解题思路:
树的遍历方式总体分为两类:
- 深度优先搜索(DFS): 先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历;
- 广度优先搜索(BFS): 层序遍历;
求树的深度需要遍历树的所有节点,本文将介绍基于 后序遍历(DFS) 和 层序遍历(BFS) 的两种解法。
方法一:后序遍历(DFS)
树的后序遍历 / 深度优先搜索往往利用 递归 或 栈 实现,本文使用递归实现。
关键点: 此树的深度和其左(右)子树的深度之间的关系。显然,此树的深度 等于 左子树的深度 与 右子树的深度 中的 最大值 $+1$ 。
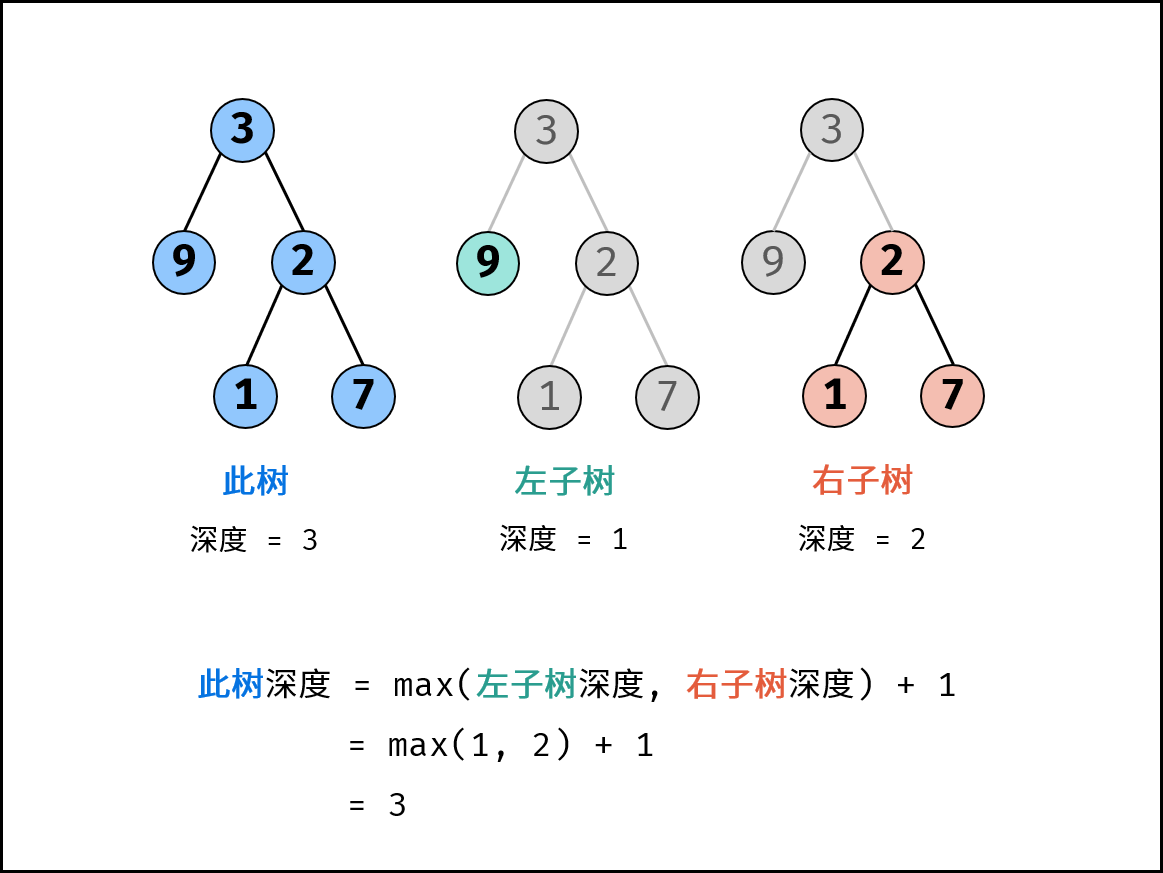
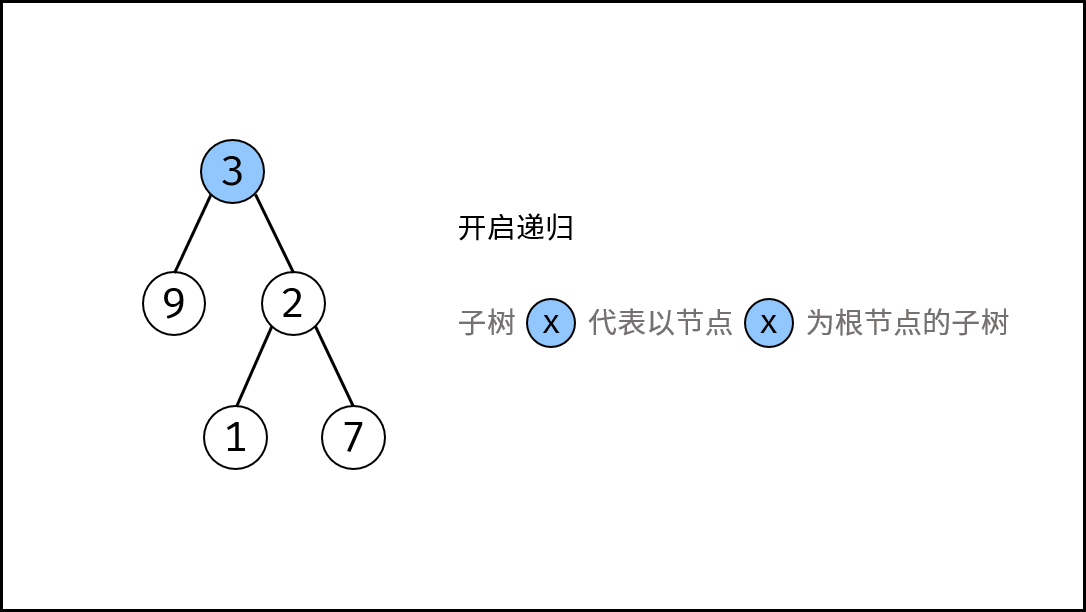
算法解析:
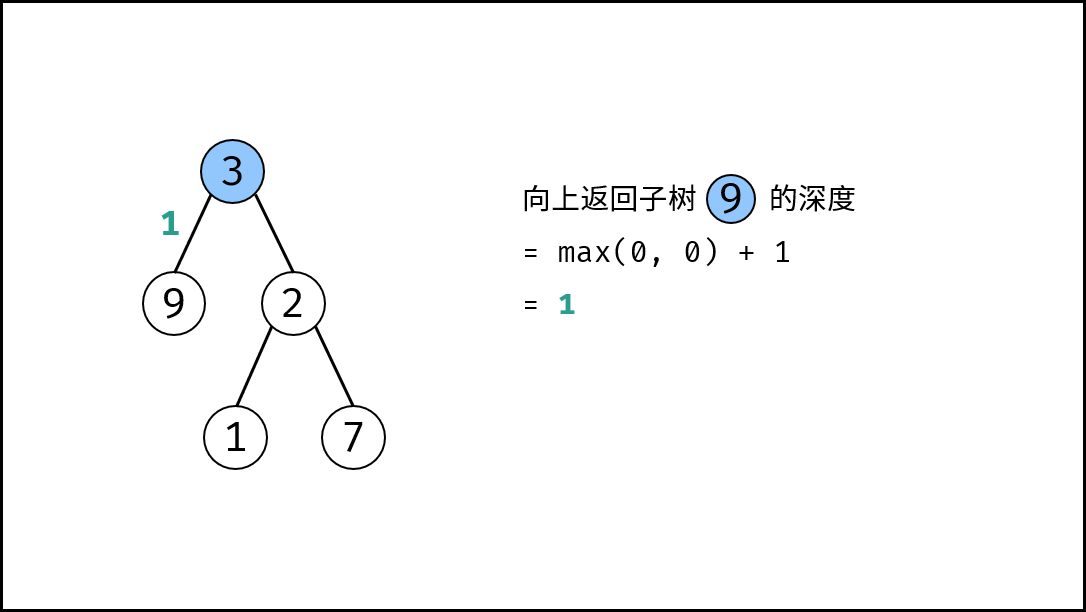
- 终止条件: 当
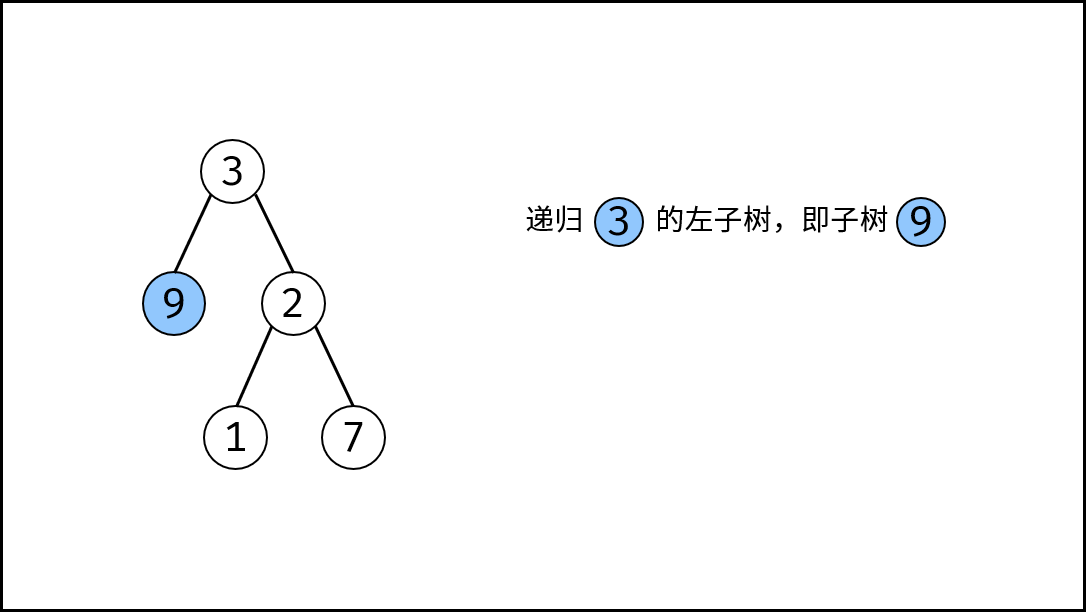
