解题思路:
本文名词规定如下:
- 将 $101112 \cdots$ 中的每一位称为 数位 ,记为 $n$ 。
- 将 $10, 11, 12, \cdots$ 称为 数字 ,记为 $num$ 。
- 数字 $10$ 是一个两位数,称此数字的 位数 为 $2$ ,记为 $digit$ 。
- 每 $digit$ 位数的起始数字(即:$1, 10, 100, \cdots$),记为 $start$ 。
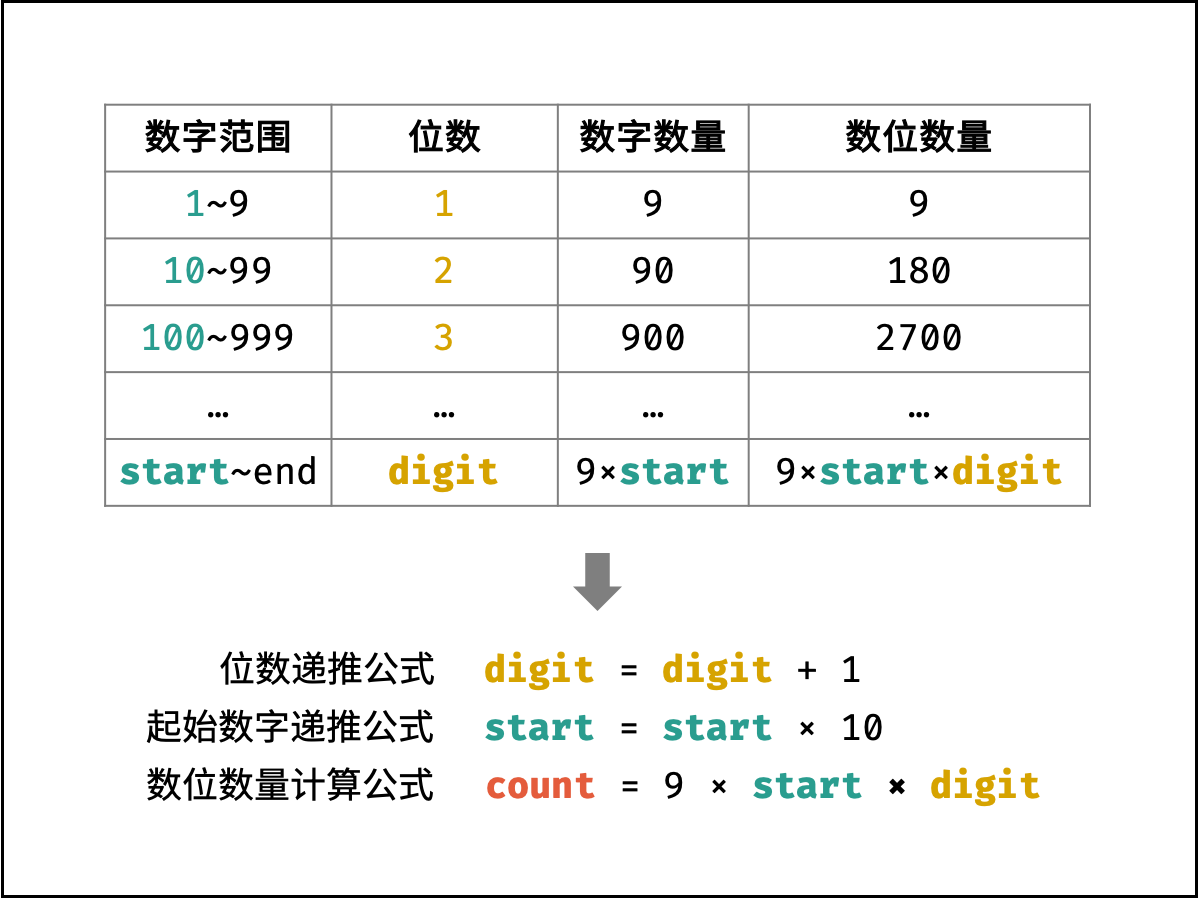
观察上表,可推出各 $digit$ 下的数位数量 $count$ 的计算公式:
$$ count = 9 \times start \times digit $$
根据以上分析,可将求解分为三步:
- 确定 $n$ 所在 数字 的 位数 ,记为 $digit$ 。
- 确定 $n$ 所在的 数字 ,记为 $num$ 。
- 确定 $n$ 是 $num$ 中的哪一数位,并返回结果。
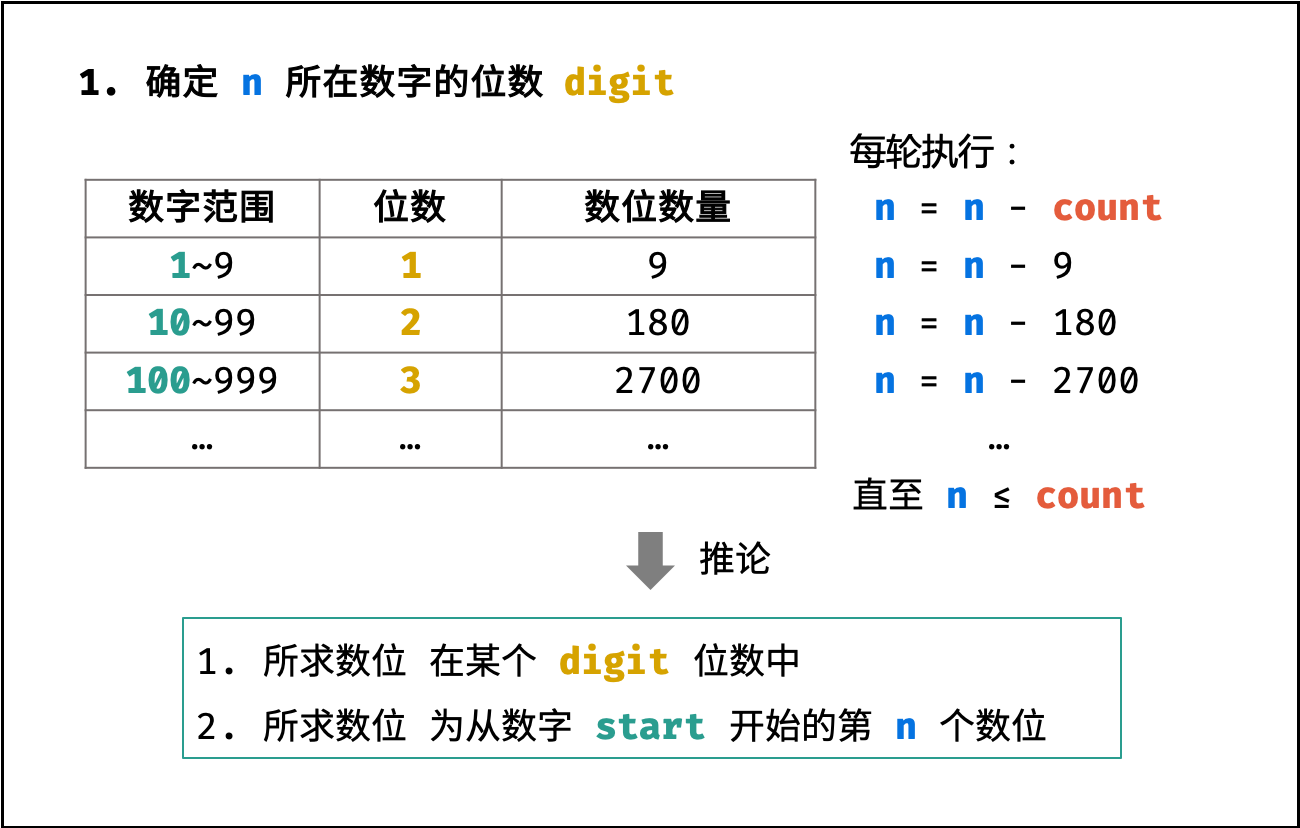
第一步:确定所求数位的所在数字的位数
如下图所示,循环执行 $n$ 减去 一位数、两位数、... 的数位数量 $count$ ,直至 $n \leq count$ 时跳出。
由于 $n$ 已经减去了一位数、两位数、...、$(digit-1)$ 位数的 数位数量 $count$ ,因而此时的 $n$ 是从起始数字 $start$ 开始计数的。
Python
digit, start, count = 1, 1, 9
while n > count:
n -= count
start *= 10 # 1, 10, 100, ...
digit += 1 # 1, 2, 3, ...
count = 9 * start * digit # 9, 180, 2700, ...Java
int digit = 1;
long start = 1;
long count = 9;
while (n > count) {
n -= count;
start *= 10; // 1, 10, 100, ...
digit += 1; // 1, 2, 3, ...
count = digit * start * 9; // 9, 180, 2700, ...
