解法一:辅助栈法
本题难点在于括号内嵌套括号,需要从内向外生成与拼接字符串,这与栈的先入后出特性对应。
算法流程:
- 构建辅助栈
stack, 遍历字符串s中每个字符c;- 当
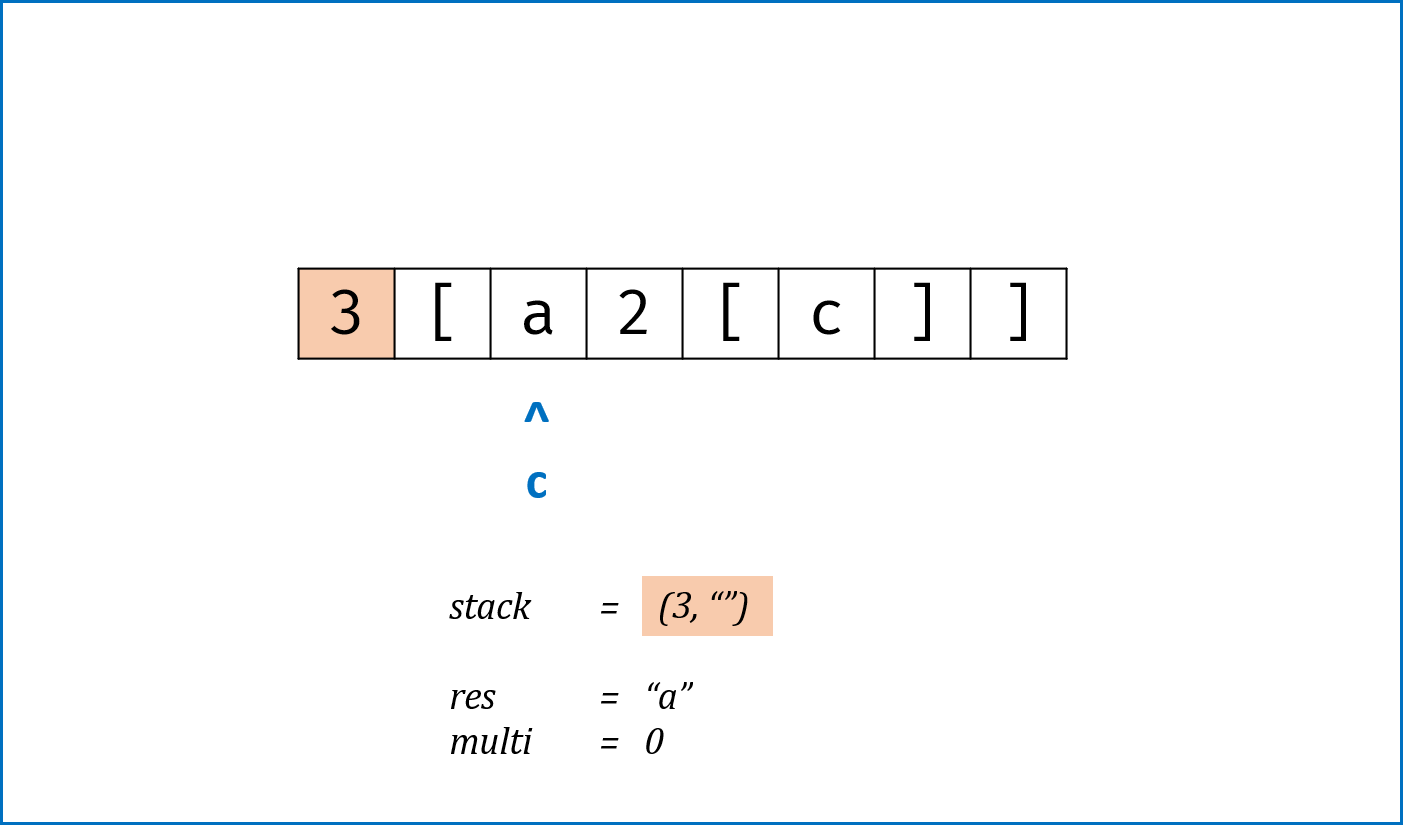
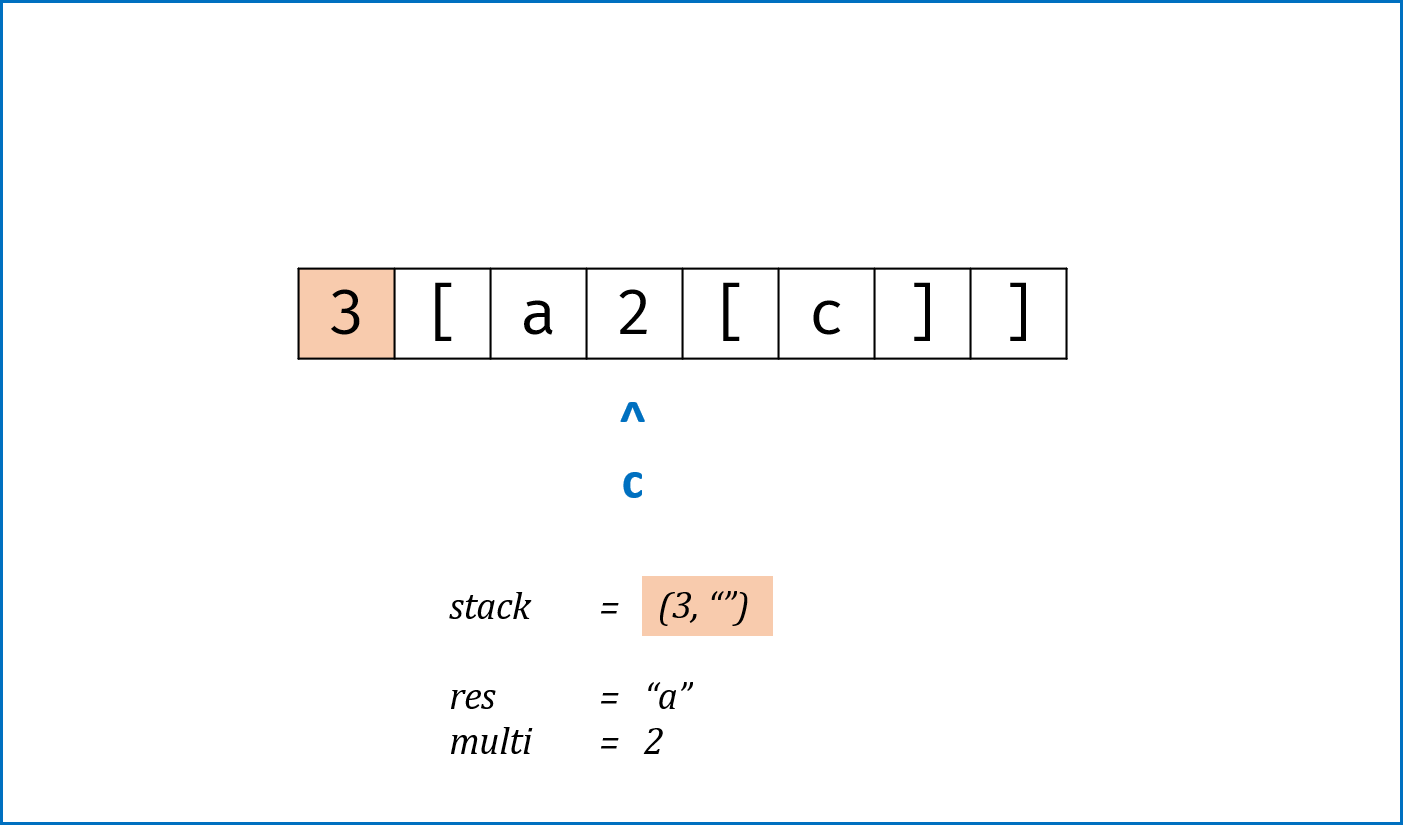
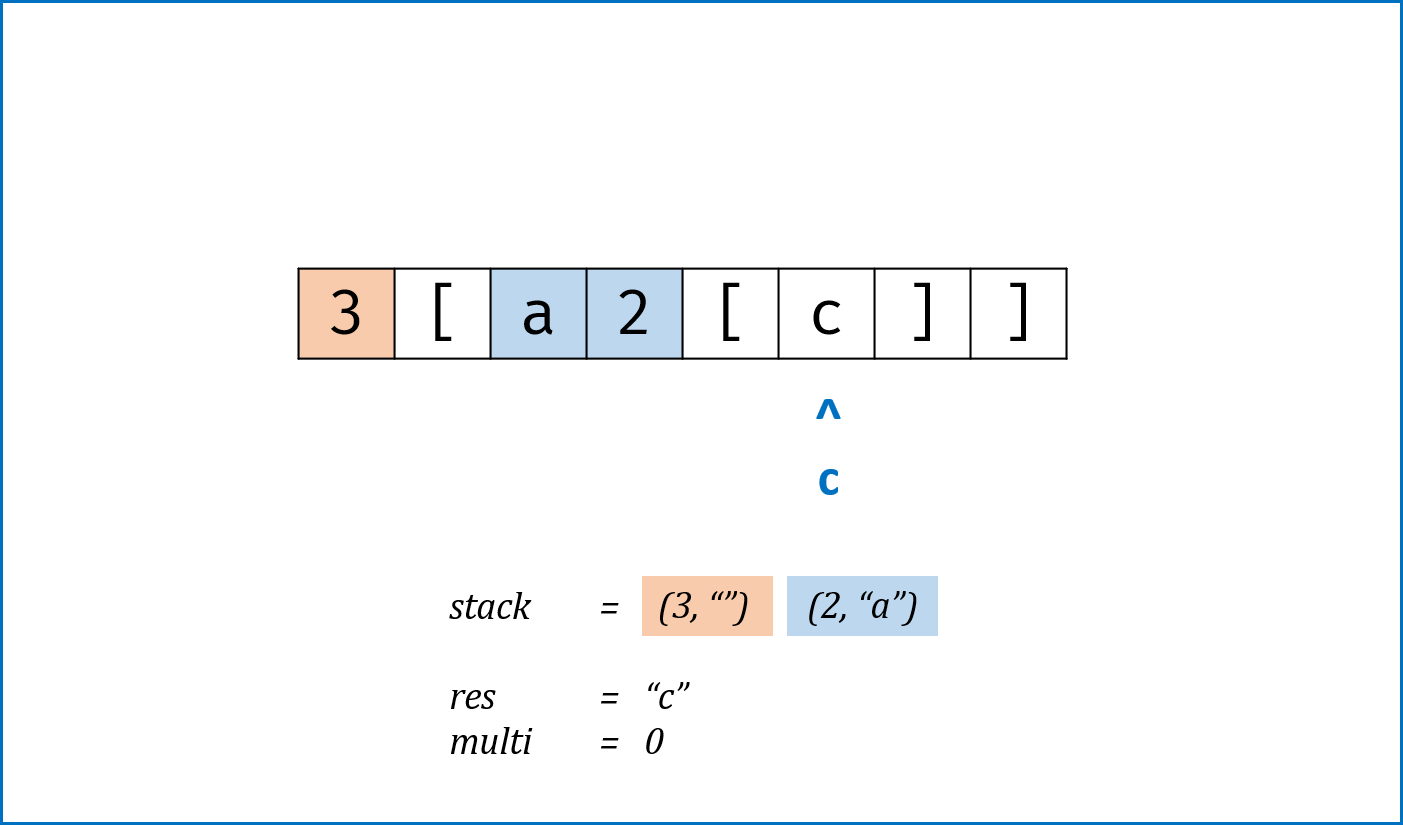
c为数字时,将数字字符转化为数字multi,用于后续倍数计算; - 当
c为字母时,在res尾部添加c; - 当
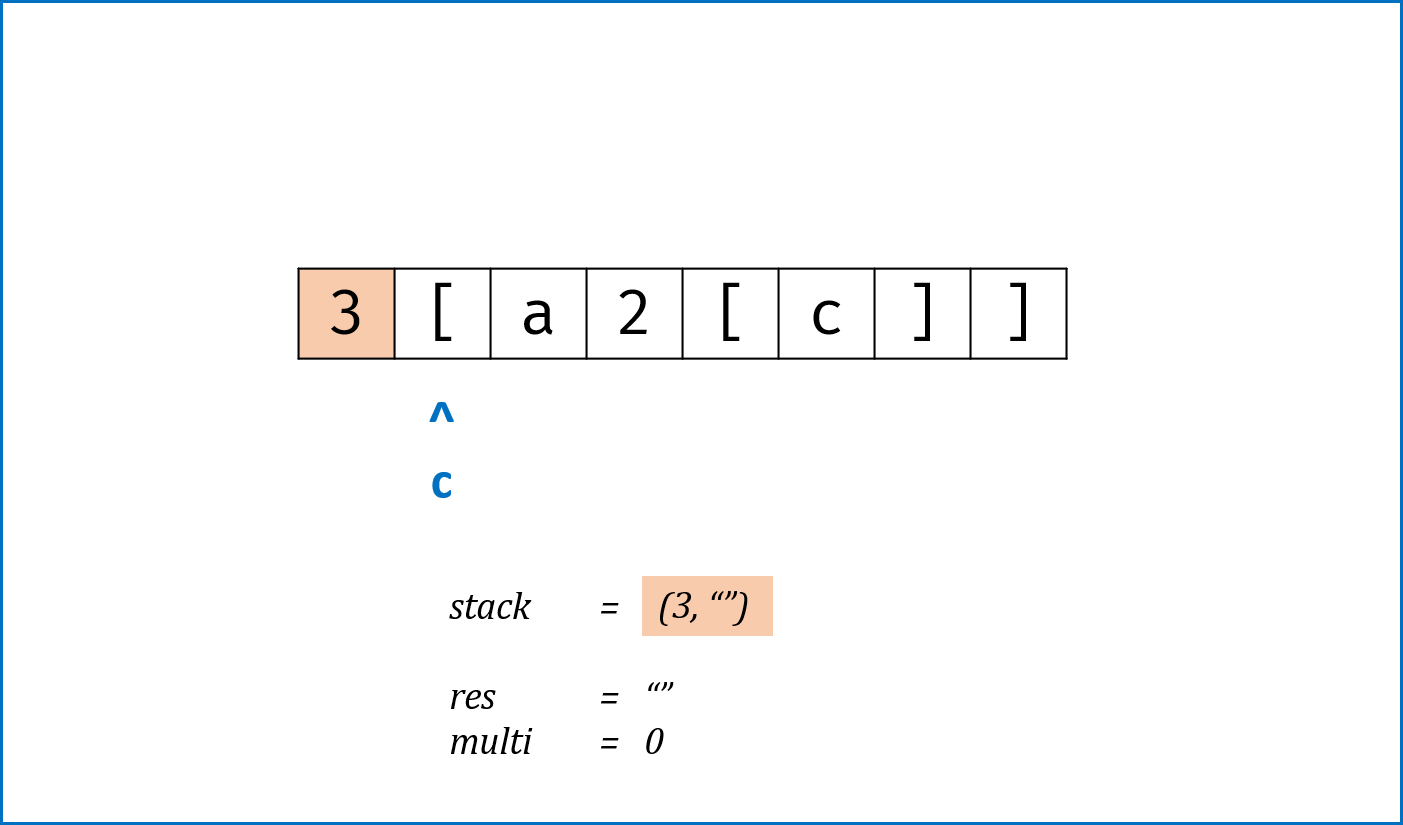
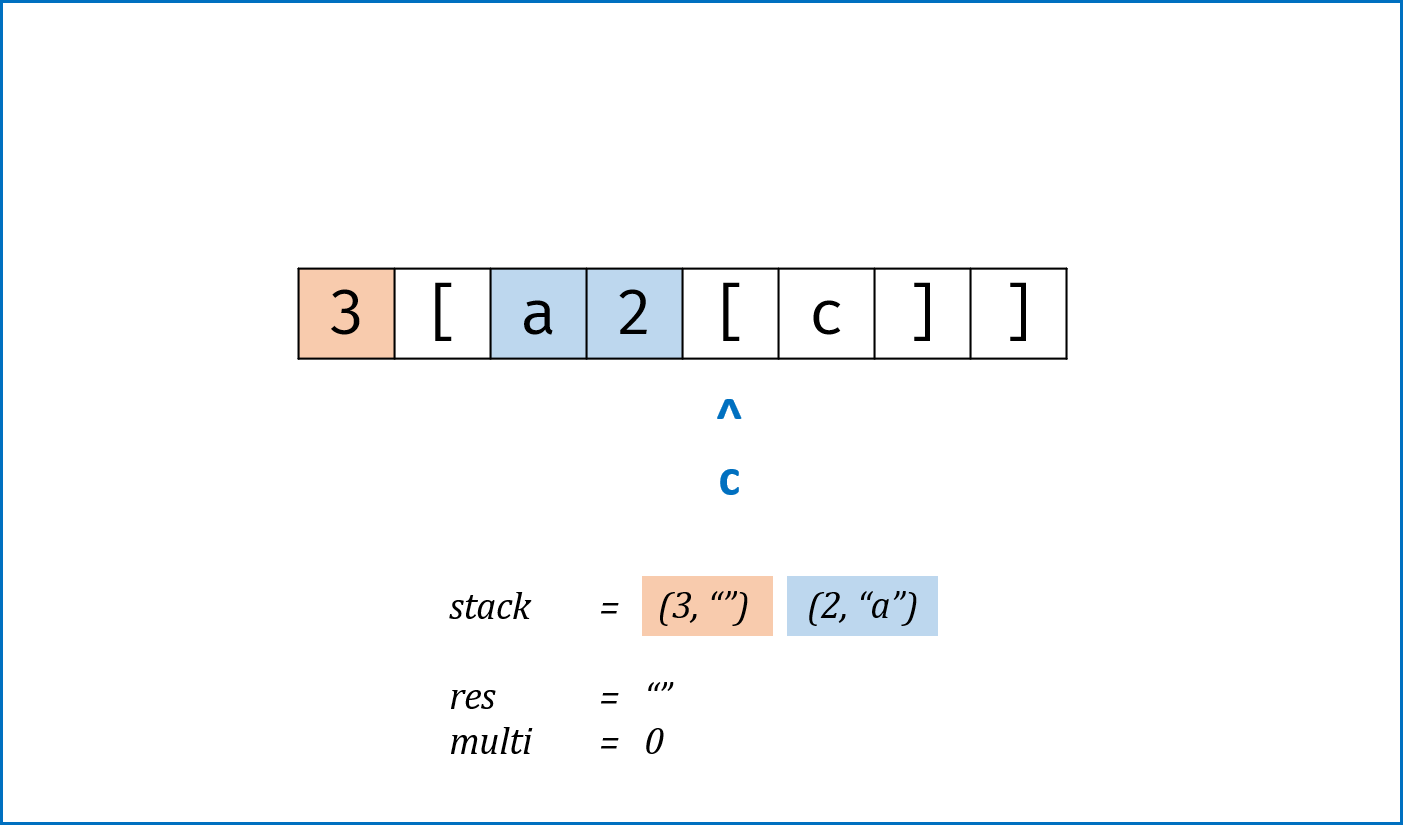
c为[时,将当前multi和res入栈,并分别置空置 $0$:- 记录此
[前的临时结果res至栈,用于发现对应]后的拼接操作; - 记录此
[前的倍数multi至栈,用于发现对应]后,获取multi × [...]字符串。 - 进入到新
