解题思路:
普通栈的 push() 和 pop() 函数的复杂度为 $O(1)$ ;而获取栈最小值 getMin() 函数需要遍历整个栈,复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。
本题难点: 将 getMin() 函数复杂度降为 $O(1)$ 。可借助辅助栈实现:
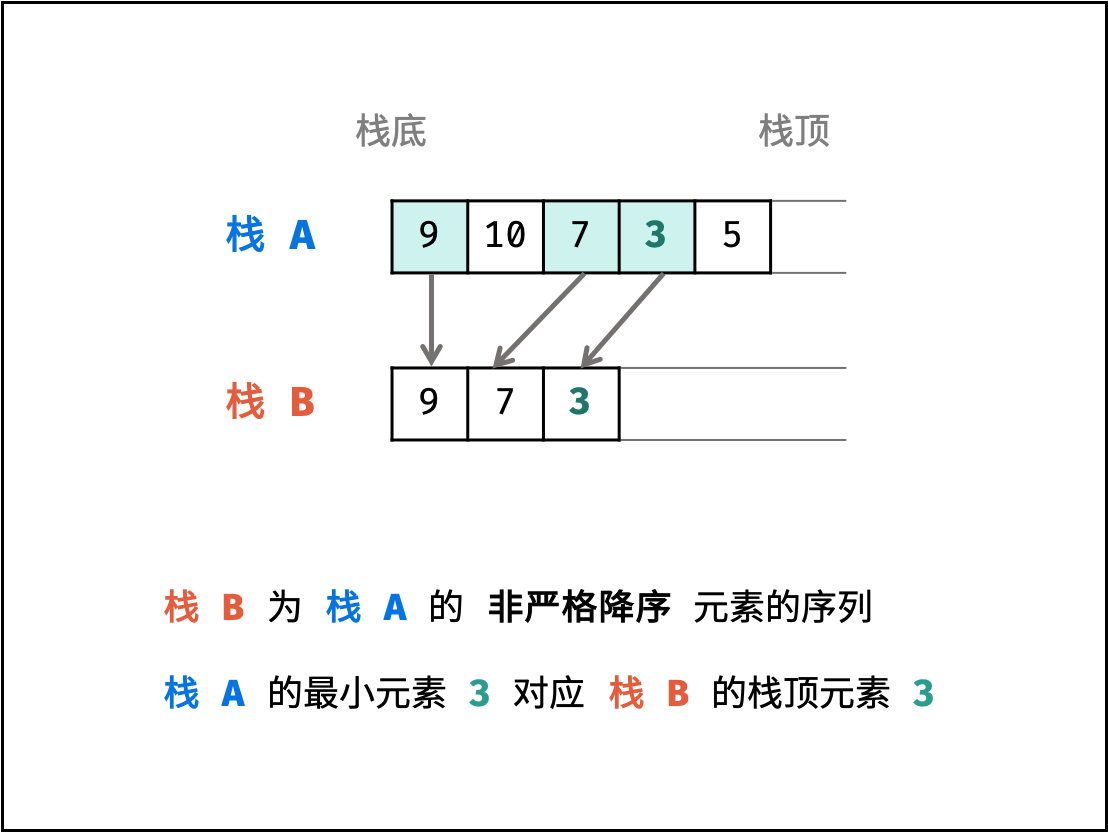
- 数据栈
A: 栈A用于存储所有元素,保证入栈push()函数、出栈pop()函数、获取栈顶top()函数的正常逻辑。 - 辅助栈
B: 栈B中存储栈A中所有 非严格降序 元素的子序列,则栈A中的最小元素始终对应栈B的栈顶元素。此时,getMin()函数只需返回栈B的栈顶元素即可。
