解题思路:
祖先的定义: 若节点 p 在节点 root 的左(右)子树中,或 p = root ,则称 root 是 p 的祖先。
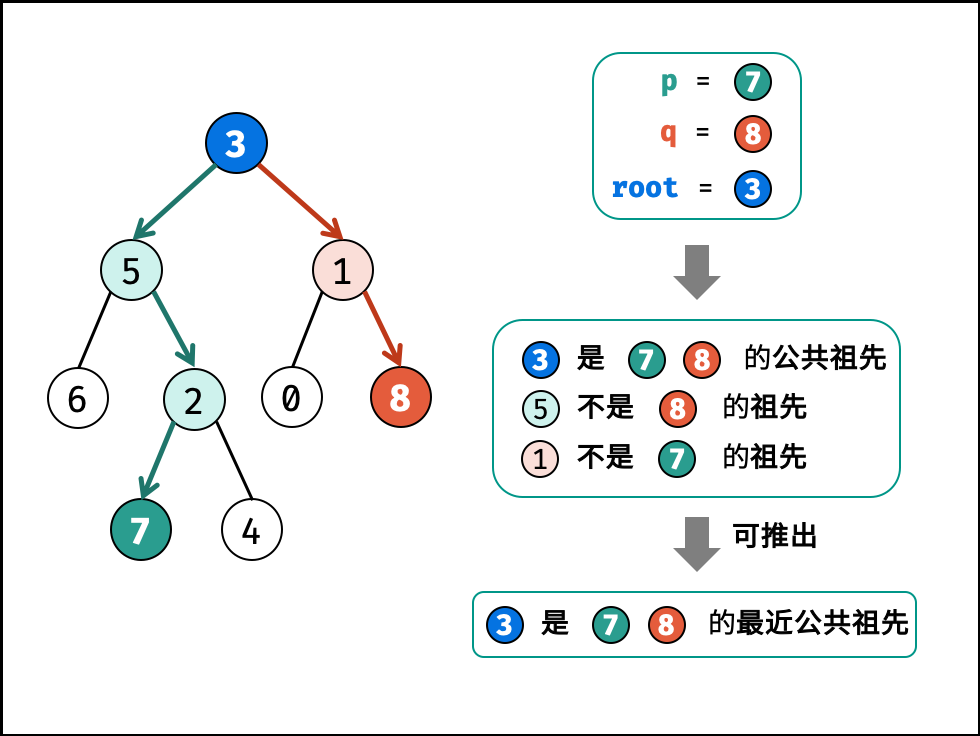
最近公共祖先的定义: 设节点 root 为节点 p , q 的某公共祖先,若其左子节点 root.left 和右子节点 root.right 都不是 p , q 的公共祖先,则称 root 是 “最近的公共祖先” 。
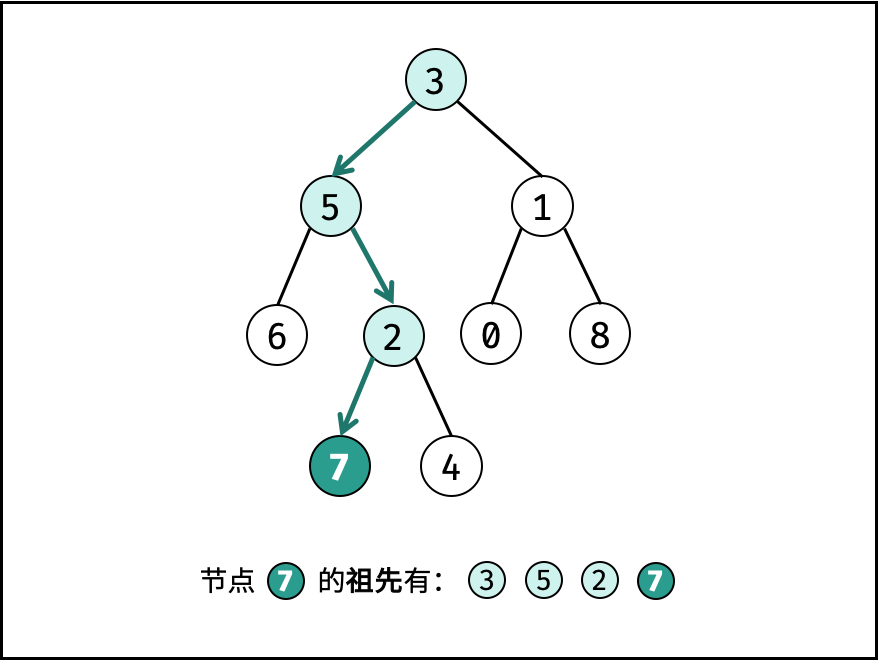
根据以上定义,若 root 是 p , q 的 最近公共祖先 ,则只可能为以下情况之一:
p和q在root的子树中,且分列root的 异侧(即分别在左、右子树中);p = root,且q在root的左或右子树中;q = root,且p在root的左或右子树中;
