解题思路:
根据题意,每个丑数都可以由其他较小的丑数通过乘以 $2$ 或 $3$ 或 $5$ 得到。
所以,可以考虑使用一个优先队列保存所有的丑数,每次取出最小的那个,然后乘以 $2$ , $3$ , $5$ 后放回队列。然而,这样做会出现重复的丑数。例如:
shell
初始化丑数列表 [1]
第一轮: 1 -> 2, 3, 5 ,丑数列表变为 [1, 2, 3, 5]
第二轮: 2 -> 4, 6, 10 ,丑数列表变为 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 10]
第三轮: 3 -> 6, 9, 15 ,出现重复的丑数 6为了避免重复,我们可以用三个指针 $a$ , $b$, $c$ ,分别表示下一个丑数是当前指针指向的丑数乘以 $2$ , $3$ , $5$ 。
利用三个指针生成丑数的算法流程:
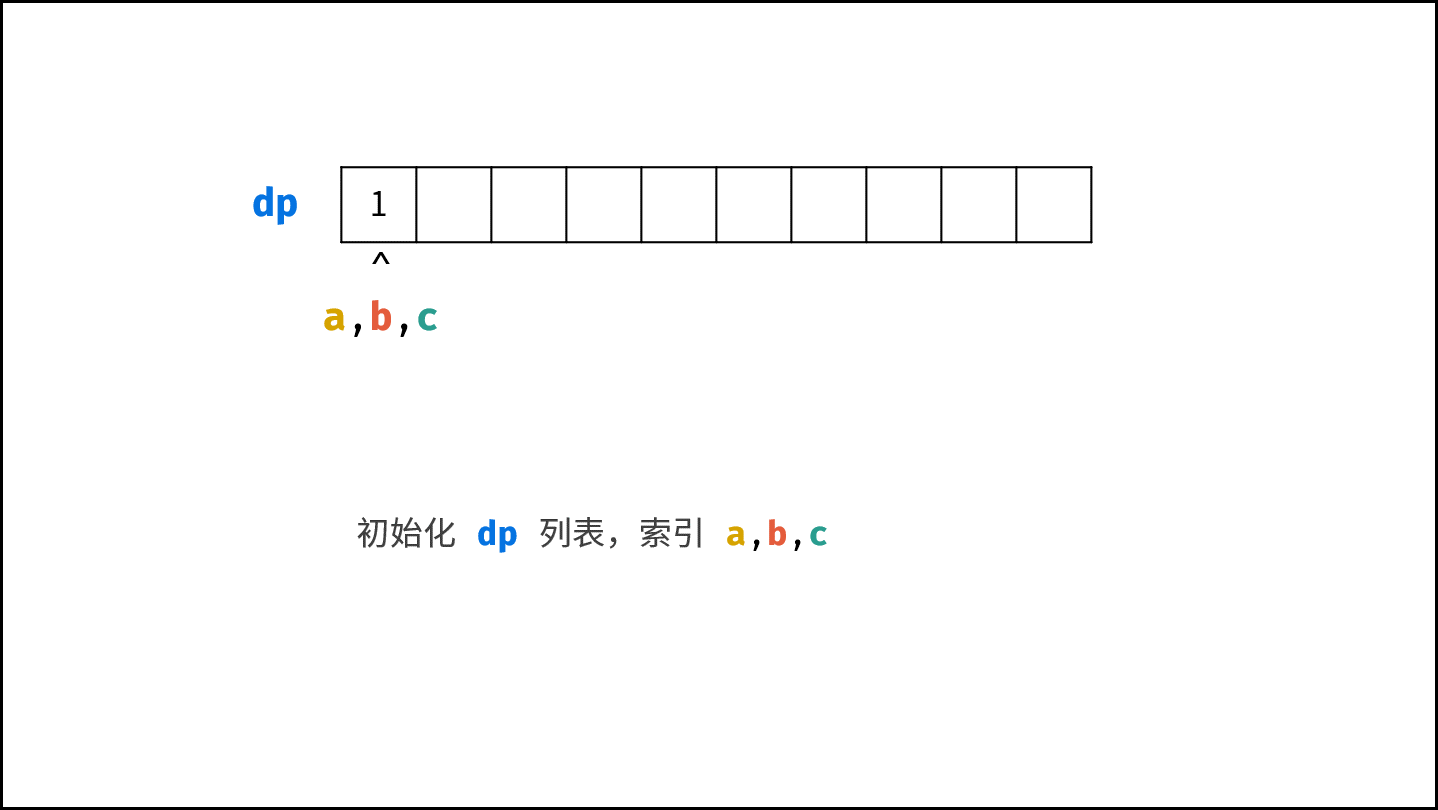
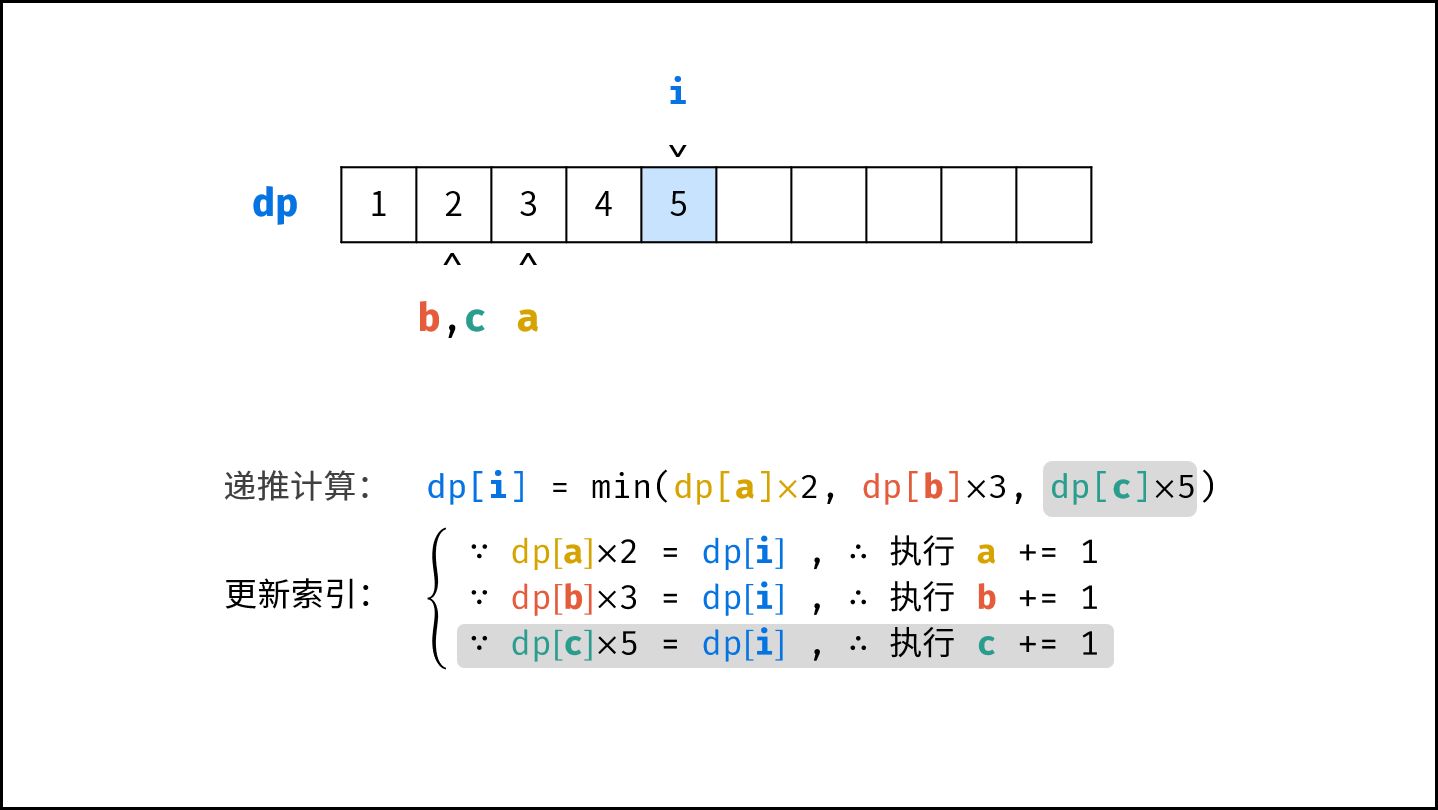
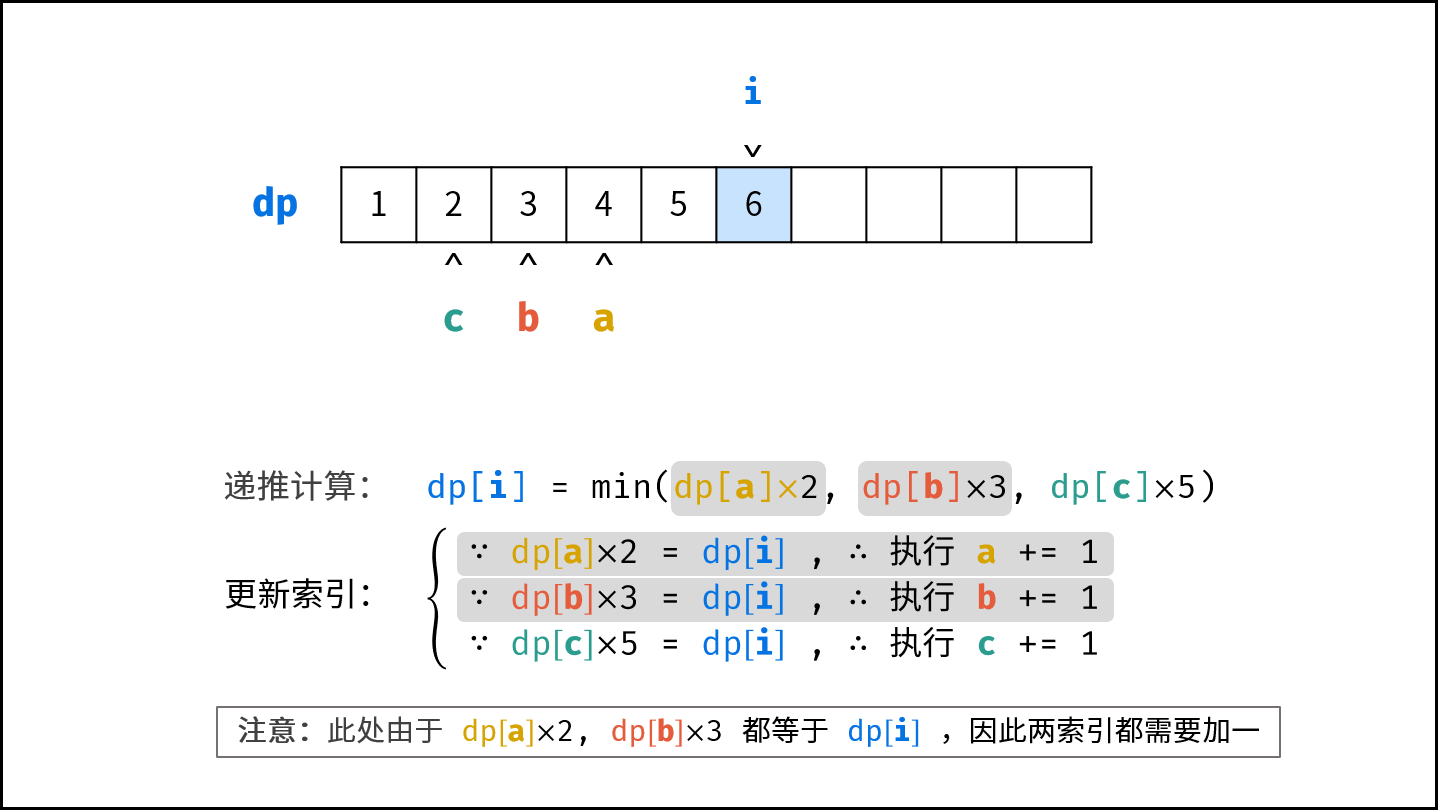
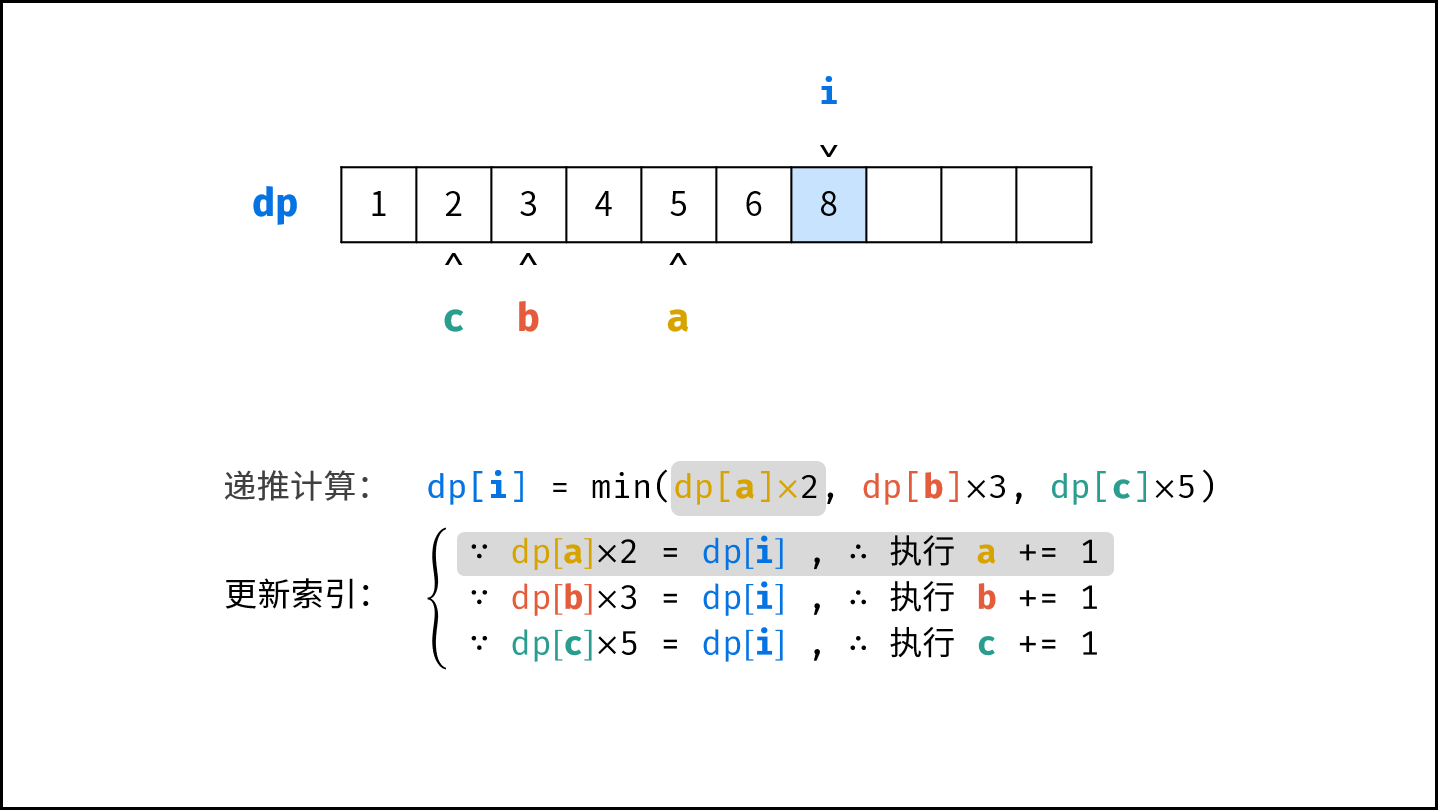
