解题思路:
本文介绍三种时间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 的解法,其中只有方法三完全满足题目要求,其中:
- 方法一使用了哈希表额外空间;
- 方法二需要修改原数组
nums;
方法一:哈希表
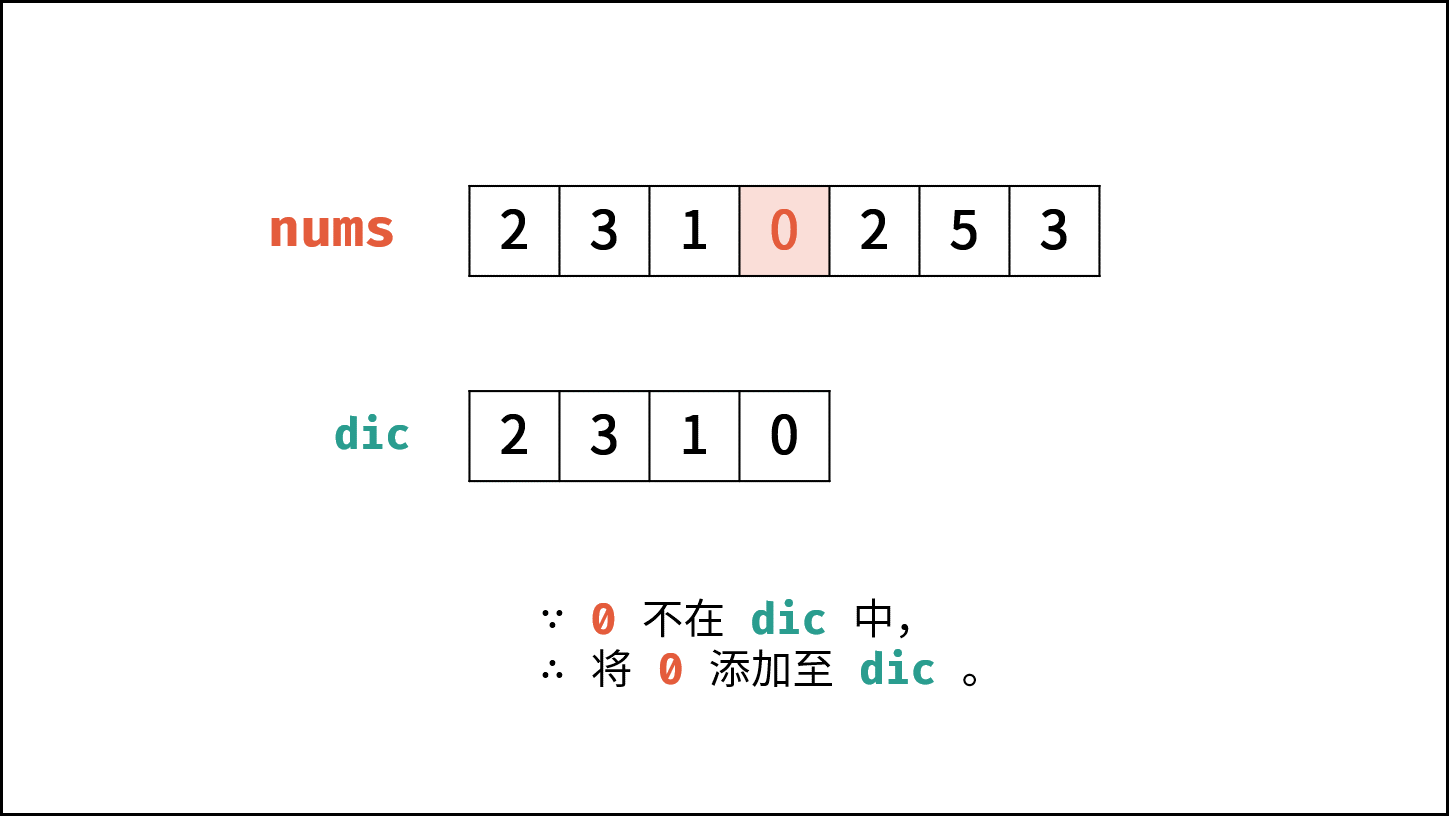
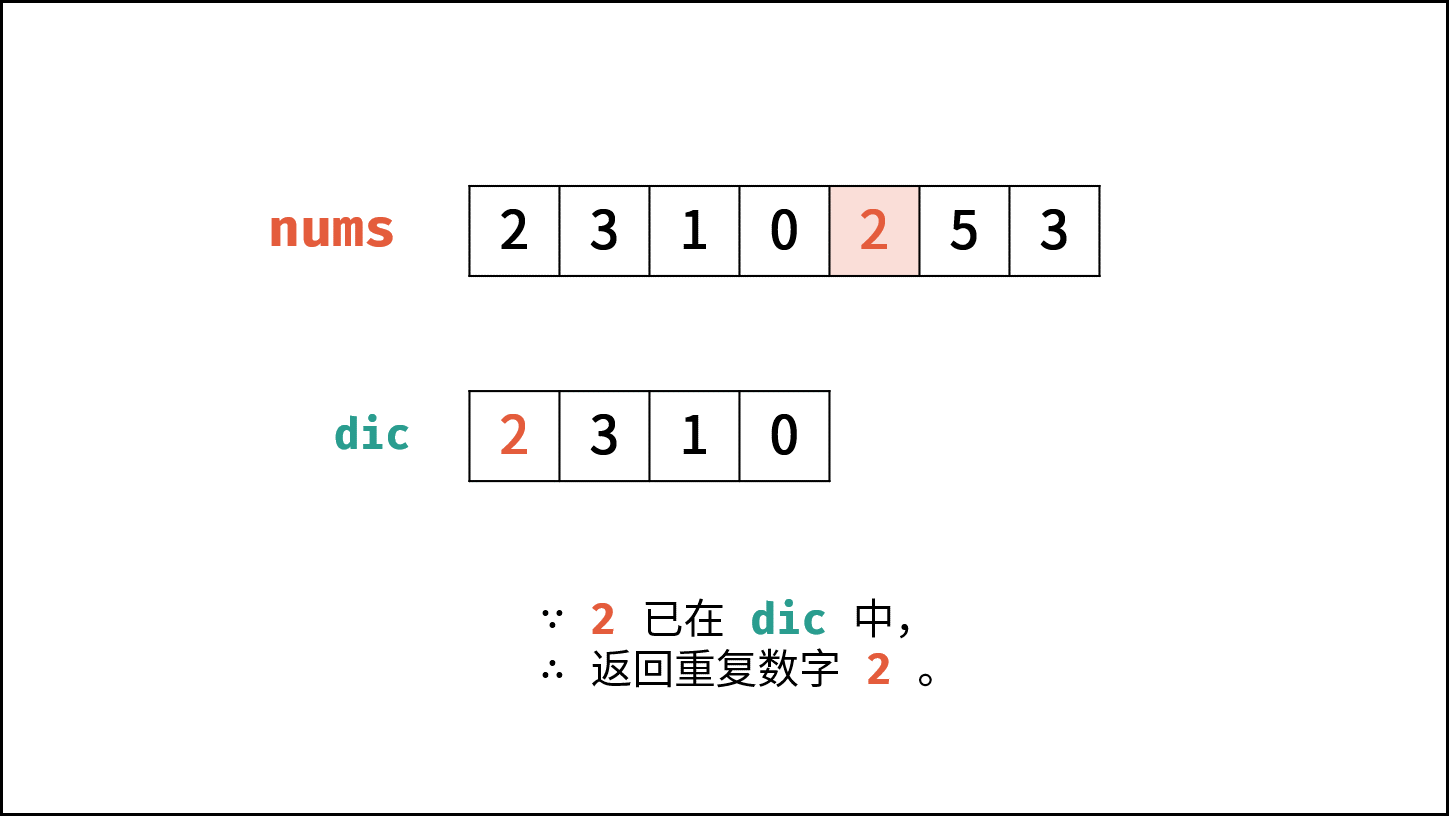
利用数据结构特点,容易想到使用哈希表(Set)记录数组的各个数字,当查找到重复数字则直接返回。
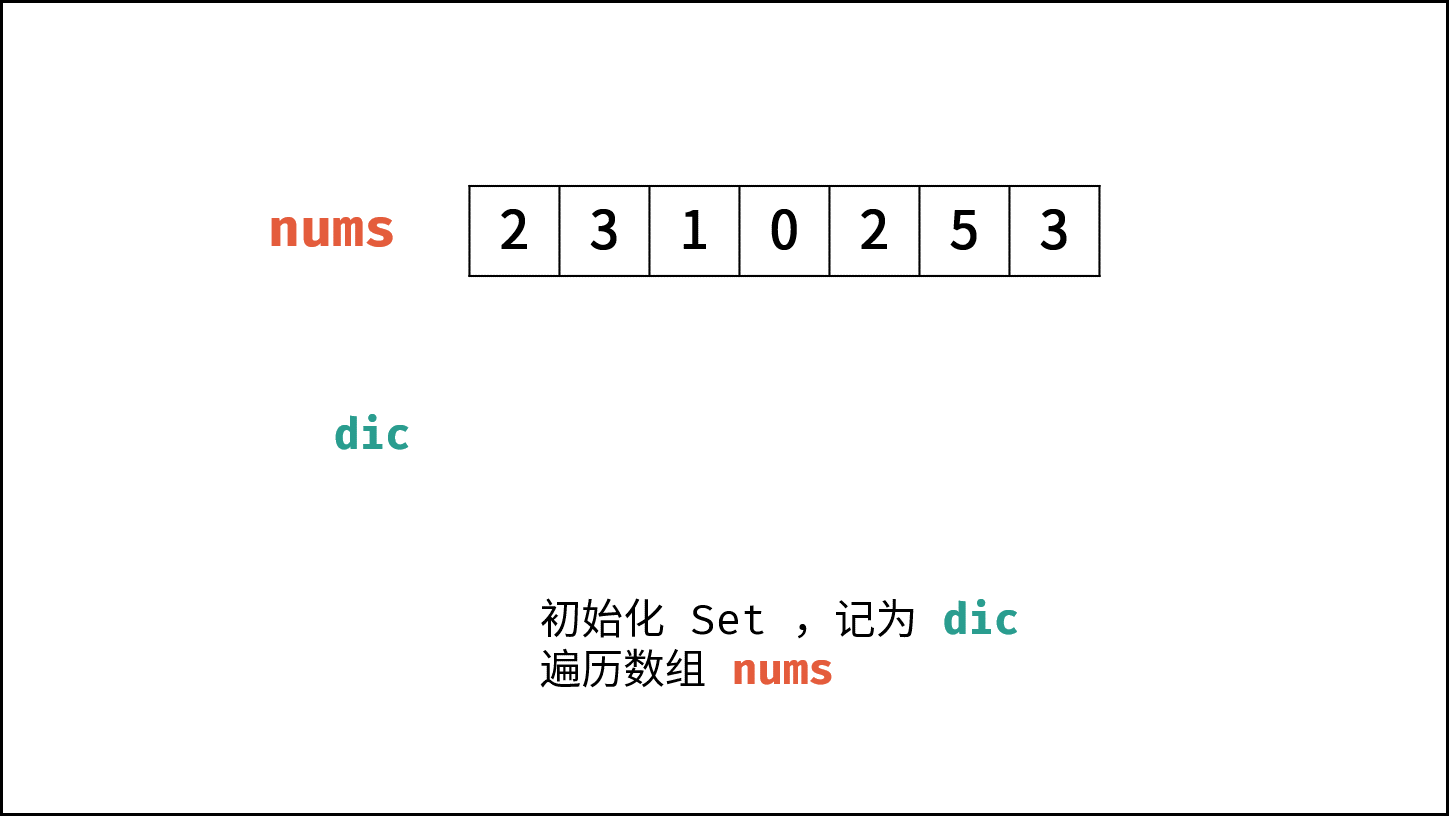
算法流程:
- 初始化: 新建 HashSet ,记为 $hmap$ 。
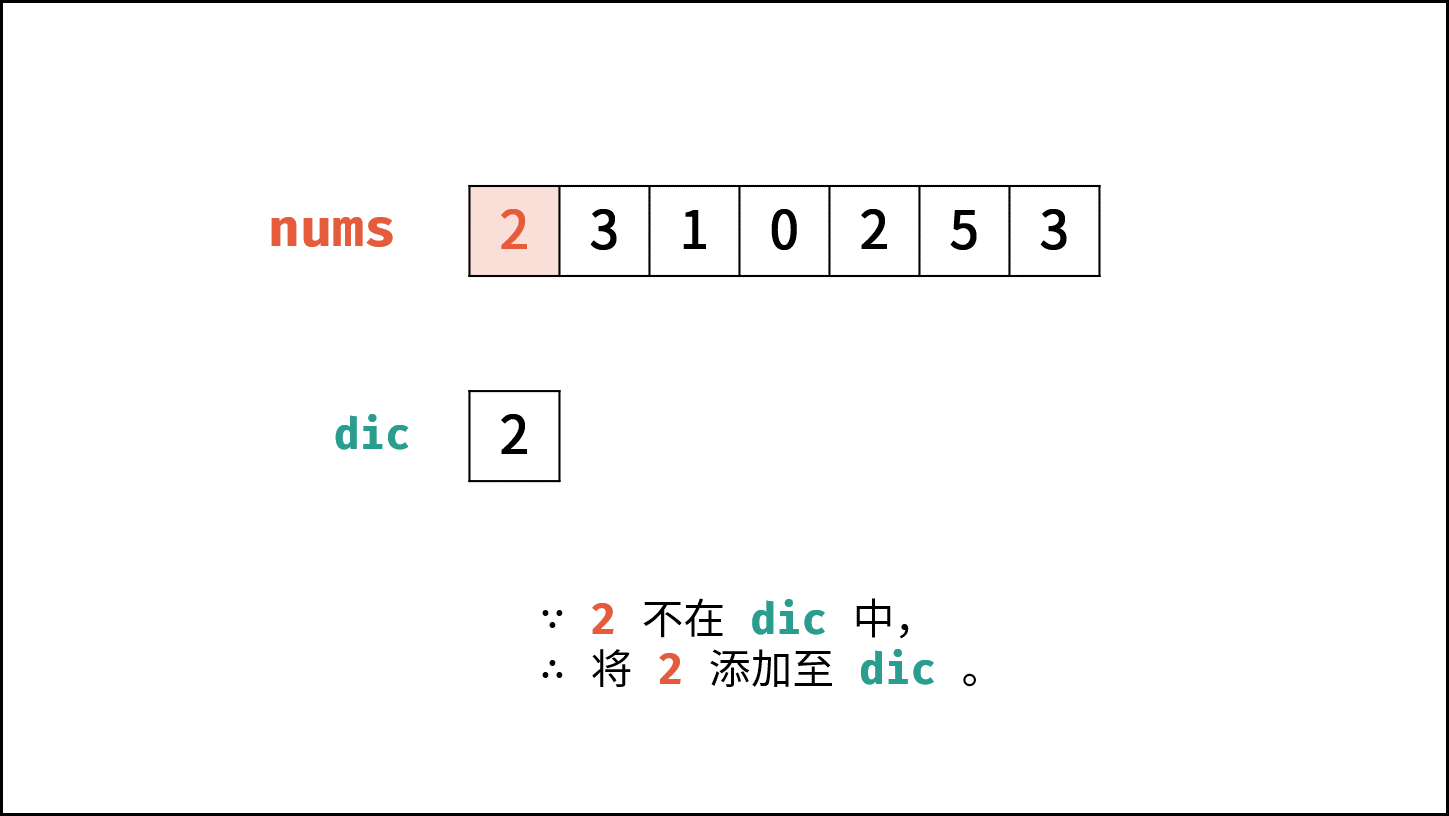
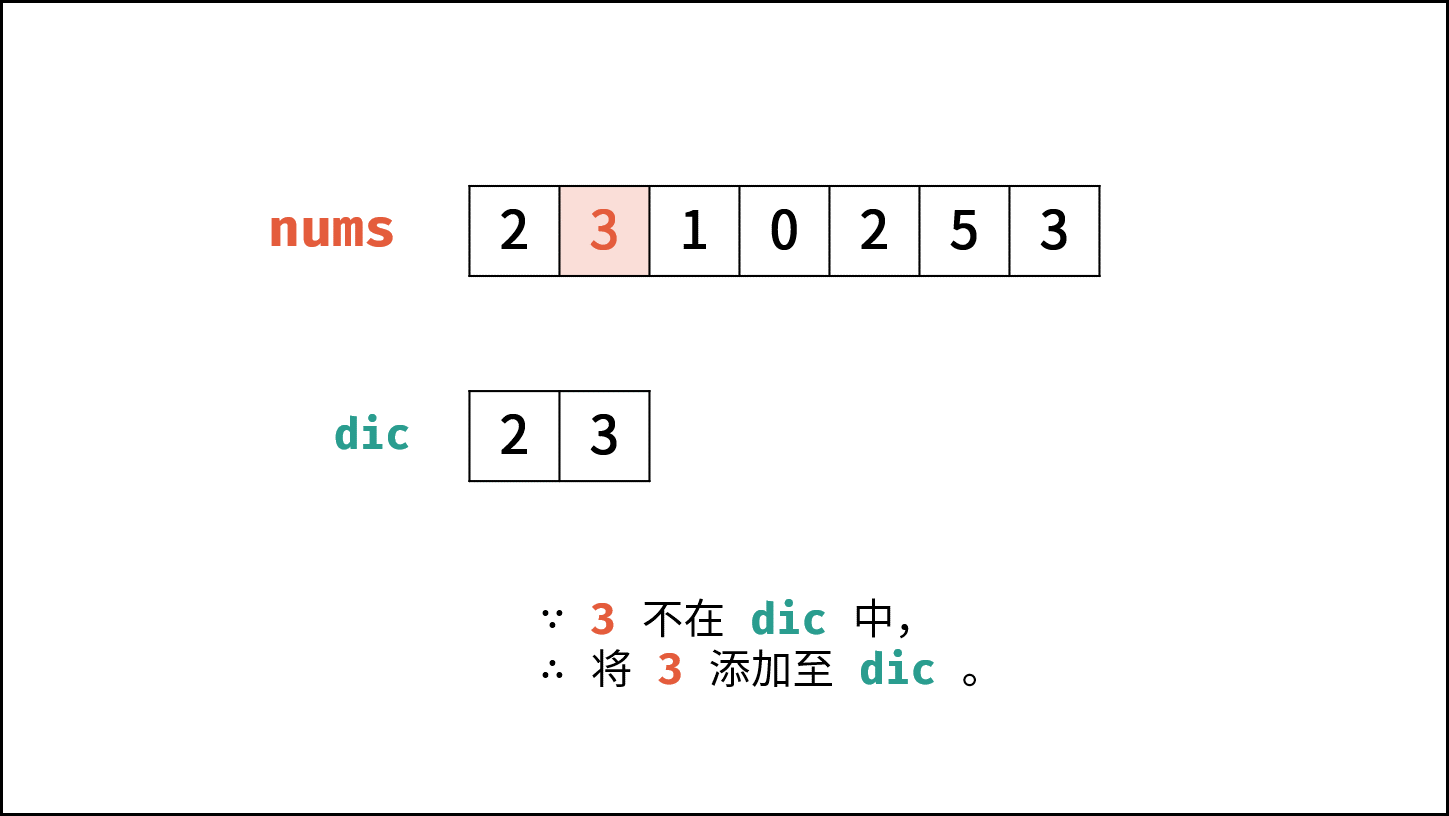
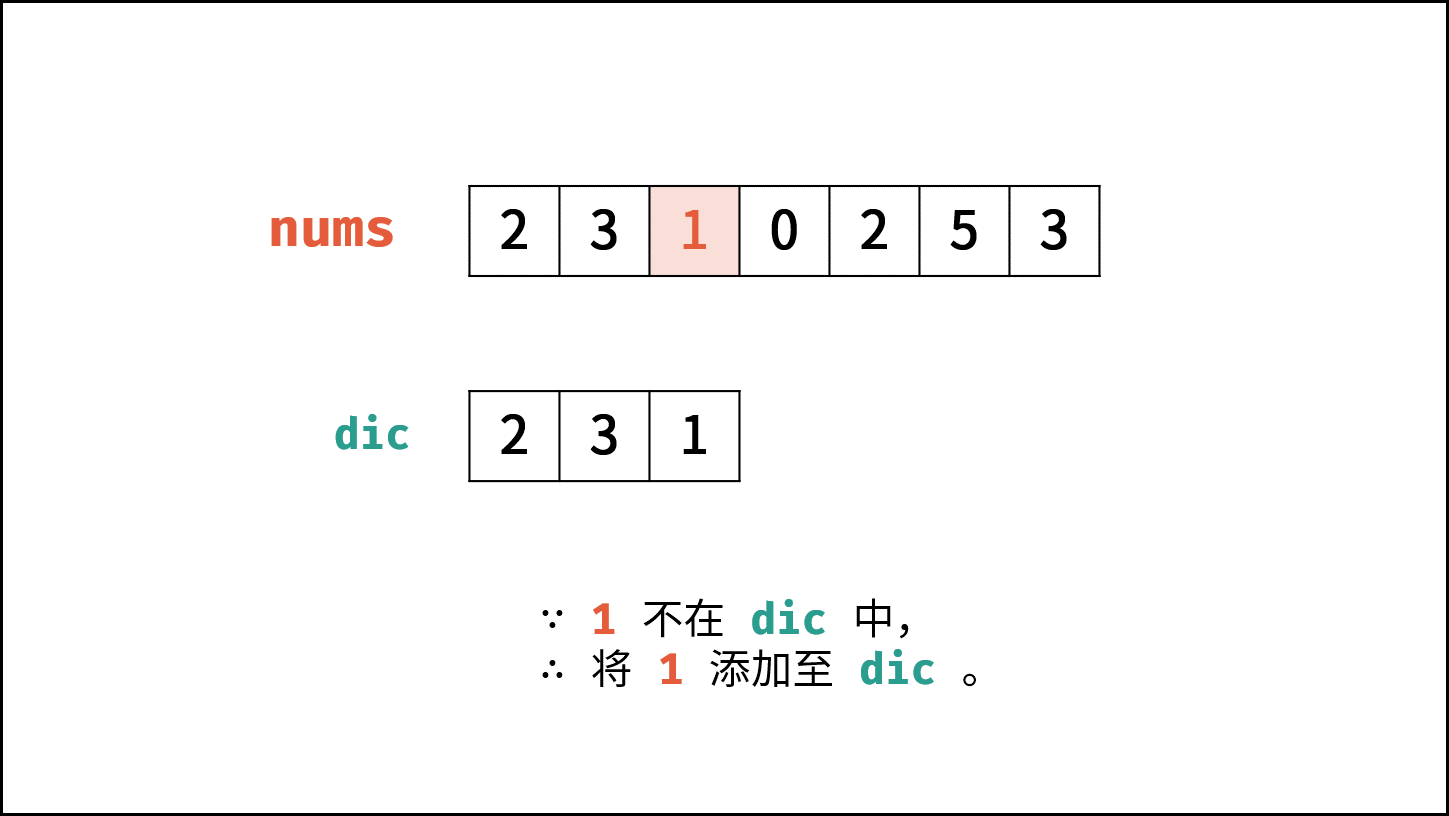
- 遍历数组 $nums$ 中的每个数字 $num$ :
- 当 $num$ 在 $hmap$ 中,说明重复,直接返回 $num$ 。
- 将 $num$ 添加至 $hmap$ 中。
- 返回 $-1$ 。本题中一定有重复数字,因此这里返回多少都可以。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