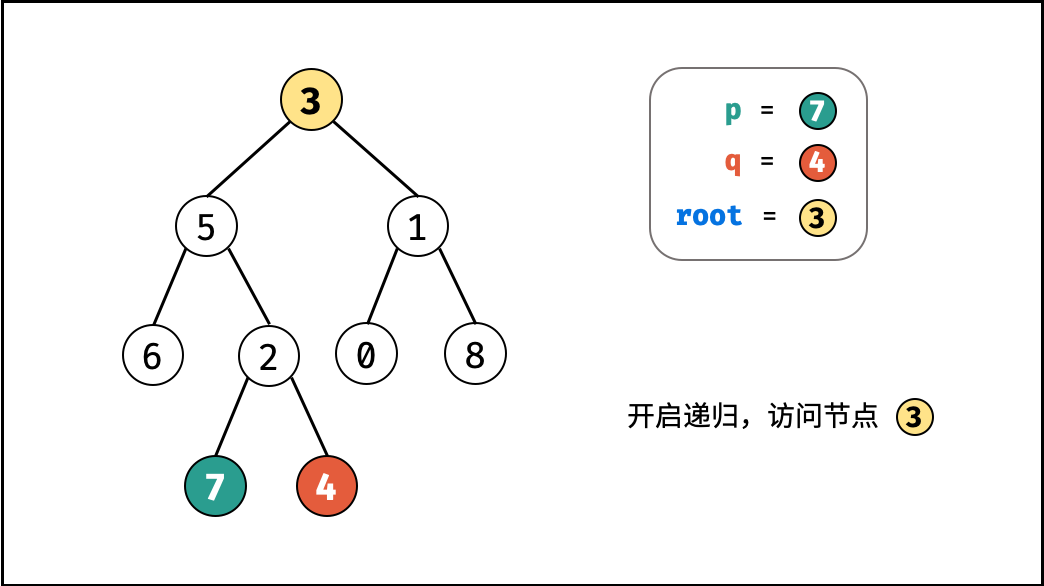
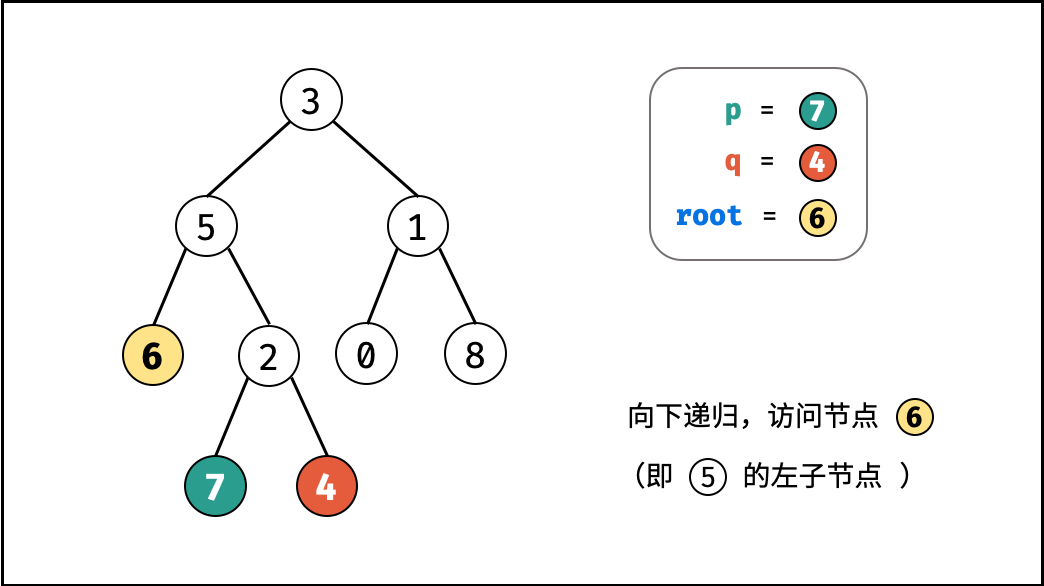
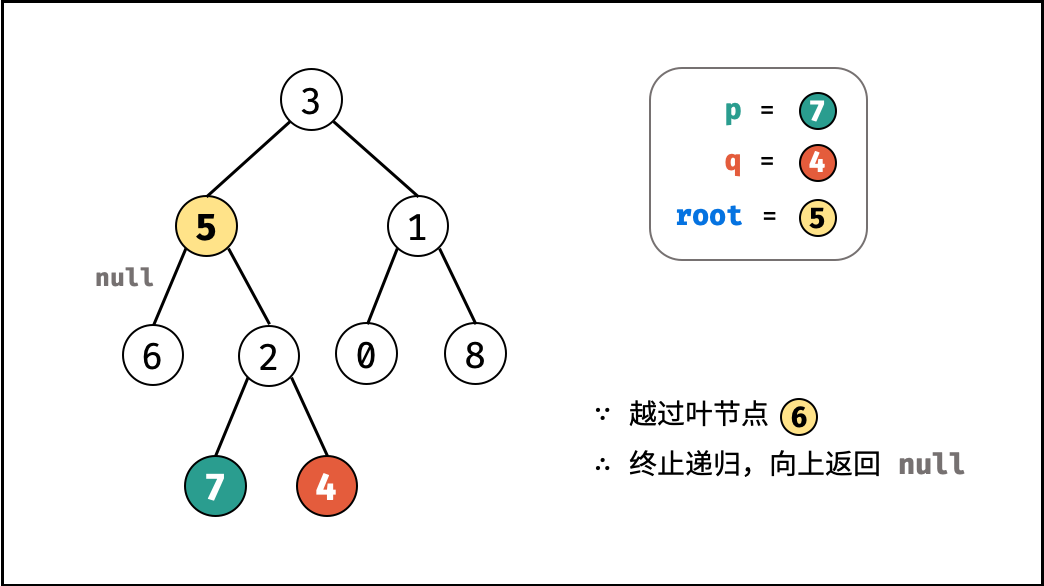
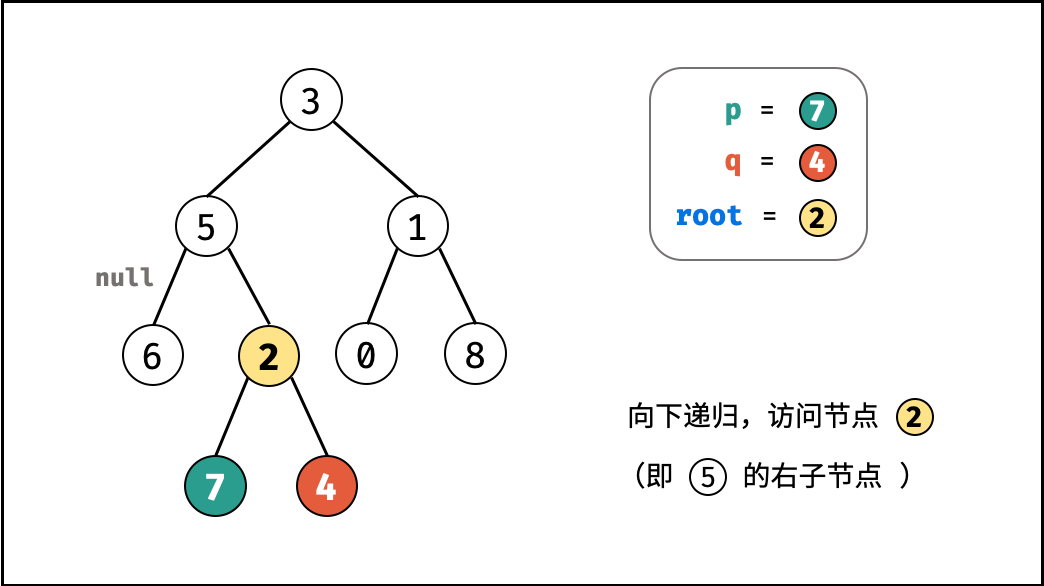
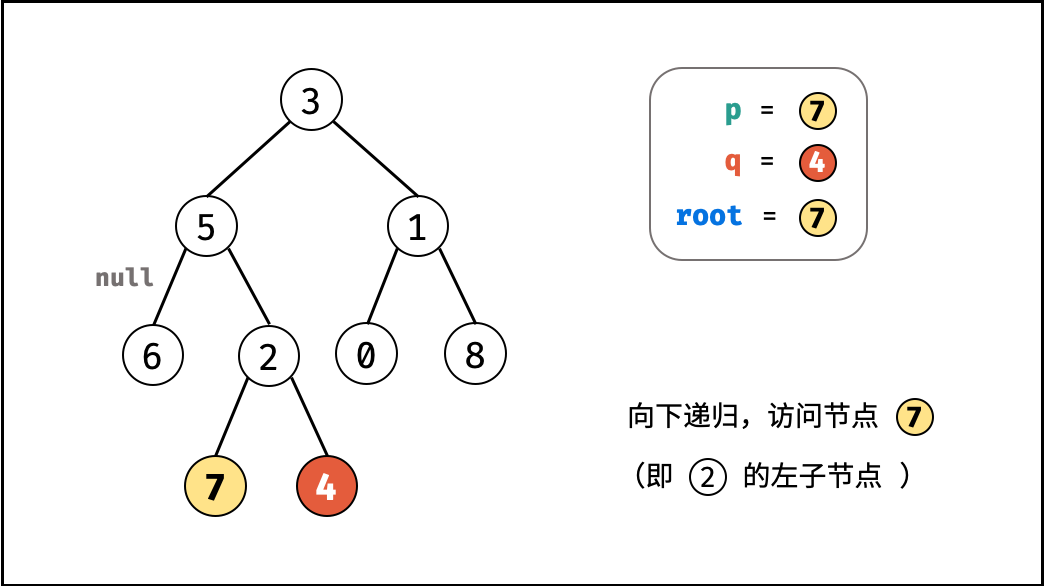
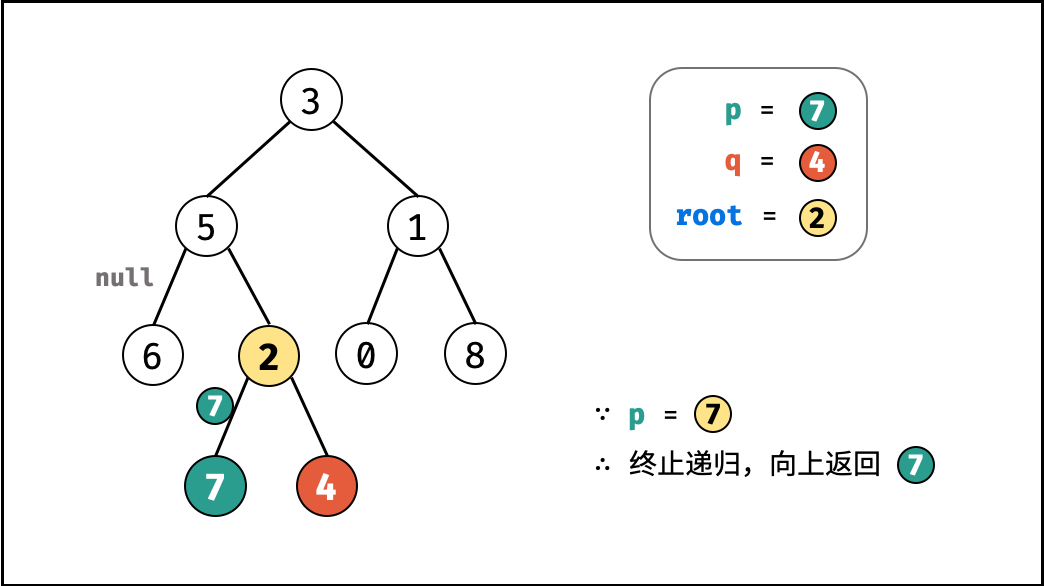
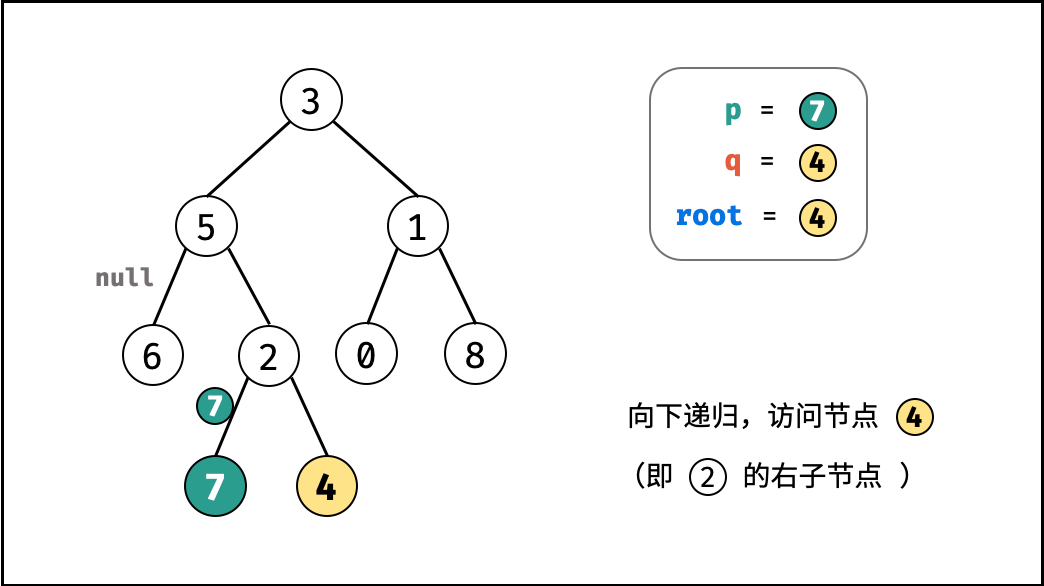
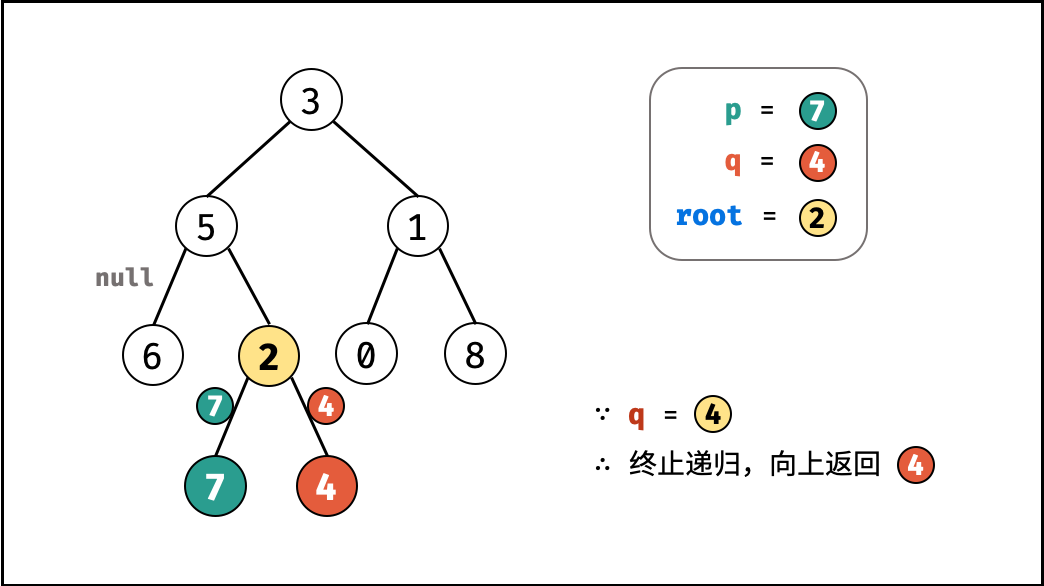
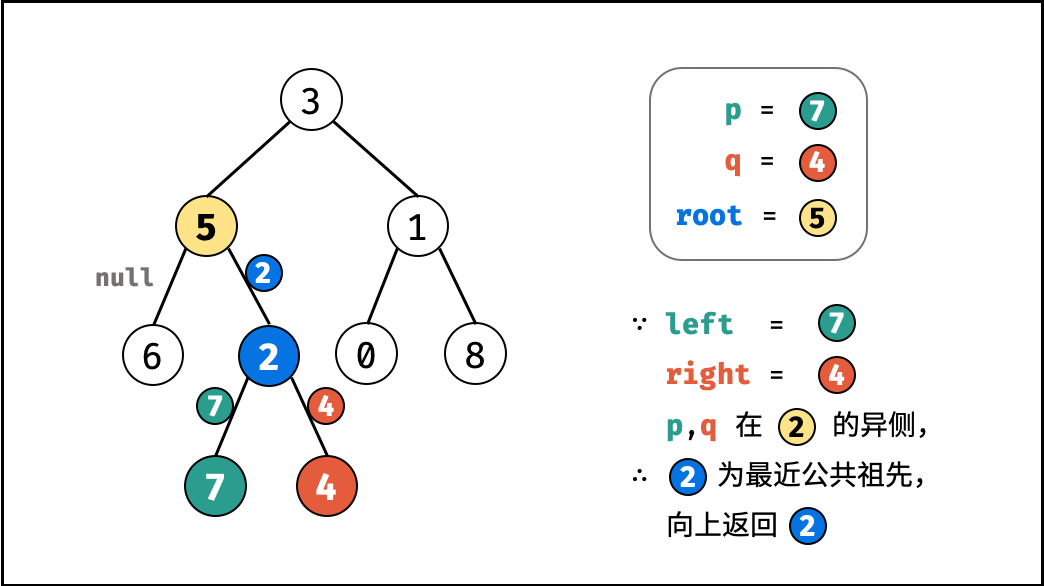