因此,只需设法维护好 栈 B 的元素,使其保持是栈 A 的非严格降序元素的子序列,即可实现 getMin() 函数的 $O(1)$ 复杂度。
函数设计:
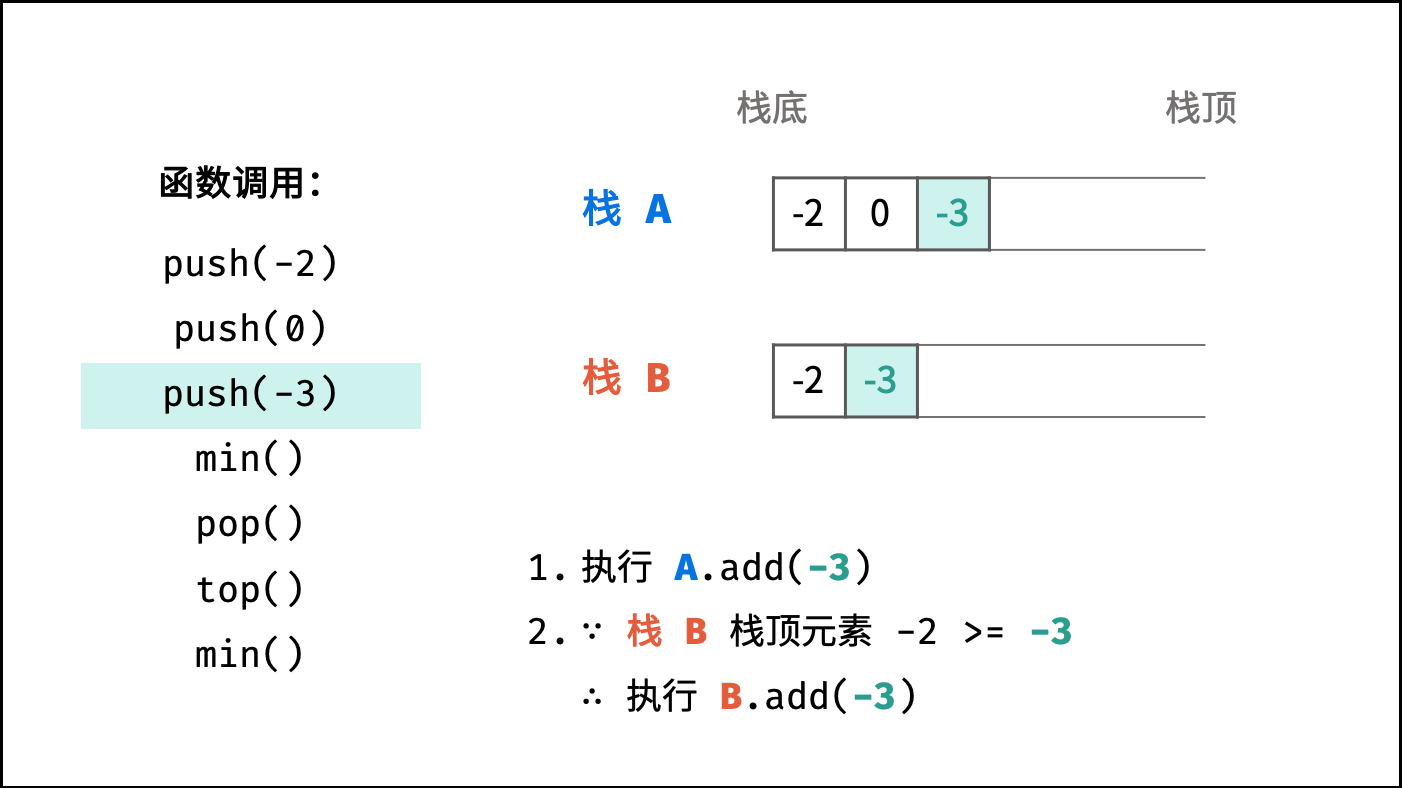
push(x) 函数: 重点为保持栈 B 的元素是 非严格降序 的;
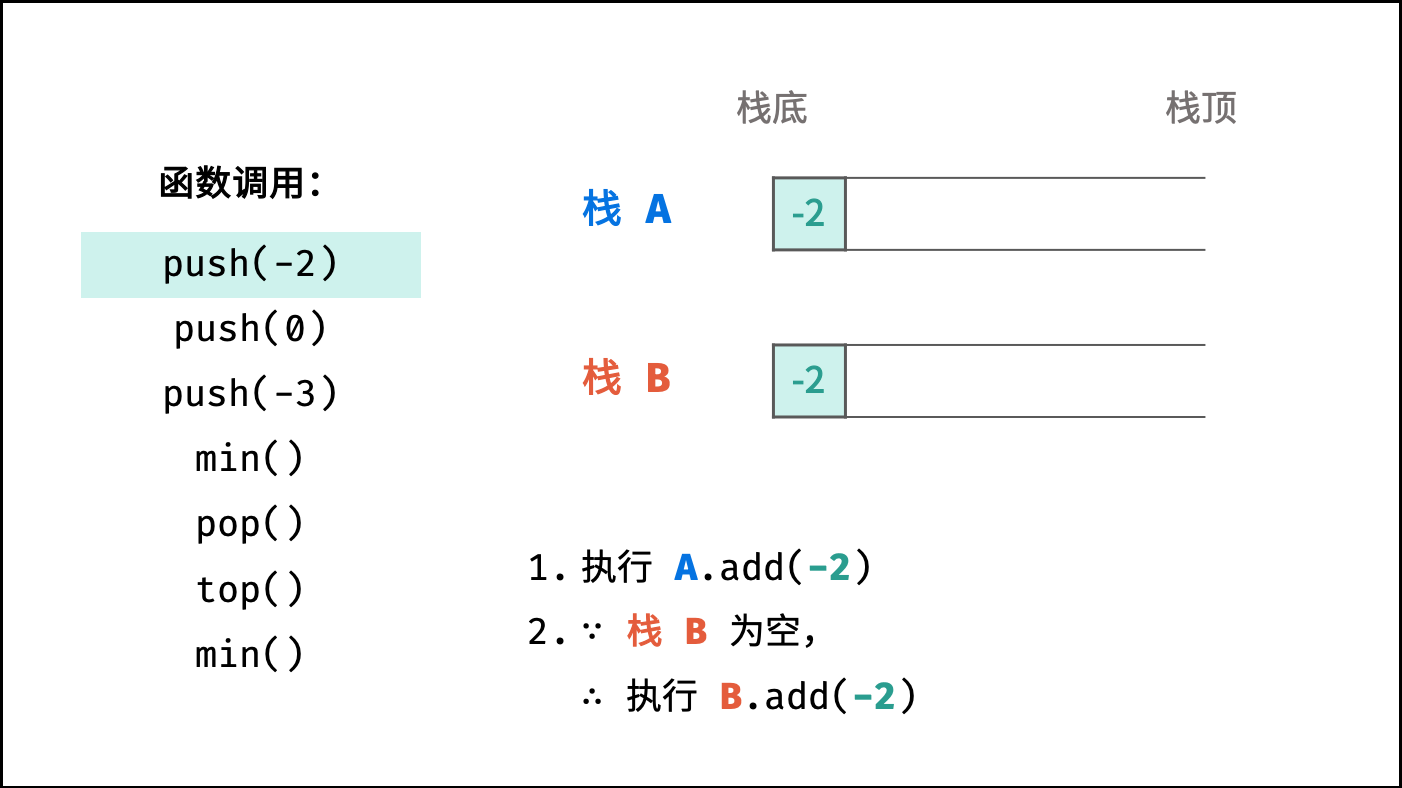
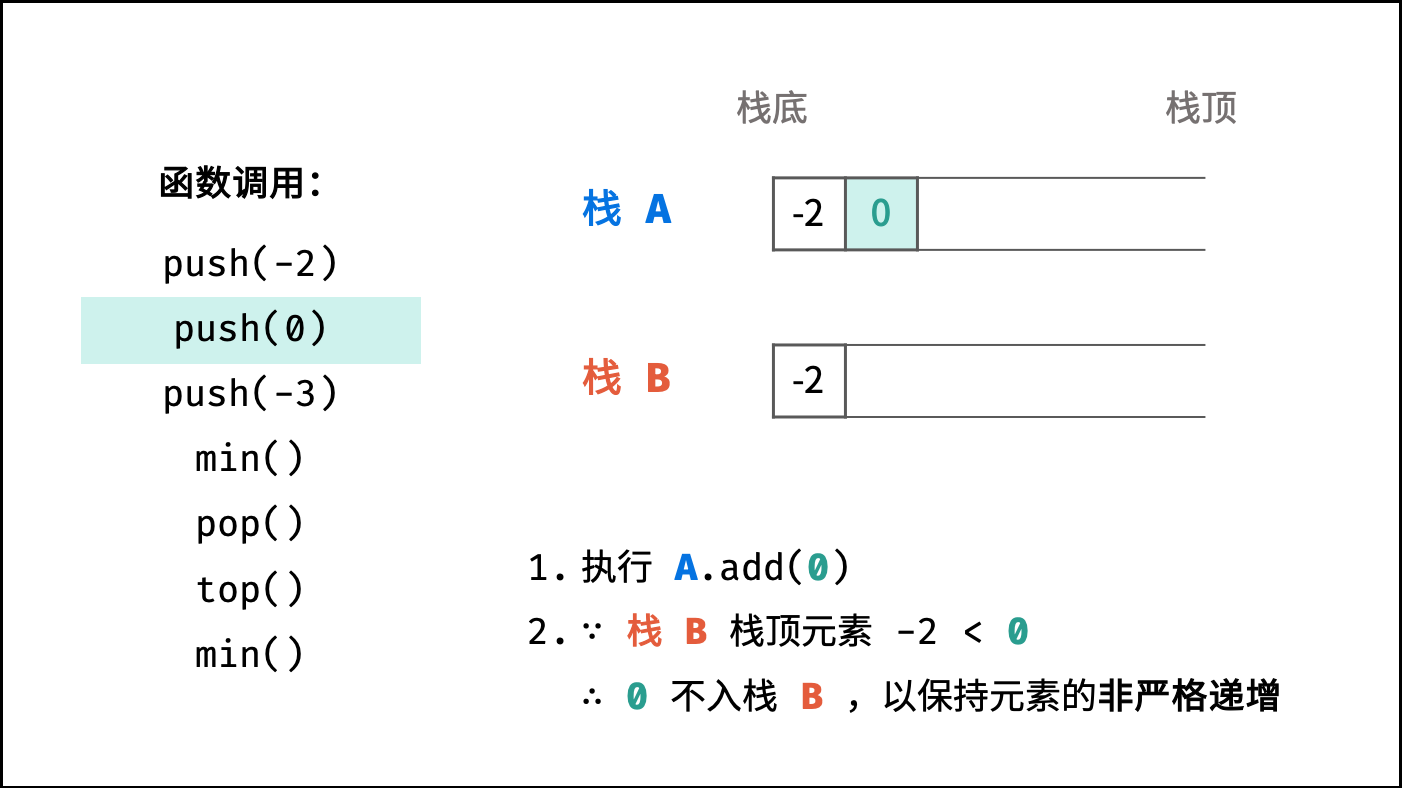
- 执行「元素
x压入栈A」 ; - 若「栈
B为空」或「x$\leq$ 栈B的栈顶元素」,则执行「元素x压入栈B」 ;