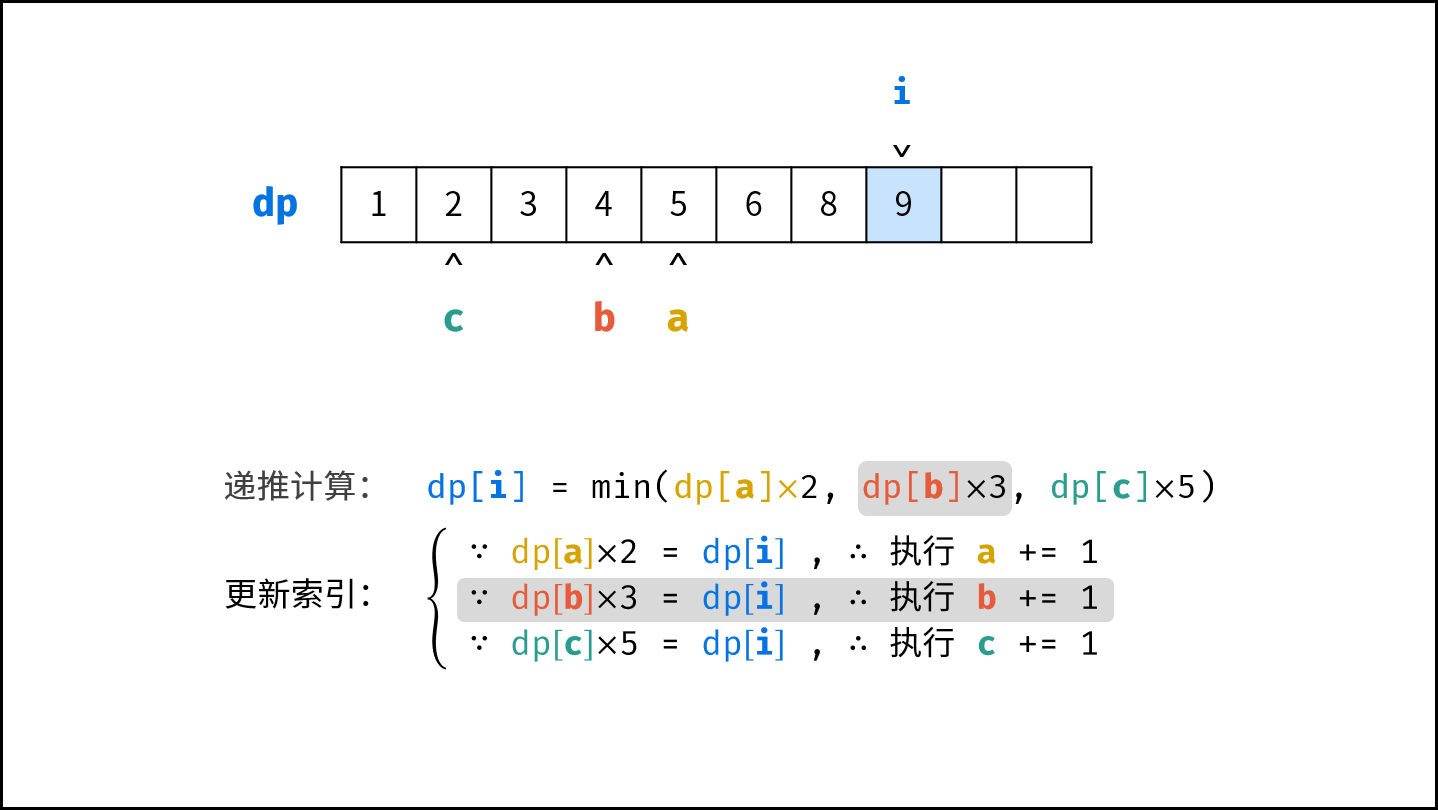
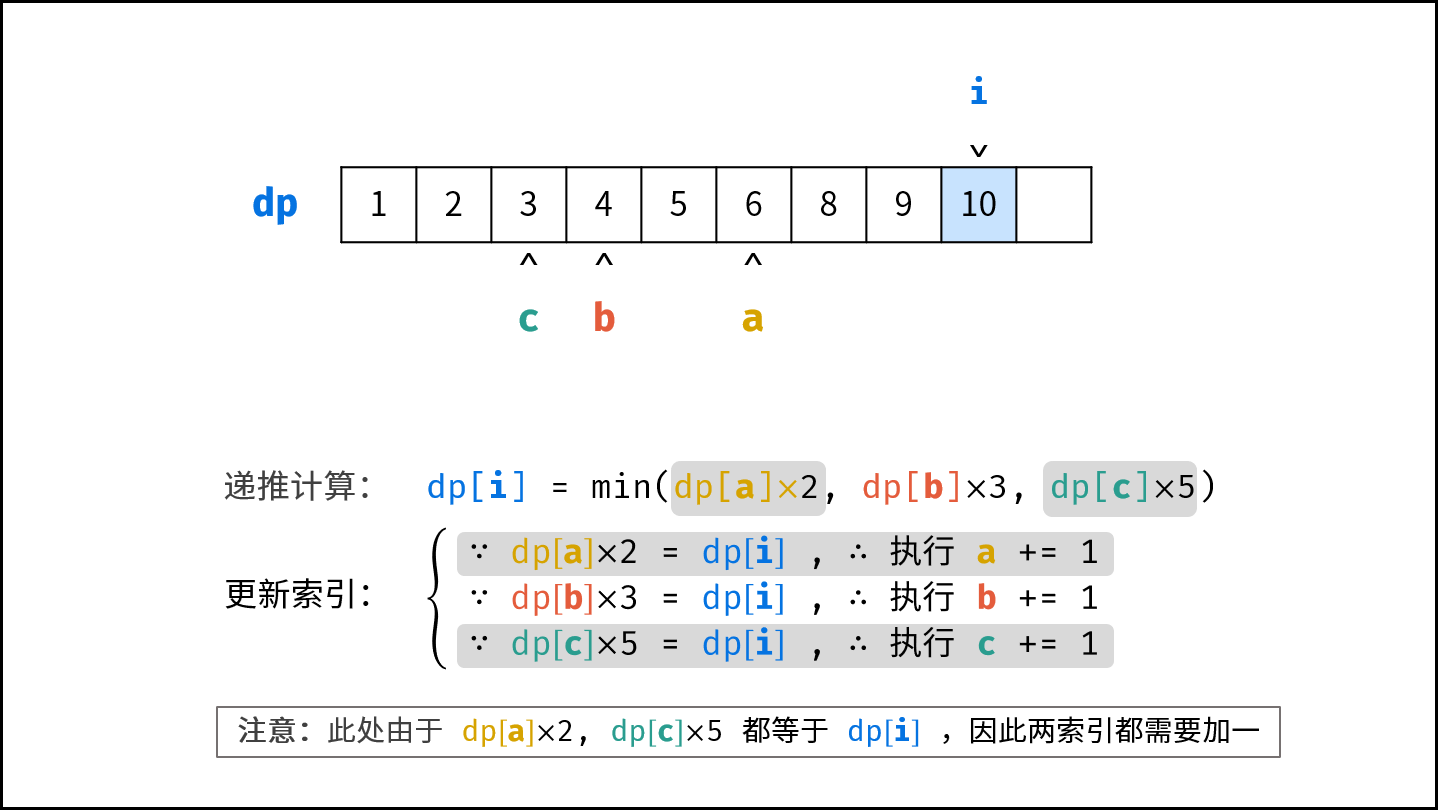
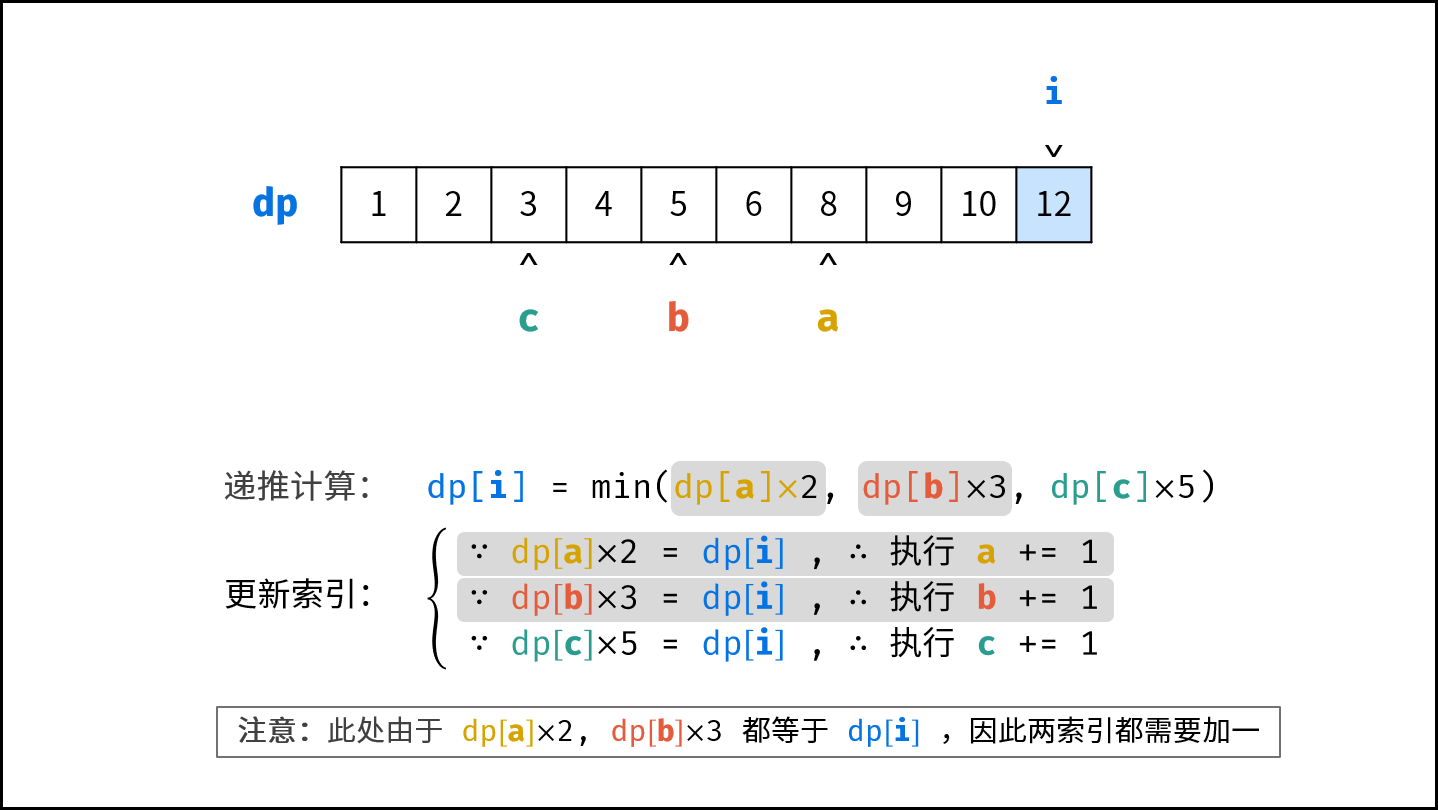
- 初始化丑数列表 $res$ ,首个丑数为 $1$ ,三个指针 $a$ , $b$, $c$ 都指向首个丑数。
- 开启循环生成丑数:
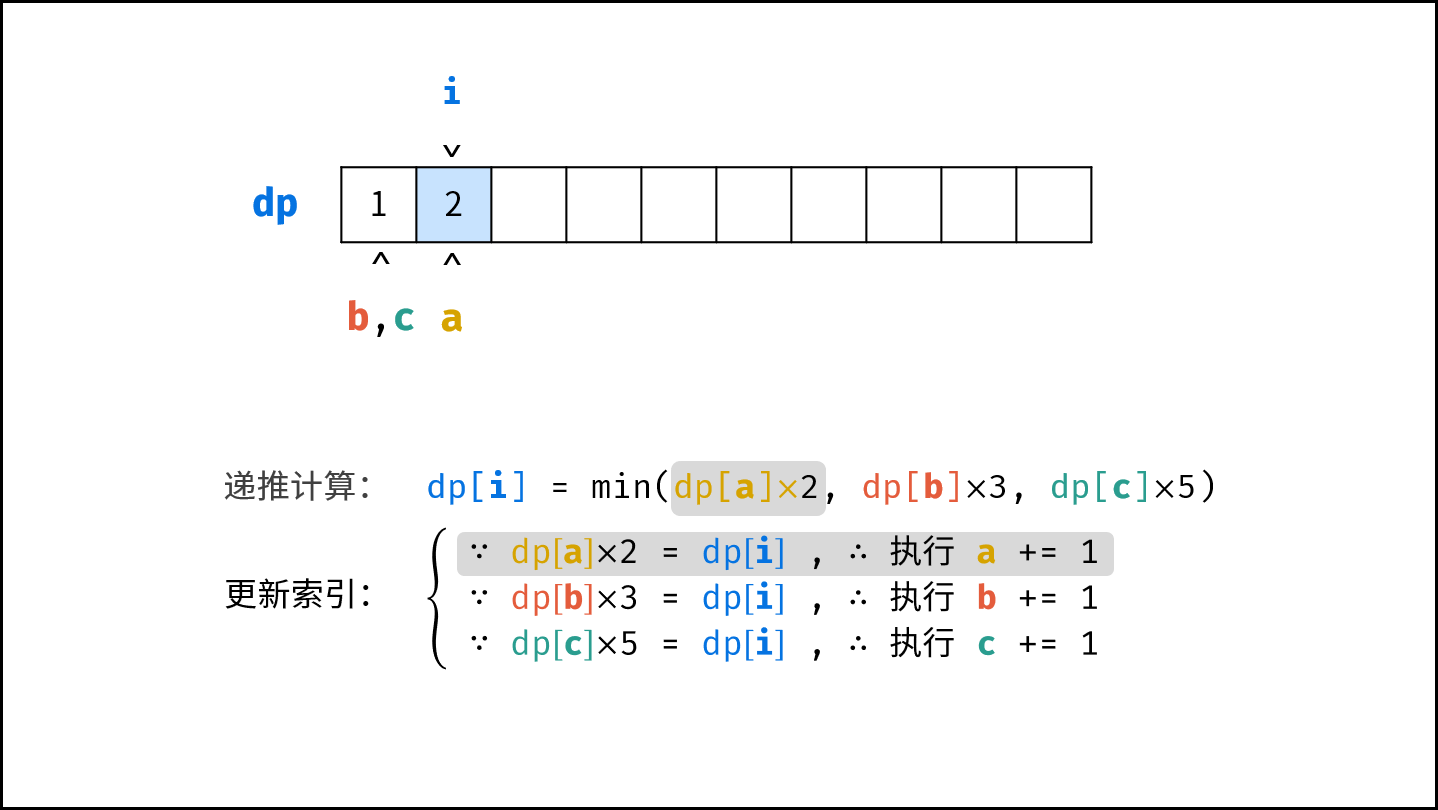