root为空,说明已越过叶节点,因此返回 深度 $0$ 。 - 递推工作: 本质上是对树做后序遍历。
- 计算节点
root的 左子树的深度 ,即调用calculateDepth(root.left); - 计算节点
root的 右子树的深度 ,即调用calculateDepth(root.right);
- 计算节点
- 返回值: 返回 此树的深度 ,即
max(calculateDepth(root.left), calculateDepth(root.right)) + 1。
< ,
, ,
, ,
,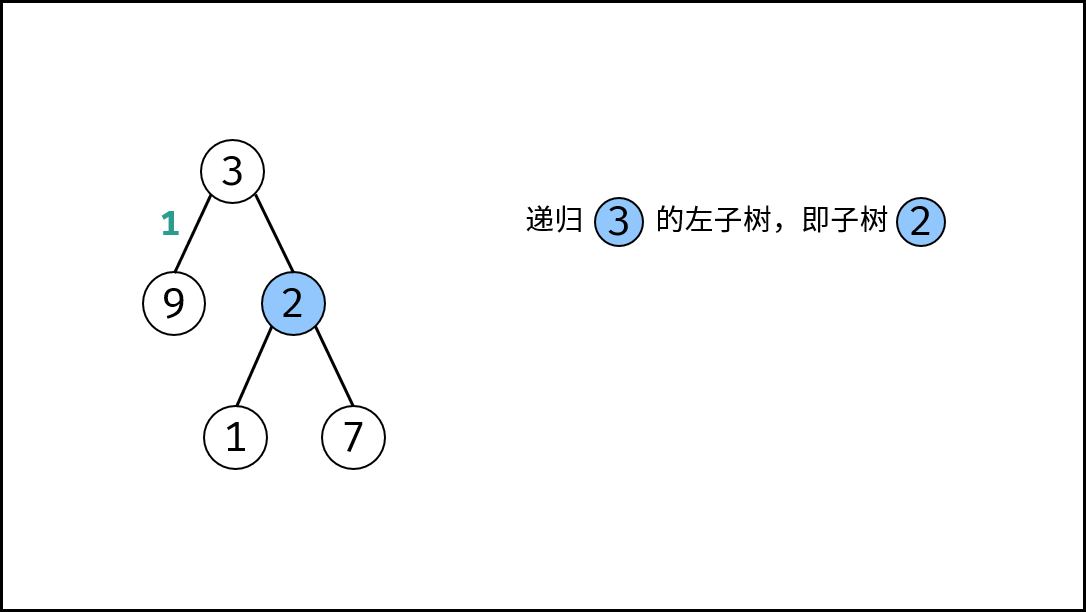 ,
,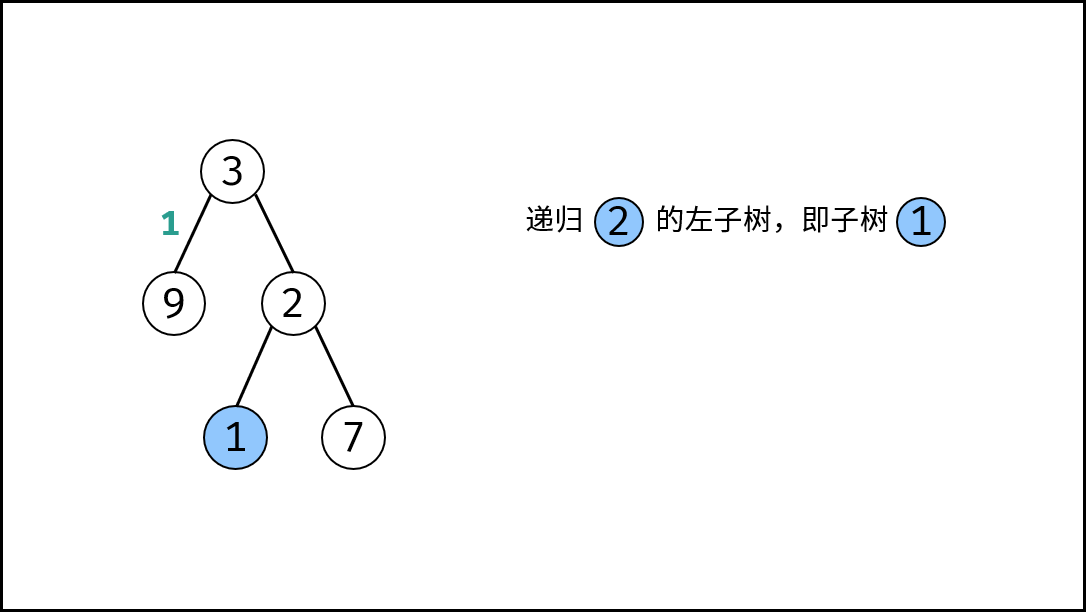 ,
,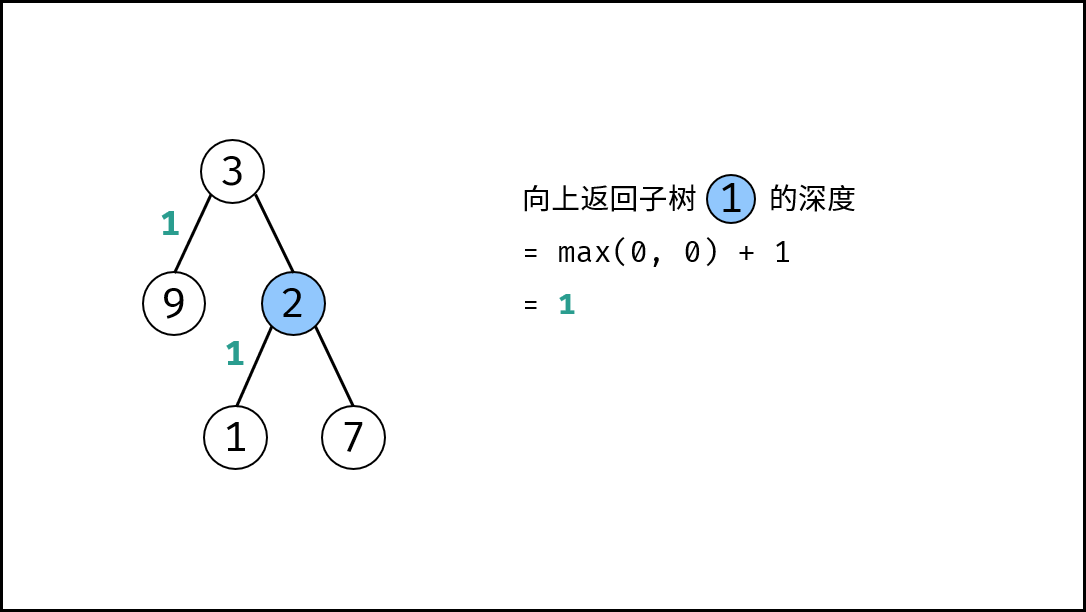 ,
,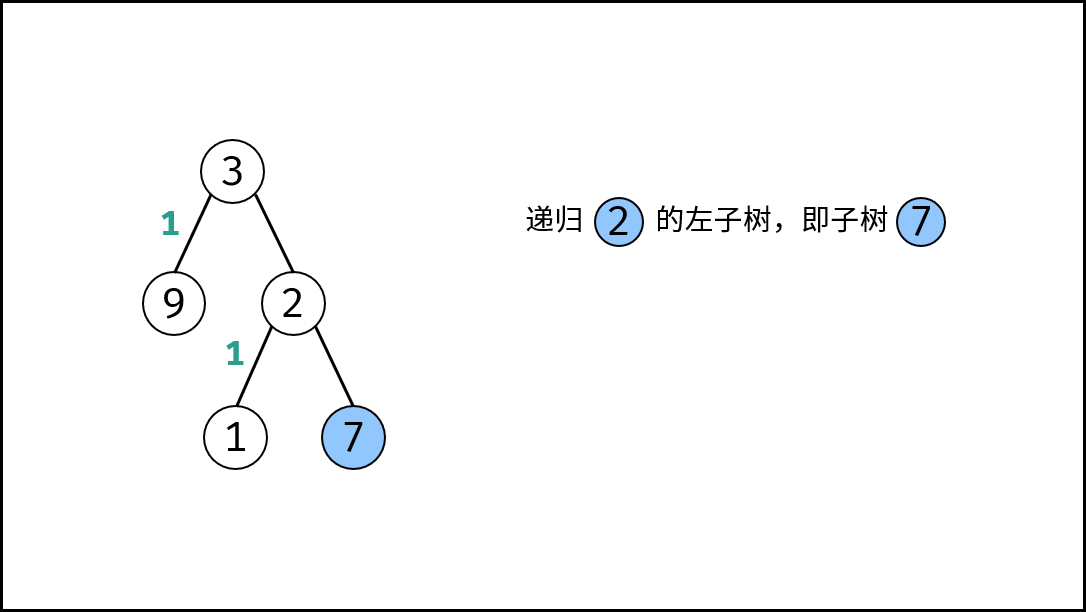 ,
,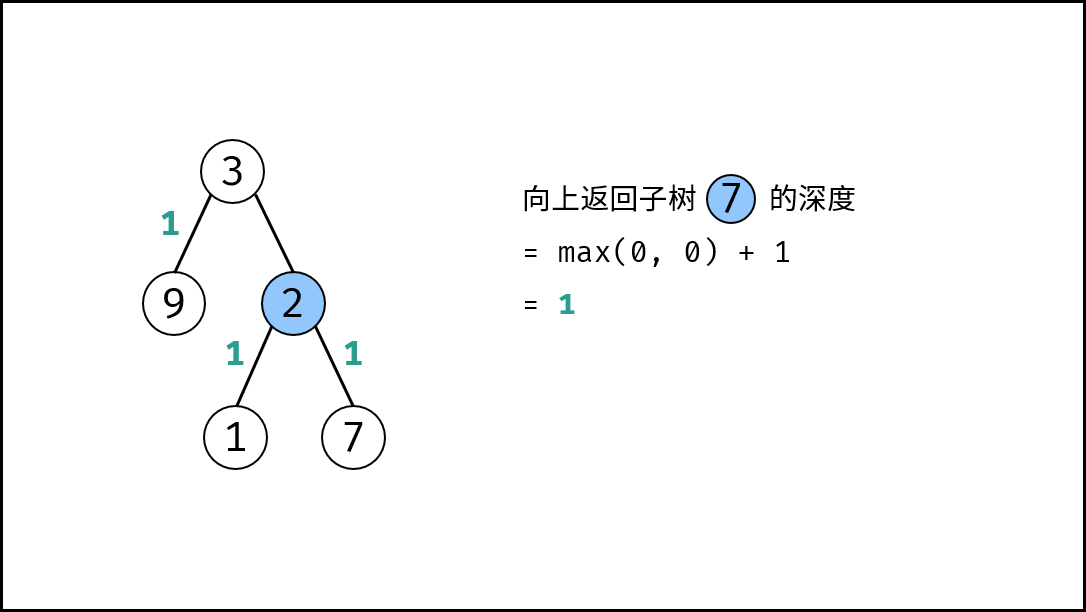 ,
,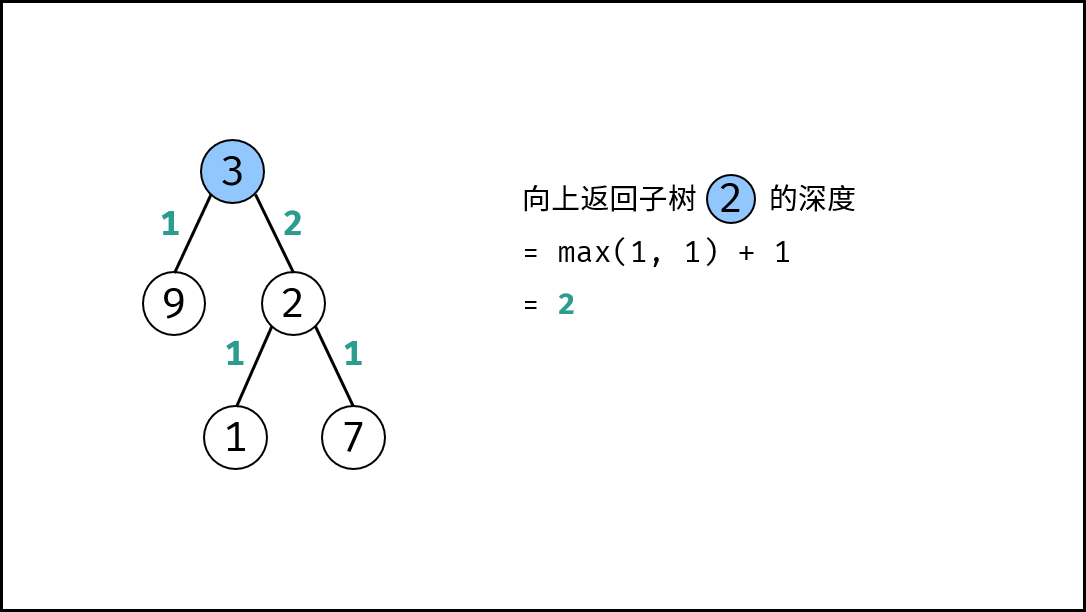 ,