[后,res和multi重新记录。
- 记录此
- 当
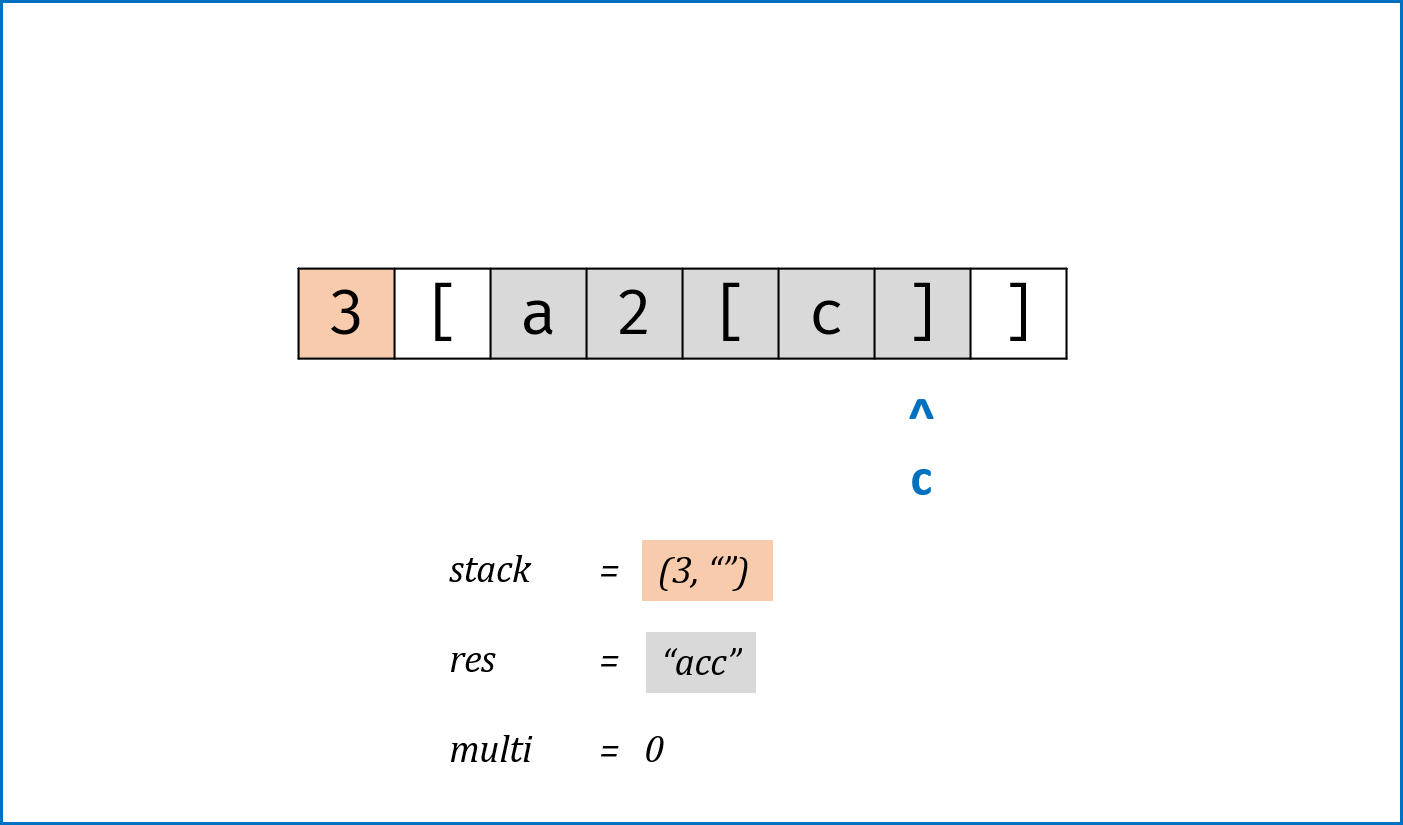
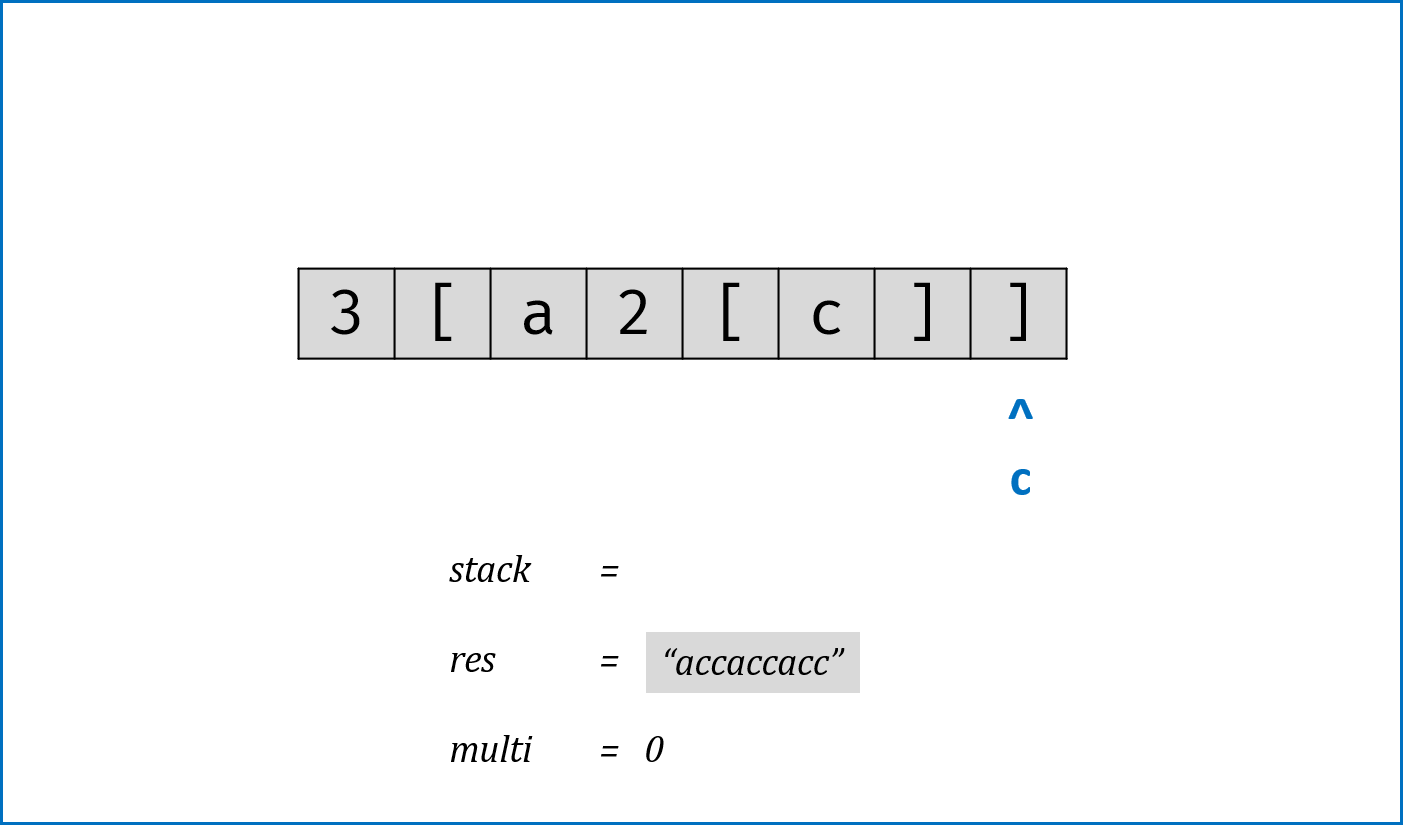
c为]时,stack出栈,拼接字符串res = last_res + cur_multi * res,其中:last_res是上个[到当前[的字符串,例如"3[a2[c]]"中的a;cur_multi是当前[到]内字符串的重复倍数,例如"3[a2[c]]"中的2。
- 当
- 返回字符串
res。
- 构建辅助栈
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$,一次遍历
s; - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$,辅助栈在极端情况下需要线性空间,例如
2[2[2[a]]]。