考虑通过递归对二叉树进行先序遍历,当遇到节点 p 或 q 时返回。从底至顶回溯,当节点 p , q 在节点 root 的异侧时,节点 root 即为最近公共祖先,则向上返回 root 。
递归解析:
- 终止条件:
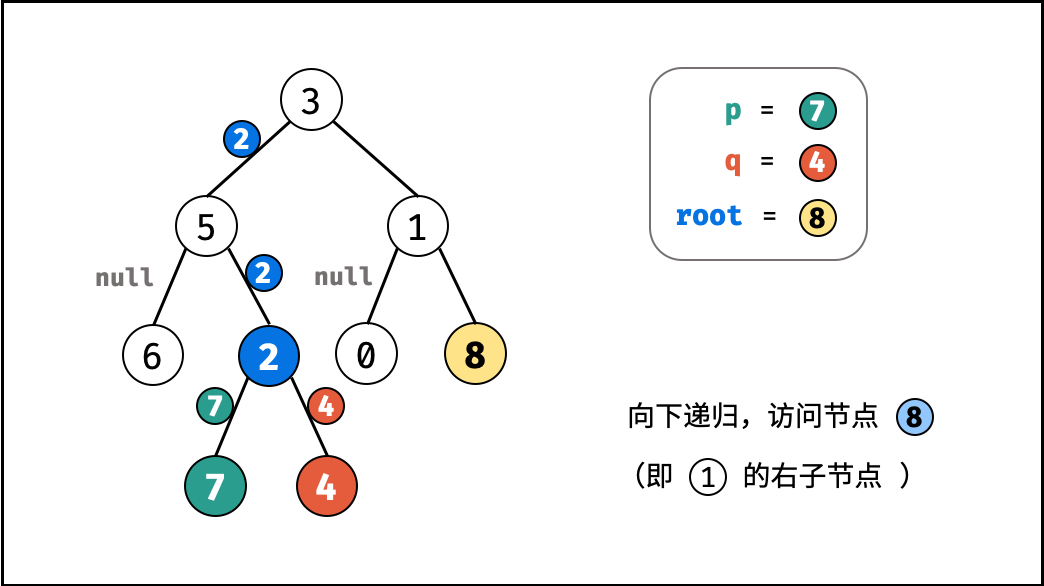
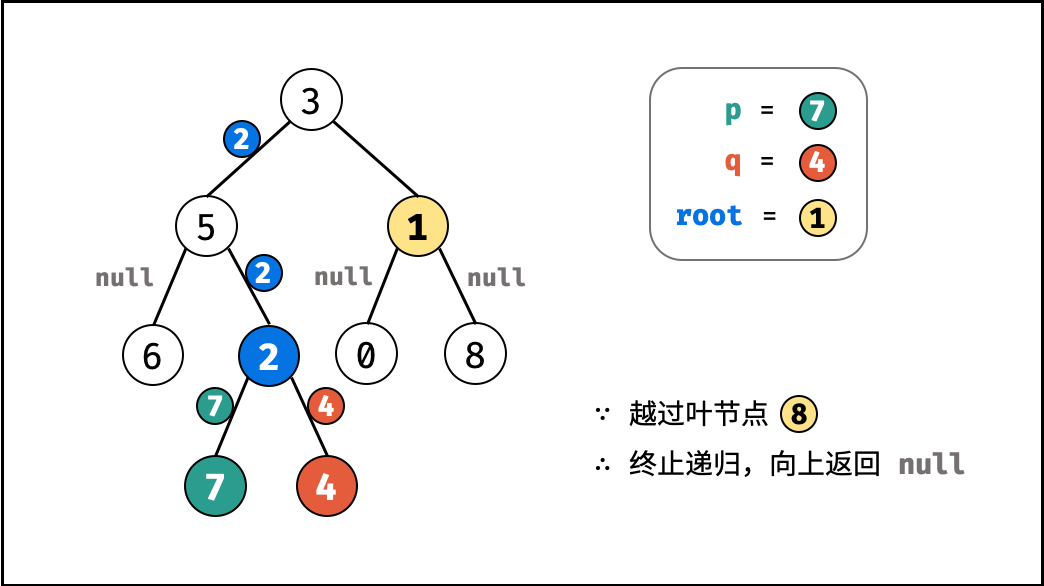
- 当越过叶节点,则直接返回 $\text{null}$ ;
- 当
root等于p,q,则直接返回root;
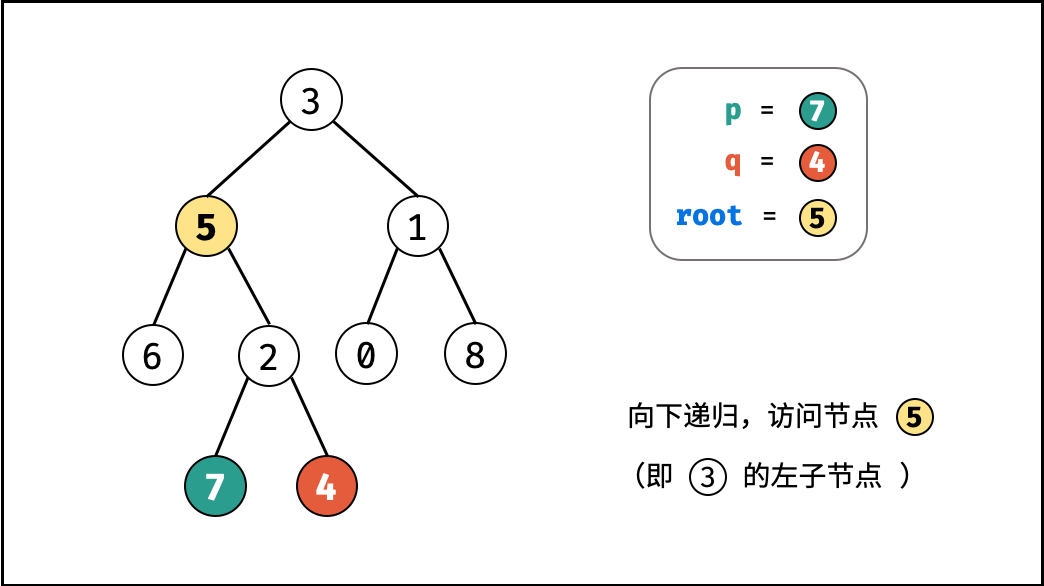
- 递推工作:
- 开启递归左子节点,返回值记为
left; - 开启递归右子节点,返回值记为
right;
- 开启递归左子节点,返回值记为
- 返回值: 根据
left和right,可展开为四种情况;- 当
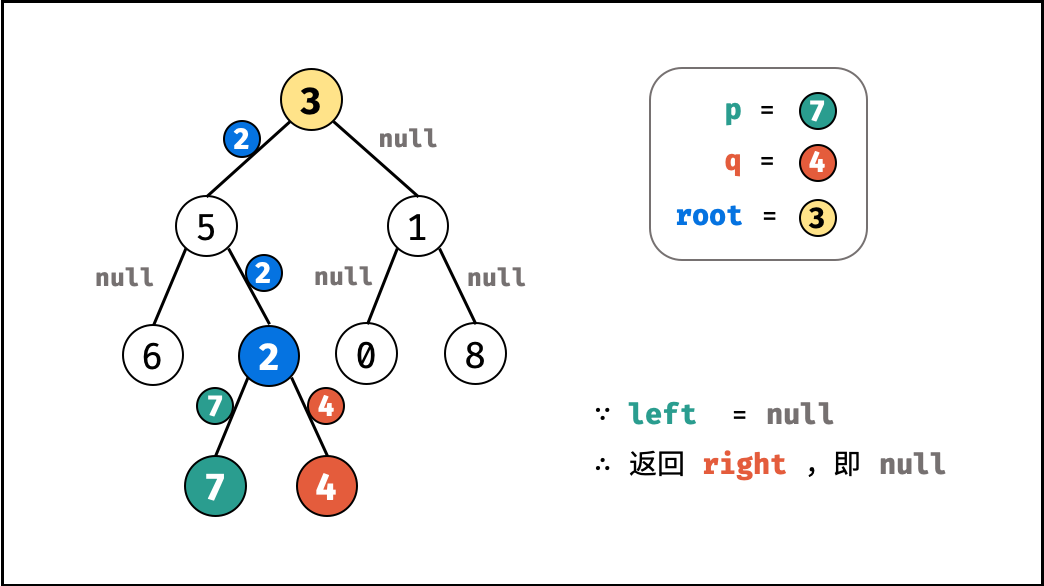
