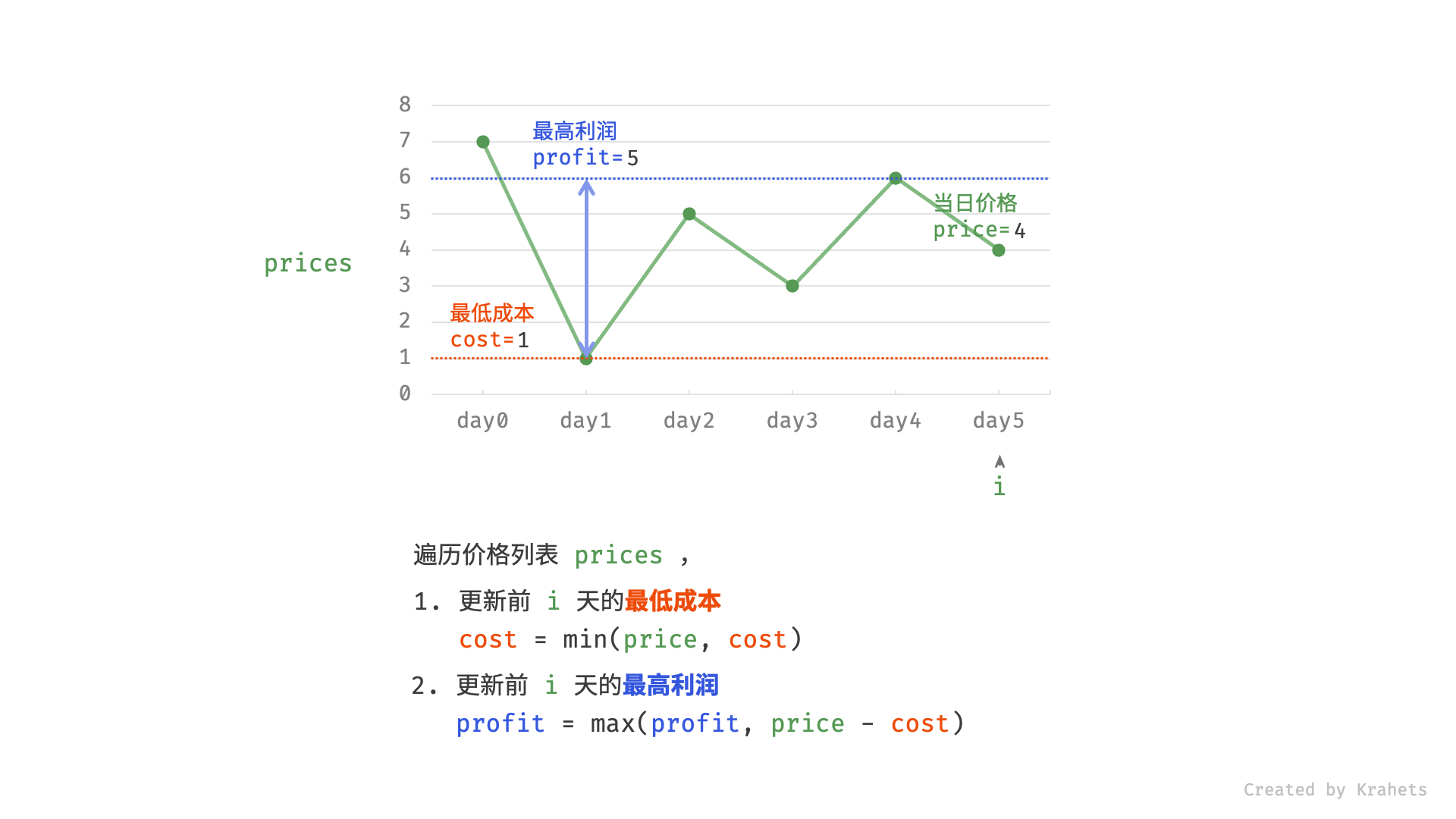
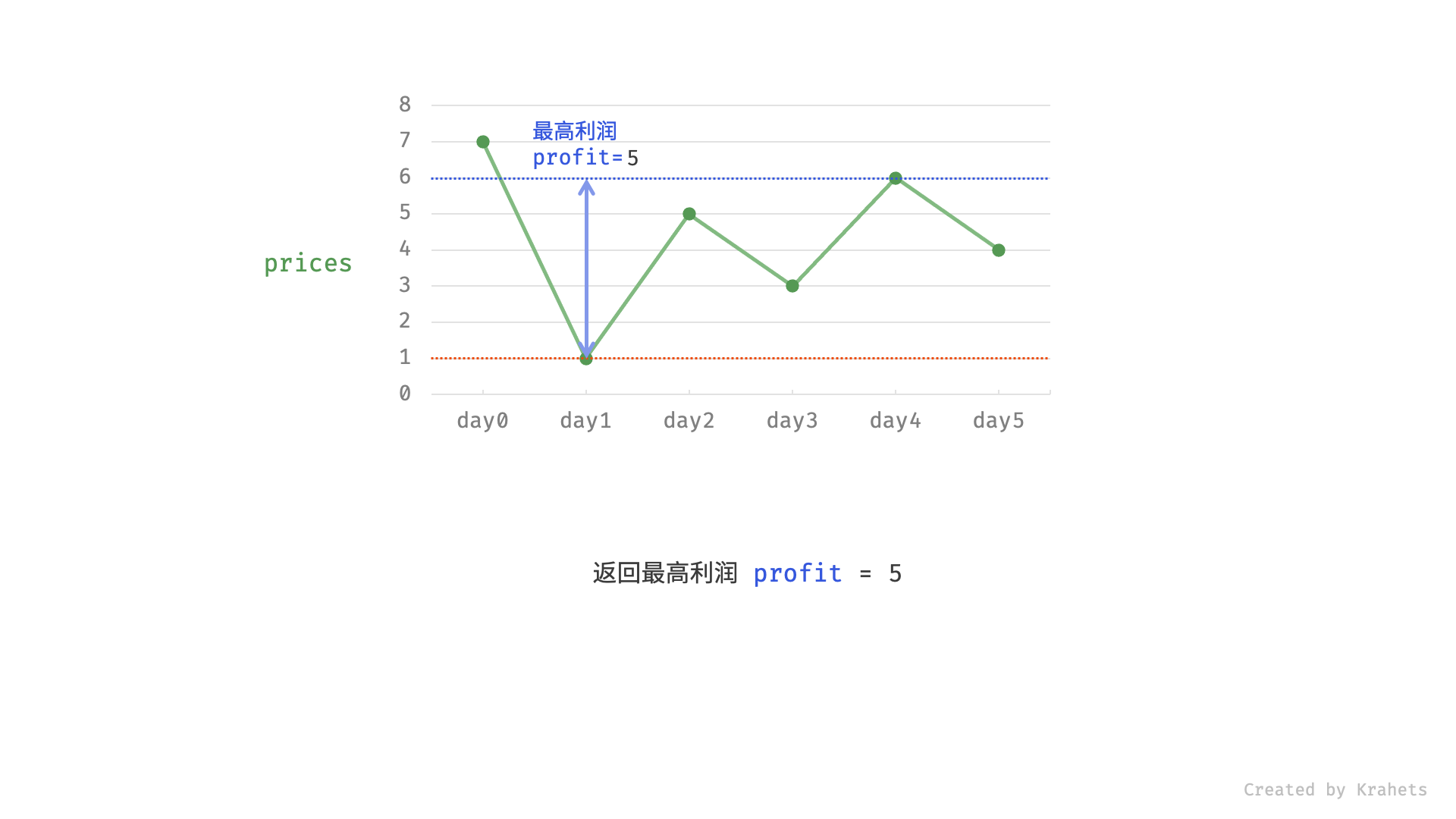
然而,暴力法会产生许多冗余计算。例如,若第 1 天价格低于第 2 天价格,即第 1 天成本更低,那么我们一定不会选择在第 2 天买入。进一步的,若在前 $i$ 天选择买入,若想达到最高利润,则一定选择价格最低的交易日买入。考虑根据此贪心思想,遍历价格列表 prices 并执行两步:
由于初始值 $i = 0$ ,为了序号对应,本文设从第 0 天开始;
- 更新前 $i$ 天的最低价格,即最低买入成本
cost; - 更新前 $i$ 天的最高利润
profit,即选择「前 $i-1$ 天最高利润profit」和「第 $i$ 天卖出的最高利润price - cost」中的最大值 ;
若感觉动图播放太快,可以一页页看 $\downarrow$
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码
Python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
cost, profit = float('+inf'), 0
for price in prices:
cost = min(cost, price)
profit = max(profit, price - cost)
return profitJava
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE, profit = 0;
for (int price : prices) {
cost = Math.min(cost, price);
profit = Math.max(profit, price - cost);
}
return profit;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int cost = INT_MAX, profit = 0;
for (int price : prices) {
cost = min(cost, price);
profit = max(profit, price - cost);
}
return profit;
}
};复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为数组
prices长度。遍历prices使用线性时间。 - 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 变量
cost,profit使用 $O(1)$ 空间。