,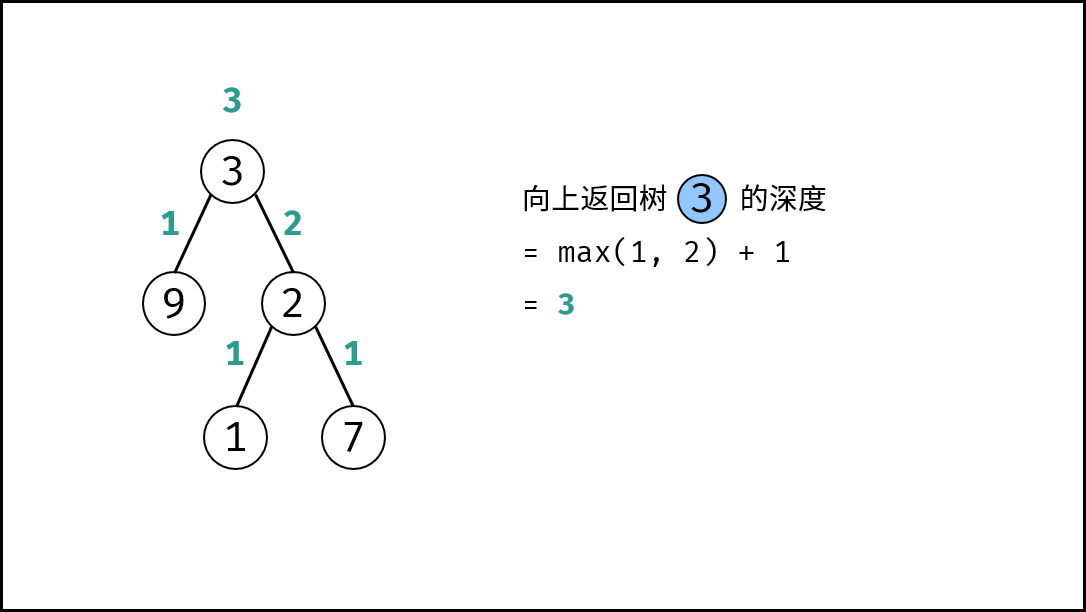 >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def calculateDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root: return 0
return max(self.calculateDepth(root.left), self.calculateDepth(root.right)) + 1Java
