解题思路:
股票买卖策略:
- 单独交易日: 设今天价格 $p_1$、明天价格 $p_2$,则今天买入、明天卖出可赚取金额 $p_2 - p_1$ (负值代表亏损)。
- 连续上涨交易日: 设此上涨交易日股票价格分别为 $p_1, p_2, ... , p_n$,则第一天买最后一天卖收益最大,即 $p_n - p_1$;等价于每天都买卖,即 $p_n - p_1=(p_2 - p_1)+(p_3 - p_2)+...+(p_n - p_{n-1})$。
- 连续下降交易日: 则不买卖收益最大,即不会亏钱。
算法流程:
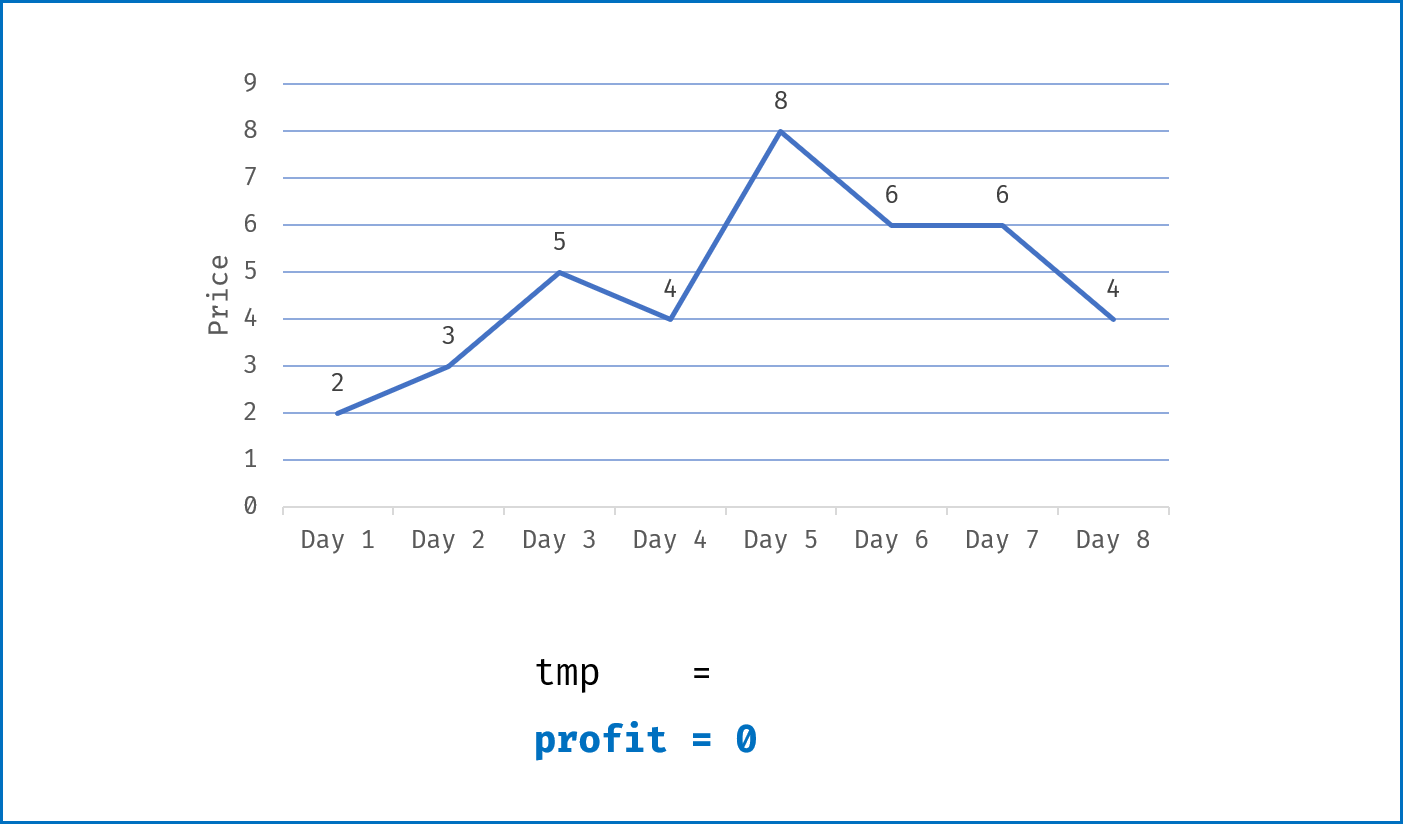
- 遍历整个股票交易日价格列表
