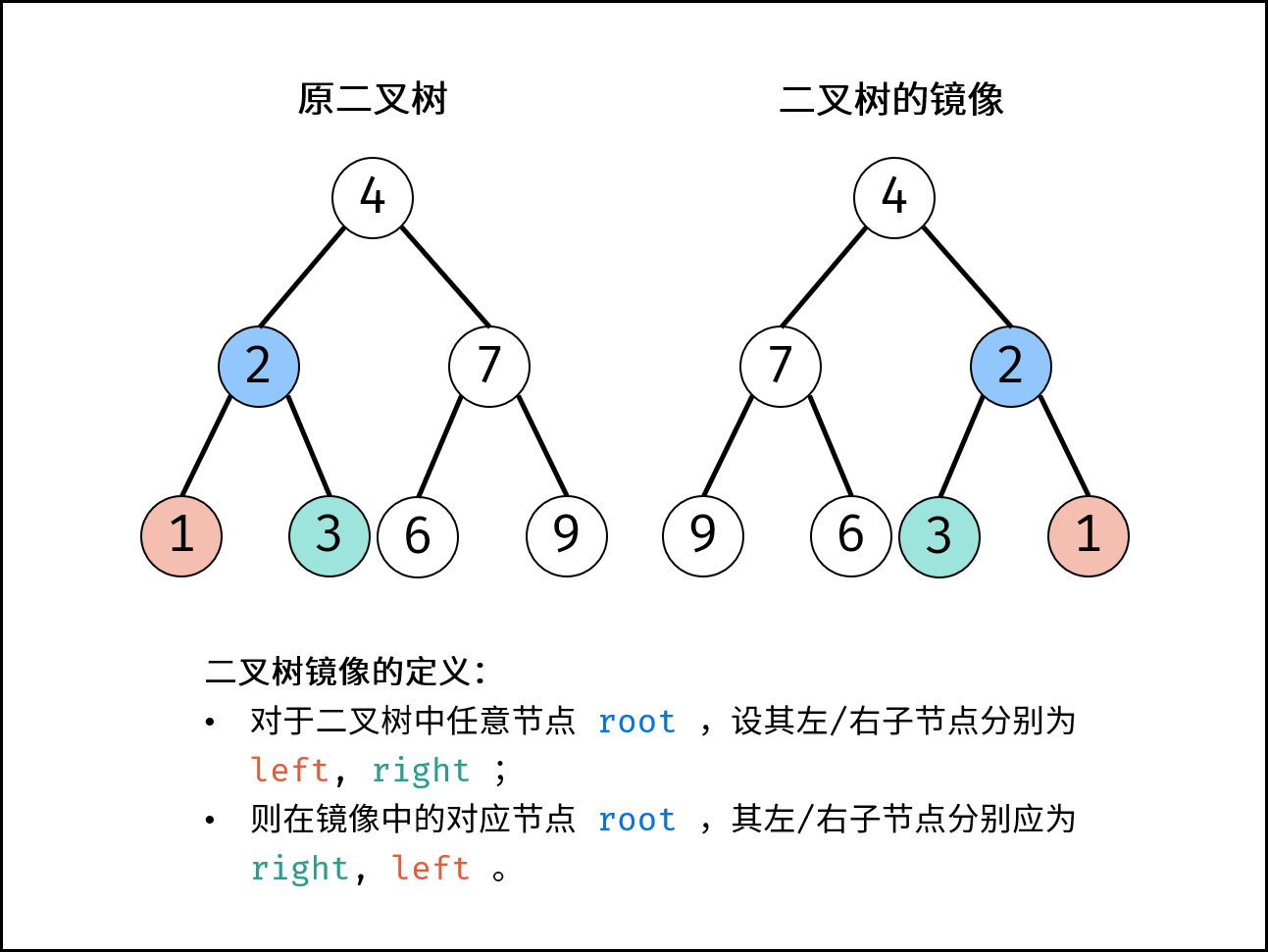
解题思路:
二叉树镜像定义: 对于二叉树中任意节点 $root$ ,设其左 / 右子节点分别为 $left, right$ ;则在二叉树的镜像中的对应 $root$ 节点,其左 / 右子节点分别为 $right, left$ 。
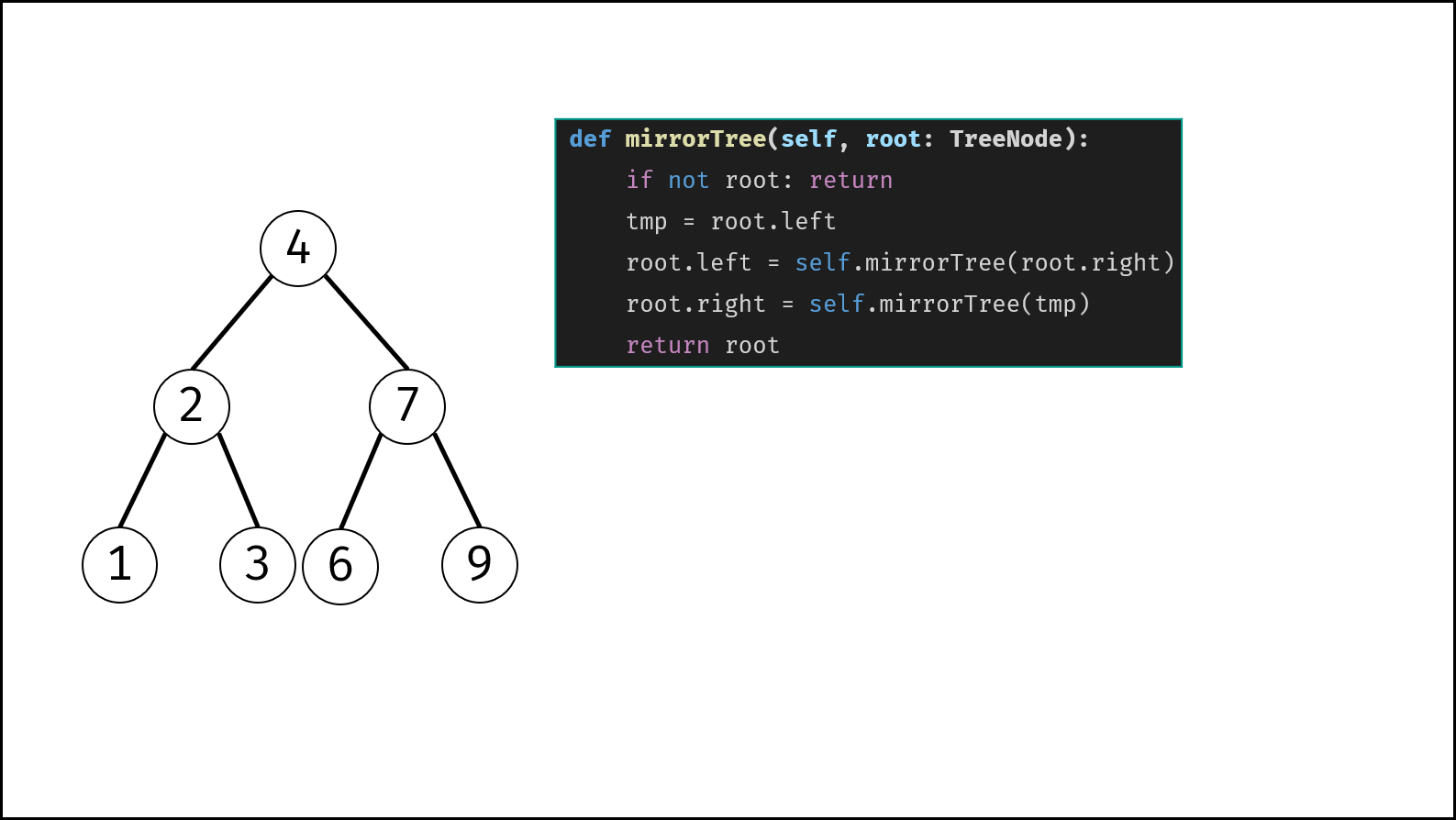
方法一:递归法
根据二叉树镜像的定义,考虑递归遍历(dfs)二叉树,交换每个节点的左 / 右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像。
递归解析:
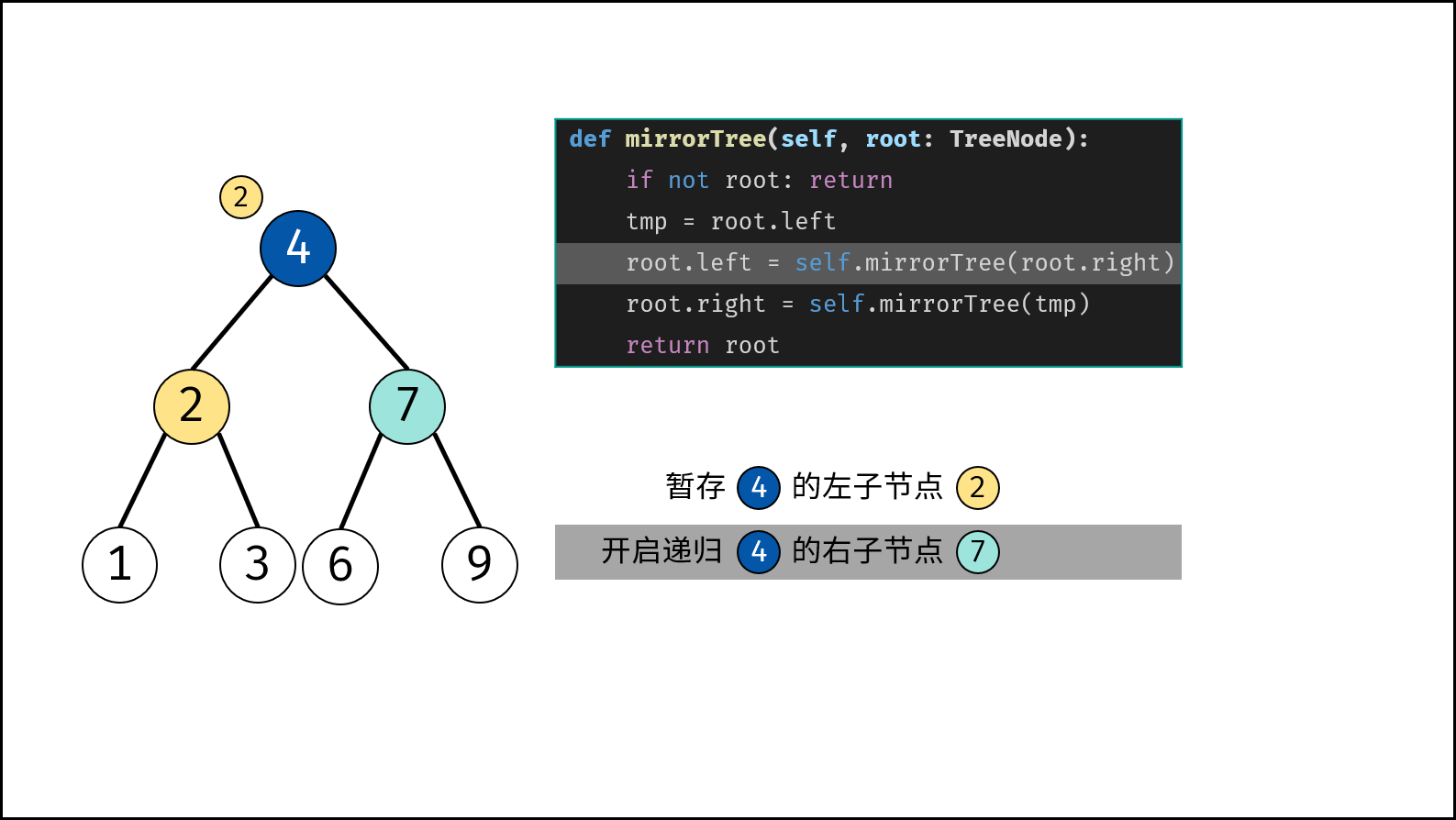
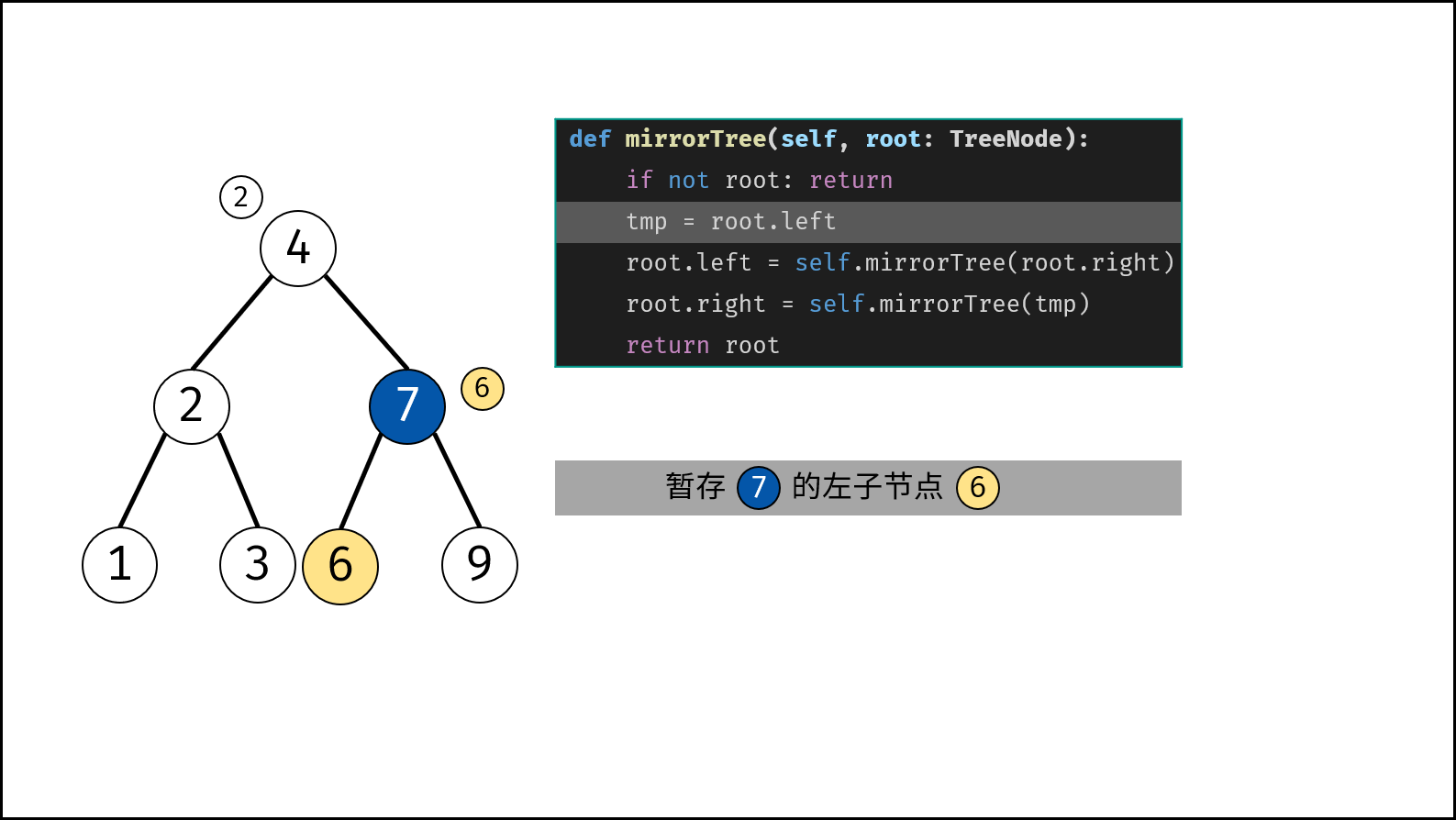
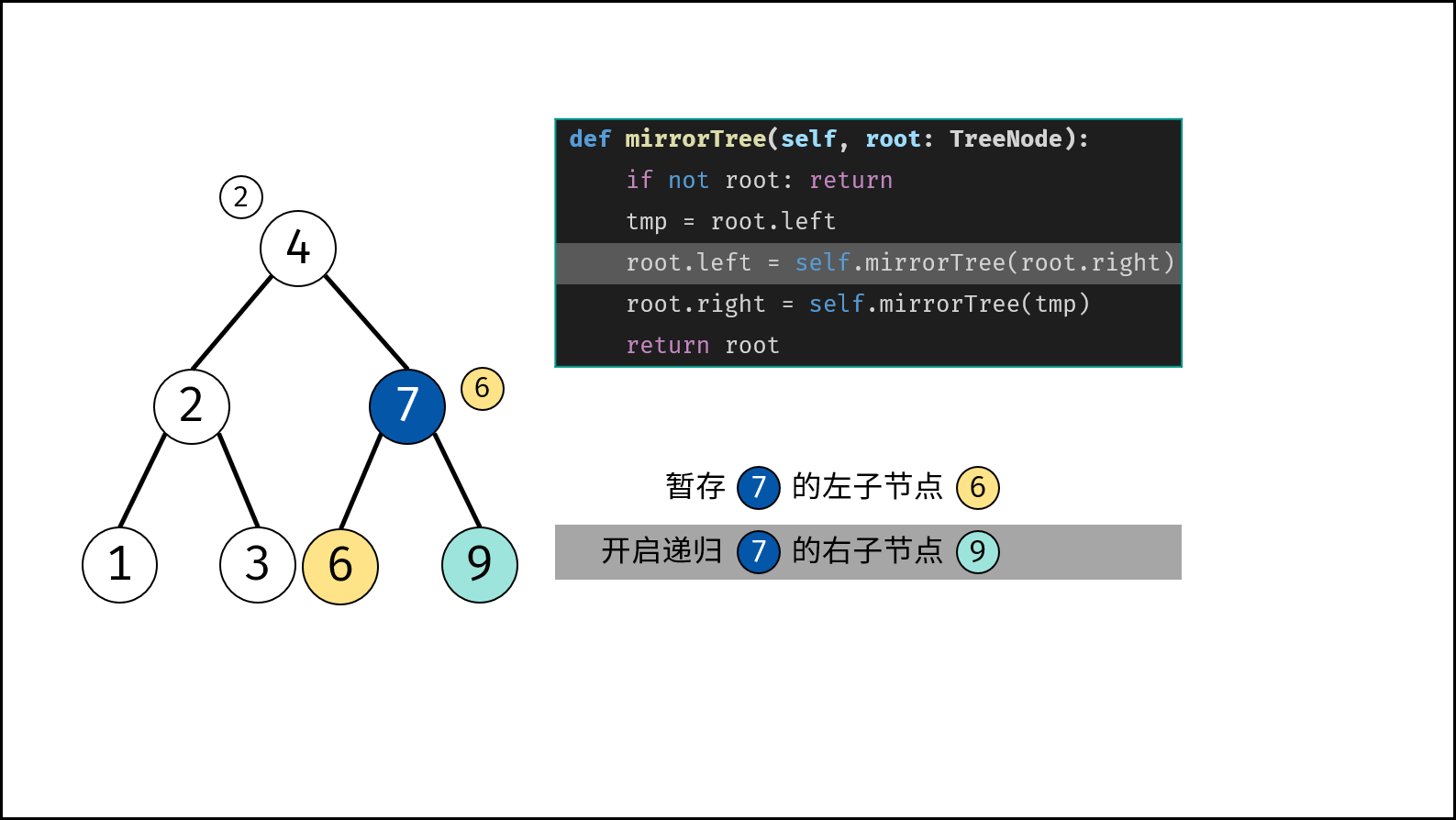
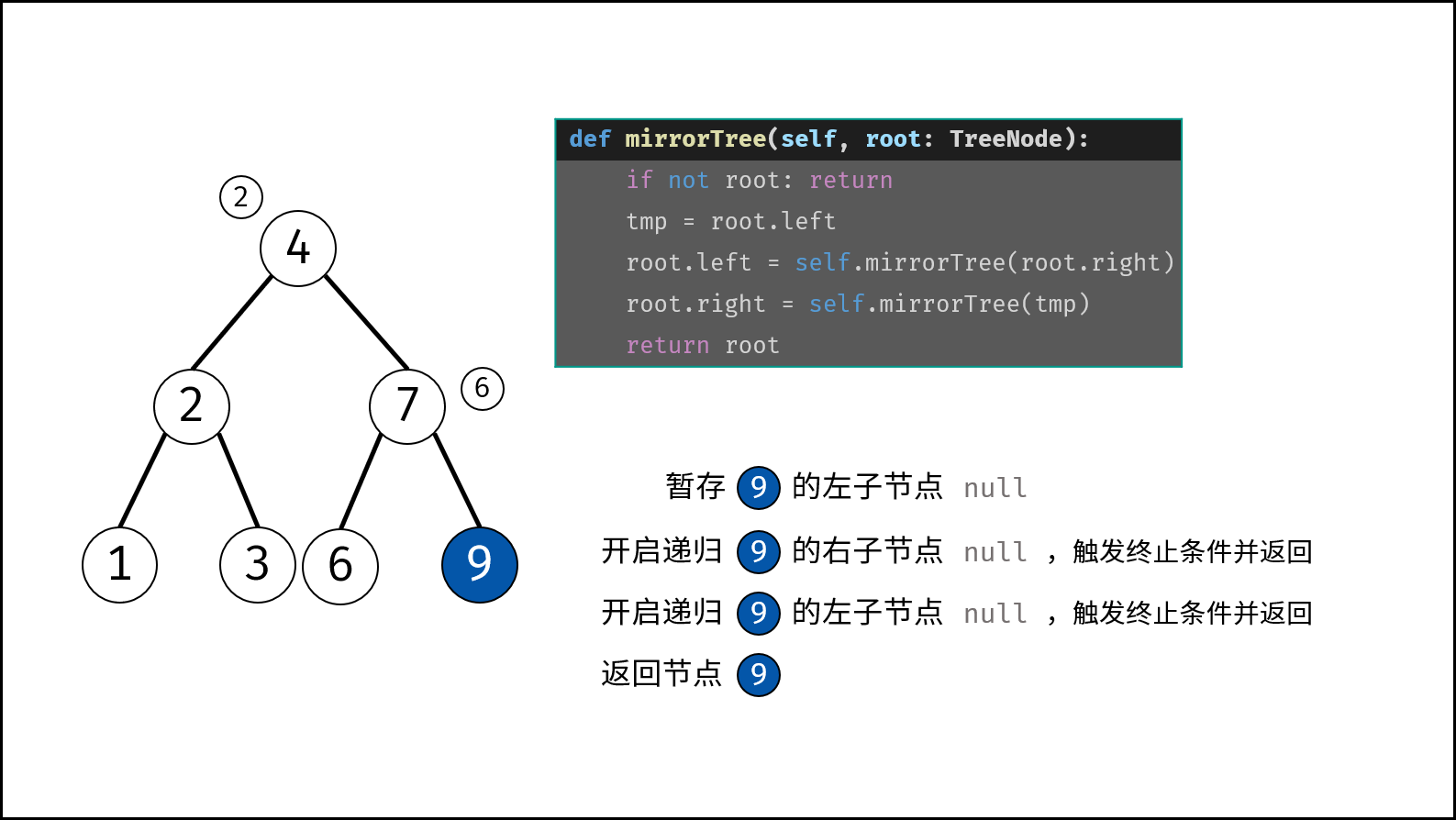
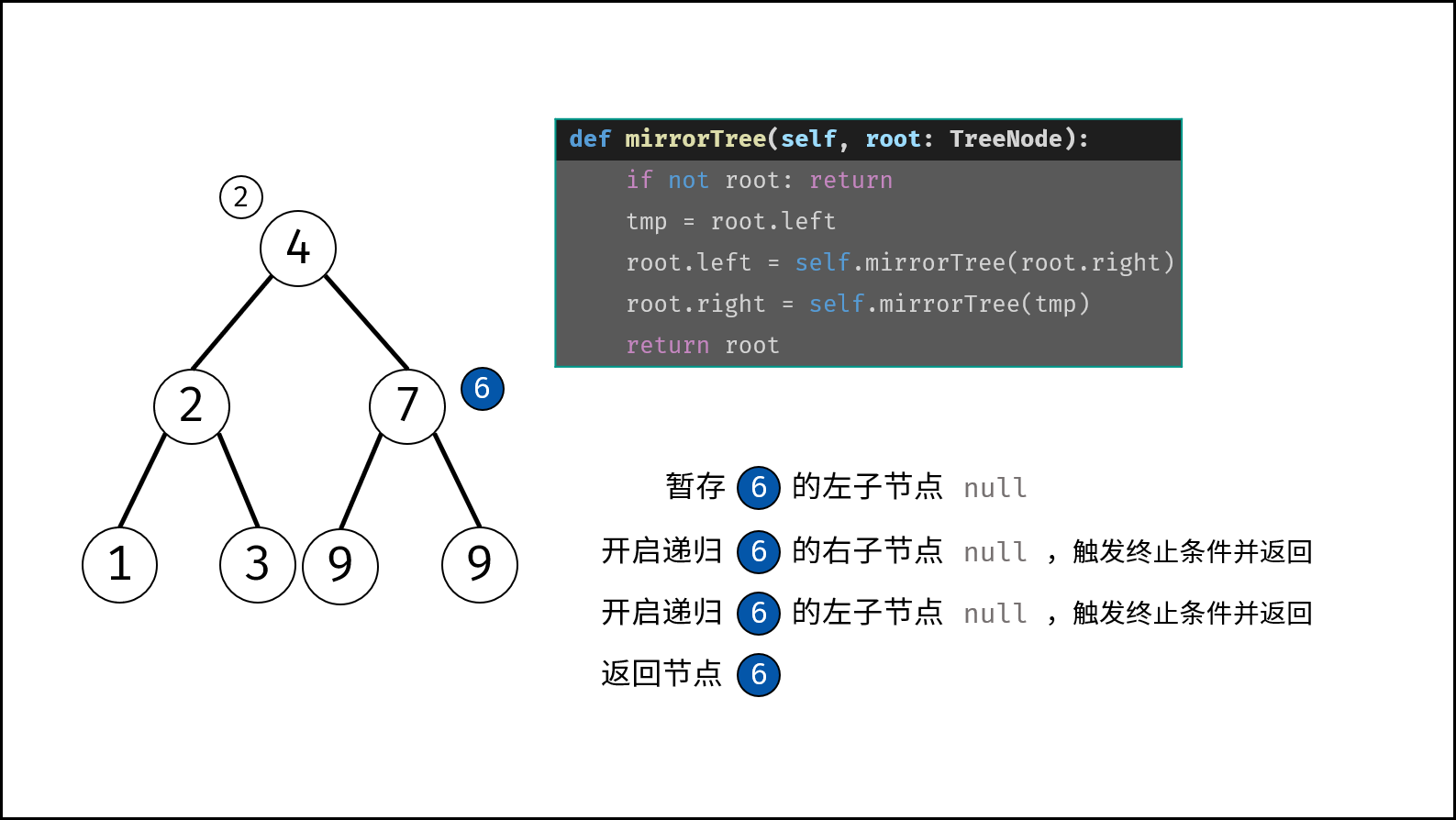