}C++
int digit = 1;
long start = 1;
long count = 9;
while (n > count) { // 1.
n -= count;
start *= 10; // 1, 10, 100, ...
digit += 1; // 1, 2, 3, ...
count = digit * start * 9; // 9, 180, 2700, ...
}结论: 所求数位 ① 在某个 $digit$ 位数中; ② 为从数字 $start$ 开始的第 $n$ 个数位。
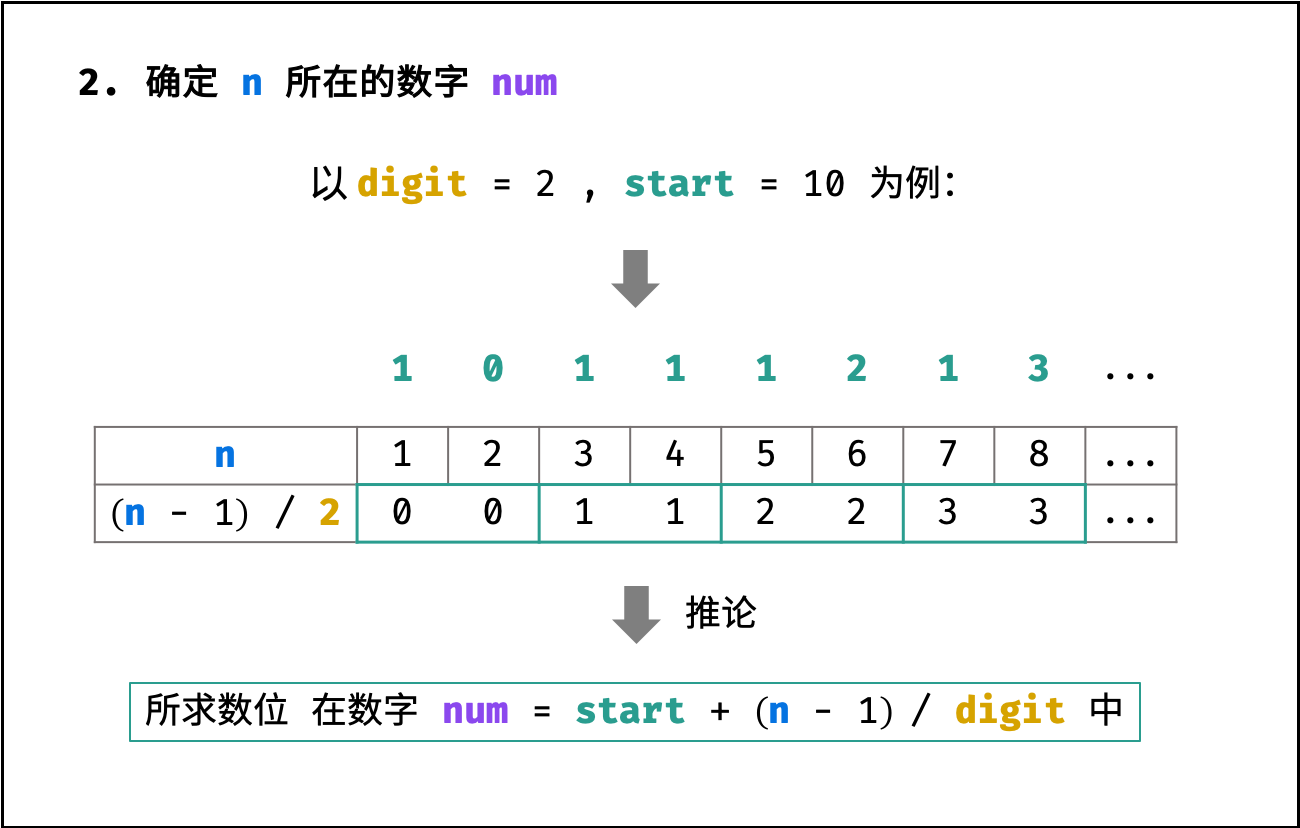
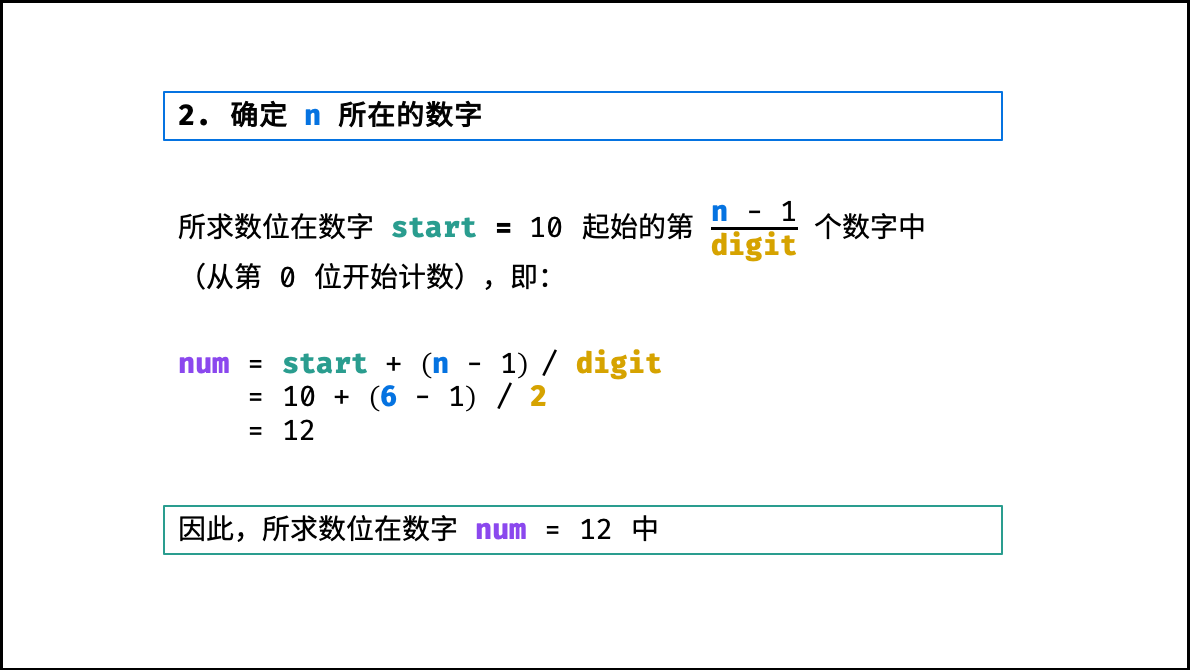
第二步:确定所求数位所在的数字
如下图所示,所求数位 在从数字 $start$ 开始的第 $[(n - 1) / digit]$ 个 数字 中( $start$ 为第 0 个数字)。
Python
num = start + (n - 1) // digitJava
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit;C++
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit;结论: 所求数位在数字 $num$ 中。
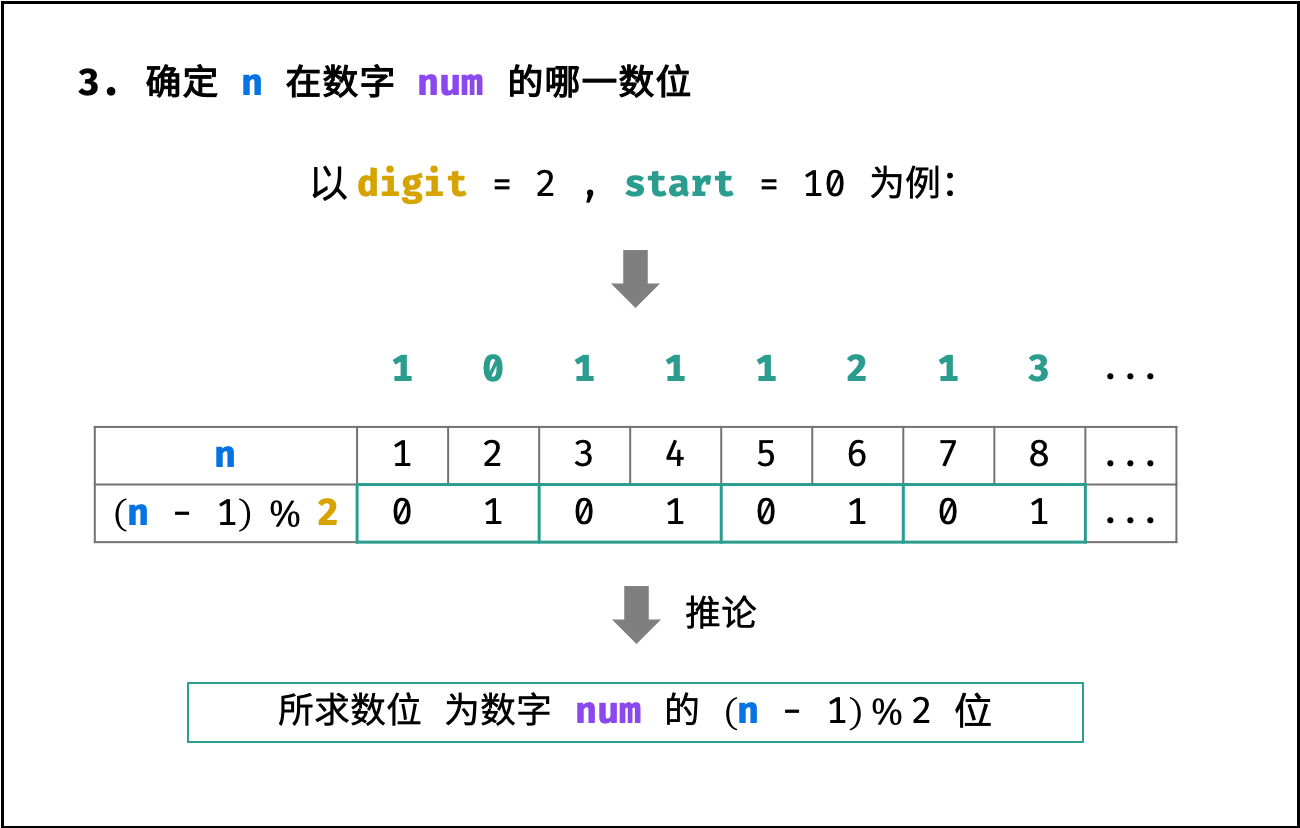
第三步:确定所求数位在 $num$ 的哪一数位
如下图所示,所求数位为数字 $num$ 的第 $(n - 1) % digit$ 位( 数字的首个数位为第 0 位)。
Python
s = str(num) # 转化为 string