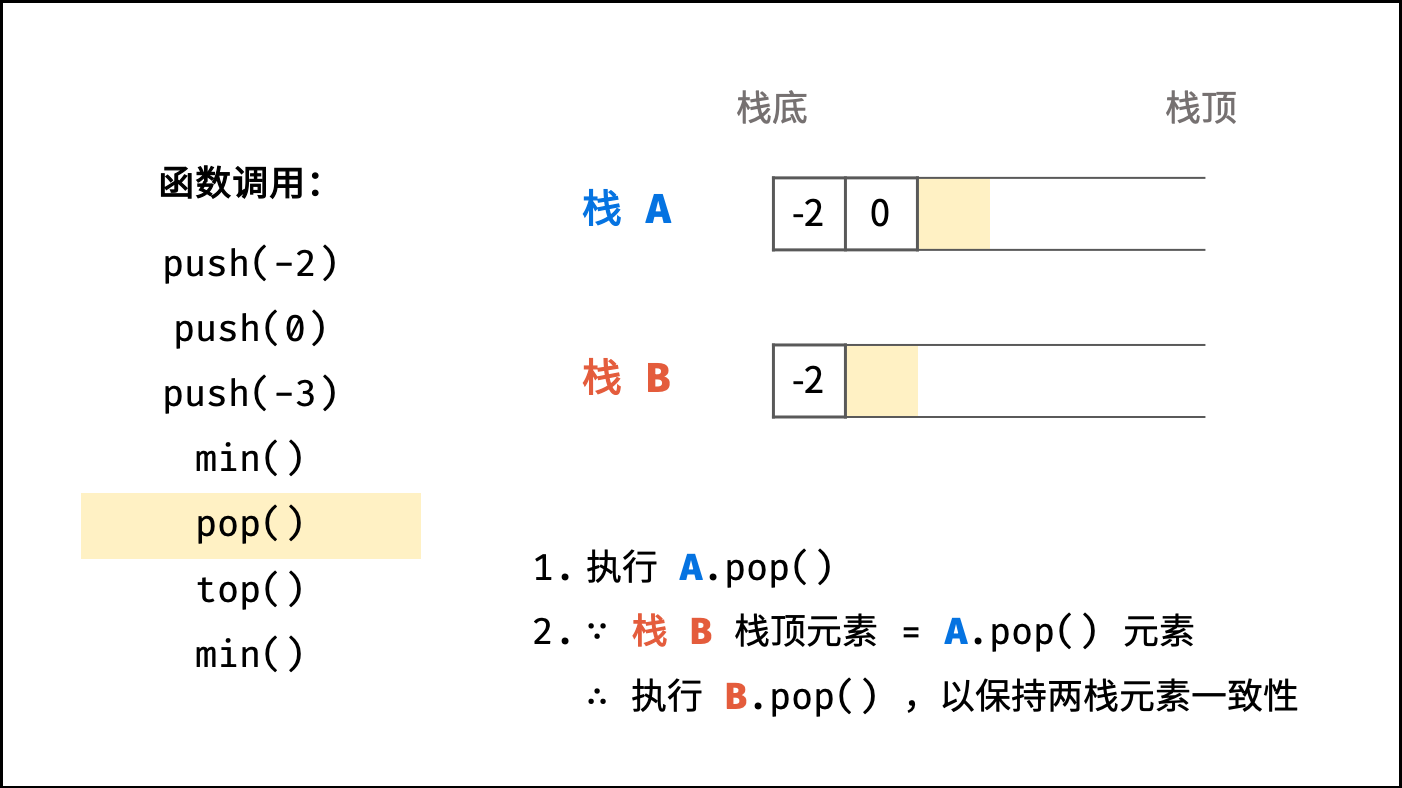
pop() 函数: 重点为保持栈 A , B 的 元素一致性 ;
- 执行「栈
A元素出栈」,将出栈元素记为y; - 若 「
y等于栈B的栈顶元素」,则执行「栈B元素出栈」;
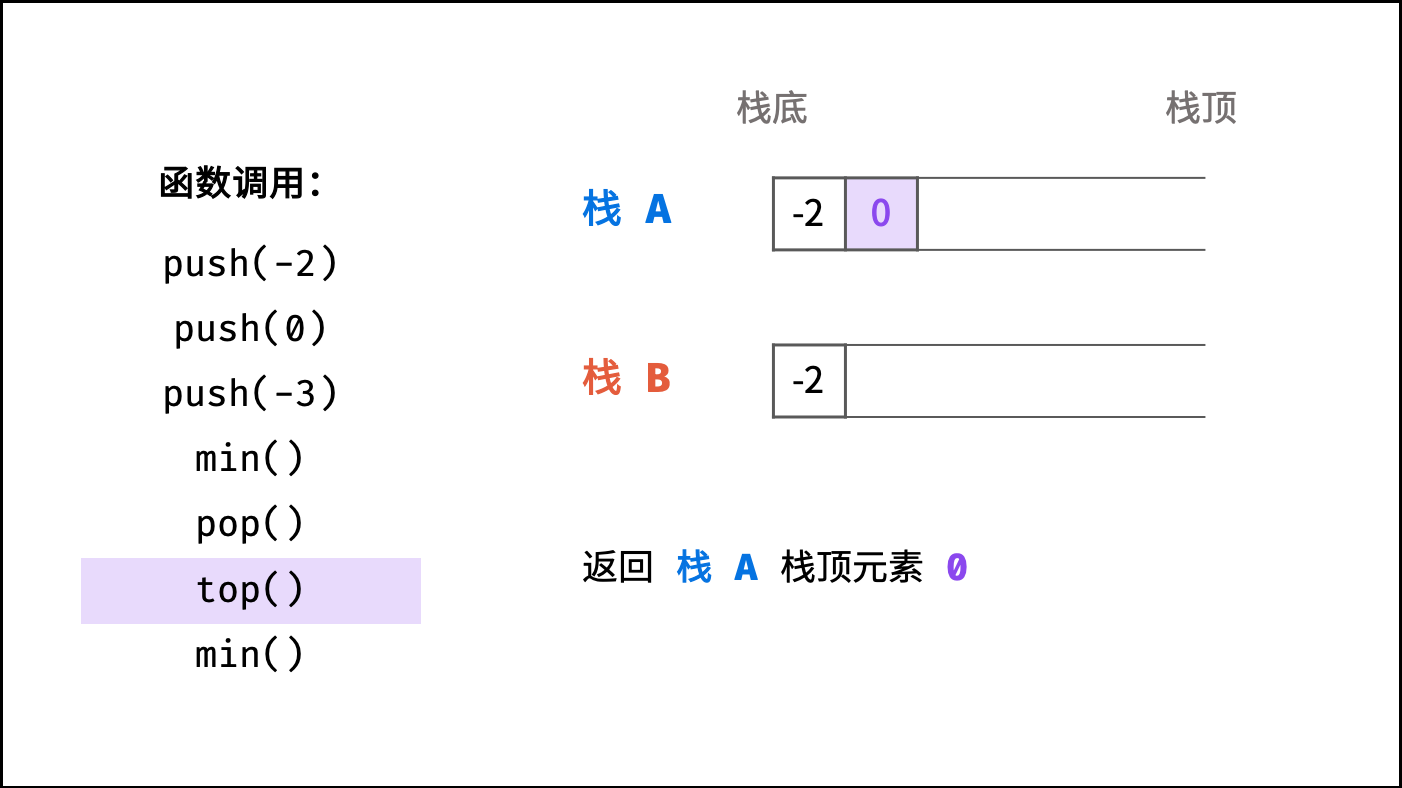
top() 函数: 直接返回栈 A 的栈顶元素,即返回 A.peek() ;
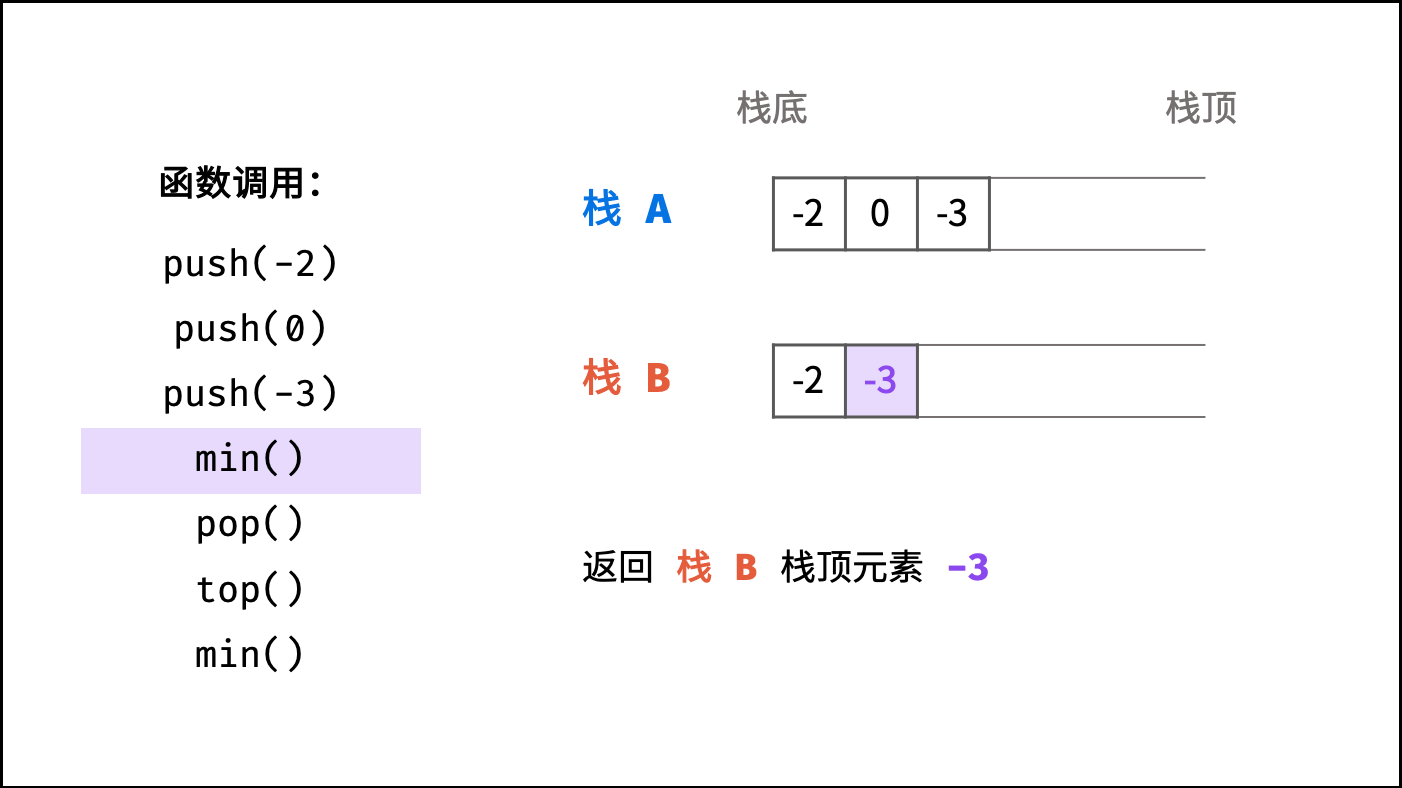
getMin() 函数: 直接返回栈 B 的栈顶元素,即返回 B.peek() ;