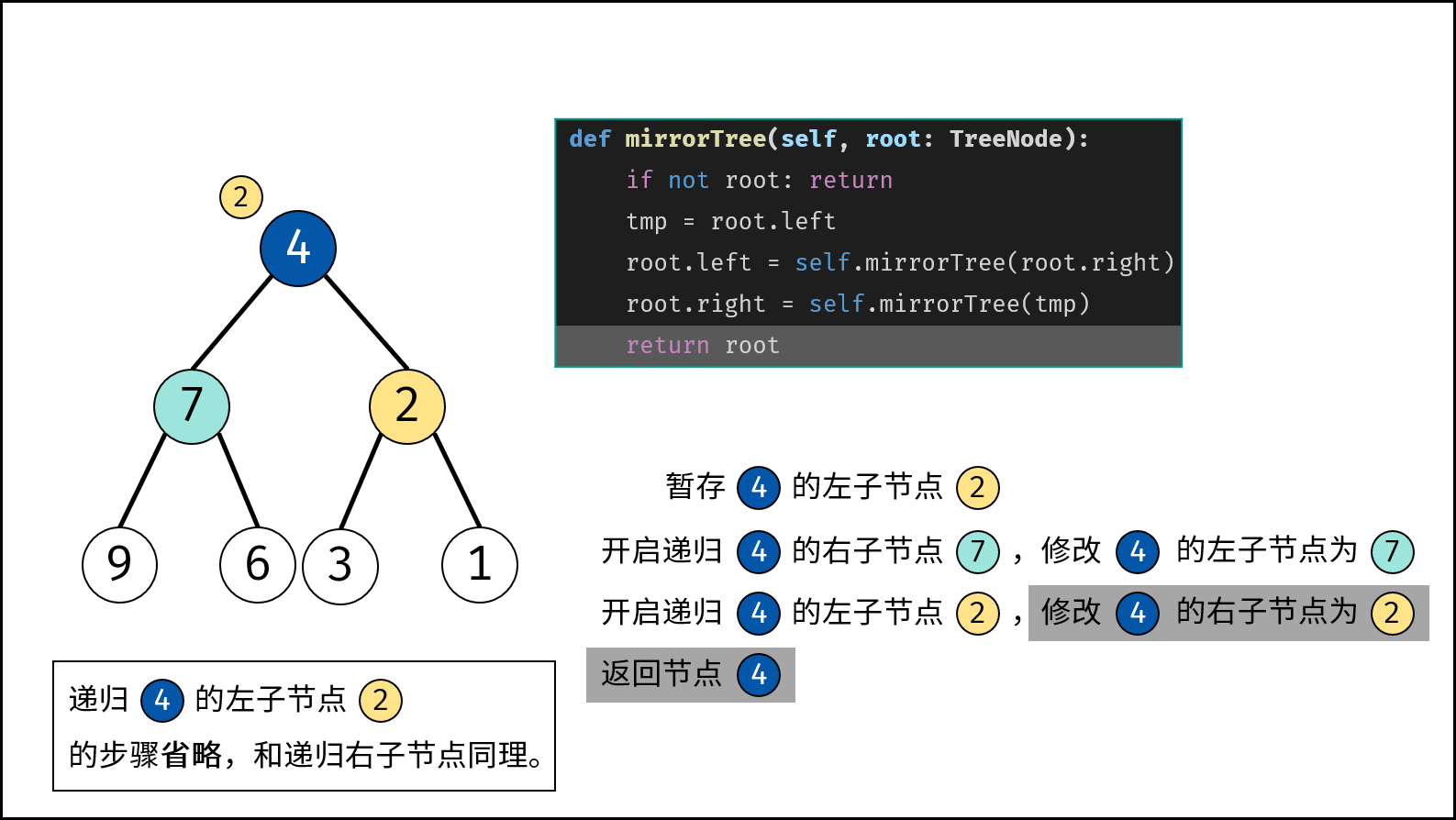
- 终止条件: 当节点 $root$ 为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 $null$ 。
- 递推工作:
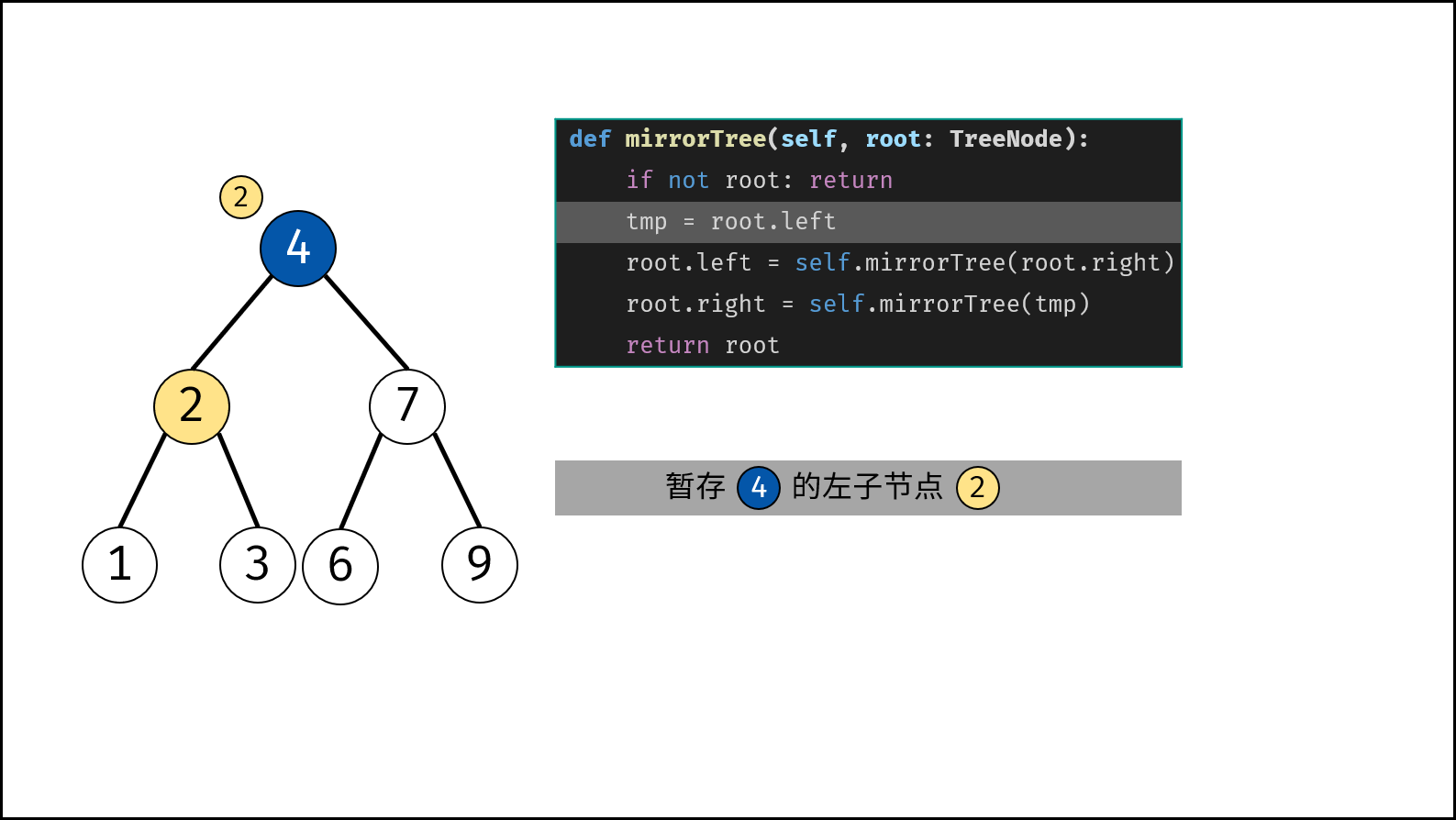
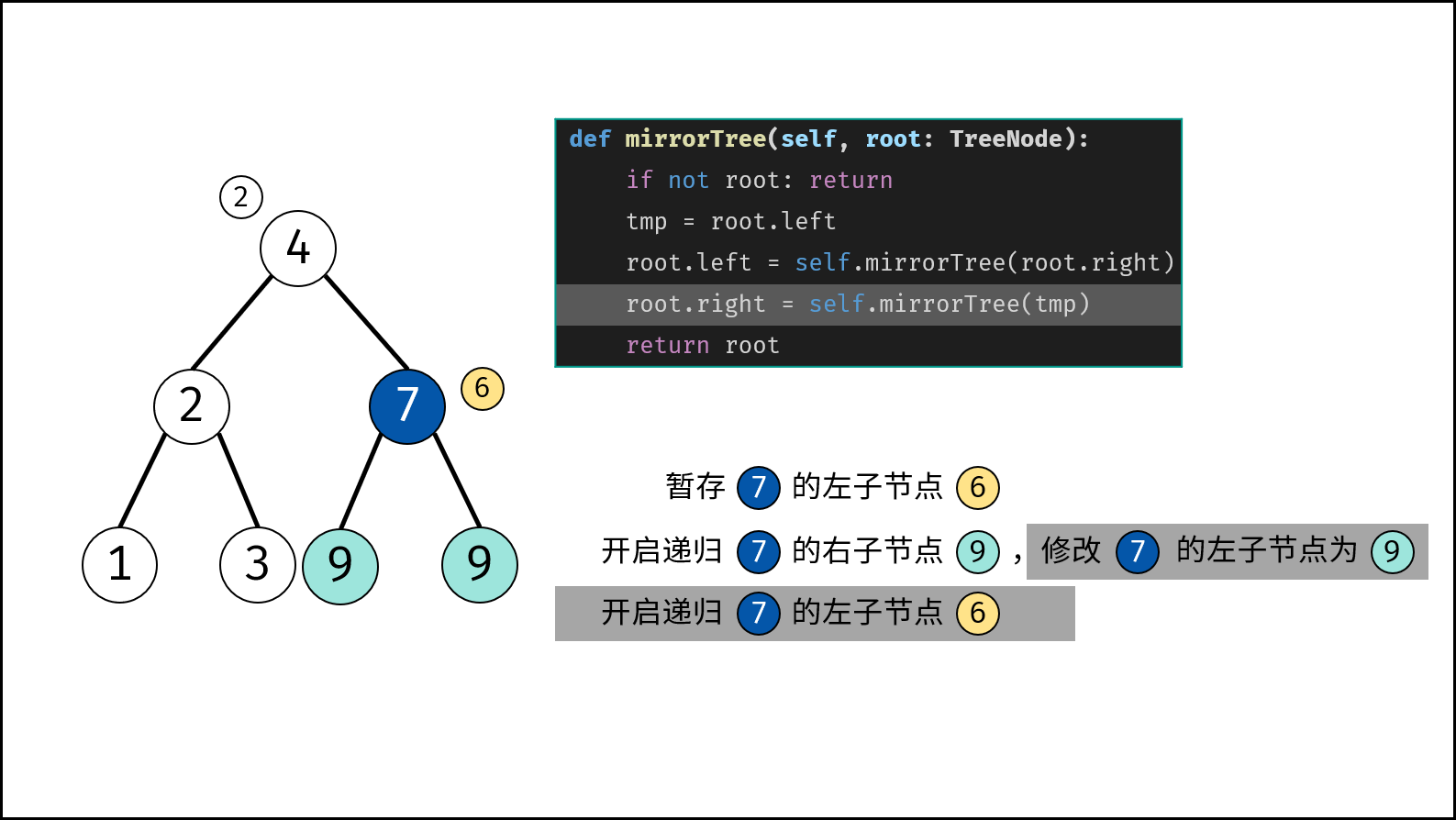
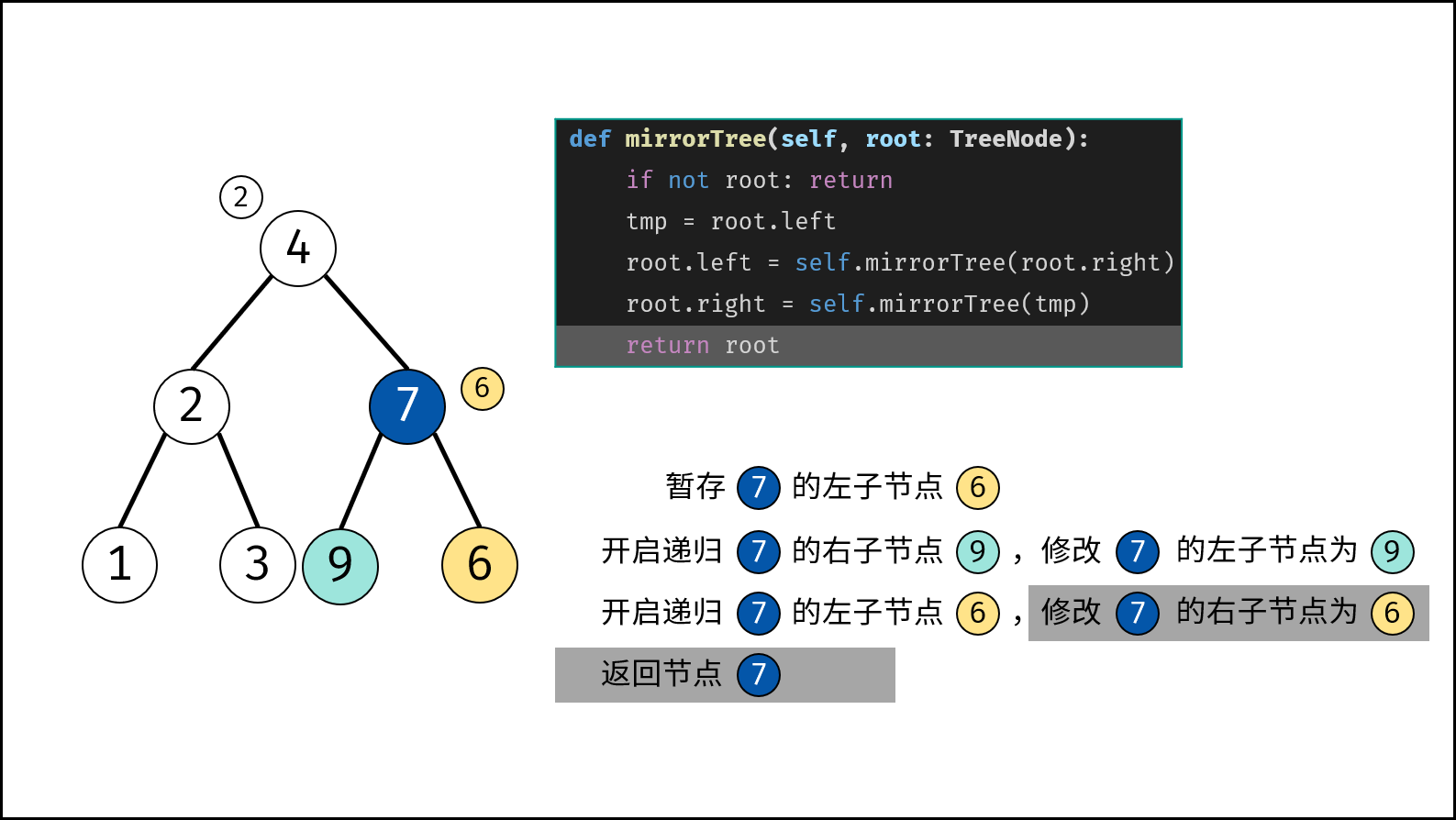
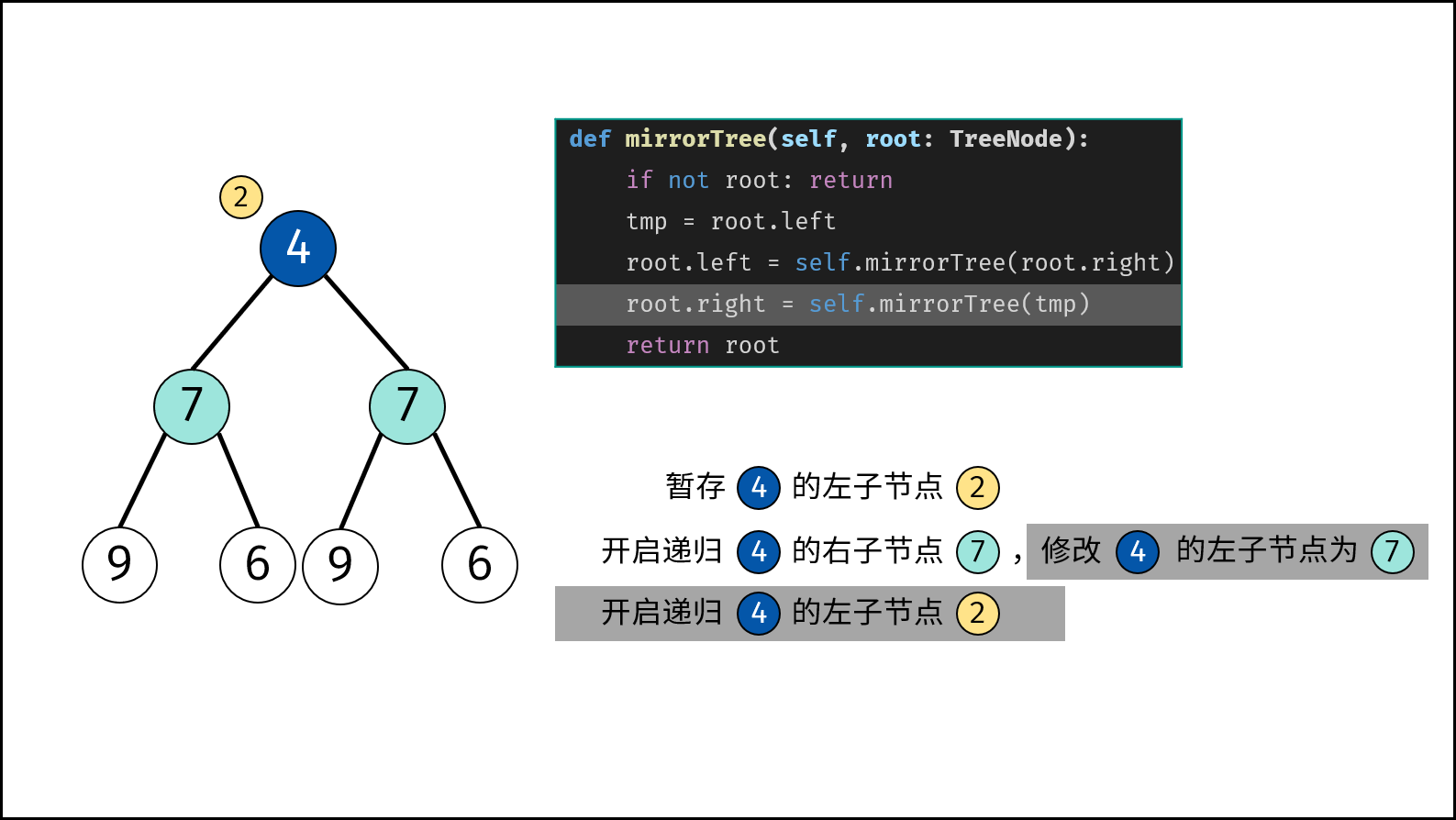
- 初始化节点 $tmp$ ,用于暂存 $root$ 的左子节点。
- 开启递归 右子节点 $invertTree(root.right)$ ,并将返回值作为 $root$ 的 左子节点 。
- 开启递归 左子节点 $invertTree(tmp)$ ,并将返回值作为 $root$ 的 右子节点 。
- 返回值: 返回当前节点 $root$ 。