class Solution:
def findDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
hmap = set()
for num in nums:
if num in hmap: return num
hmap.add(num)
return -1class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> hmap = new HashSet<>();
for(int num : nums) {
if(hmap.contains(num)) return num;
hmap.add(num);
}
return -1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, bool> map;
for(int num : nums) {
if(map[num]) return num;
map[num] = true;
}
return -1;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 遍历数组使用 $O(N)$ ,HashSet 添加与查找元素皆为 $O(1)$ 。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : HashSet 占用 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间。
方法二:原地交换
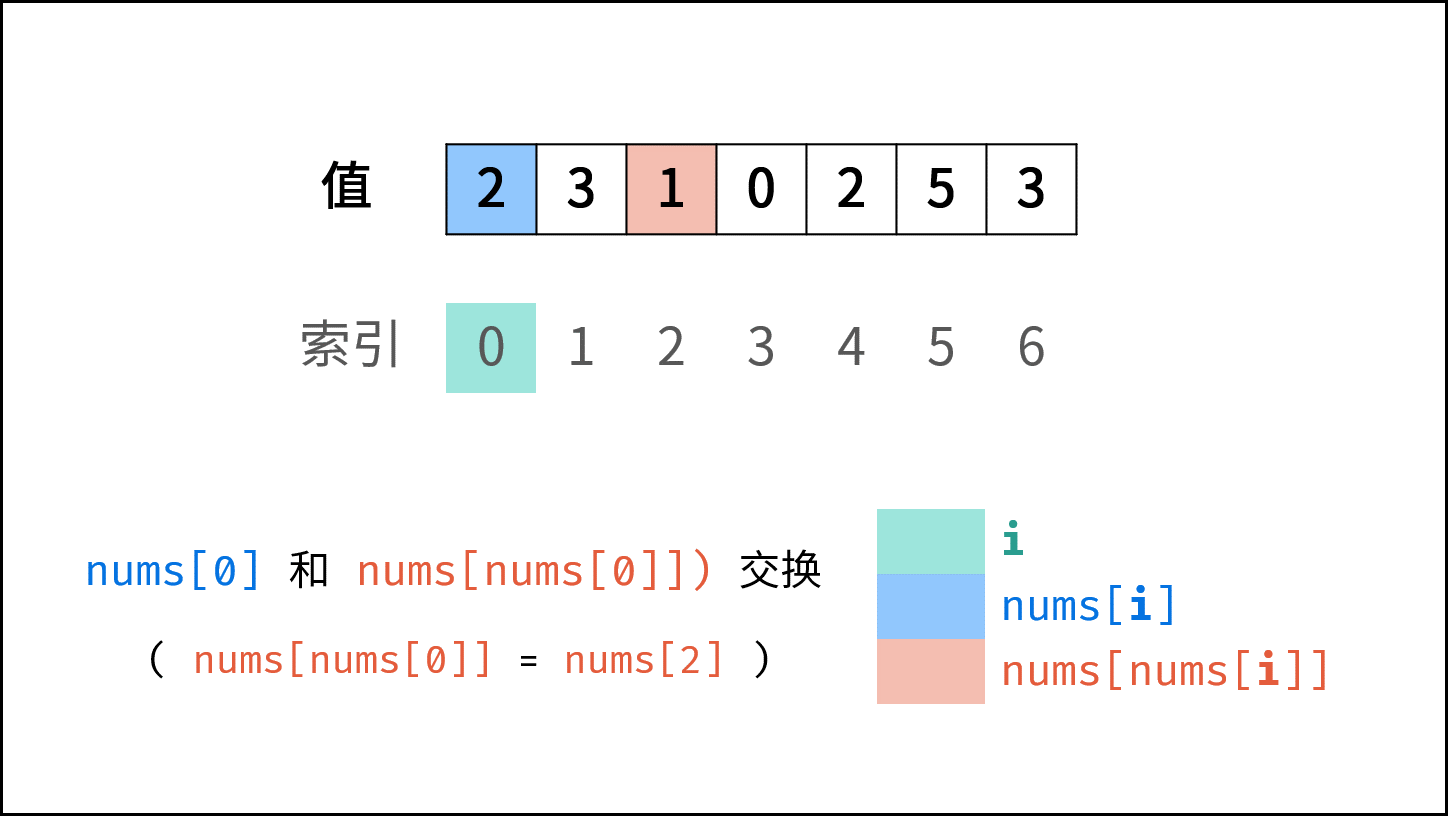
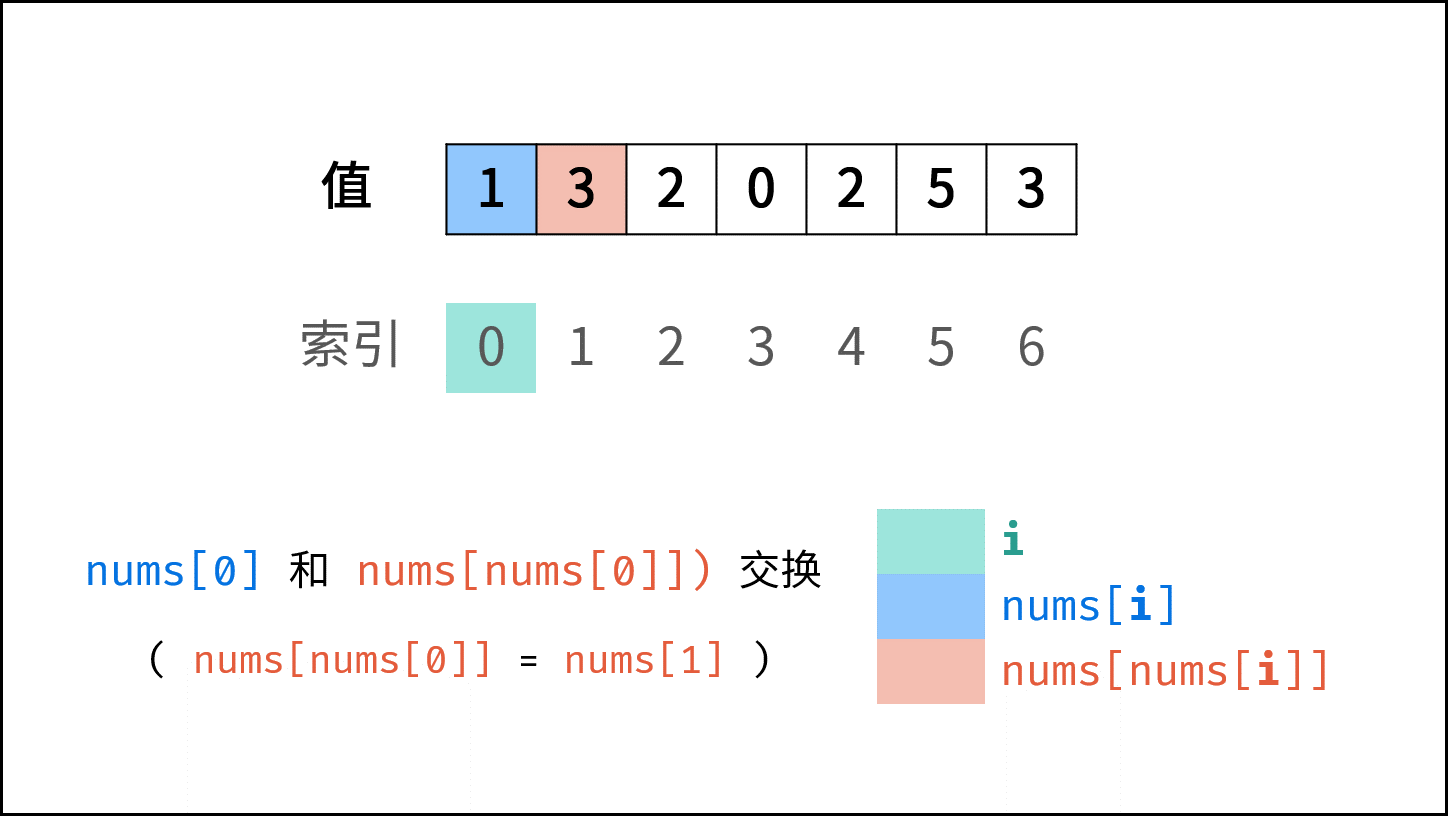
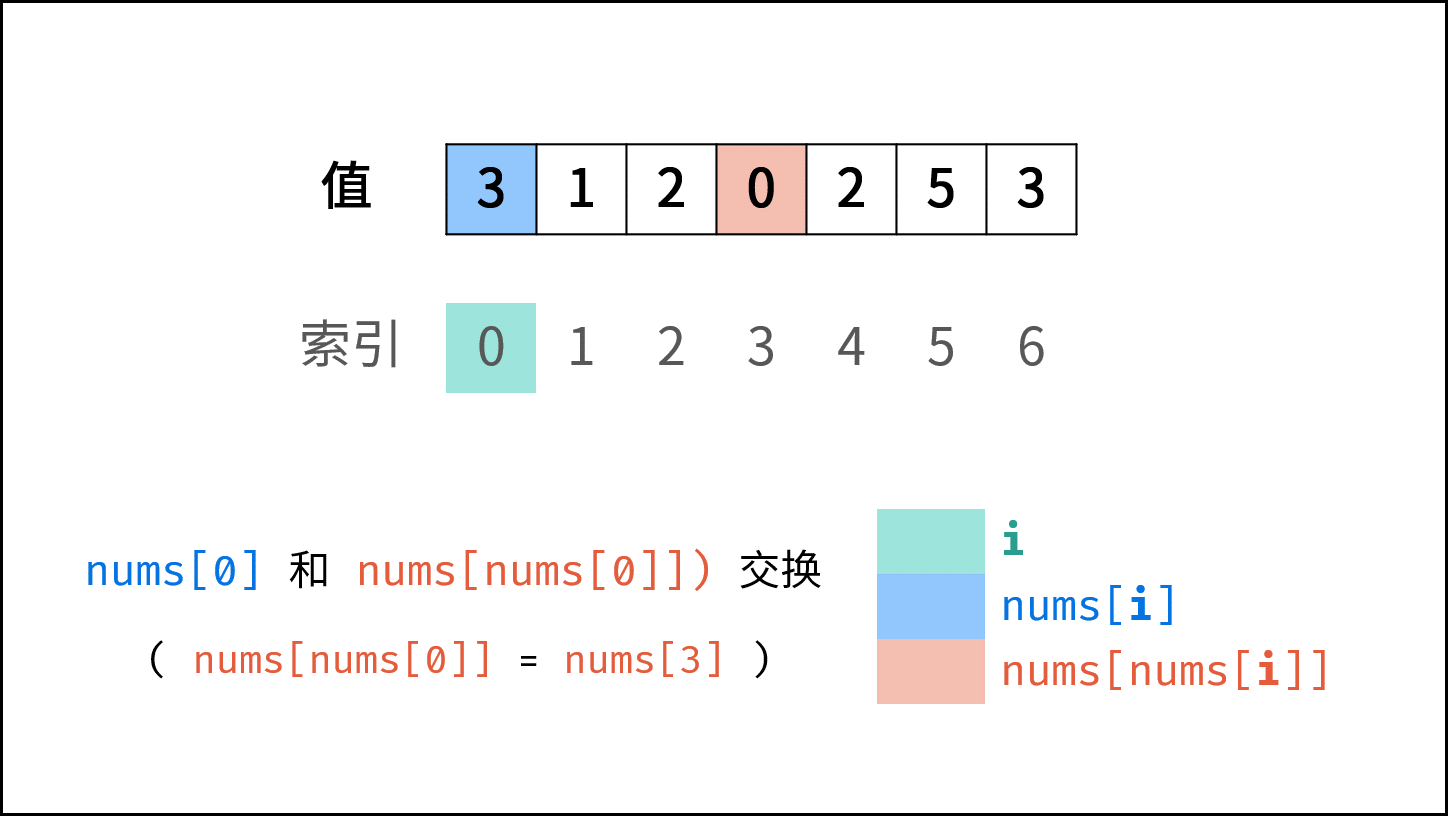
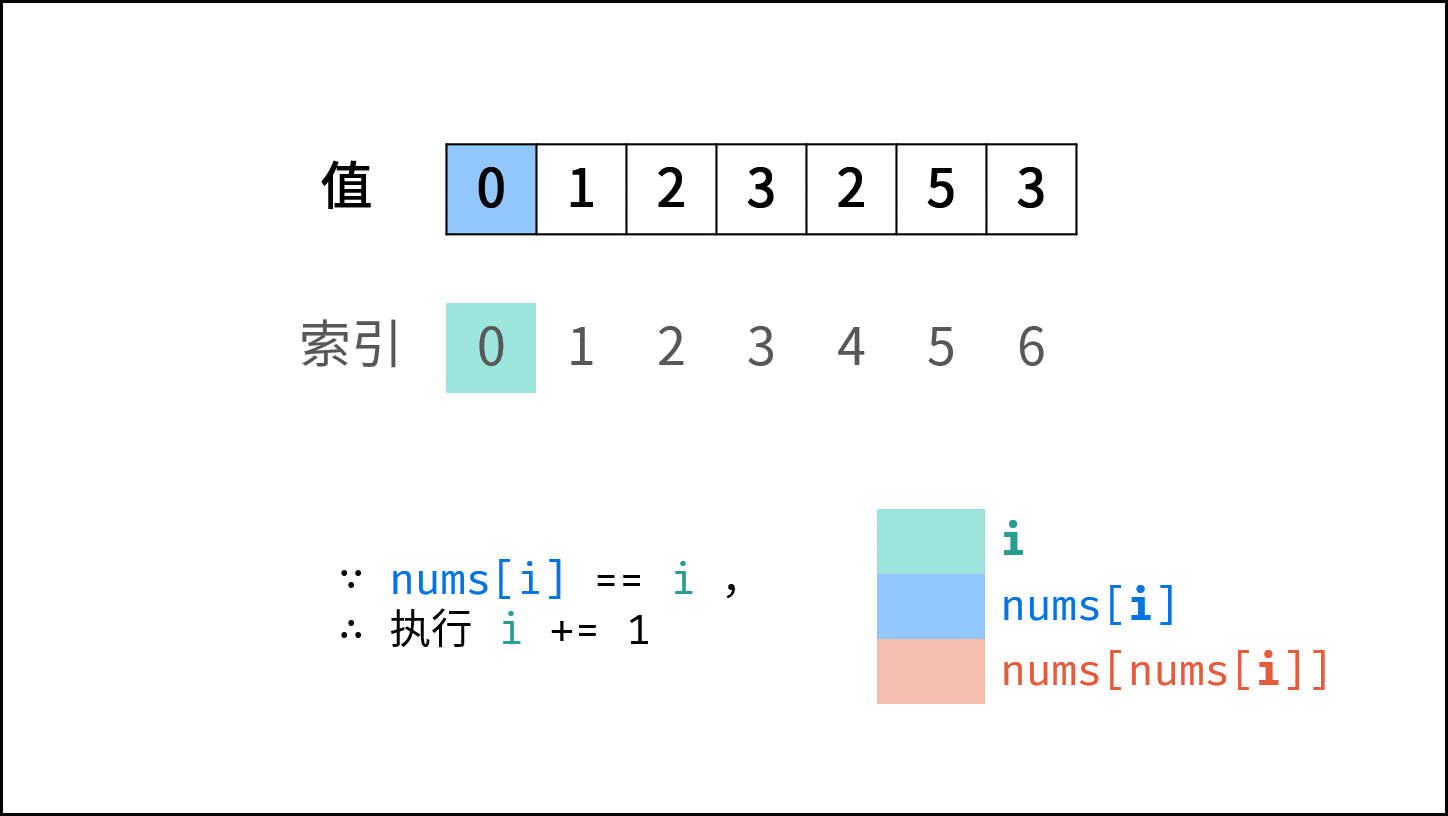
题目说明尚未被充分使用,即 在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0 ~ n-1 的范围内 。 此说明含义:数组元素的 索引 和 值 是 一对多 的关系。 因此,可遍历数组并通过交换操作,使元素的 索引 与 值 一一对应(即 $nums[i] = i$ )。因而,就能通过索引映射对应的值,起到与字典等价的作用。
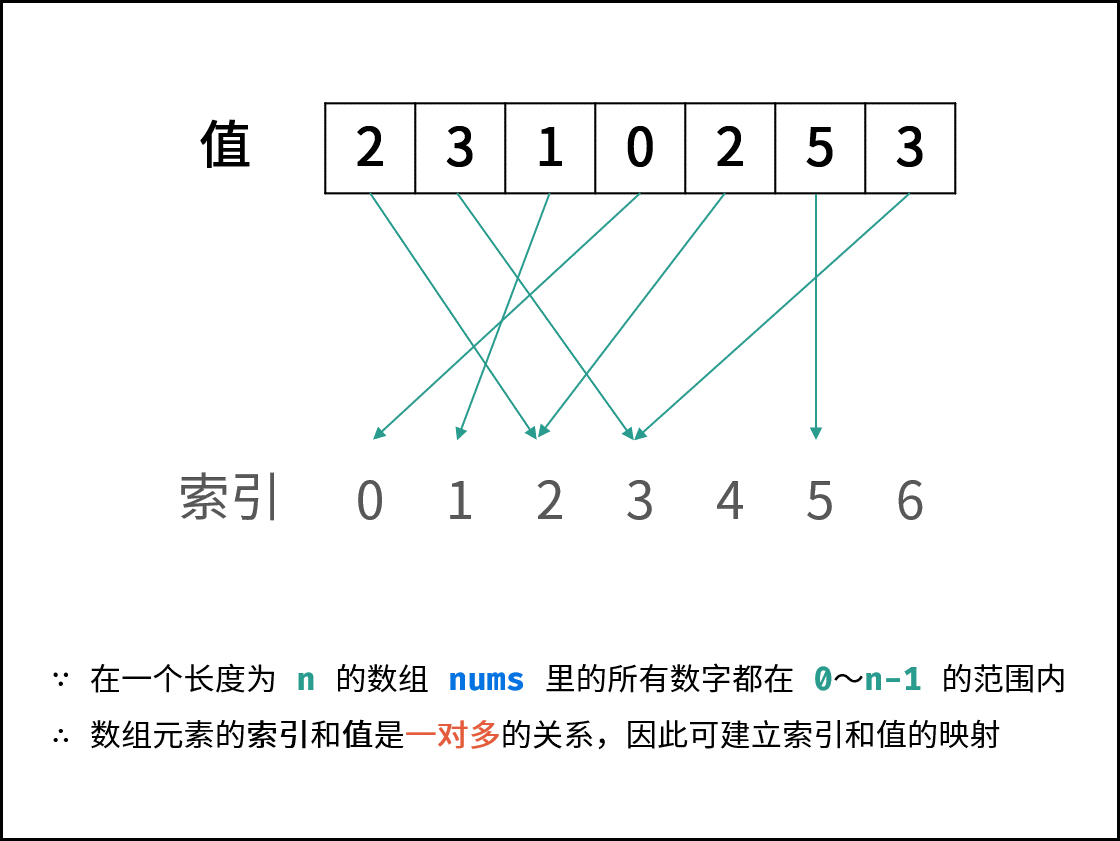
遍历中,第一次遇到数字 $x$ 时,将其交换至索引 $x$ 处;而当第二次遇到数字 $x$ 时,一定有 $nums[x] = x$ ,此时即可得到一组重复数字。
算法流程:
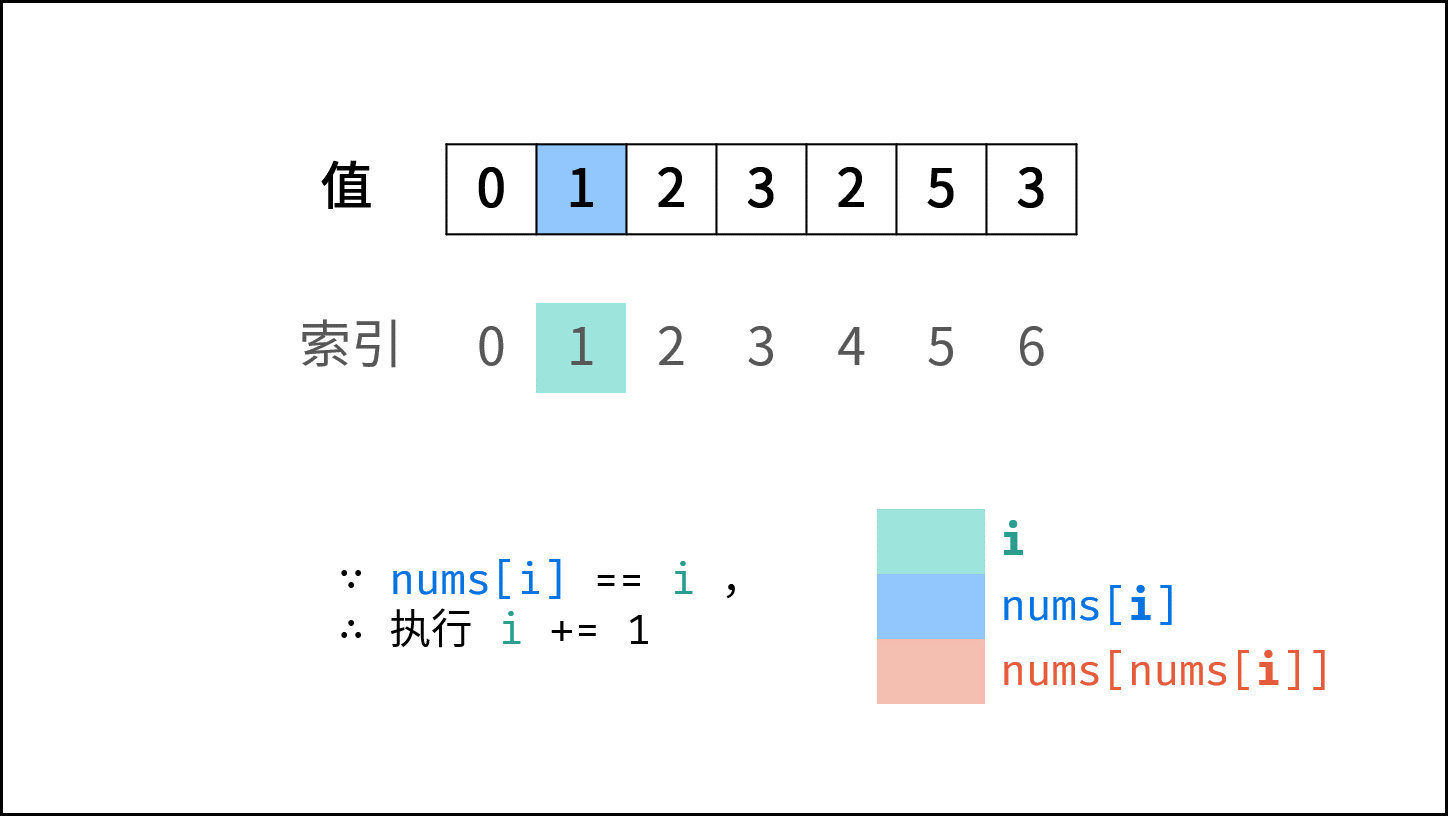
