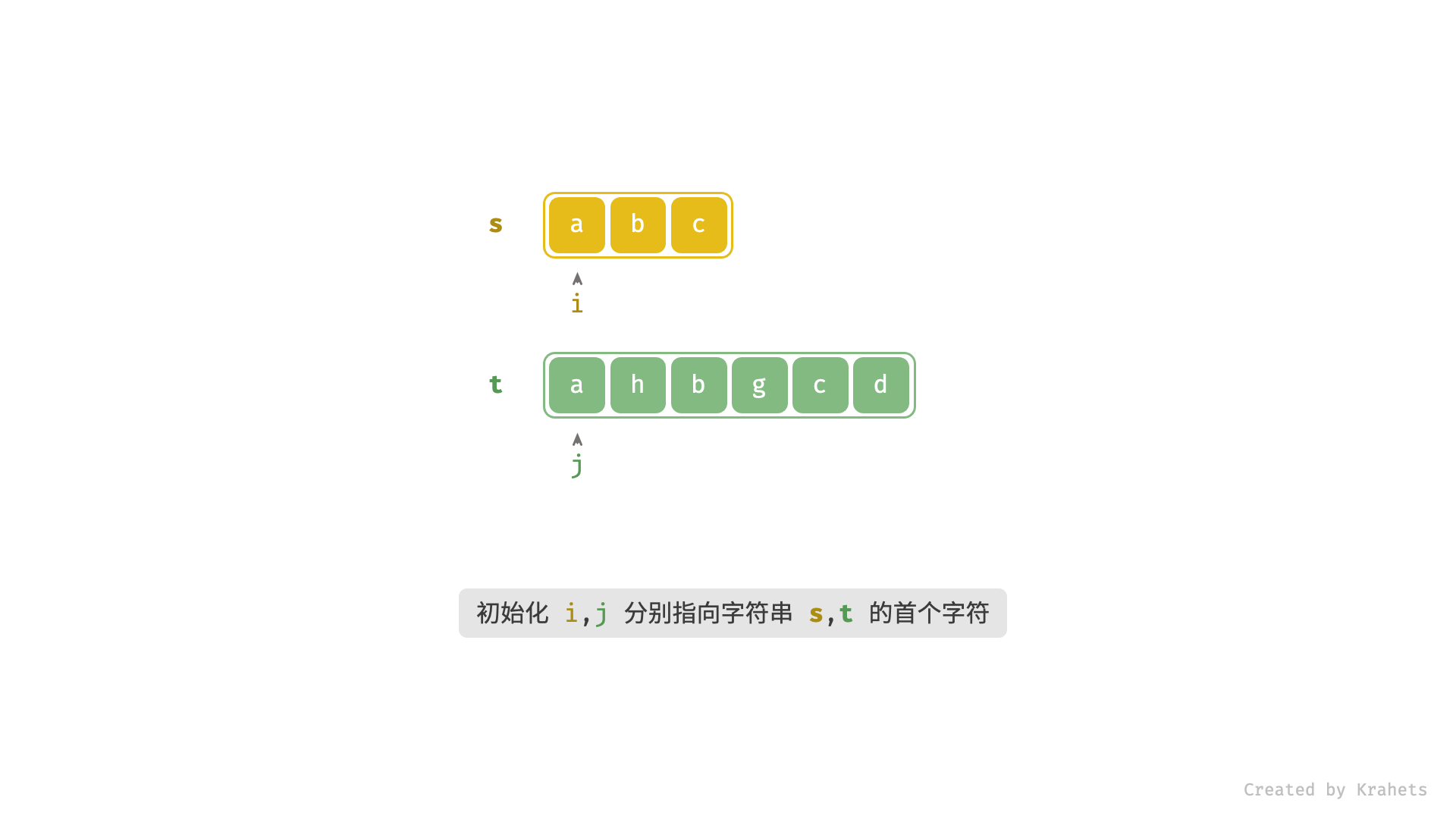
解题思路
设置双指针 i , j 分别指向字符串 s , t 的首个字符,遍历字符串 t :
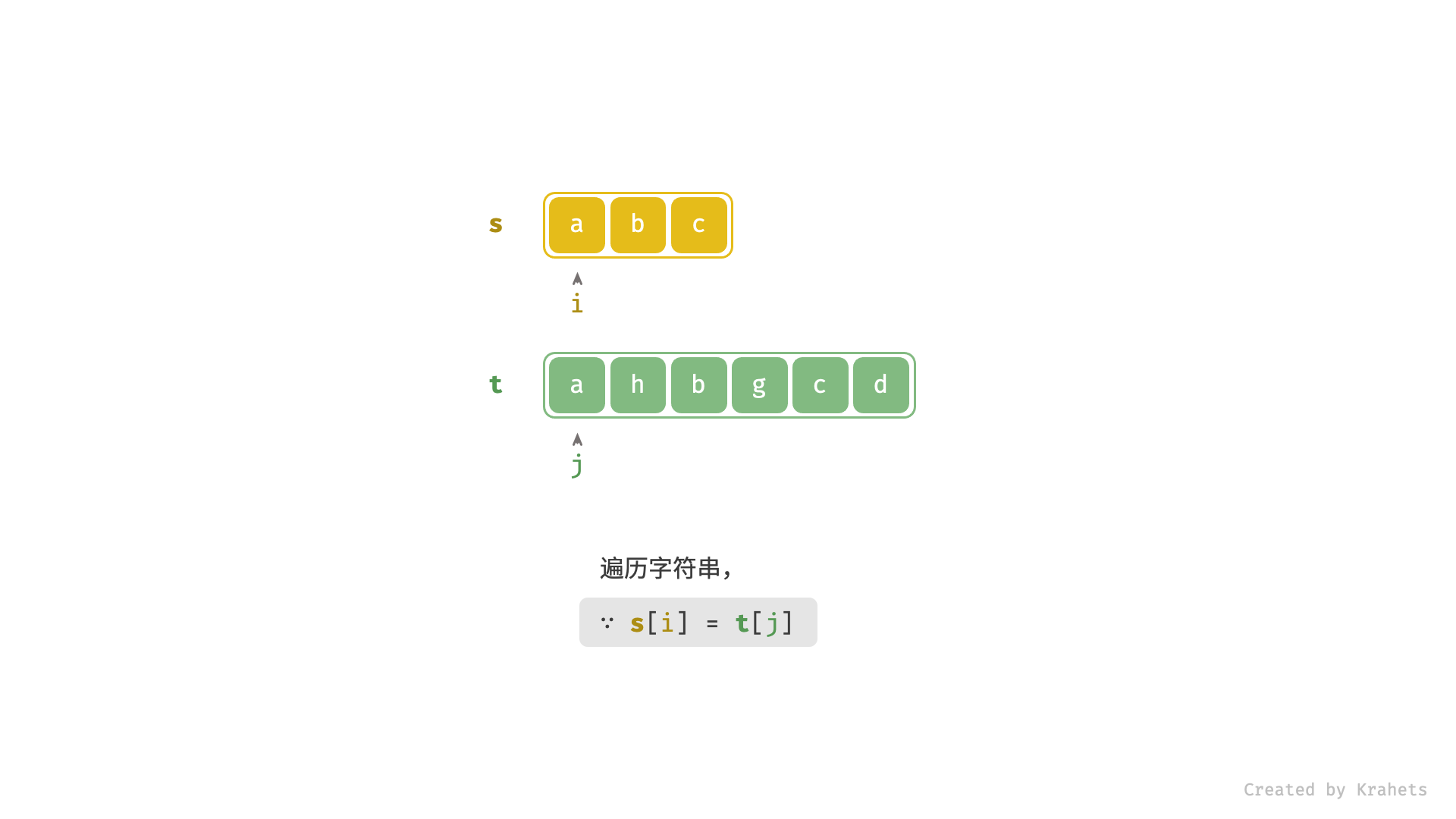
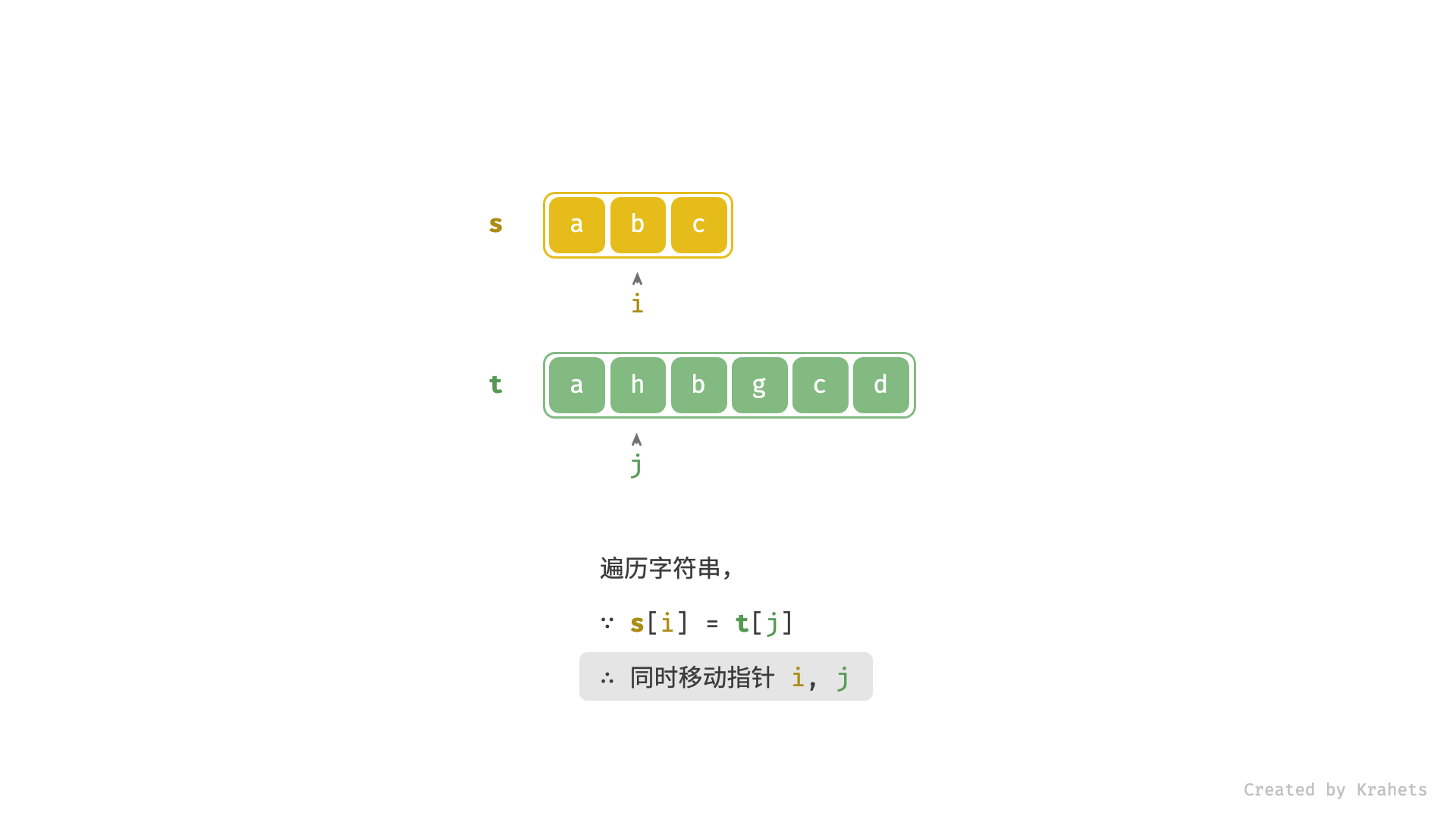
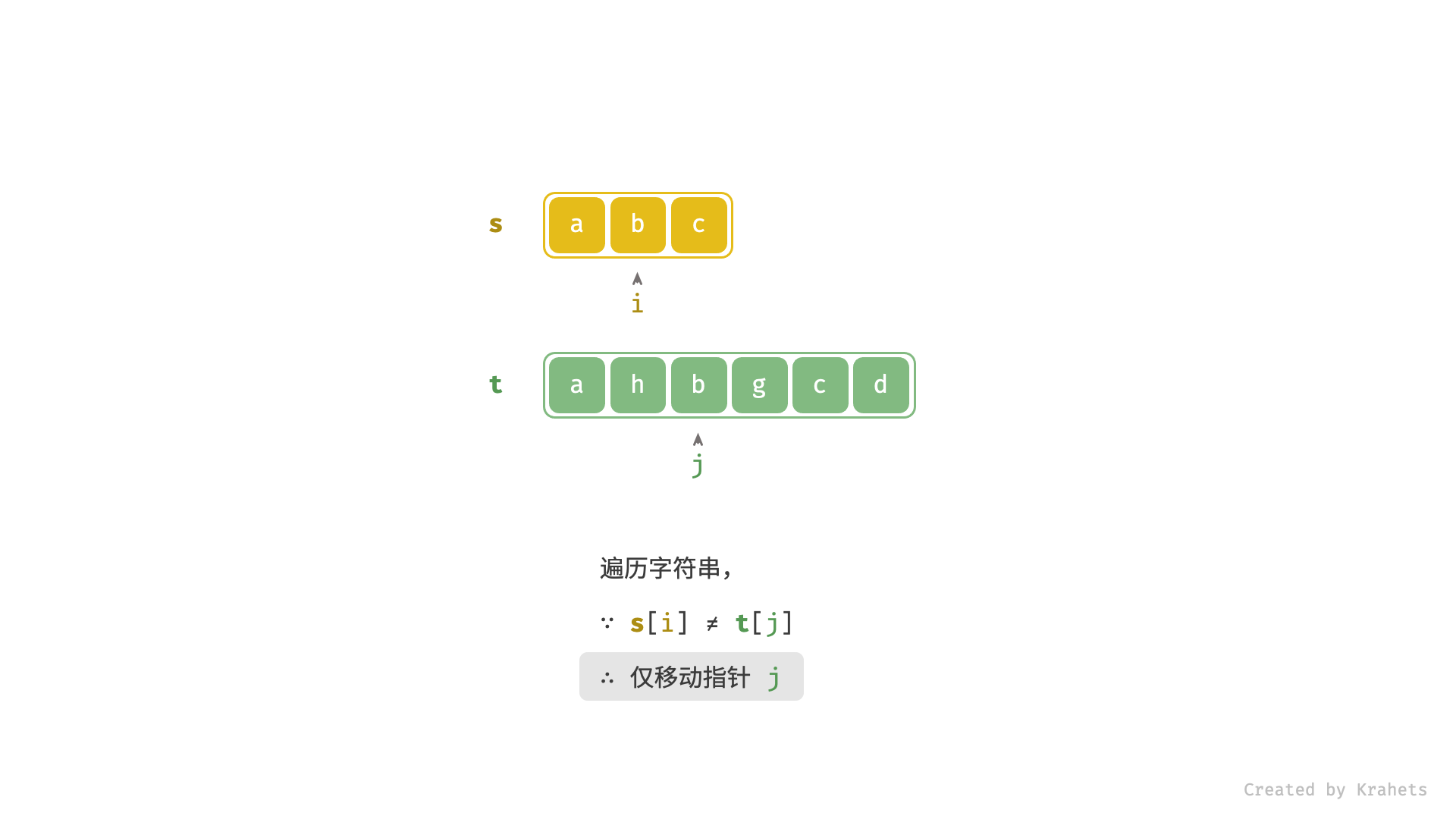