Q: 为何需要暂存 $root$ 的左子节点? A: 在递归右子节点 “$root.left = invertTree(root.right);$” 执行完毕后, $root.left$ 的值已经发生改变,此时递归左子节点 $invertTree(root.left)$ 则会出问题。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python 利用平行赋值的写法(即 $a, b = b, a$ ),可省略暂存操作。其原理是先将等号右侧打包成元组 $(b,a)$ ,再序列地分给等号左侧的 $a, b$ 序列。
Python
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root: return
tmp = root.left
root.left = self.invertTree(root.right)
root.right = self.invertTree(tmp)
return rootPython
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root: return
root.left, root.right = self.invertTree(root.right), self.invertTree(root.left)
return rootJava
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = invertTree(root.right);
root.right = invertTree(tmp);
return root;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
root->left = invertTree(root->right);
root->right = invertTree(tmp);
return root;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为二叉树的节点数量,建立二叉树镜像需要遍历树的所有节点,占用 $O(N)$ 时间。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下(当二叉树退化为链表),递归时系统需使用 $O(N)$ 大小的栈空间。
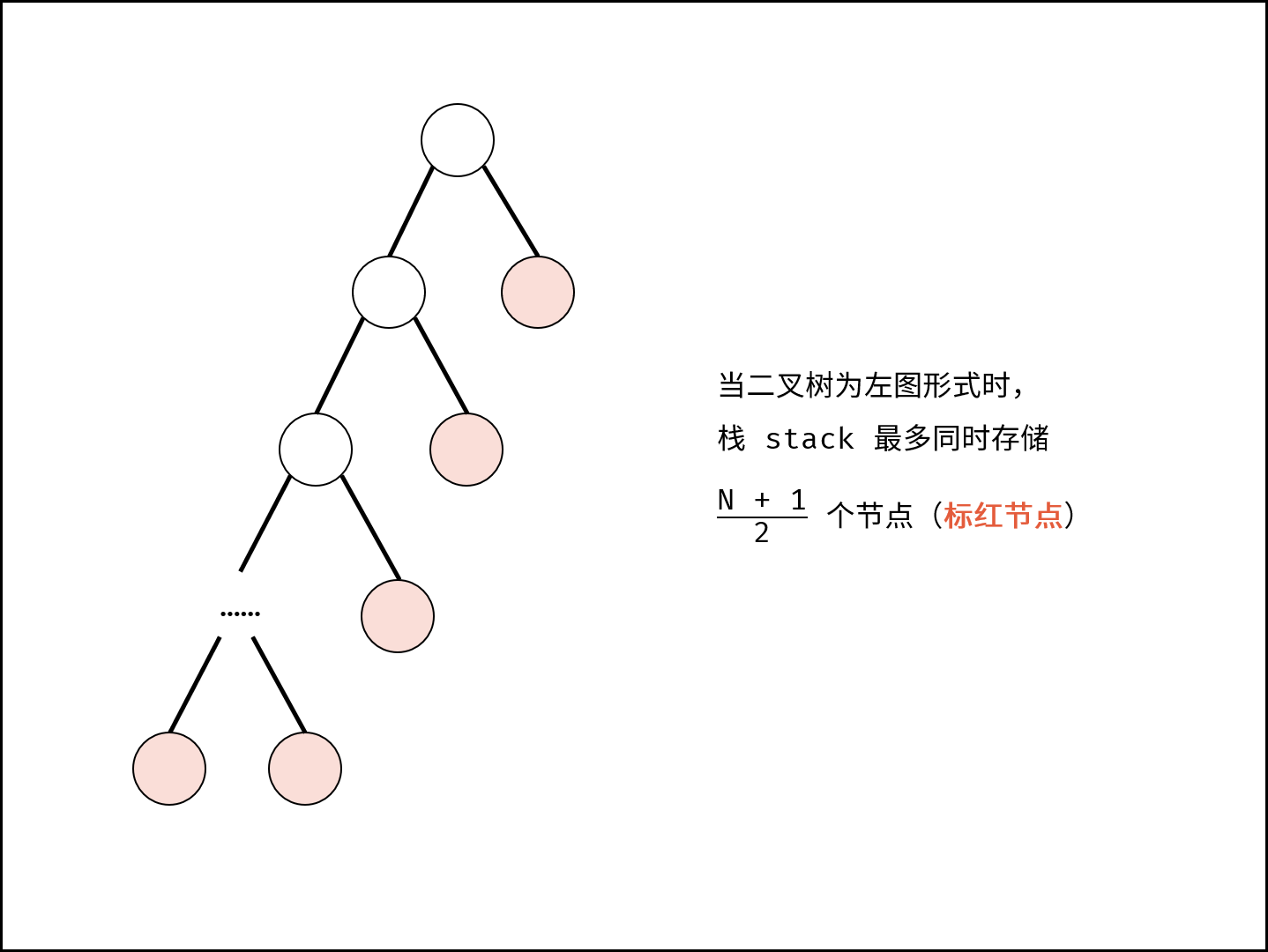
方法二:辅助栈(或队列)
利用栈(或队列)遍历树的所有节点 $node$ ,并交换每个 $node$ 的左 / 右子节点。
算法流程:
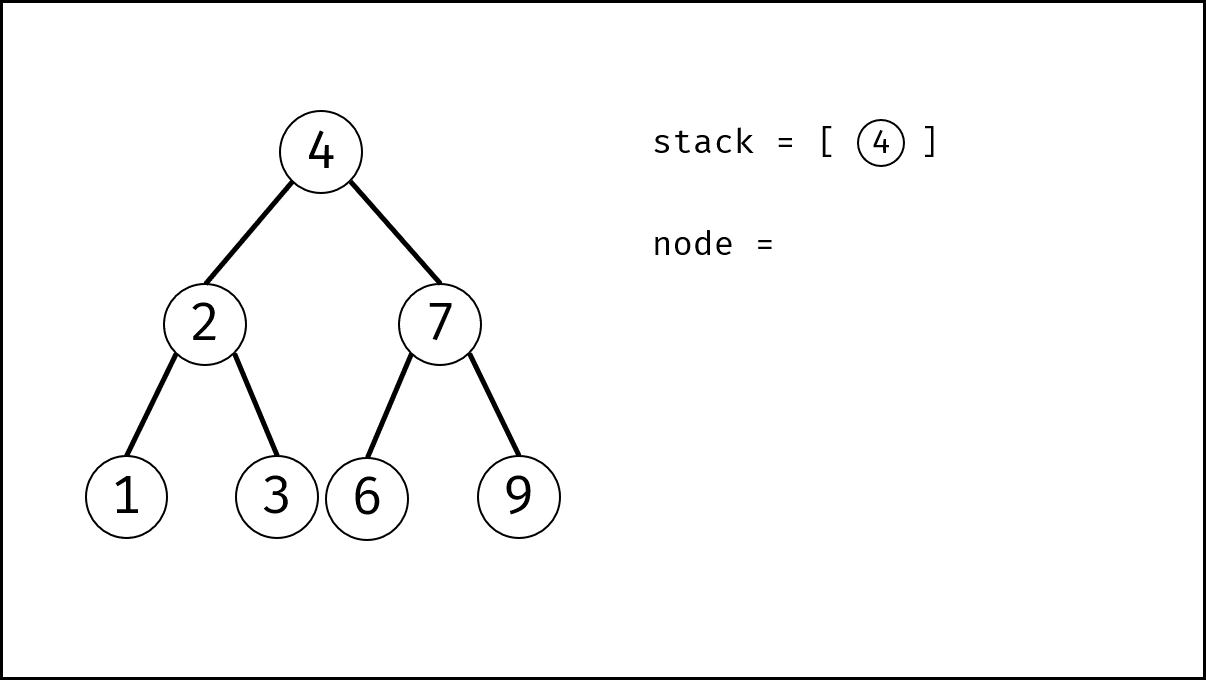
- 特例处理: 当 $root$ 为空时,直接返回 $null$ 。
- 初始化: 栈(或队列),本文用栈,并加入根节点 $root$ 。
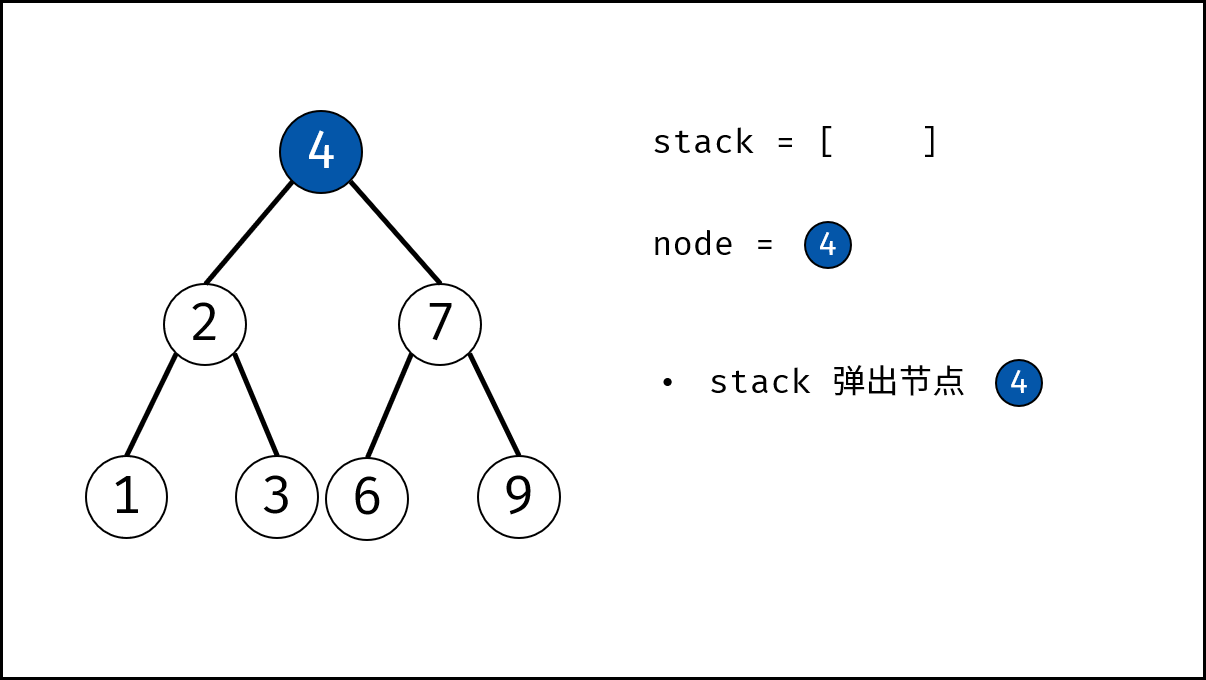
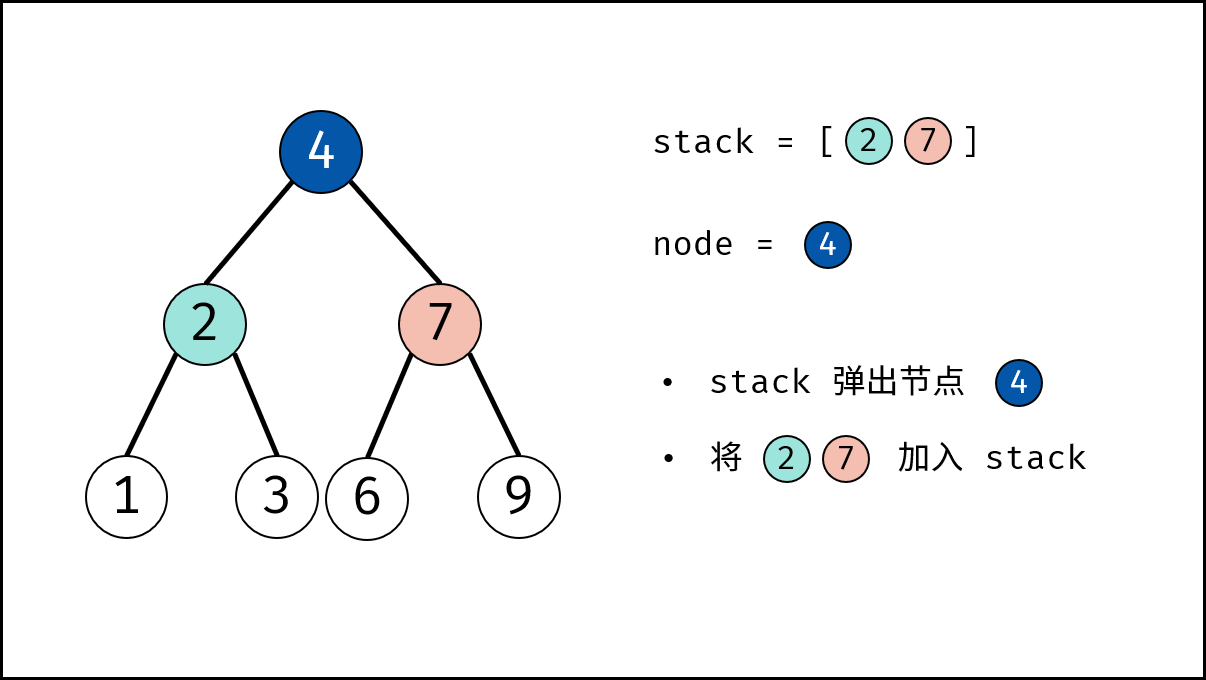
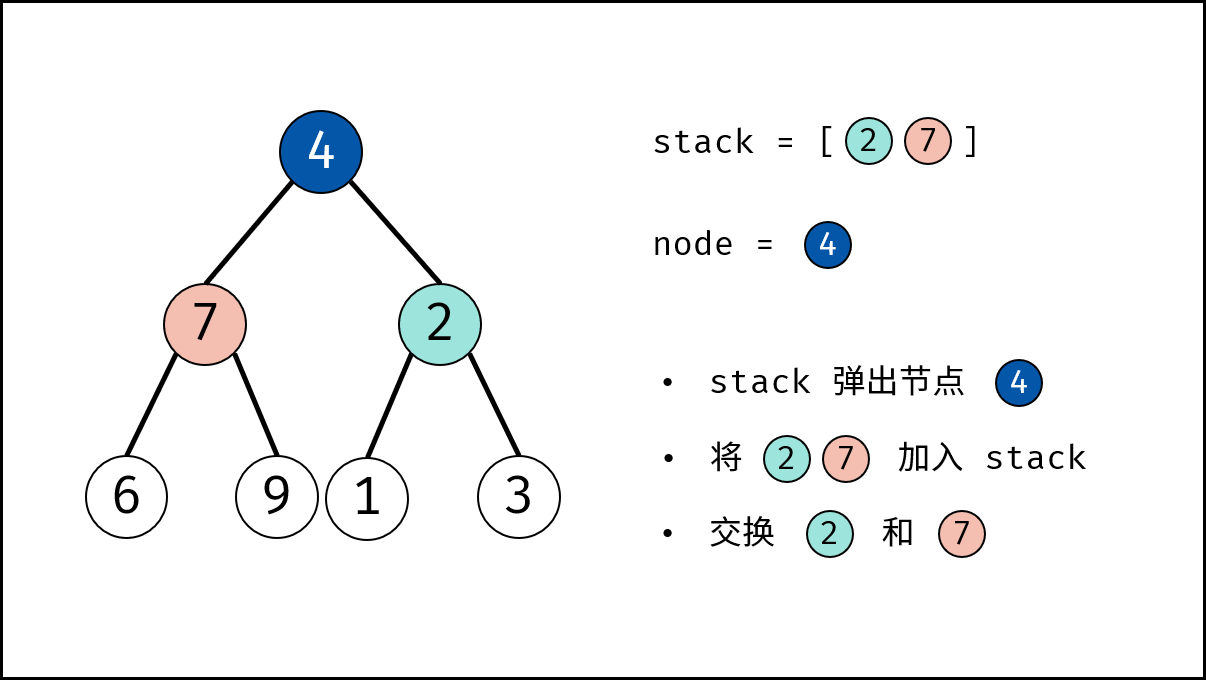
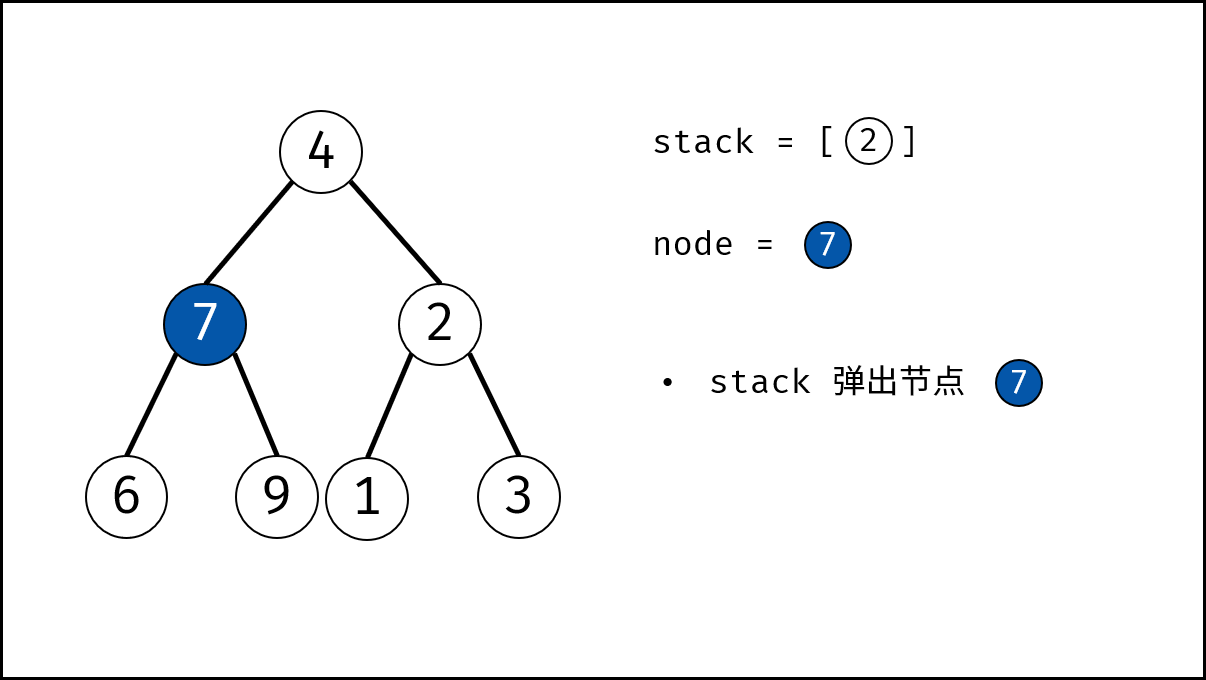
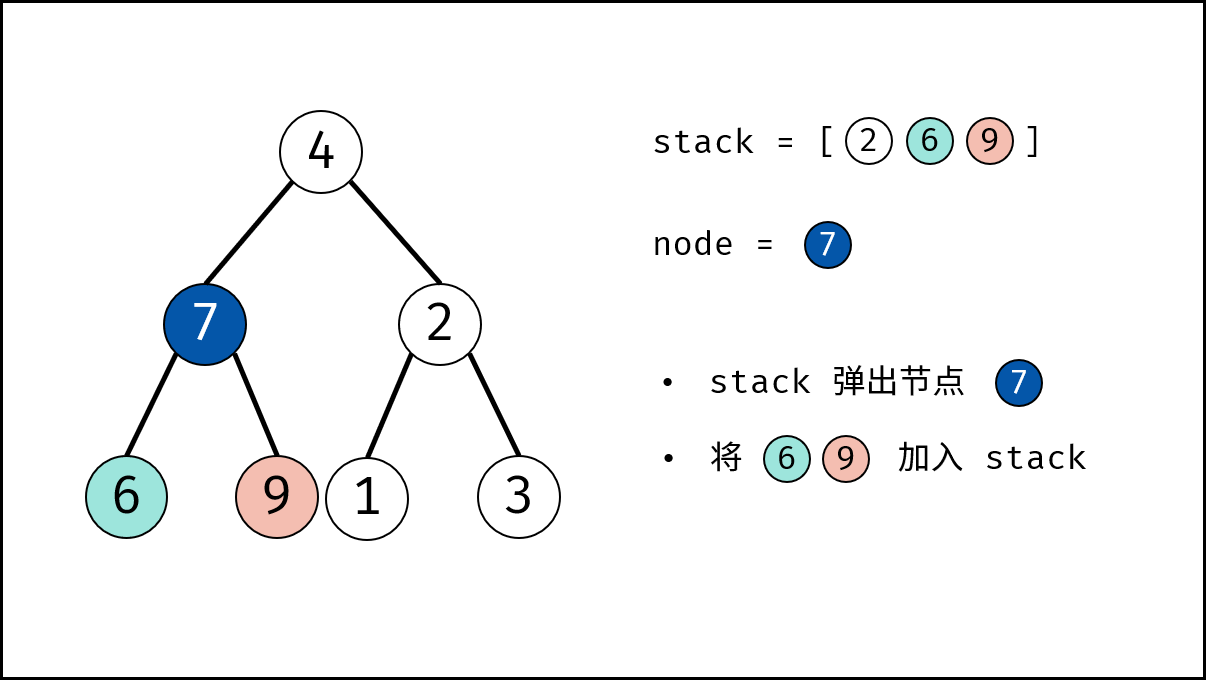
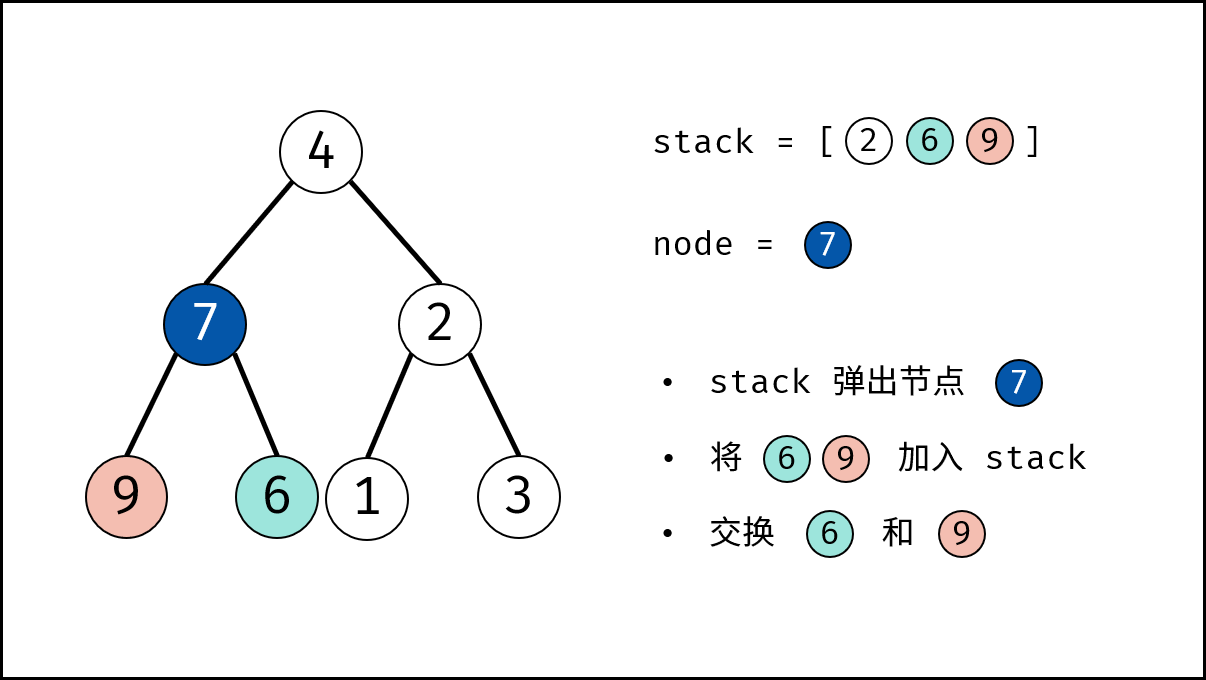