class Solution {
public int calculateDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(calculateDepth(root.left), calculateDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
int calculateDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
return max(calculateDepth(root->left), calculateDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : $N$ 为树的节点数量,计算树的深度需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下(当树退化为链表时),递归深度可达到 $N$ 。
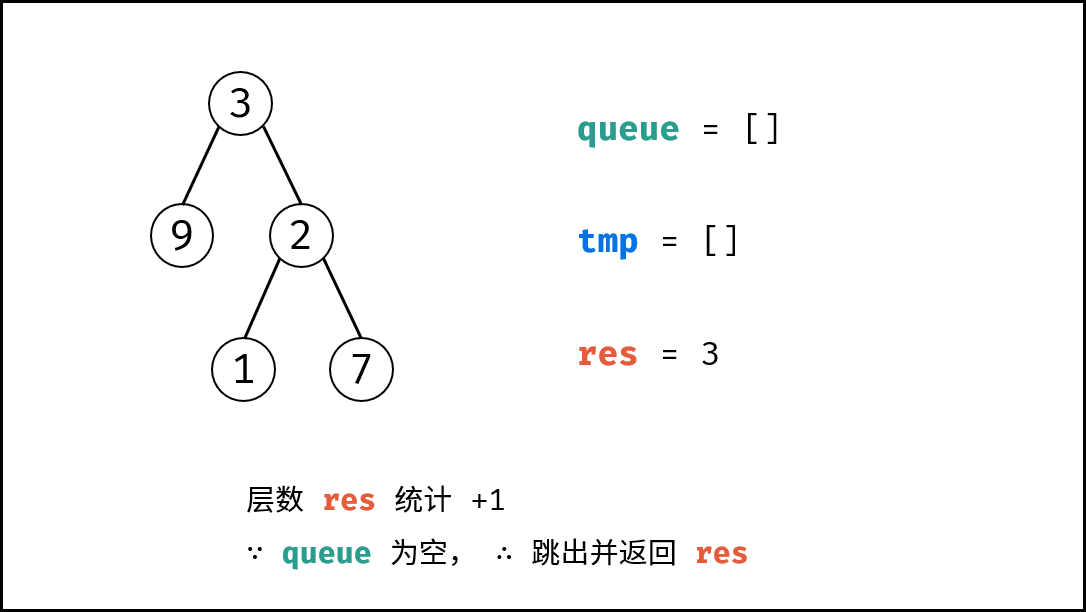