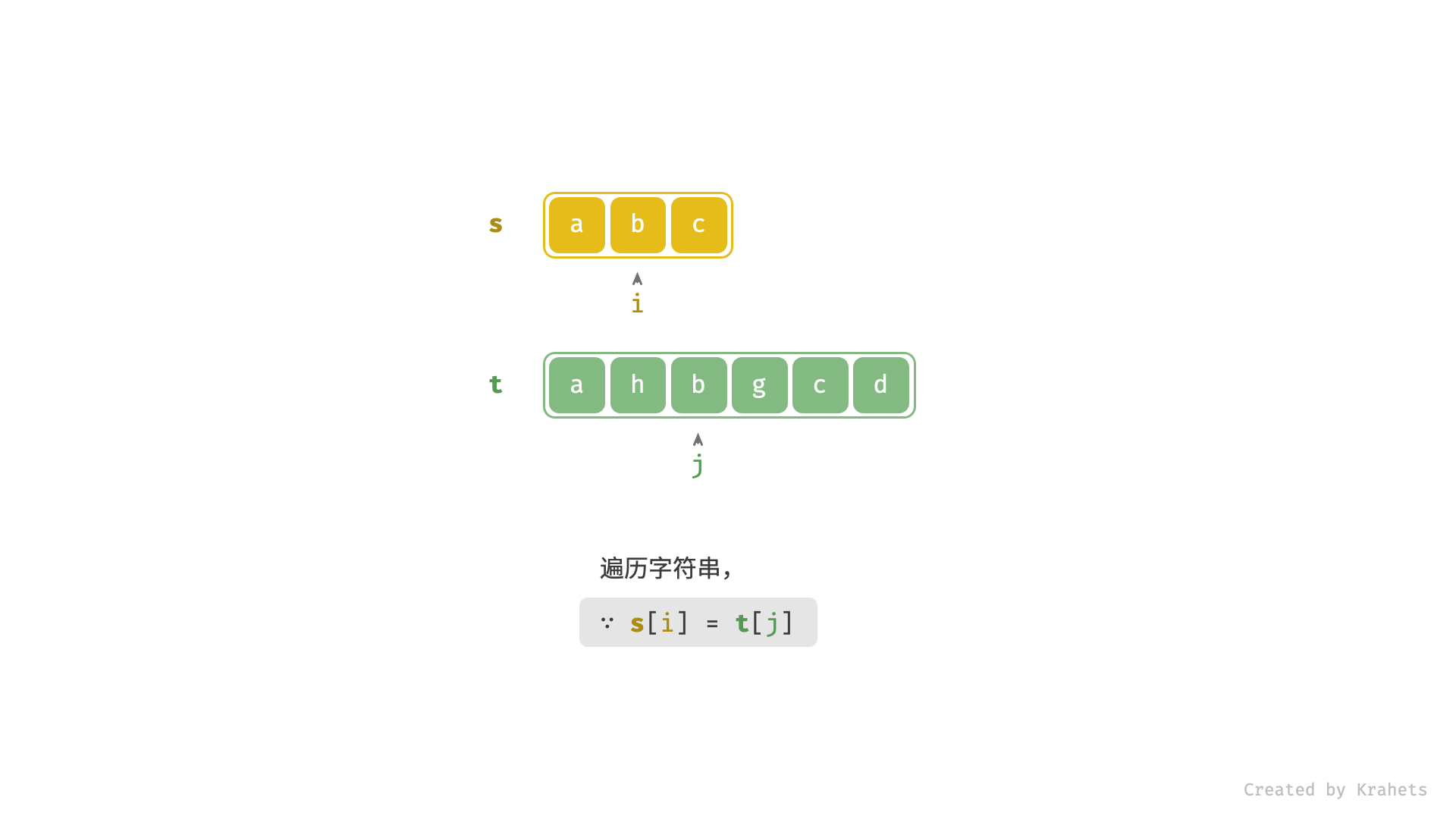
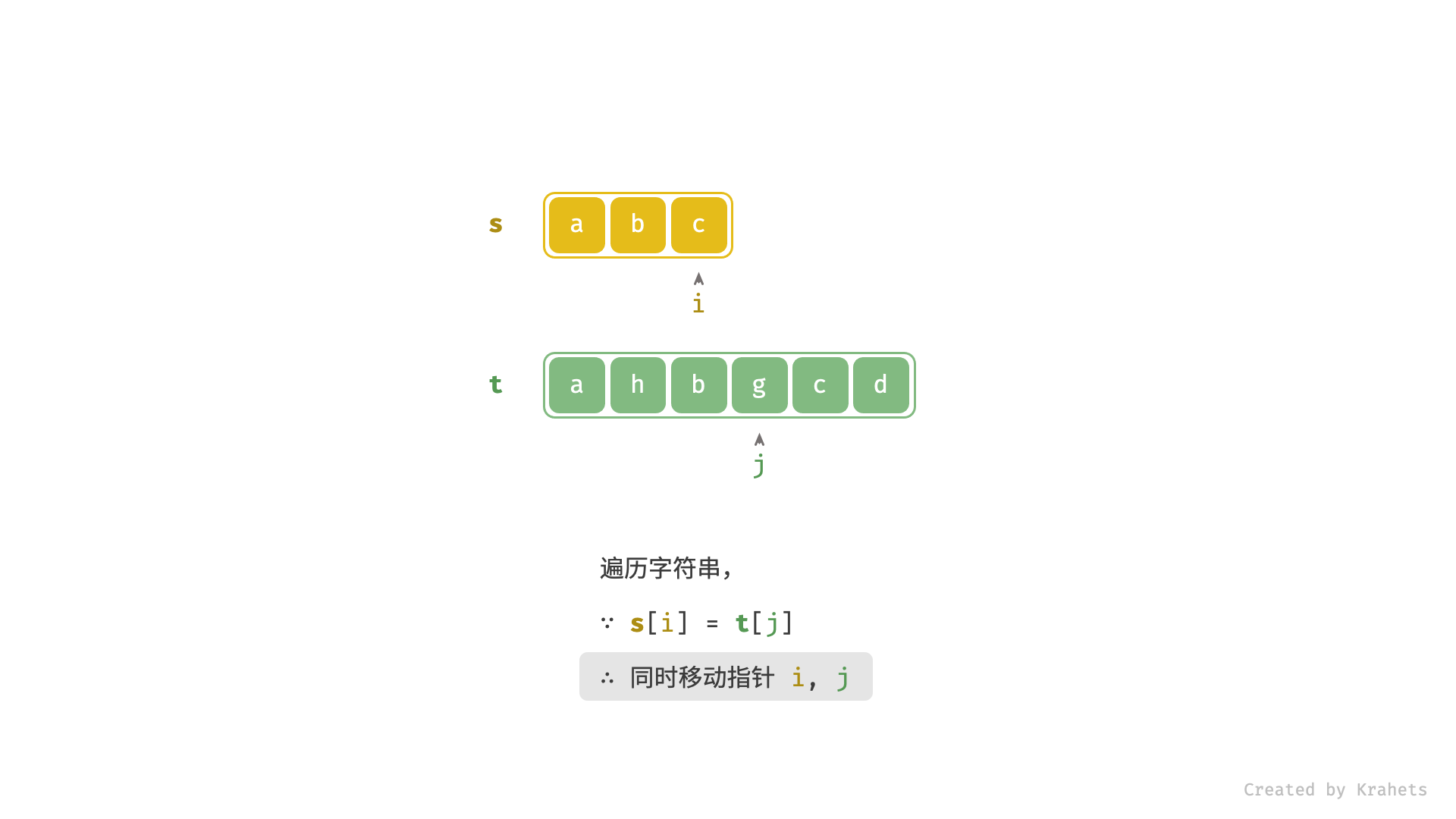
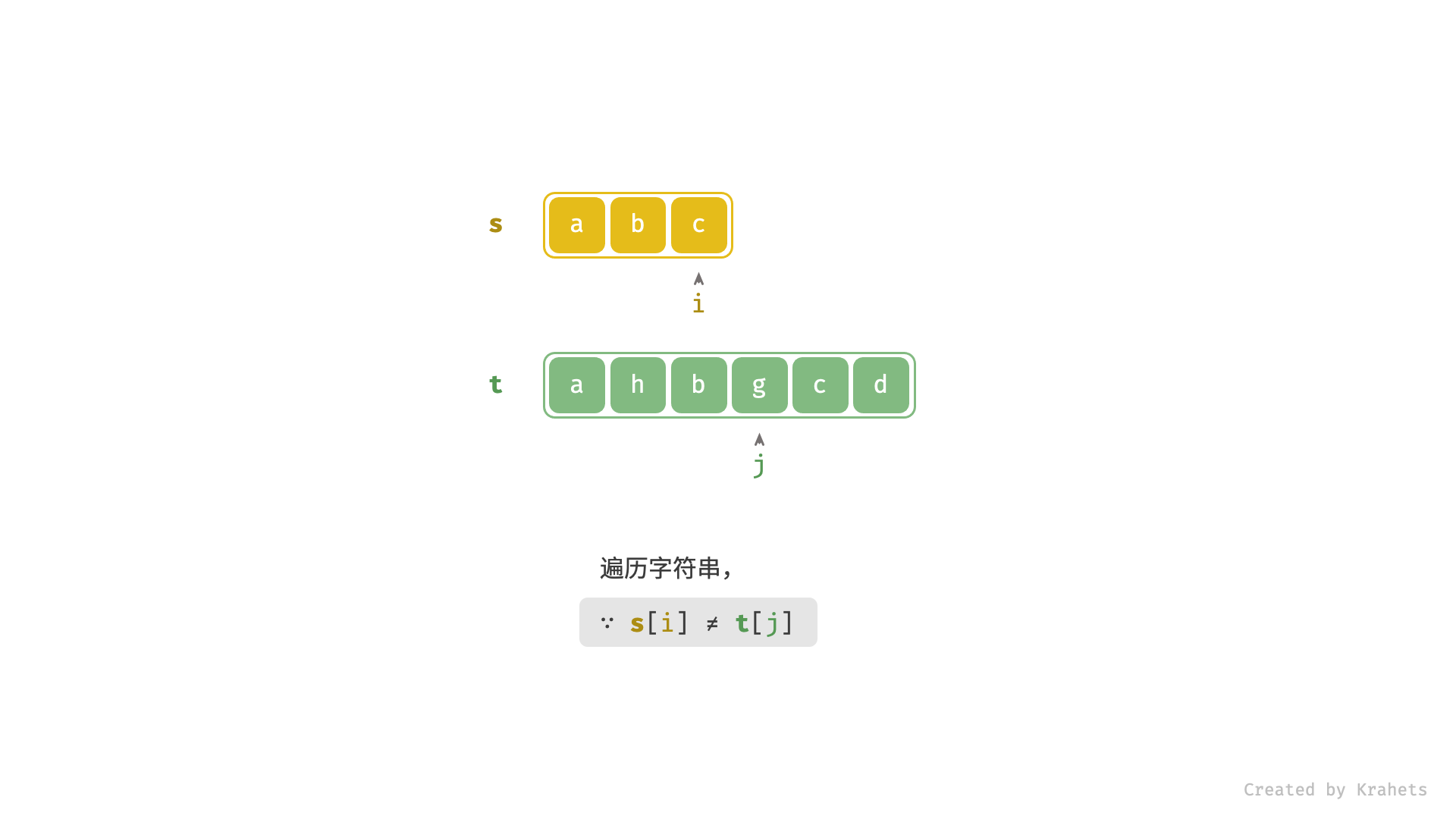
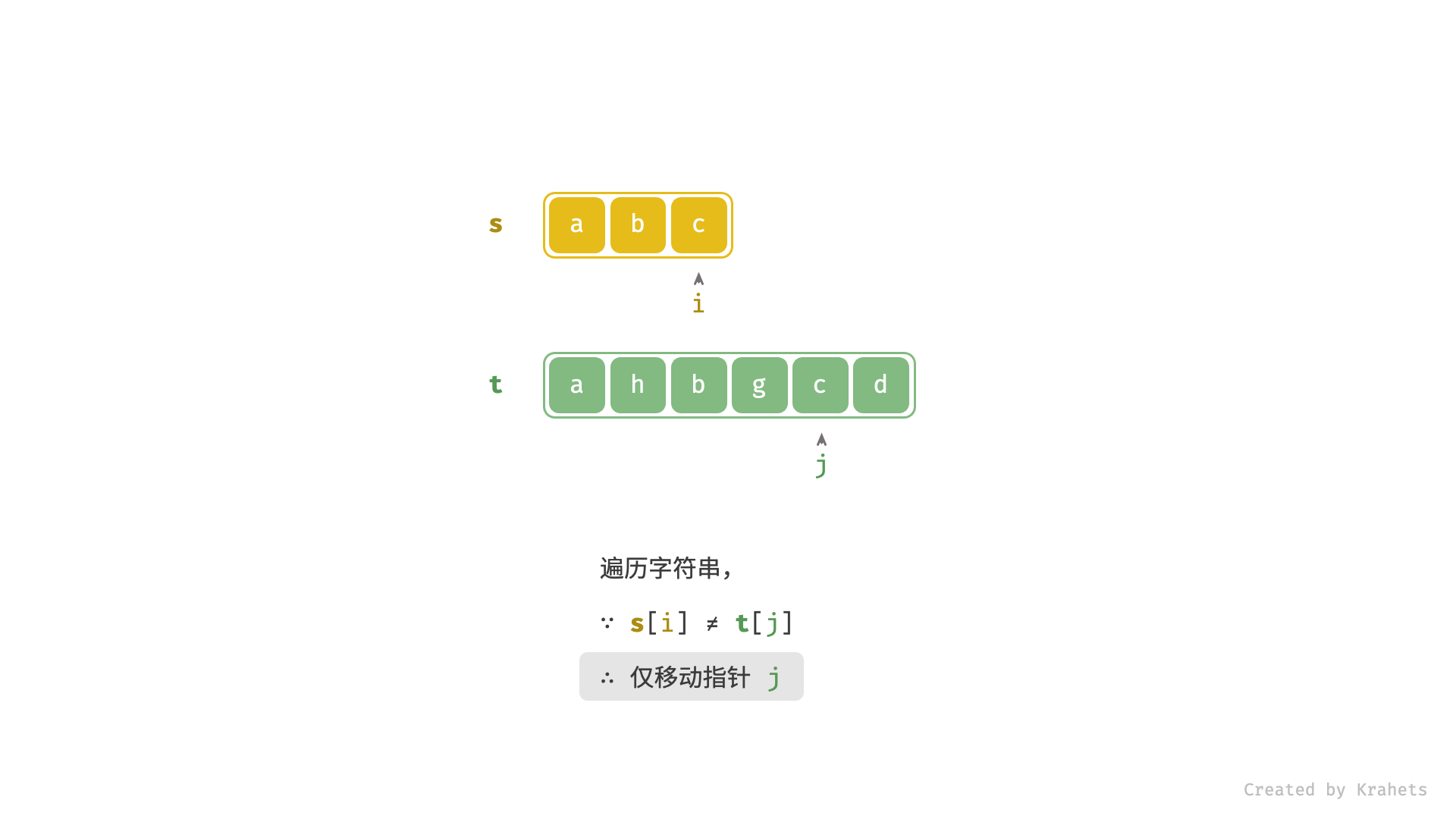
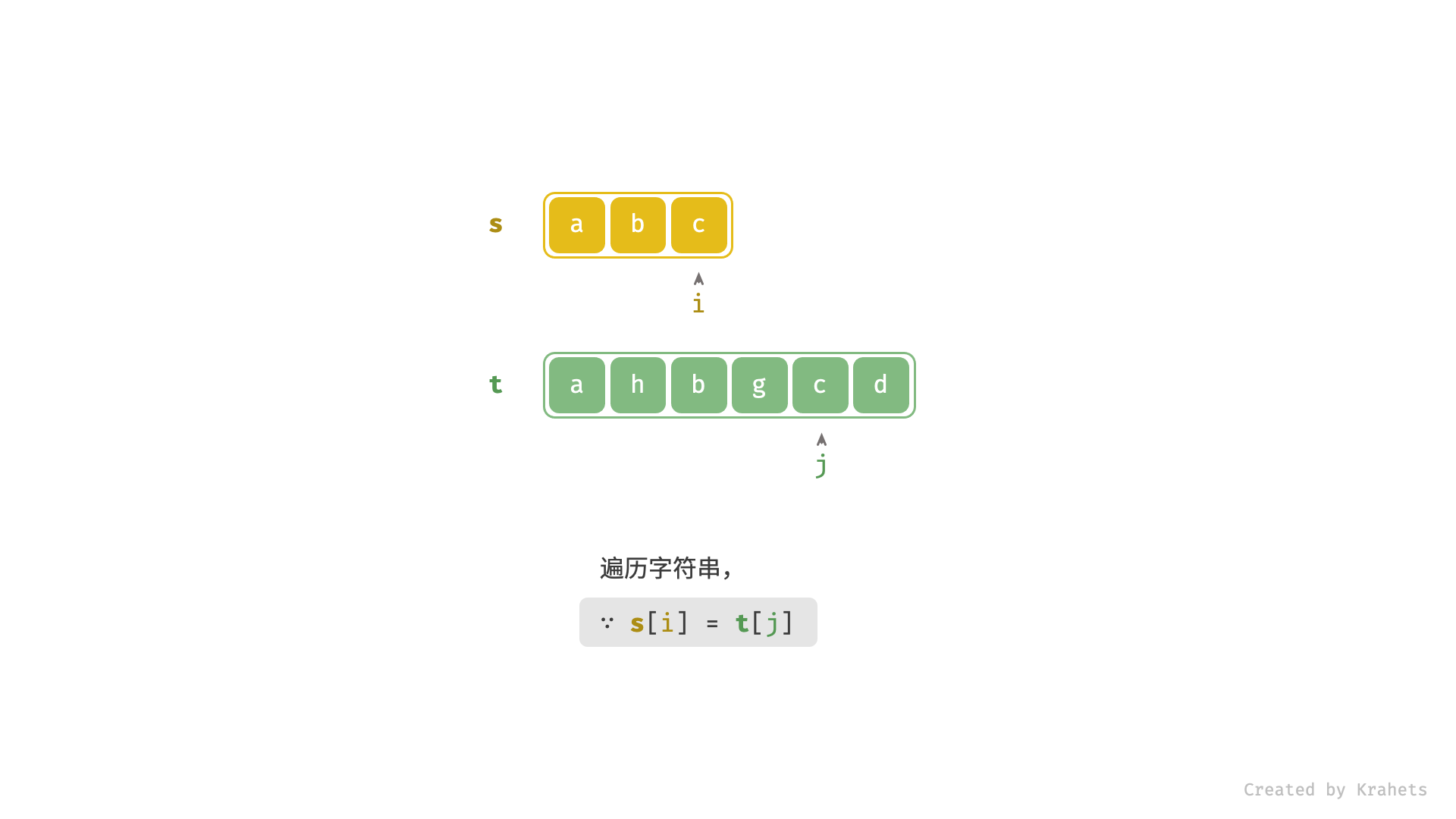