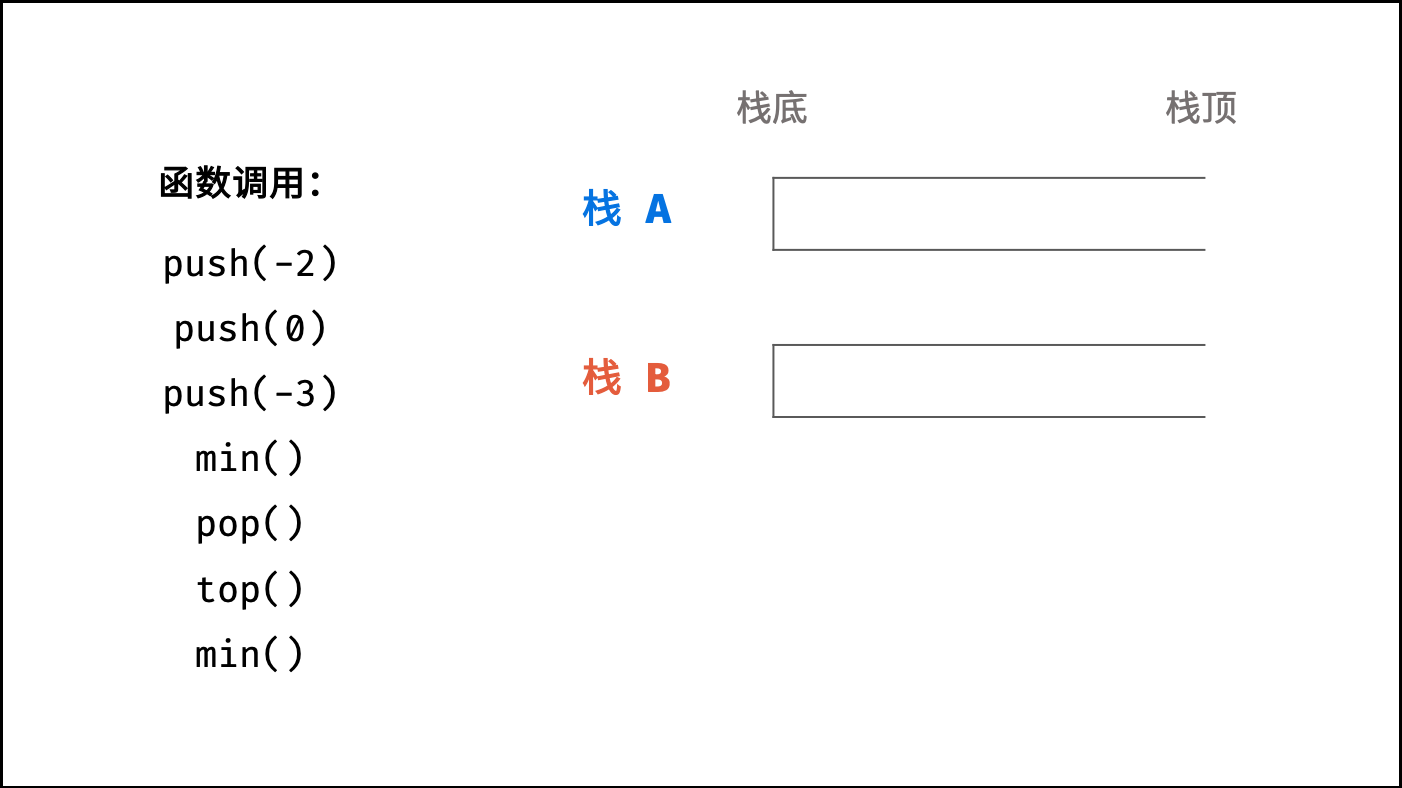
下图中的
min()对应本题的getMin()。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,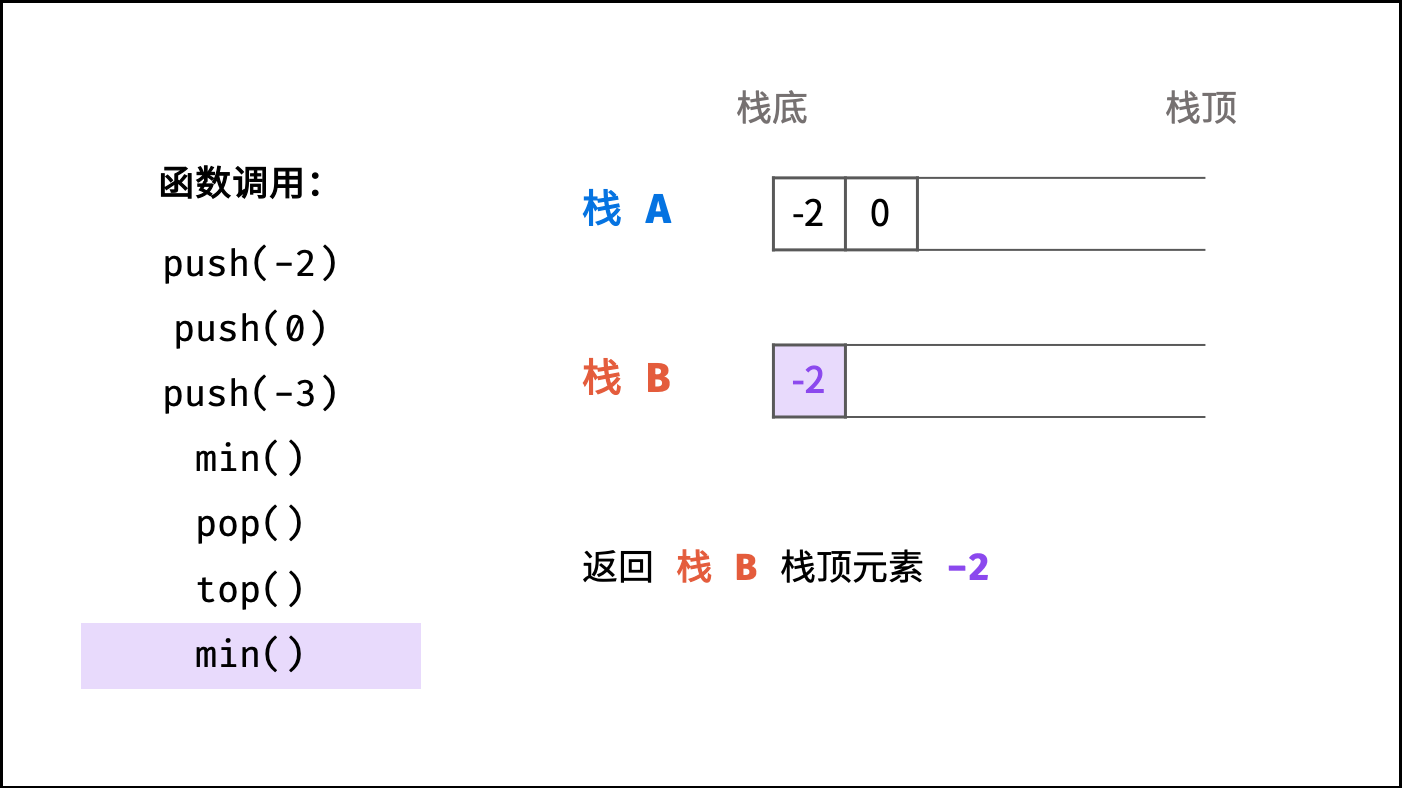 >
>
采用 “非严格” 降序原因:
在栈 A 具有 重复 最小值元素时,非严格降序可防止栈 B 提前弹出最小值元素,示例如下:
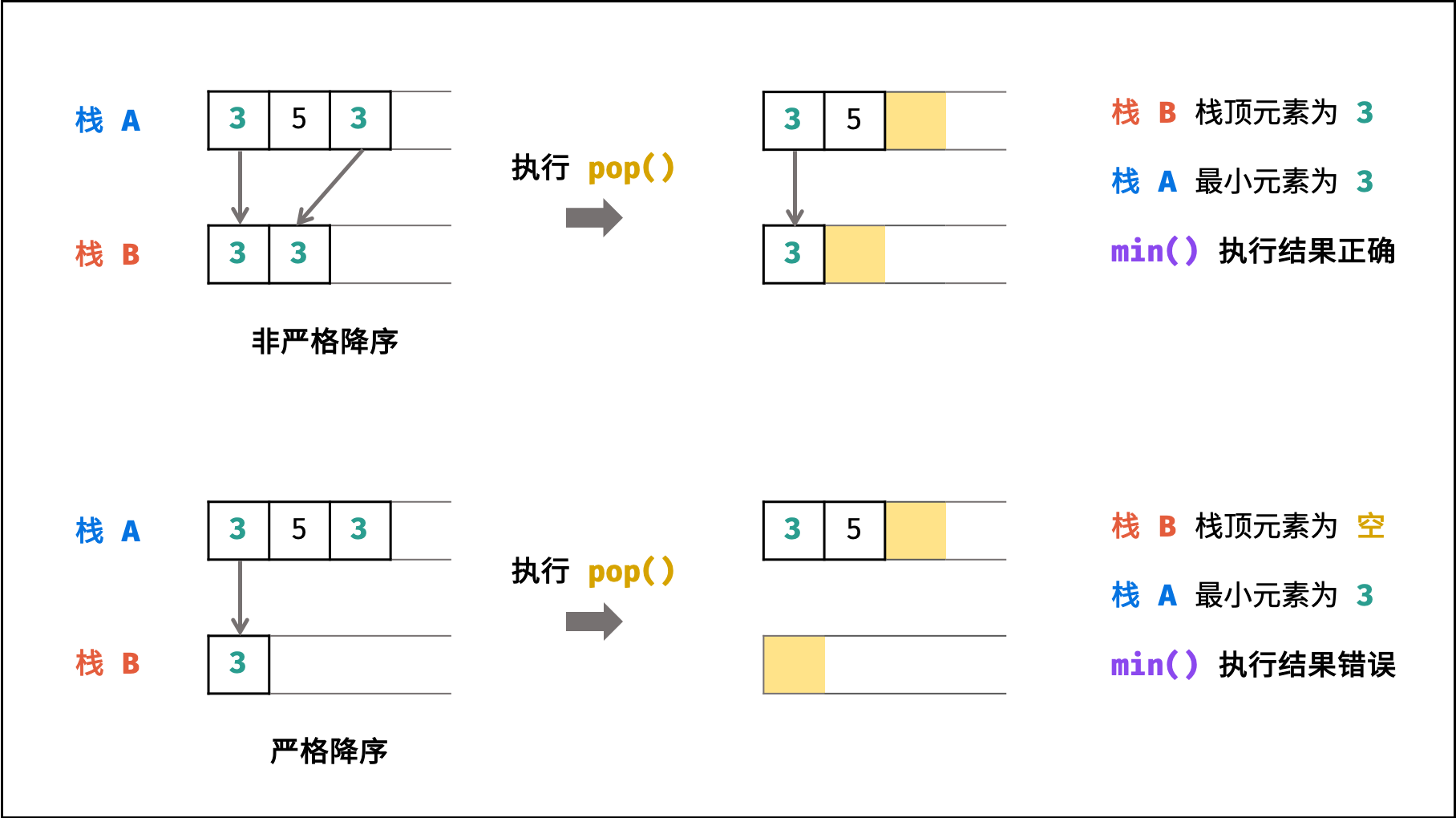
代码:
Java 代码中,由于 Stack 中存储的是 int 的包装类 Integer ,因此需要使用 equals() 代替 == ,以比较对象的值。
Python
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.A, self.B = [], []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.A.append(x)
if not self.B or self.B[-1] >= x:
self.B.append(x)
def pop(self) -> None:
if self.A.pop() == self.B[-1]:
self.B.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.A[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.B[-1]Java
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> A, B;
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.add(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek() >= x)
B.add(x);
}
public void pop() {
if(A.pop().equals(B.peek()))
B.pop();
}
public int top() {
return A.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return B.peek();
}
}C++
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> A, B;
MinStack() {}
void push(int x) {
A.push(x);
if(B.empty() || B.top() >= x)
B.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(A.top() == B.top())
B.pop();
A.pop();
}
int top() {
return A.top();
}
int getMin() {
return B.top();
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(1)$ :
push(),pop(),top(),getMin()四个函数的时间复杂度均为常数级别。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 当共有 $N$ 个待入栈元素时,辅助栈
B最差情况下存储 $N$ 个元素,使用 $O(N)$ 额外空间。