left和right同时为空 :说明root的左 / 右子树中都不包含p,q,返回 $\text{null}$ ; - 当
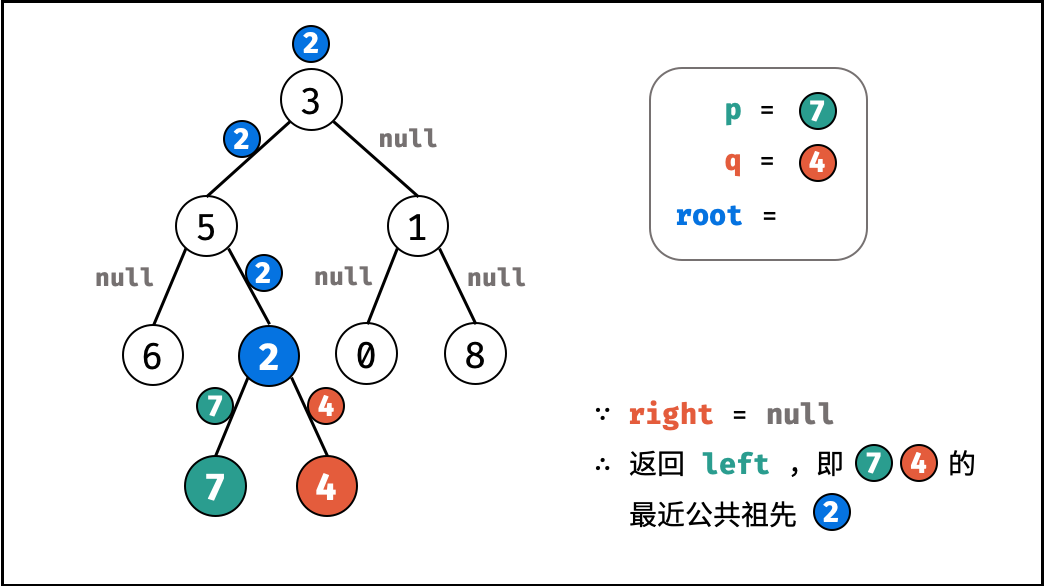
left和right同时不为空 :说明p,q分列在root的 异侧 (分别在 左 / 右子树),因此root为最近公共祖先,返回root; - 当
left为空 ,right不为空 :p,q都不在root的左子树中,直接返回right。具体可分为两种情况:p,q其中一个在root的 右子树 中,此时right指向p(假设为p);p,q两节点都在root的 右子树 中,此时的right指向 最近公共祖先节点 ;
- 当
left不为空 ,right为空 :与情况3.同理;
- 当
观察发现,情况