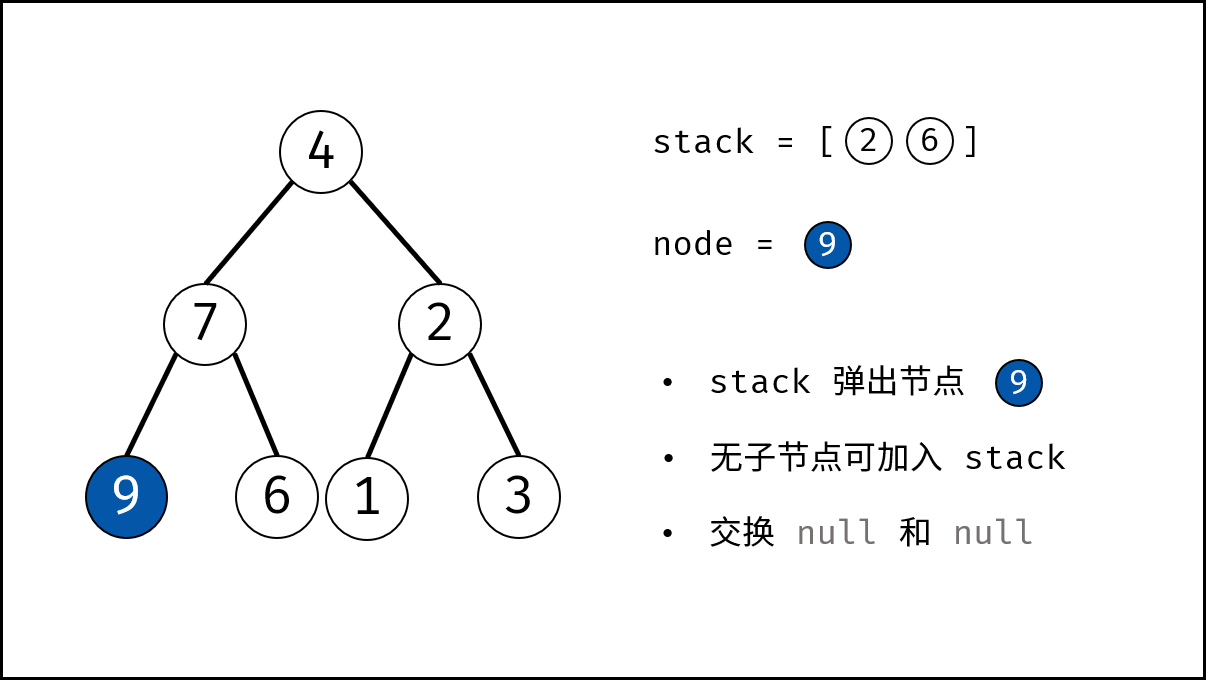
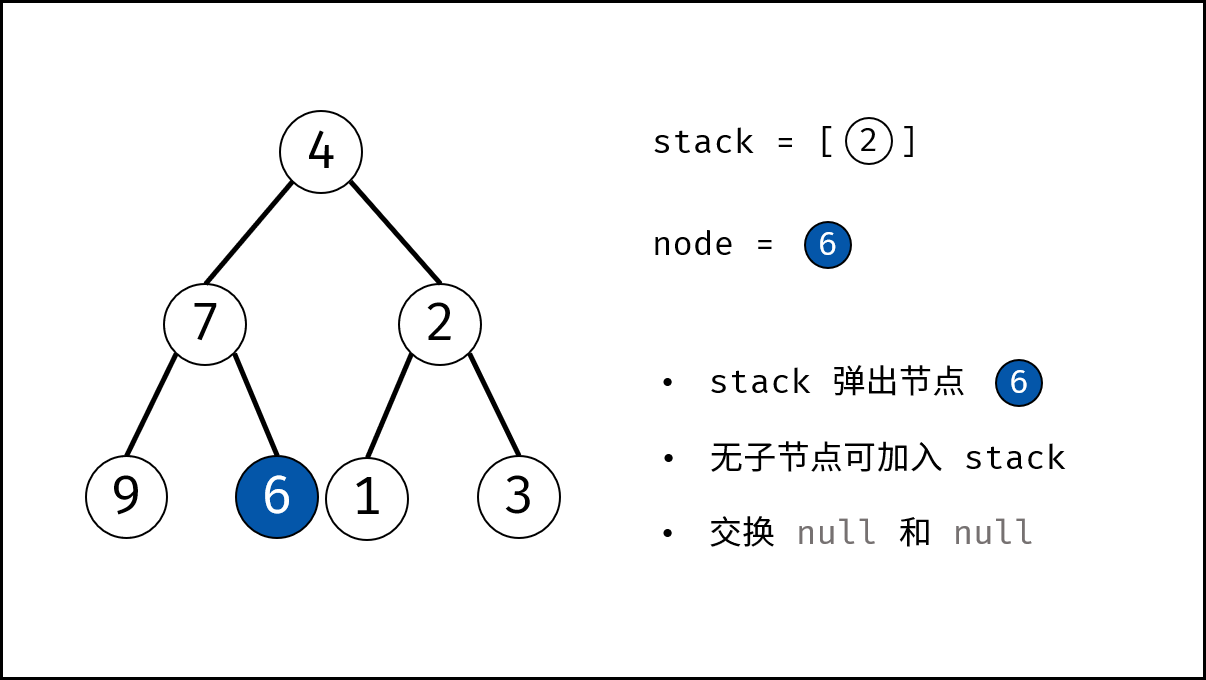
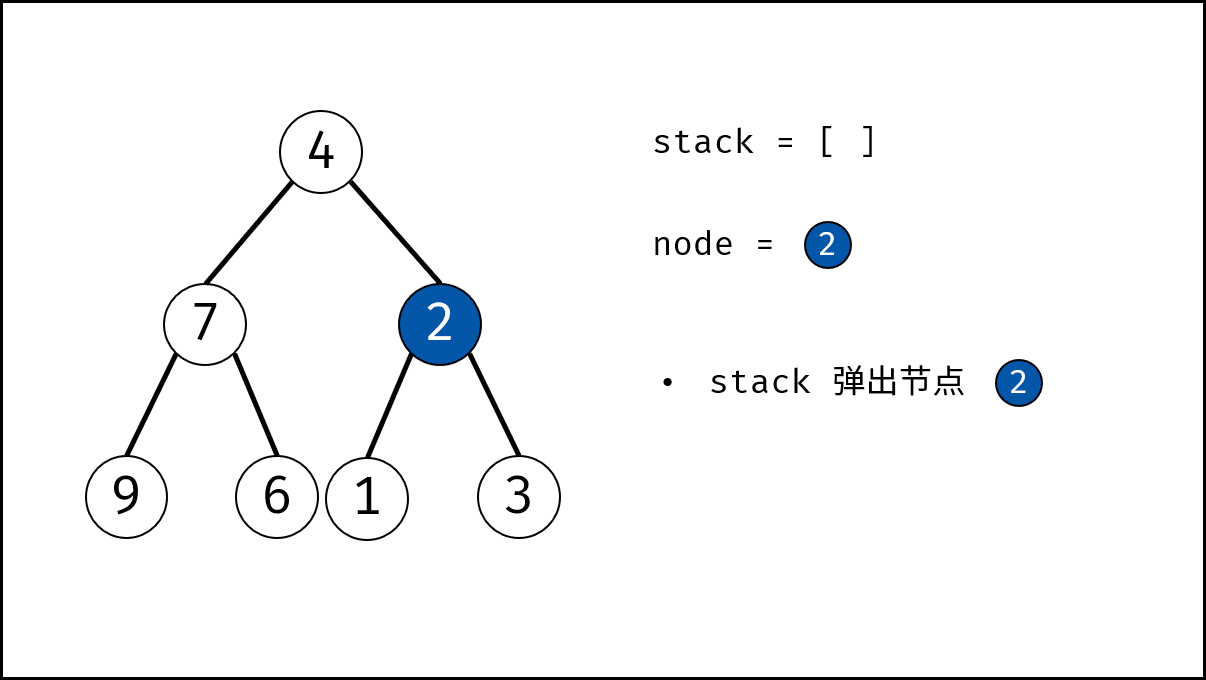
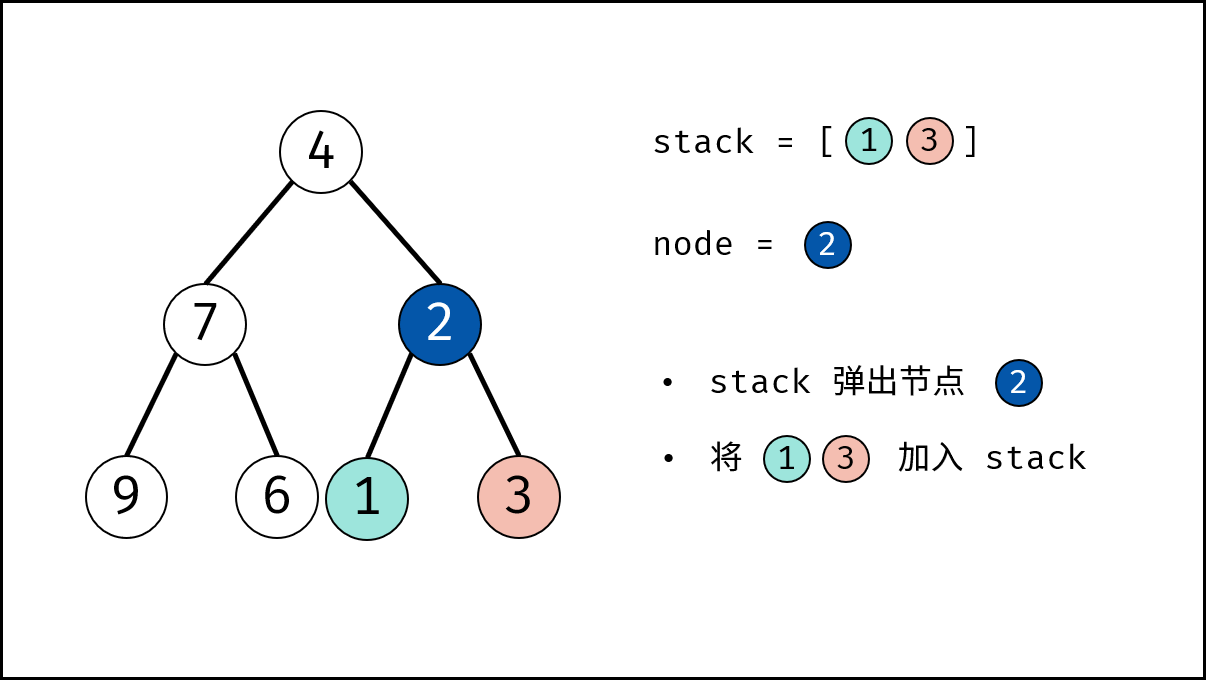
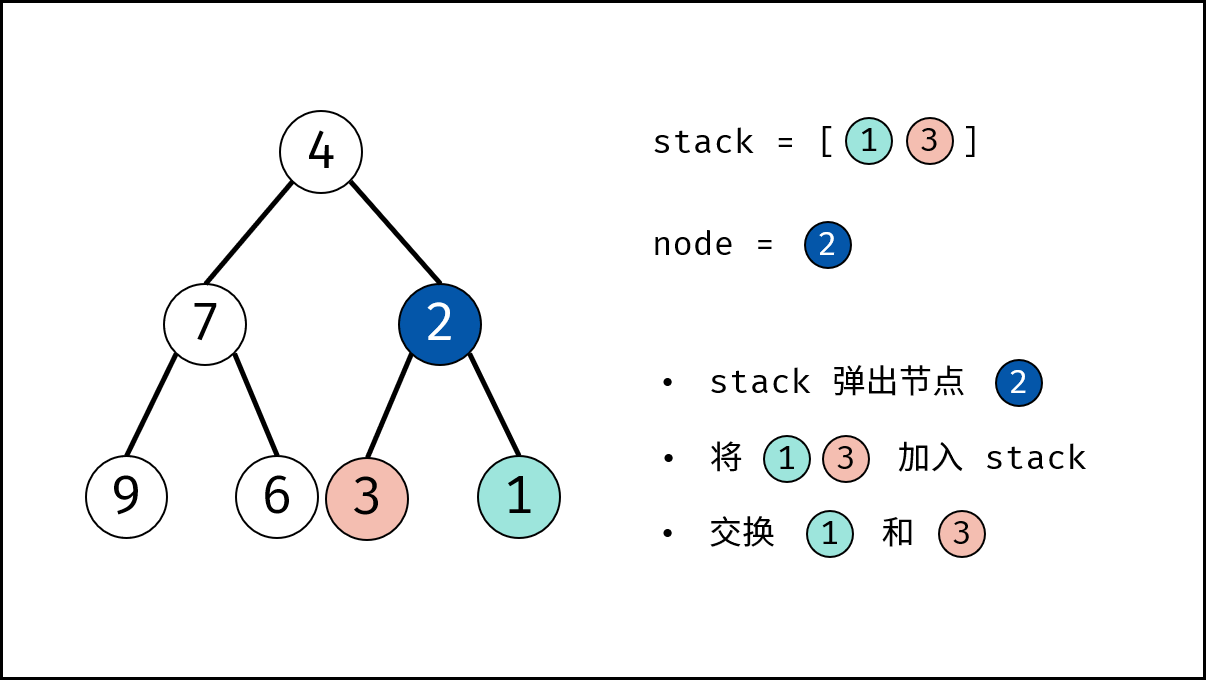
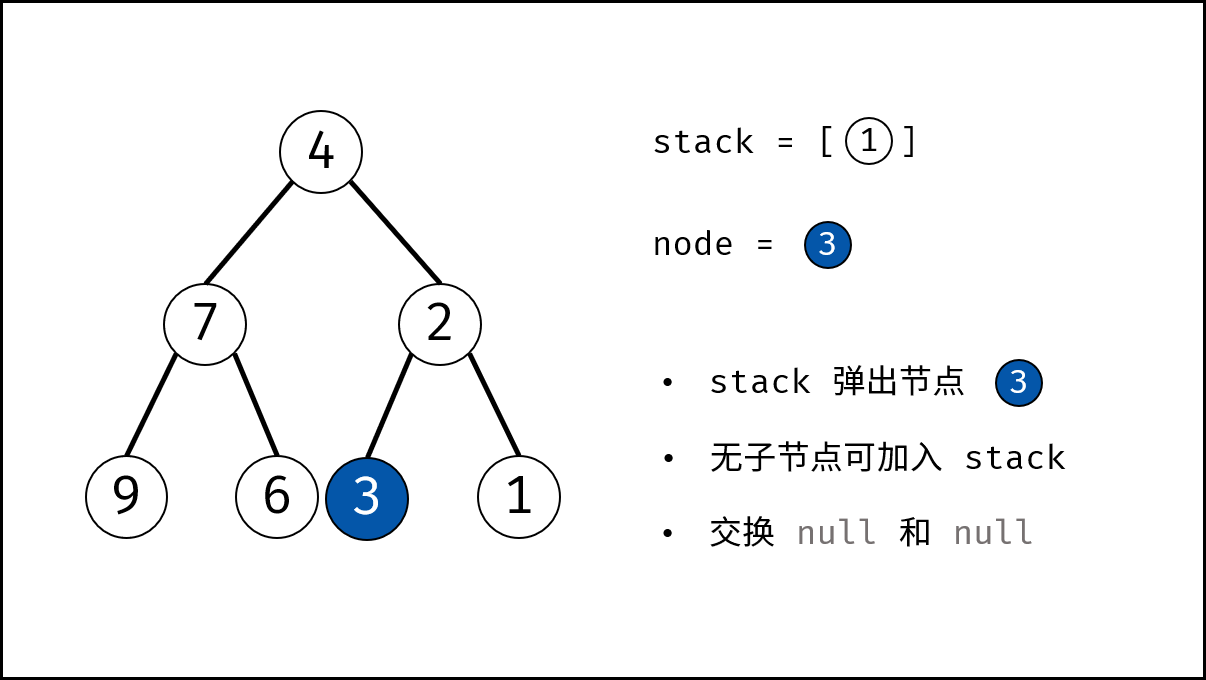
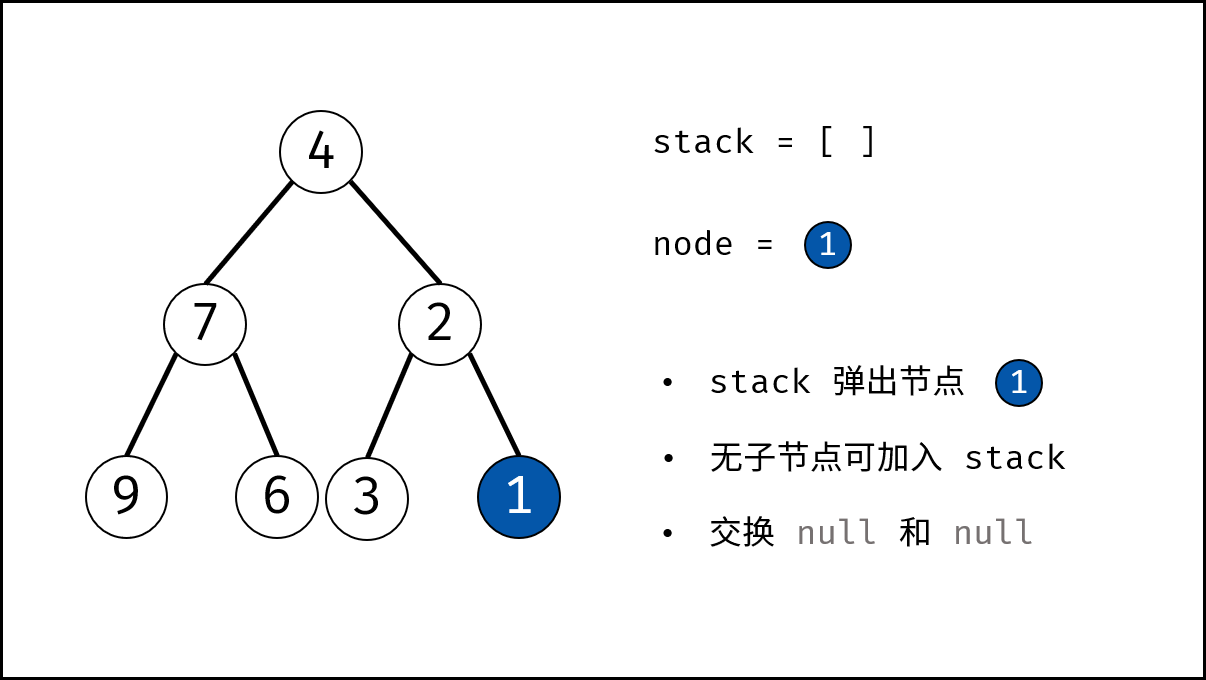
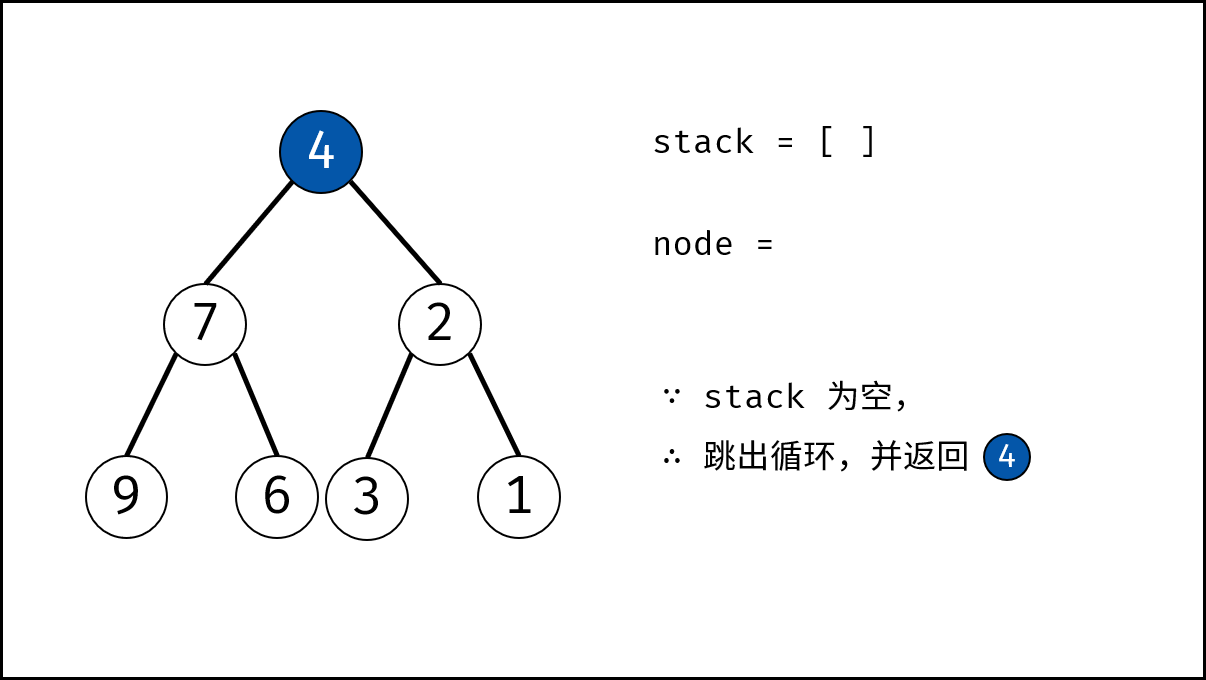
- 循环交换: 当栈 $stack$ 为空时跳出。
- 出栈: 记为 $node$ 。
- 添加子节点: 将 $node$ 左和右子节点入栈。
- 交换: 交换 $node$ 的左 / 右子节点。
- 返回值: 返回根节点 $root$ 。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root: return
stack = [root]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node.left: stack.append(node.left)
if node.right: stack.append(node.right)
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
return rootJava
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>() {{ add(root); }};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node.left != null) stack.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) stack.add(node.right);
TreeNode tmp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = tmp;
}
return root;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (node->left != nullptr) stack.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) stack.push(node->right);
TreeNode* tmp = node->left;
node->left = node->right;
node->right = tmp;
}
return root;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为二叉树的节点数量,建立二叉树镜像需要遍历树的所有节点,占用 $O(N)$ 时间。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 如下图所示,最差情况下,栈 $stack$ 最多同时存储 $\frac{N + 1}{2}$ 个节点,占用 $O(N)$ 额外空间。