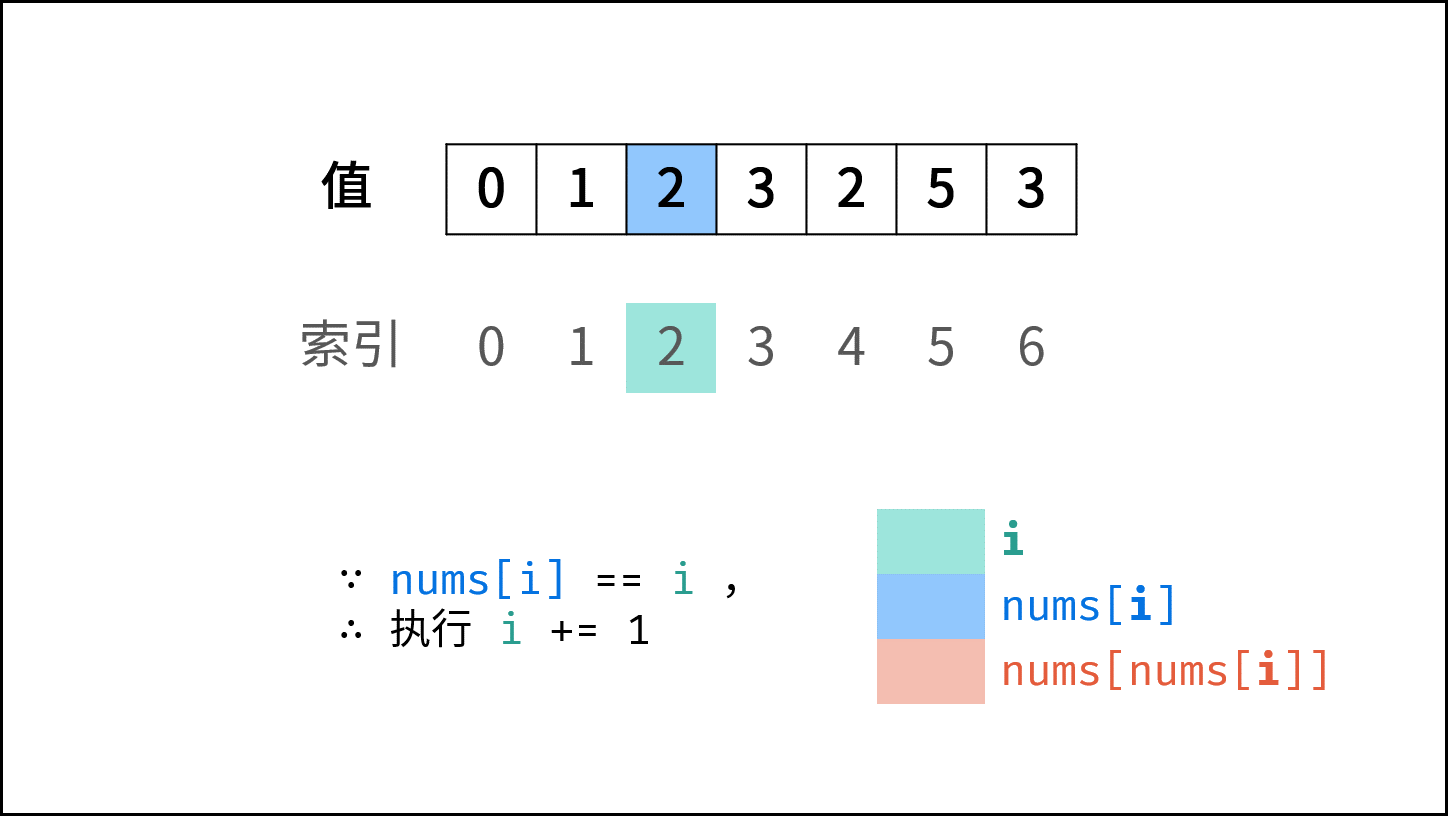
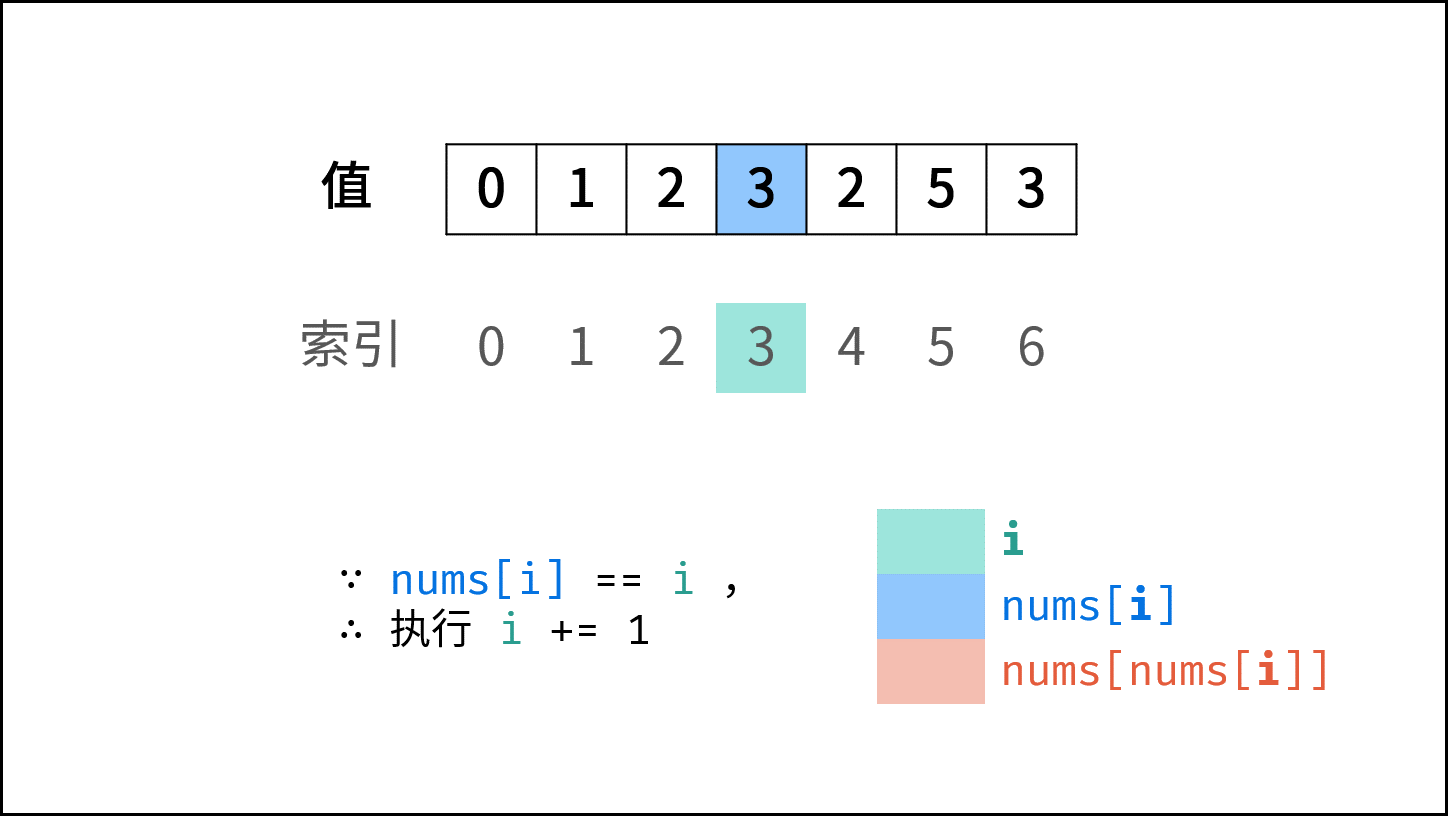
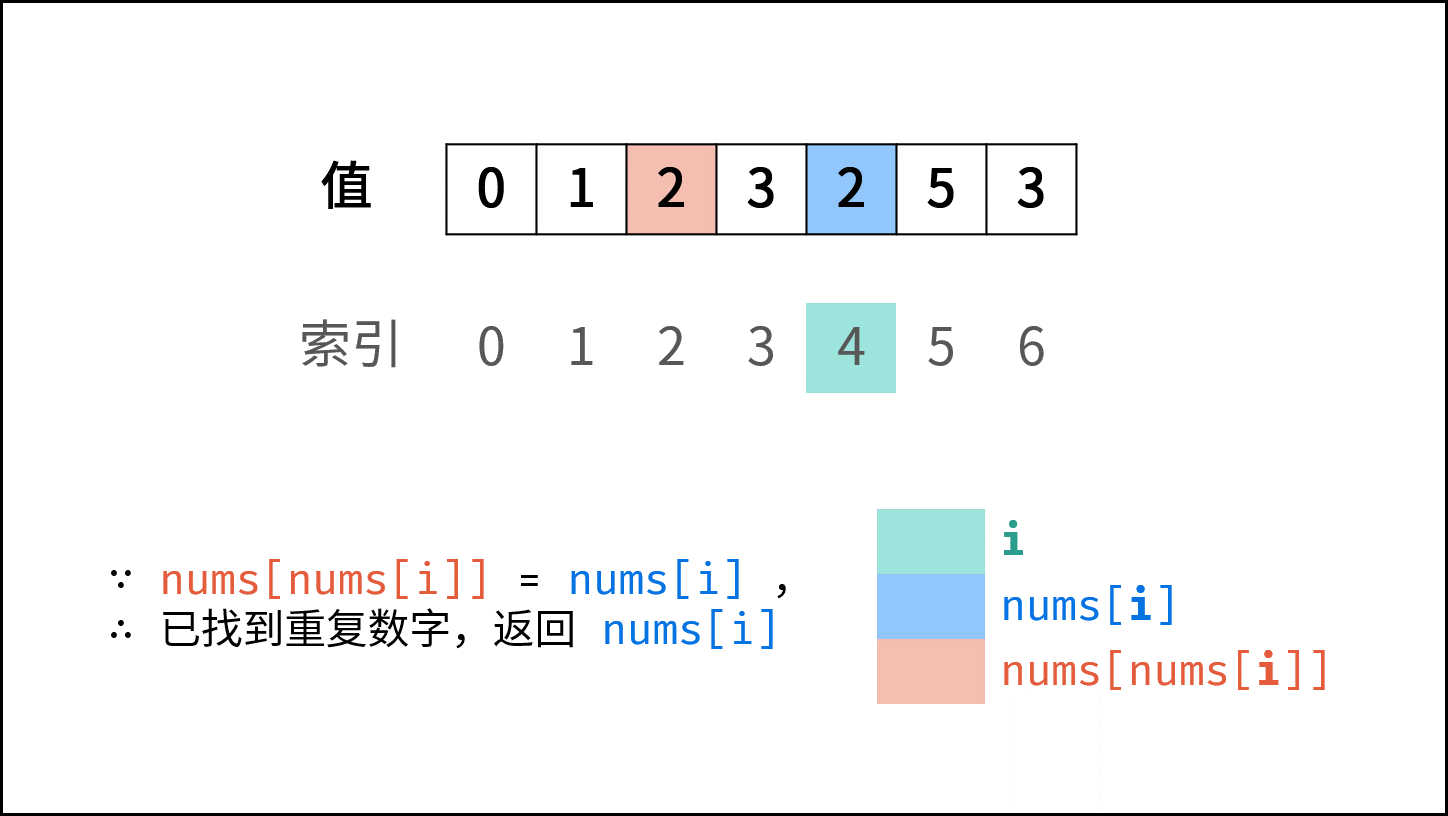
遍历数组 $nums$ ,设索引初始值为 $i = 0$ :
- 若 $nums[i] = i$ : 说明此数字已在对应索引位置,无需交换,因此跳过。
- 若 $nums[nums[i]] = nums[i]$ : 代表索引 $nums[i]$ 处和索引 $i$ 处的元素值都为 $nums[i]$ ,即找到一组重复值,返回此值 $nums[i]$ 。
- 否则: 交换索引为 $i$ 和 $nums[i]$ 的元素值,将此数字交换至对应索引位置。
若遍历完毕尚未返回,则返回 $-1$ 。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python 中, $a, b = c, d$ 操作的原理是先暂存元组 $(c, d)$ ,然后 “按左右顺序” 赋值给 a 和 b 。 因此,若写为 $nums[i], nums[nums[i]] = nums[nums[i]], nums[i]$ ,则 $nums[i]$ 会先被赋值,之后 $nums[nums[i]]$ 指向的元素则会出错。
class Solution:
def findDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
i = 0
while i < len(nums):
if nums[i] == i:
i += 1
continue
if nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]: return nums[i]
nums[nums[i]], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[nums[i]]
return -1class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int i = 0;
while(i < nums.length) {
if(nums[i] == i) {
i++;
continue;
}
if(nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]) return nums[i];
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[tmp];
nums[tmp] = tmp;
}
return -1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int i = 0;
while(i < nums.size()) {
if(nums[i] == i) {
i++;
continue;
}
if(nums[nums[i]] == nums[i])
return nums[i];
swap(nums[i],nums[nums[i]]);
}
return -1;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 遍历数组使用 $O(N)$ ,每轮遍历的判断和交换操作使用 $O(1)$ 。
- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 使用常数复杂度的额外空间。
方法三:环形链表
根据题意,数组索引和元素的取值范围 $\in [1, n]$ 。我们考虑建立一个 $n$ 个节点的链表:
- $n$ 个节点的值:$1$ , $2$ , $\cdots$ , $n$ ;
- 对于每个节点 $i$ ,其
next引用指向节点 $nums[i]$ 。
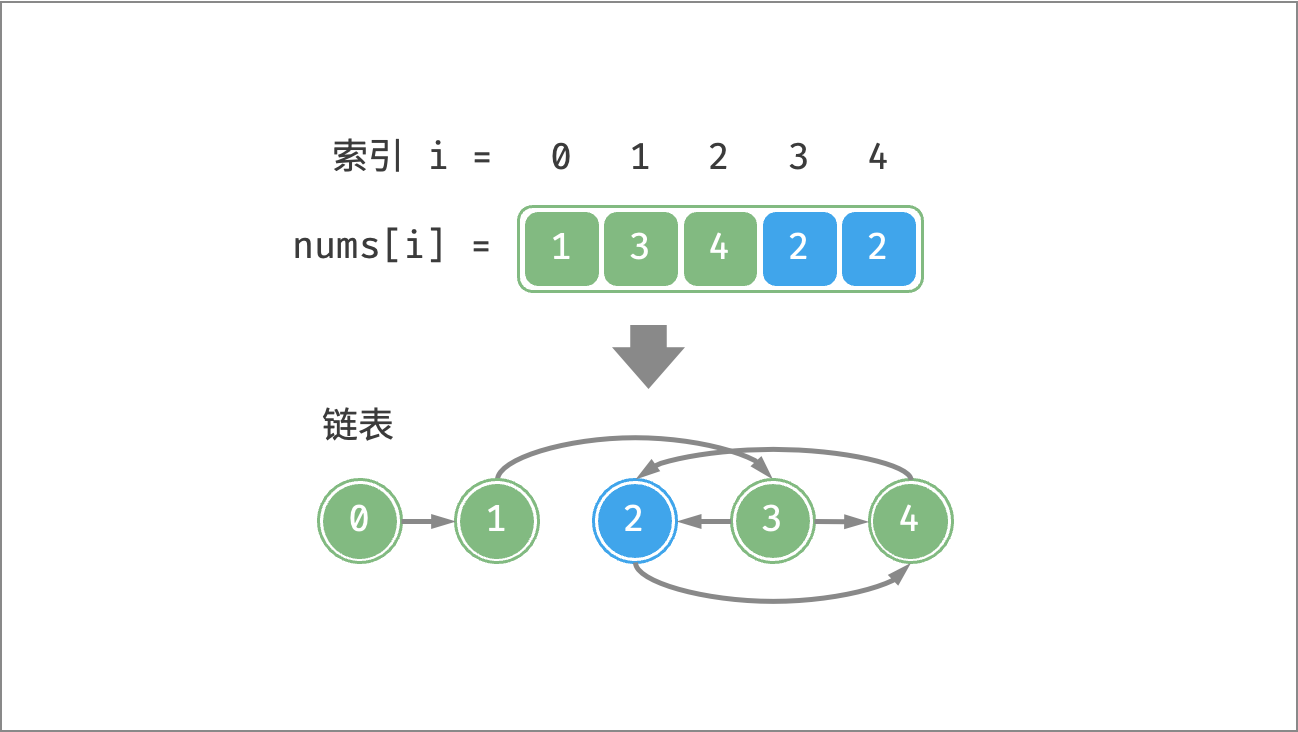
假设重复元素为 $x$ ,那么在这个链表中,一定同时有两条边指向节点 $x$ 。例如在上图中,有两条边都指向节点 $2$ 。因此可得到推论:此链表中一定存在环,且节点 $x$ 是环的入口。