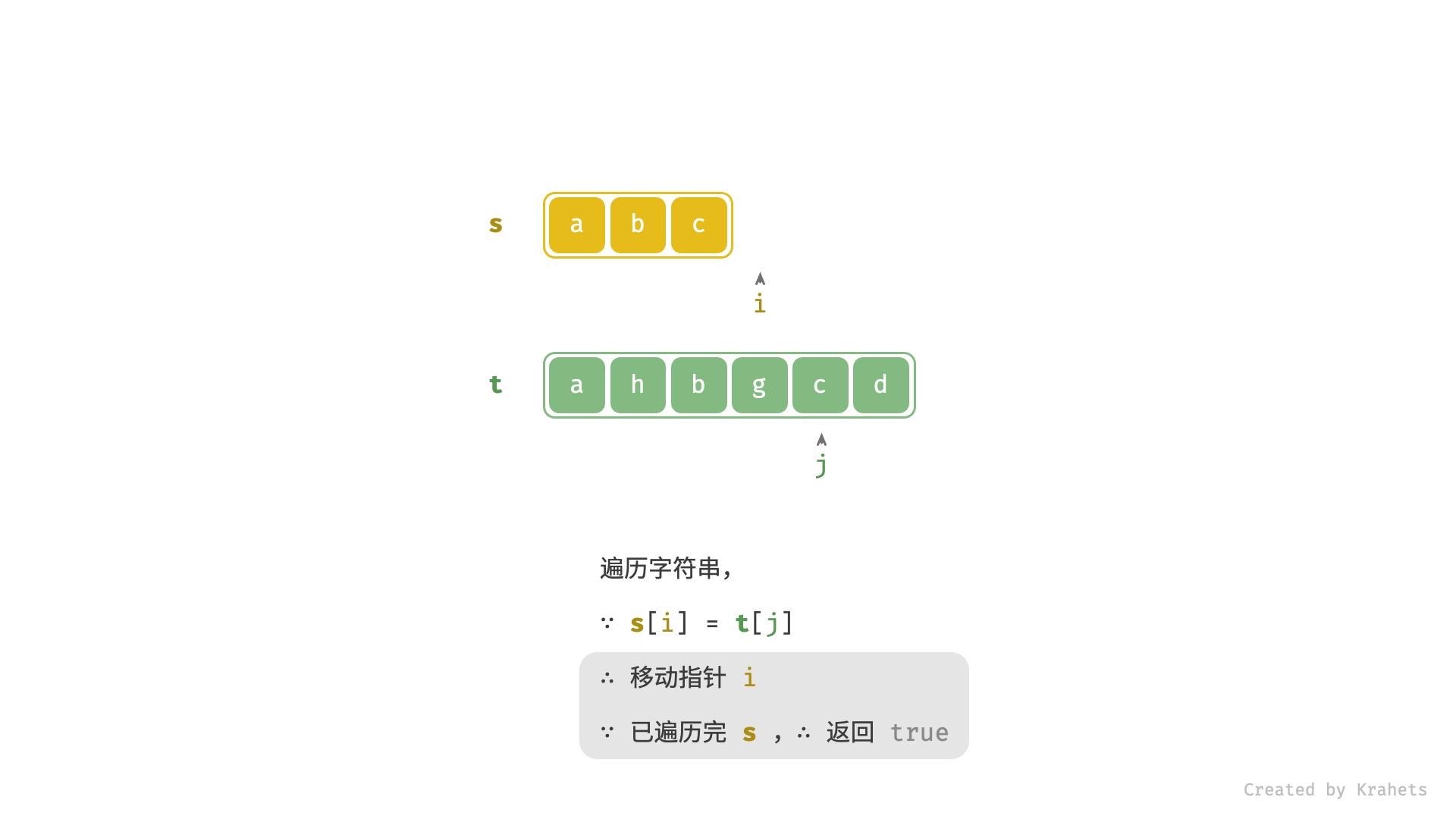
- 当
s[i] == t[j]时,代表匹配成功,此时同时i++,j++;- 进而,若
i已走过s尾部,代表s是t的子序列,此时应提前返回 true ;
- 进而,若
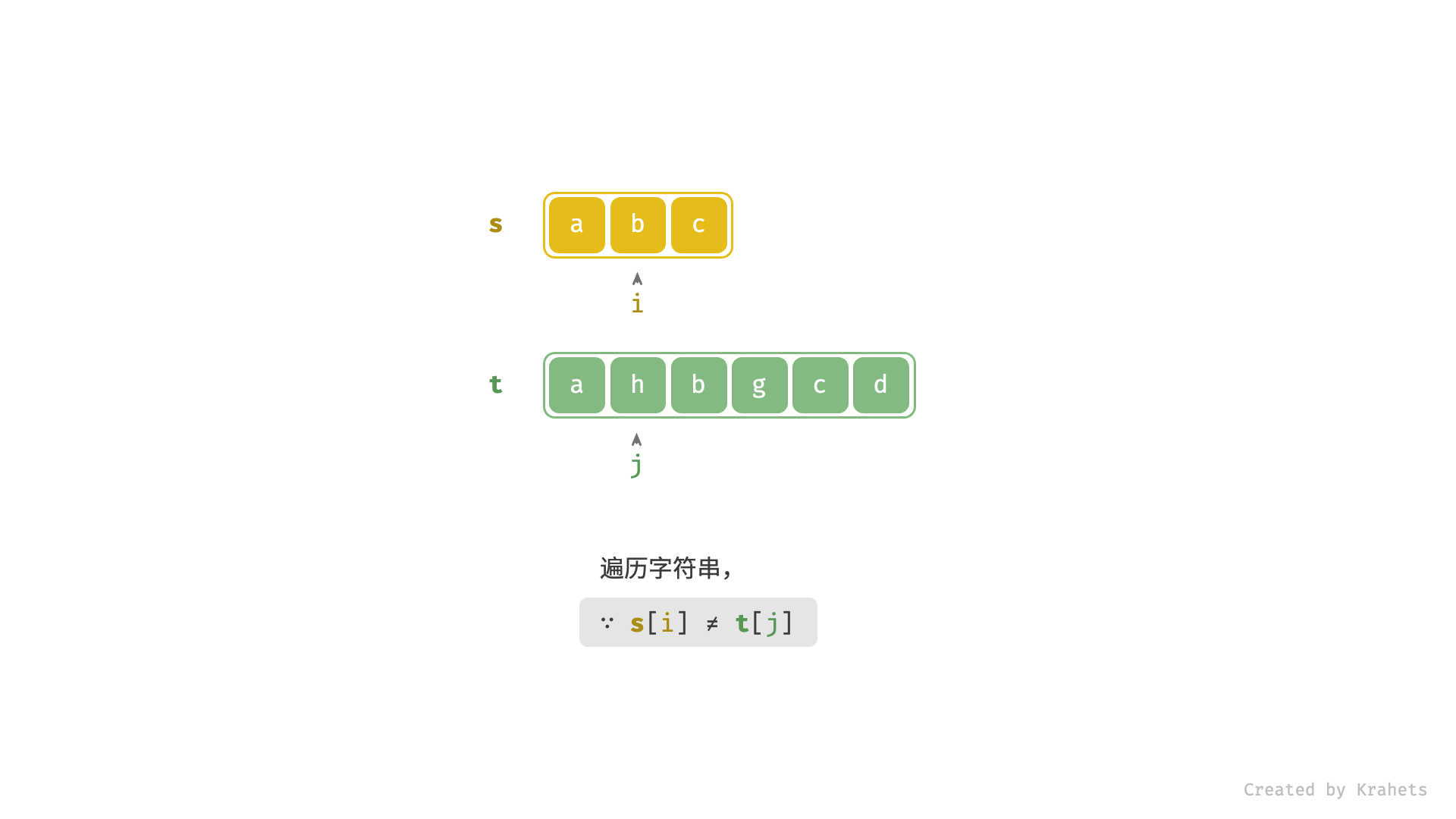
- 当
s[i] != t[j]时,代表匹配失败,此时仅j++;
若遍历完字符串 t 后,字符串 s 仍未遍历完,代表 s 不是 t 的子序列,此时返回 false 。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
上为静态图,下为动态图,内容一致。
代码
Python
class Solution:
def isSubsequence(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
if not s: return True
i = 0
for c in t:
if s[i] == c:
i += 1
# 若已经遍历完 s ,则提前返回 true
if i == len(s):
return True
return FalseJava
class Solution {
public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() == 0) return true;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < t.length(); j++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(j)) {
// 若已经遍历完 s ,则提前返回 true
if (++i == s.length())
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
if (s.size() == 0) return true;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < t.size(); j++) {
if (s[i] == t[j]) {
// 若已经遍历完 s ,则提前返回 true
if (++i == s.size())
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为字符串
t的长度。最差情况下需完整遍历t。 - 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :
i,j变量使用常数大小空间。