price,策略是所有上涨交易日都买卖(赚到所有利润),所有下降交易日都不买卖(永不亏钱)。
- 设
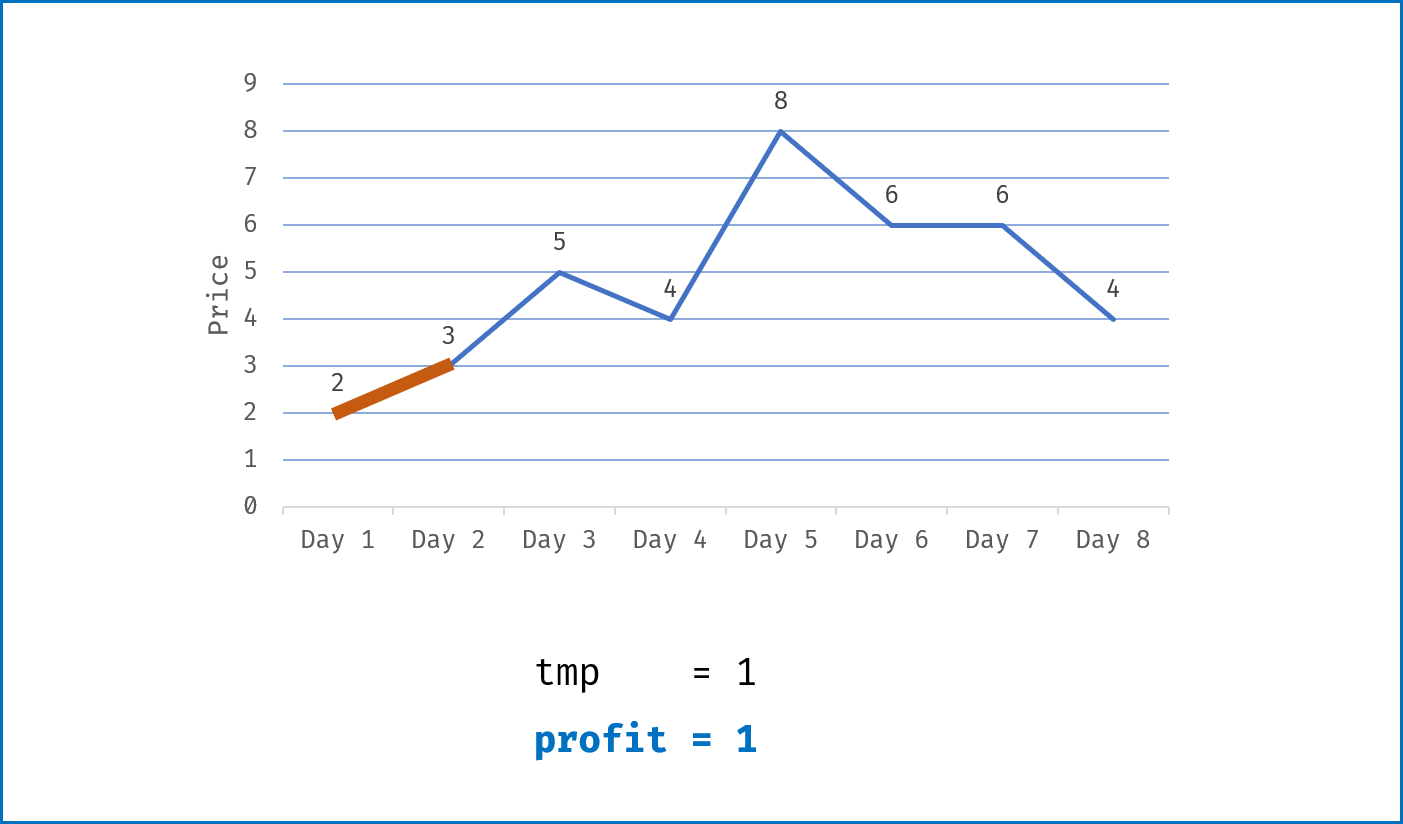
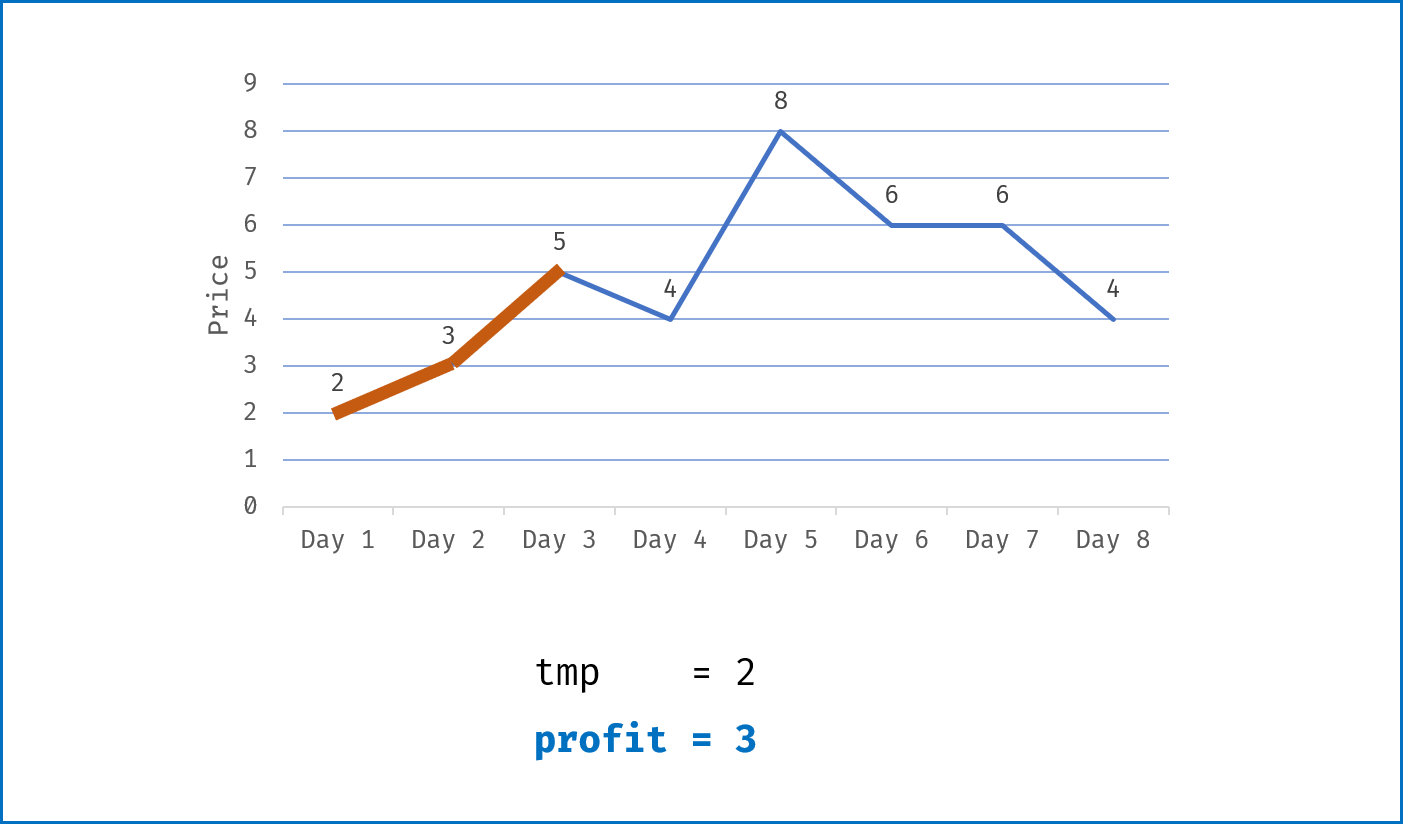
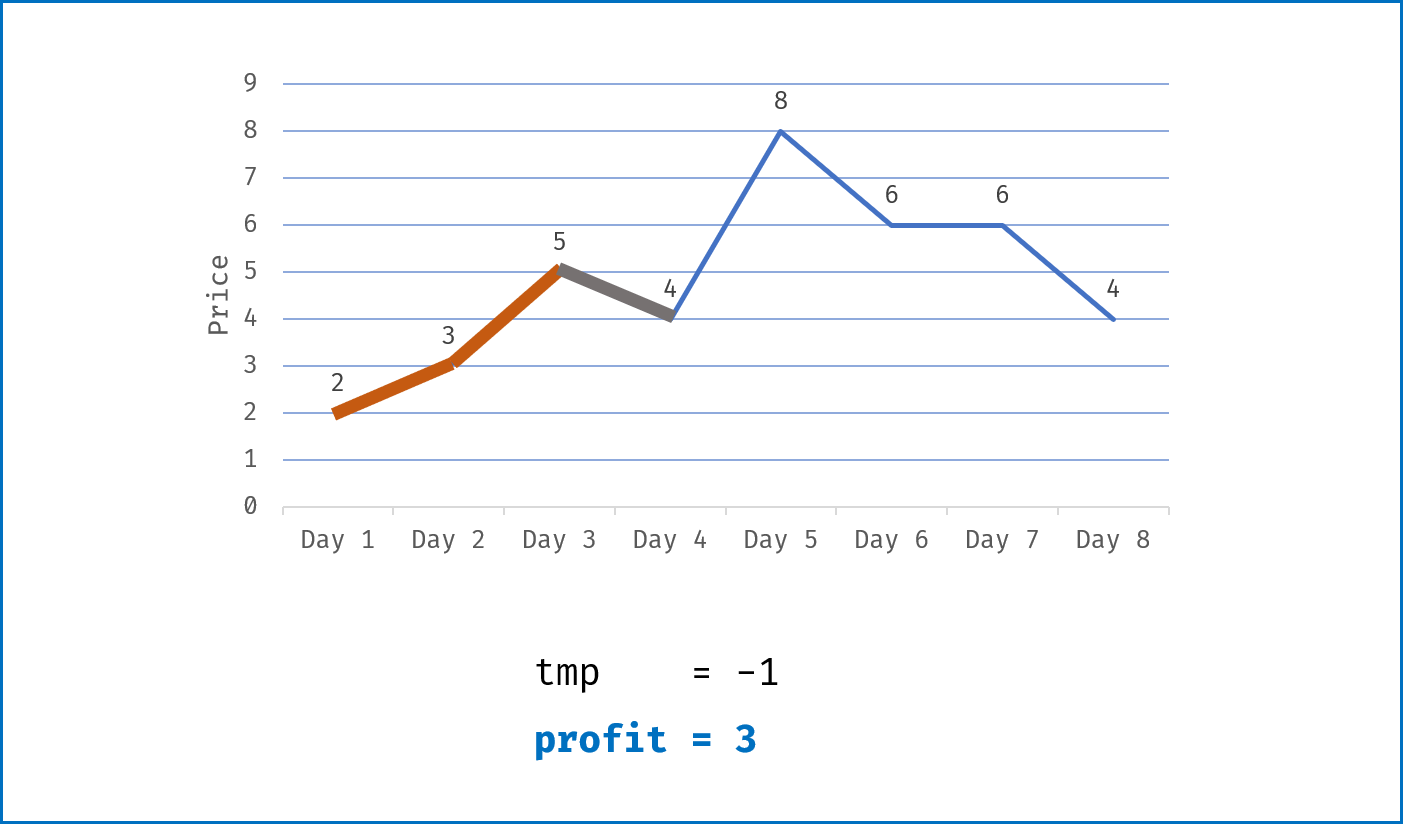