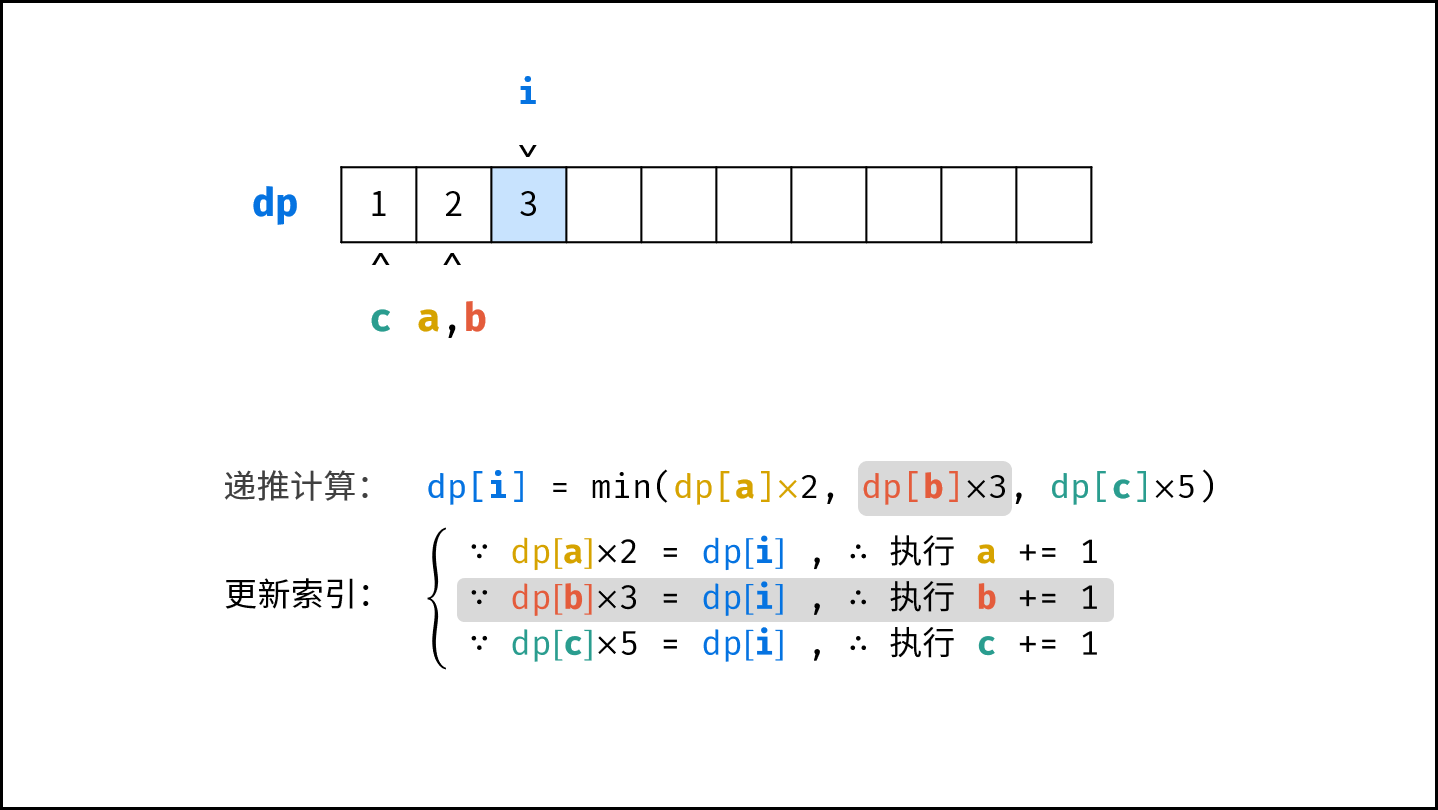
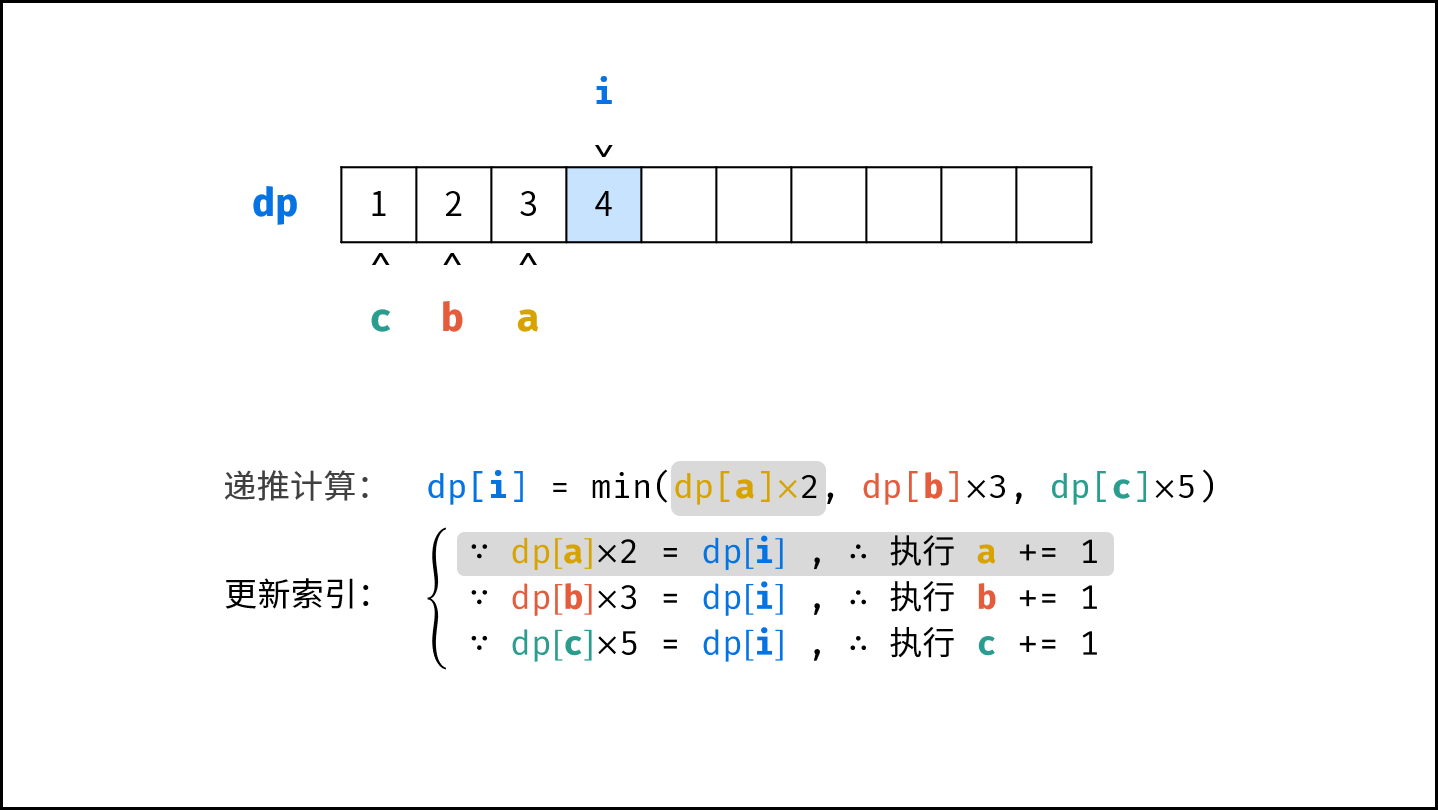
- 计算下一个丑数的候选集 $res[a] \cdot 2$ , $res[b] \cdot 3$ , $res[c] \cdot 5$ 。
- 选择丑数候选集中最小的那个作为下一个丑数,填入 $res$ 。
- 将被选中的丑数对应的指针向右移动一格。
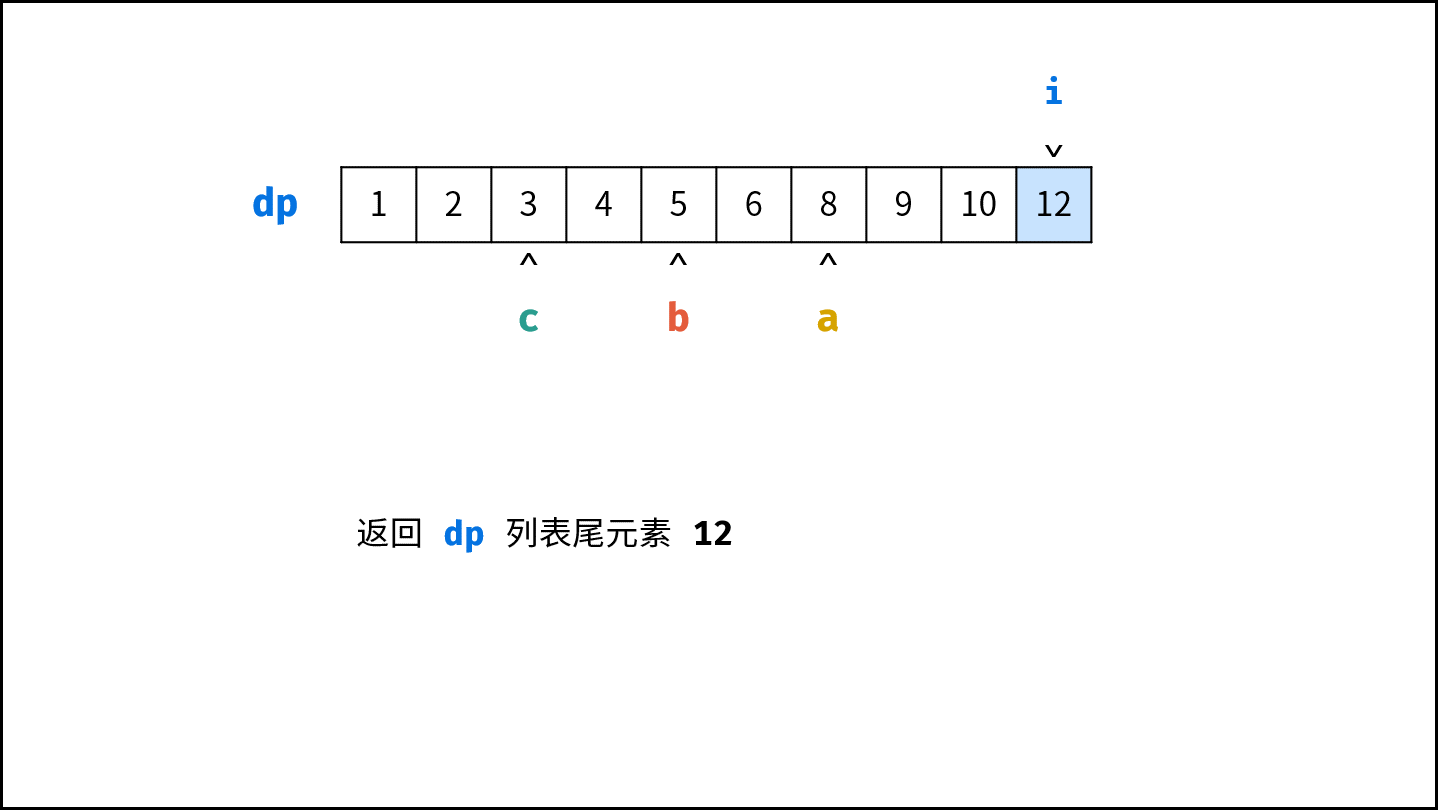