1.可合并至3.和4.内,详见文章末尾代码。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,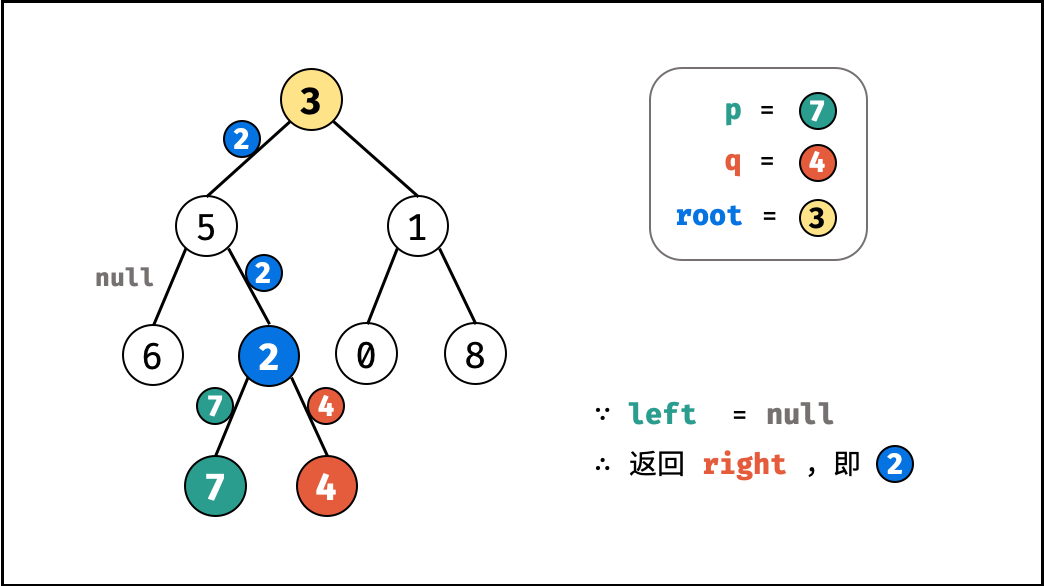 ,
,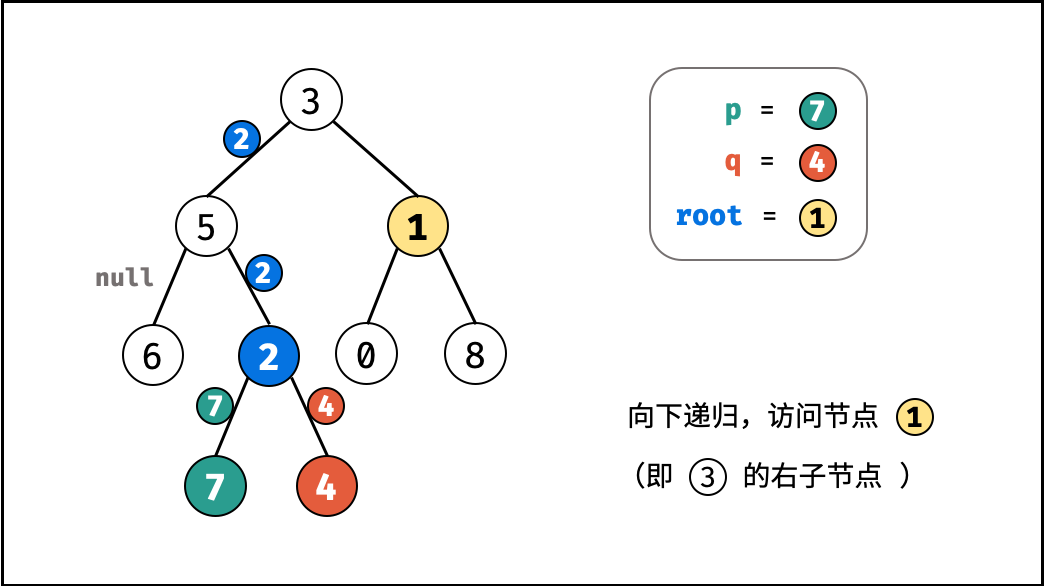 ,
,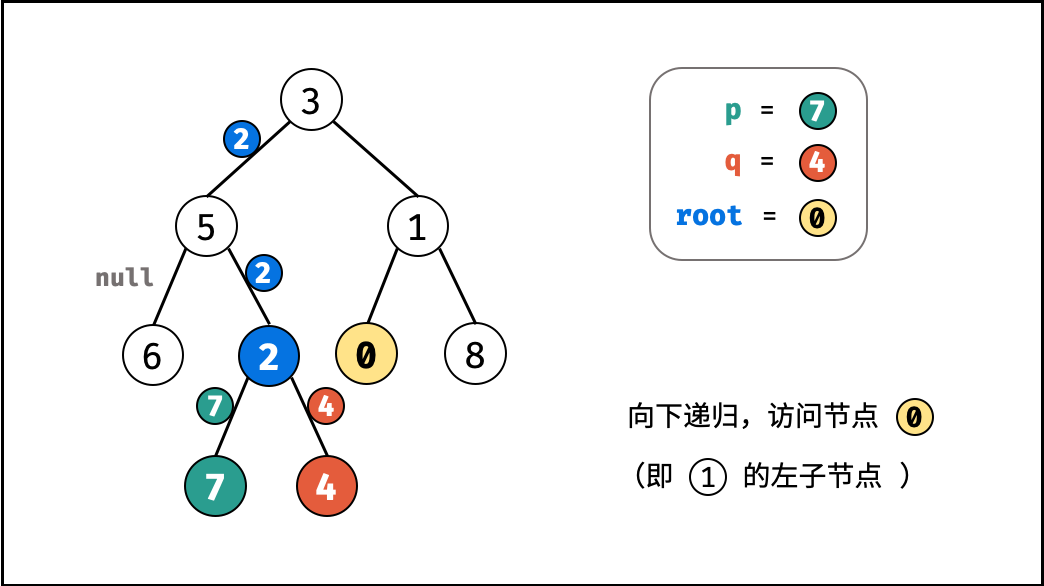 ,
,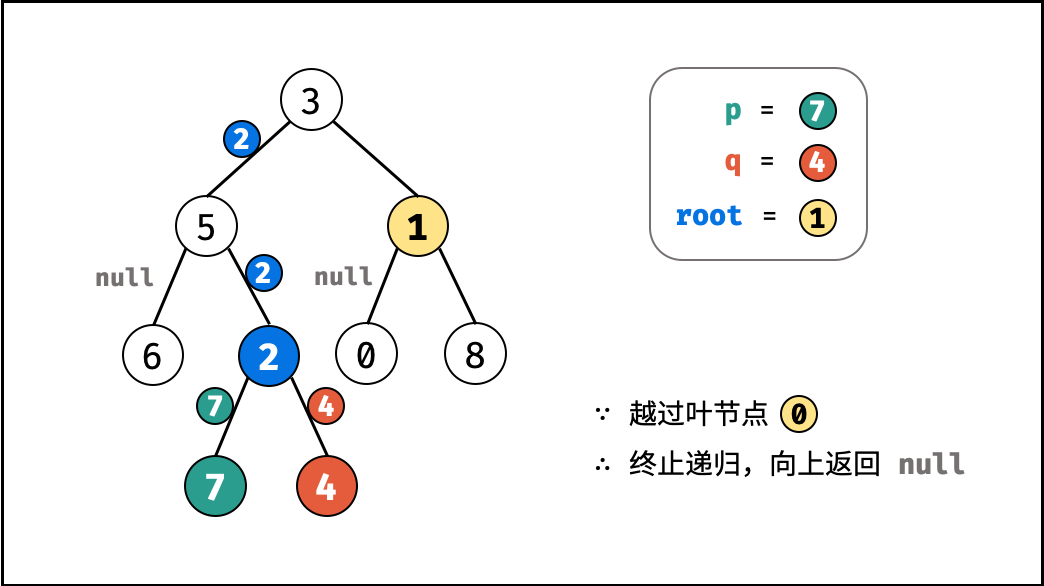 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root or root == p or root == q: return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if not left: return right
if not right: return left
return rootJava
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null) return right;
if(right == null) return left;
return root;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr) return right;
if(right == nullptr) return left;
return root;
}
};情况 1. , 2. , 3. , 4. 的展开写法如下。
Python
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root or root == p or root == q: return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if not left and not right: return # 1.
if not left: return right # 3.
if not right: return left # 4.
return root # 2. if left and right:Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null && right == null) return null; // 1.
if(left == null) return right; // 3.
if(right == null) return left; // 4.
return root; // 2. if(left != null and right != null)
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return nullptr; // 1.
if(left == nullptr) return right; // 3.
if(right == nullptr) return left; // 4.
return root; // 2. if(left != null and right != null)
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为二叉树节点数;最差情况下,需要递归遍历树的所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下,递归深度达到 $N$ ,系统使用 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间。