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$,一次遍历
<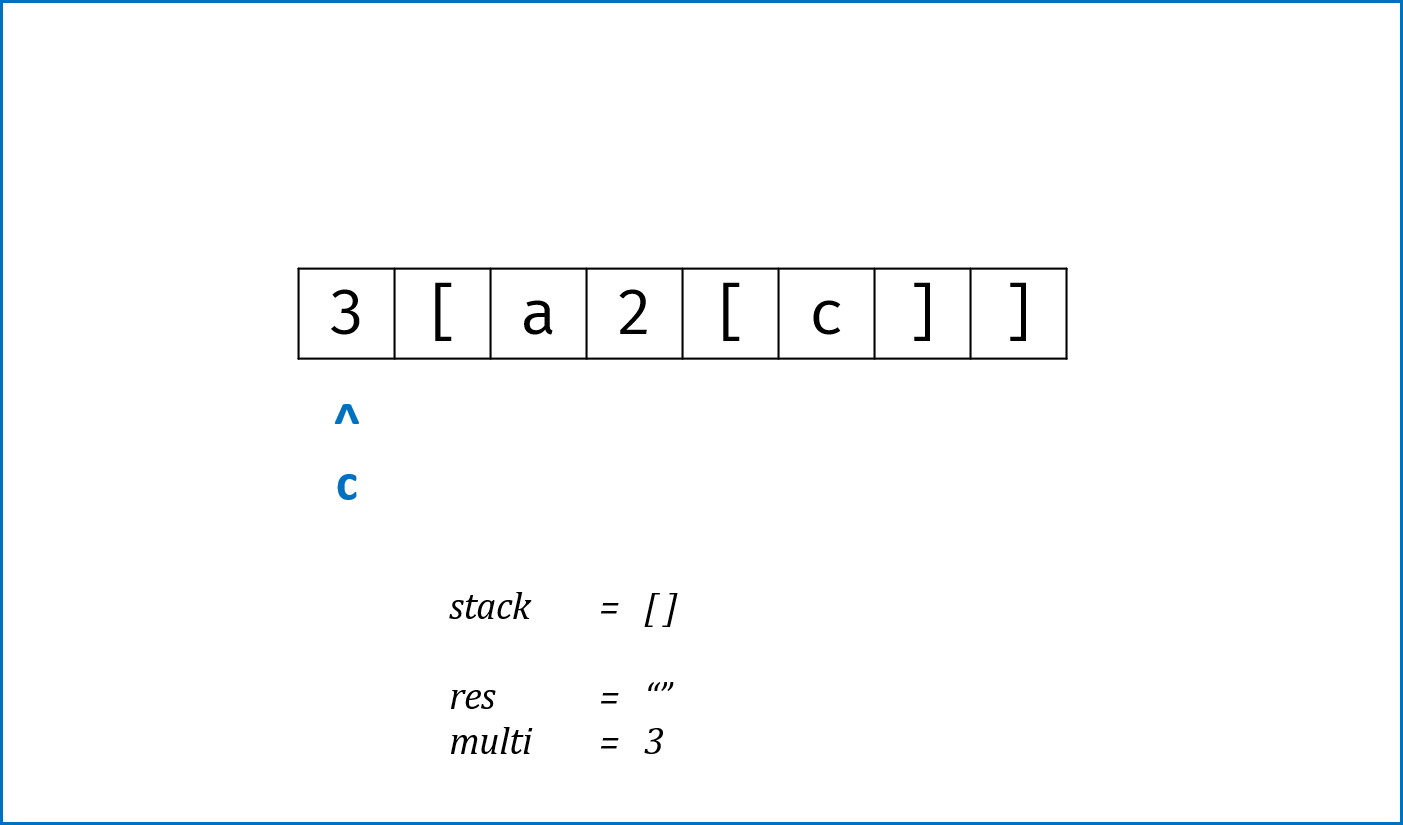 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
Python
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
stack, res, multi = [], "", 0
for c in s:
if c == '[':
stack.append([multi, res])
res, multi = "", 0
elif c == ']':
cur_multi, last_res = stack.pop()
res = last_res + cur_multi * res
elif '0' <= c <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(c)