- 返回 $res$ 的最后一个元素即可。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def nthUglyNumber(self, n: int) -> int:
res, a, b, c = [1] * n, 0, 0, 0
for i in range(1, n):
n2, n3, n5 = res[a] * 2, res[b] * 3, res[c] * 5
res[i] = min(n2, n3, n5)
if res[i] == n2: a += 1
if res[i] == n3: b += 1
if res[i] == n5: c += 1
return res[-1]Java
class Solution {
public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
int[] res = new int[n];
res[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int n2 = res[a] * 2, n3 = res[b] * 3, n5 = res[c] * 5;
res[i] = Math.min(Math.min(n2, n3), n5);
if (res[i] == n2) a++;
if (res[i] == n3) b++;
if (res[i] == n5) c++;
}
return res[n - 1];
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
int res[n];
res[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int n2 = res[a] * 2, n3 = res[b] * 3, n5 = res[c] * 5;
res[i] = min(min(n2, n3), n5);
if (res[i] == n2) a++;
if (res[i] == n3) b++;
if (res[i] == n5) c++;
}
return res[n - 1];
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(n)$ : 计算 $res$ 列表需遍历 $n-1$ 轮。
- 空间复杂度 $O(n)$ : 长度为 $n$ 的 $res$ 列表使用 $O(n)$ 的额外空间。