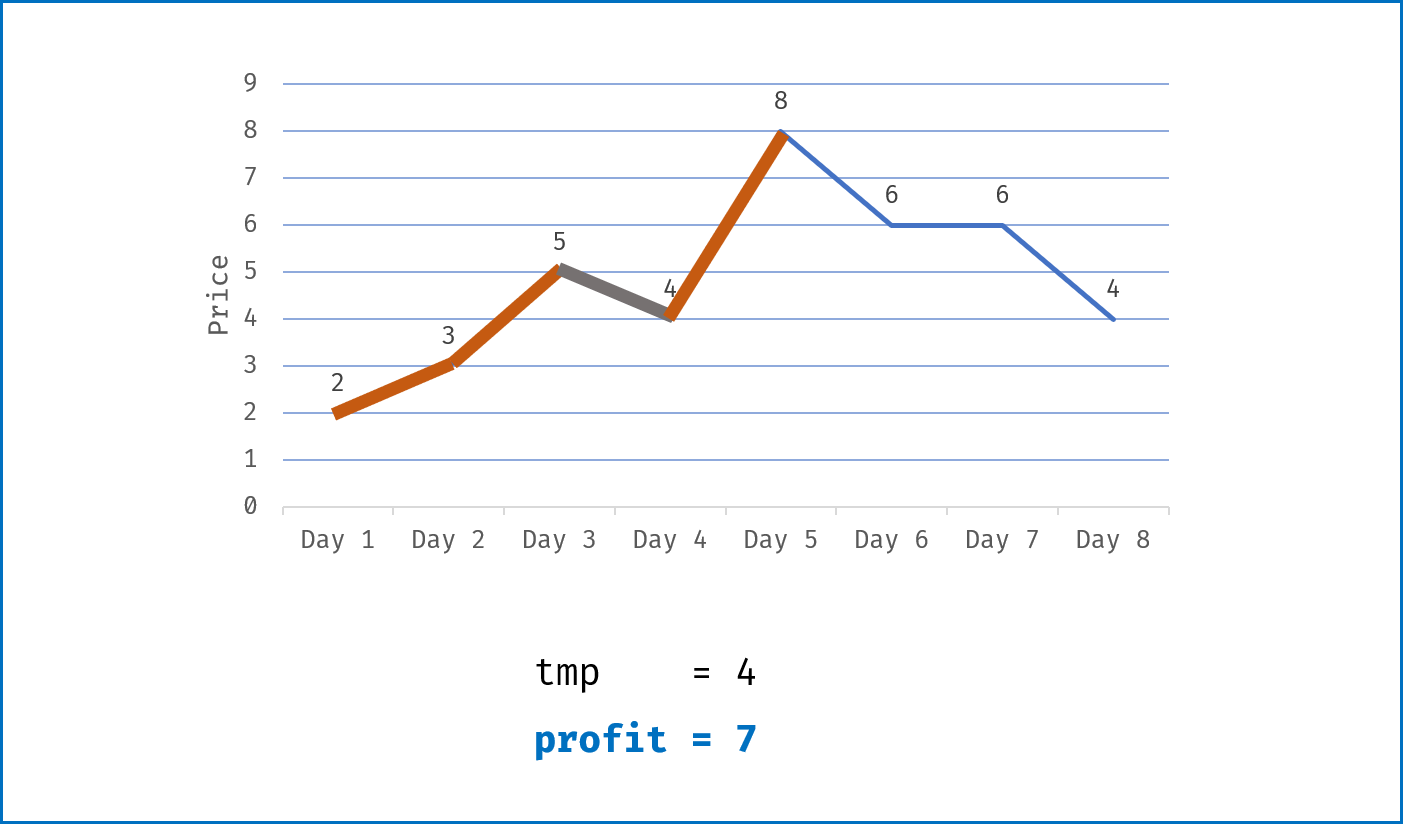
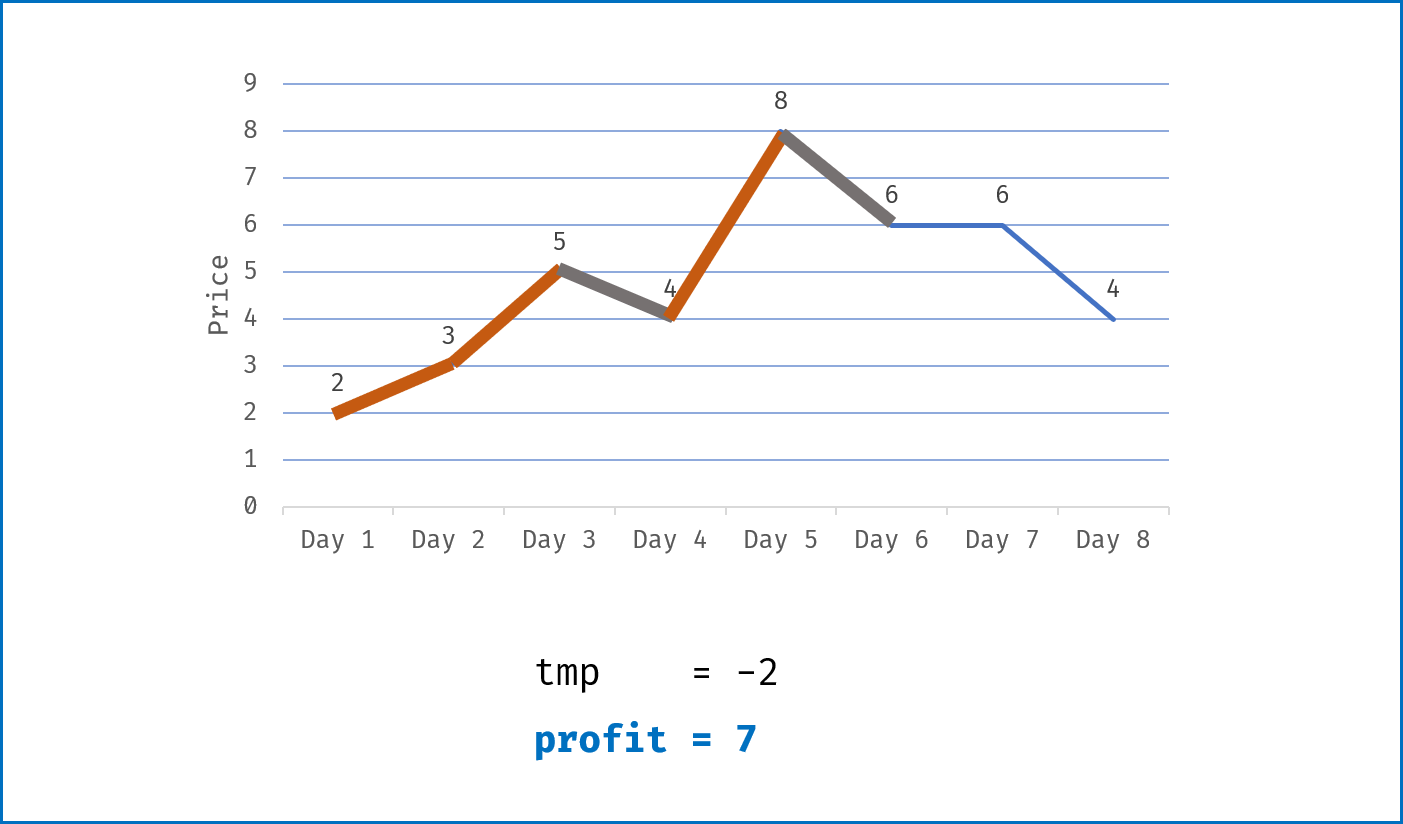
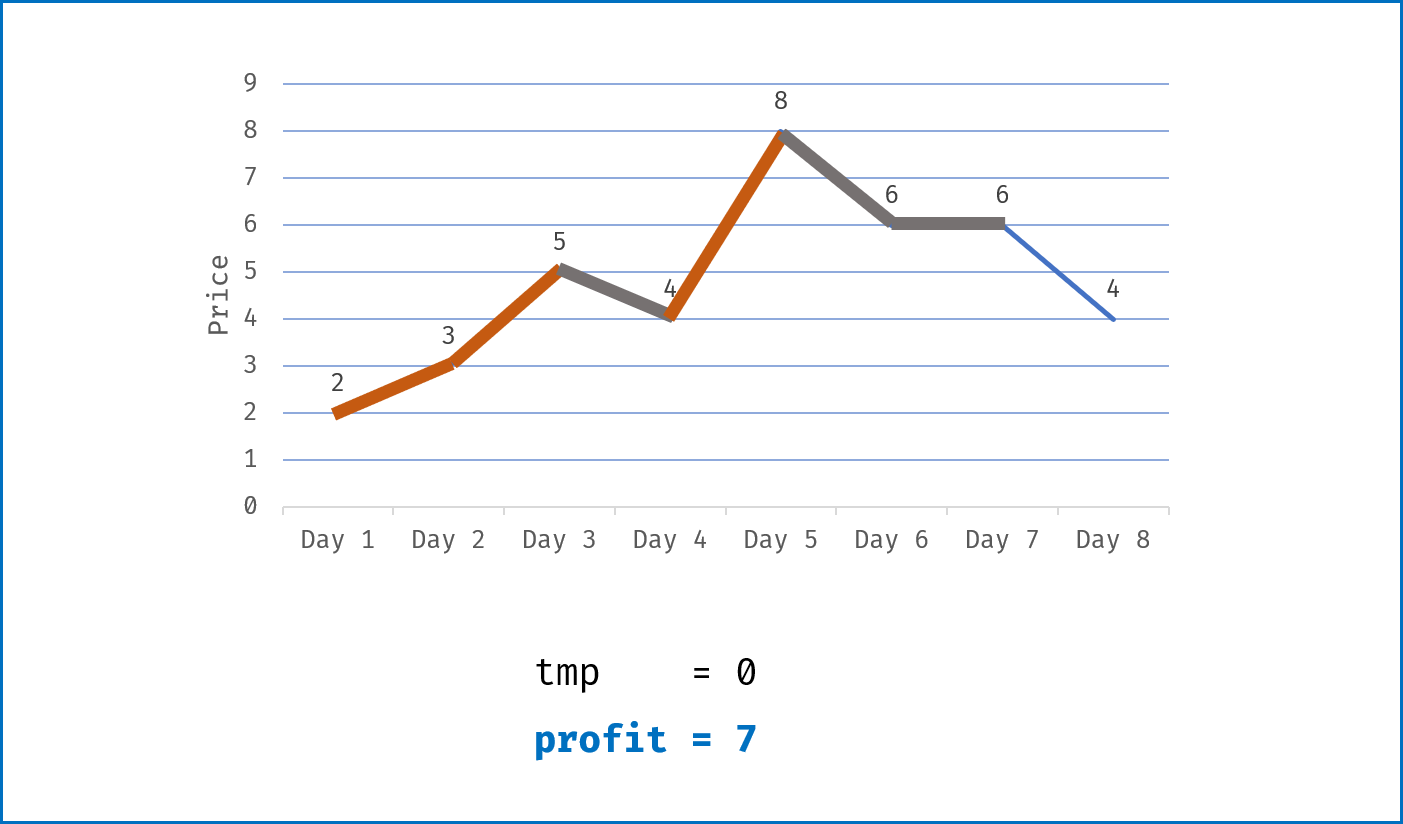
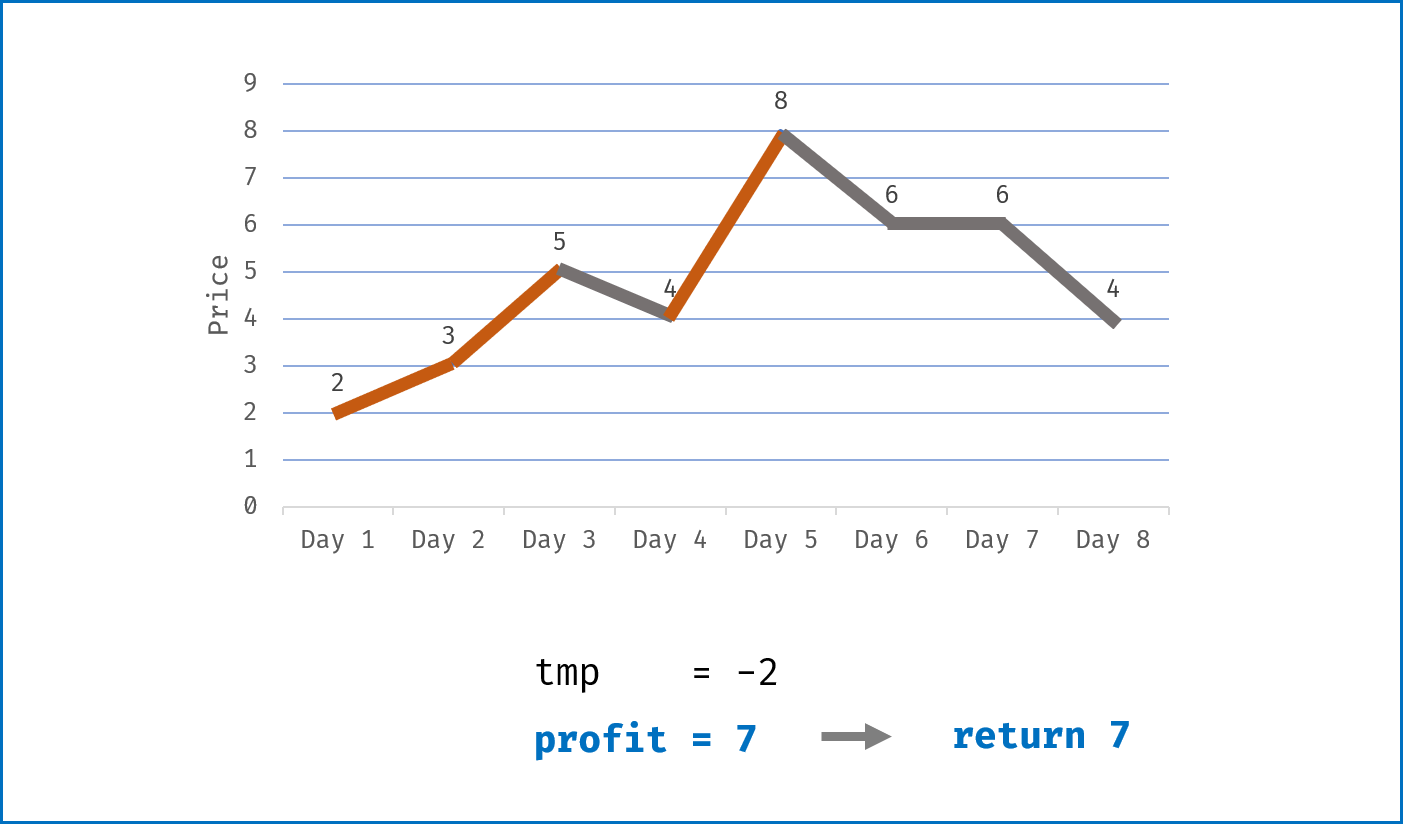
tmp为第i-1日买入与第i日卖出赚取的利润,即tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1]; - 当该天利润为正
tmp > 0,则将利润加入总利润profit;当利润为 $0$ 或为负,则直接跳过; - 遍历完成后,返回总利润
profit。
- 遍历整个股票交易日价格列表
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 只需遍历一次
price; - 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : 变量使用常数额外空间。
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 只需遍历一次
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
profit = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1]
if tmp > 0: profit += tmp
return profitJava
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
if (tmp > 0) profit += tmp;
}
return profit;
}
}