res = int(s[(n - 1) % digit]) # 获得 num 的 第 (n - 1) % digit 个数位,并转化为 intJava
String s = Long.toString(num); // 转化为 string
int res = s.charAt((n - 1) % digit) - '0'; // 获得 num 的 第 (n - 1) % digit 个数位,并转化为 intC++
string s = to_string(num); // 转化为 string
int res = s[(n - 1) % digit] - '0'; // 获得 num 的 第 (n - 1) % digit 个数位,并转化为 int结论: 所求数位是 $res$ 。
完整流程如下图所示。
< ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def findNthDigit(self, n: int) -> int:
digit, start, count = 1, 1, 9
while n > count: # 1.
n -= count
start *= 10
digit += 1
count = 9 * start * digit
num = start + (n - 1) // digit # 2.
return int(str(num)[(n - 1) % digit]) # 3.Java
class Solution {
public int findNthDigit(int n) {
int digit = 1;
long start = 1;
long count = 9;
while (n > count) { // 1.
n -= count;
start *= 10;
digit += 1;
count = digit * start * 9;
}
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit; // 2.
return Long.toString(num).charAt((n - 1) % digit) - '0'; // 3.
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
int findNthDigit(int n) {
int digit = 1;
long start = 1;
long count = 9;
while (n > count) { // 1.
n -= count;
start *= 10;
digit += 1;
count = digit * start * 9;
}
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit; // 2.
return to_string(num)[(n - 1) % digit] - '0'; // 3.
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(\log n)$ : 所求数位 $n$ 对应数字 $num$ 的位数 $digit$ 最大为 $O(\log n)$ ;第一步最多循环 $O(\log n)$ 次;第三步中将 $num$ 转化为字符串使用 $O(\log n)$ 时间;因此总体为 $O(\log n)$ 。
- 空间复杂度 $O(\log n)$ : 将数字 $num$ 转化为字符串
str(num),占用 $O(\log n)$ 的额外空间。