换句话说,找出重复元素 $x$ 等价于找出链表中环的入口。这个问题实际上就是环形链表 II,唯一的不同点在于我们需要在数组中进行链表操作。
代码:
class Solution:
def findDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
def next(i):
return nums[i]
slow = fast = 0
# 第一次相遇
while True:
slow = next(slow)
fast = next(next(fast))
if slow == fast:
break
slow = 0
# 第二次相遇
while slow != fast:
slow = next(slow)
fast = next(fast)
return slowpublic class Solution {
private int next(int[] nums, int index) {
return nums[index];
}
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
// 第一次相遇
do {
slow = next(nums, slow);
fast = next(nums, next(nums, fast));
} while (slow != fast);
slow = 0;
// 第二次相遇
while (slow != fast) {
slow = next(nums, slow);
fast = next(nums, fast);
}
return slow;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nums;
int next(int index) {
// 直接返回当前索引处的值作为下一个索引
return nums[index];
}
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
this->nums = nums;
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
// 第一次相遇
do {
slow = next(slow);
fast = next(next(fast));
} while (slow != fast);
slow = 0;
// 第二次相遇
while (slow != fast) {
slow = next(slow);
fast = next(fast);
}
return slow;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 遍历链表使用 $O(N)$ 。
- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 使用常数复杂度的额外空间。