else:
res += c
return resJava
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int multi = 0;
LinkedList<Integer> stack_multi = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<String> stack_res = new LinkedList<>();
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()) {
if(c == '[') {
stack_multi.addLast(multi);
stack_res.addLast(res.toString());
multi = 0;
res = new StringBuilder();
}
else if(c == ']') {
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
int cur_multi = stack_multi.removeLast();
for(int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) tmp.append(res);
res = new StringBuilder(stack_res.removeLast() + tmp);
}
else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') multi = multi * 10 + Integer.parseInt(c + "");
else res.append(c);
}
return res.toString();
}
}解法二:递归法
总体思路与辅助栈法一致,不同点在于将
[和]分别作为递归的开启与终止条件:- 当
s[i] == ']'时,返回当前括号内记录的res字符串与]的索引i(更新上层递归指针位置); - 当
s[i] == '['时,开启新一层递归,记录此[...]内字符串tmp和递归后的最新索引i,并执行res + multi * tmp拼接字符串。 - 遍历完毕后返回
res。
- 当
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$,递归会更新索引,因此实际上还是一次遍历
s; - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$,极端情况下递归深度将会达到线性级别。
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$,递归会更新索引,因此实际上还是一次遍历
Python
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
def dfs(s, i):
res, multi = "", 0
while i < len(s):
if '0' <= s[i] <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(s[i])
elif s[i] == '[':
i, tmp = dfs(s, i + 1)
res += multi * tmp
multi = 0
elif s[i] == ']':
return i, res
else:
res += s[i]
i += 1
return res
return dfs(s,0)Java
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
return dfs(s, 0)[0];
}
private String[] dfs(String s, int i) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int multi = 0;
while(i < s.length()) {
if(s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9')
multi = multi * 10 + Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
else if(s.charAt(i) == '[') {
String[] tmp = dfs(s, i + 1);
i = Integer.parseInt(tmp[0]);
while(multi > 0) {
res.append(tmp[1]);
multi--;
}
}
else if(s.charAt(i) == ']')
return new String[] { String.valueOf(i), res.toString() };
else
res.append(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
i++;
}
return new String[] { res.toString() };
}
}