方法二:层序遍历(BFS)
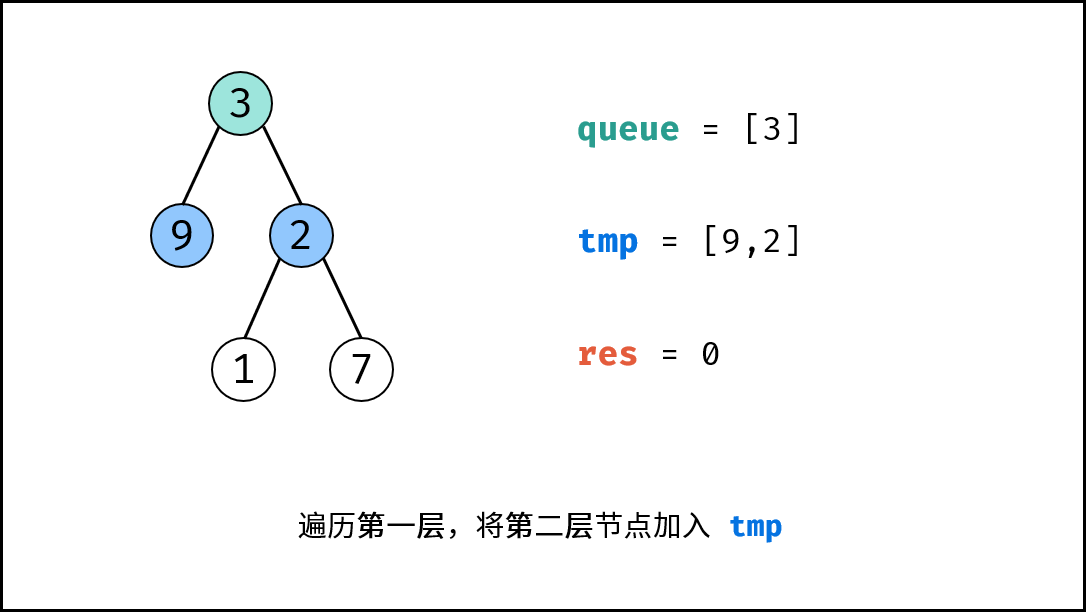
树的层序遍历 / 广度优先搜索往往利用 队列 实现。
关键点: 每遍历一层,则计数器 $+1$ ,直到遍历完成,则可得到树的深度。
算法解析:
- 特例处理: 当
root为空,直接返回 深度 $0$ 。 - 初始化: 队列
queue(加入根节点root),计数器res = 0。 - 循环遍历: 当
queue为空时跳出。- 初始化一个空列表
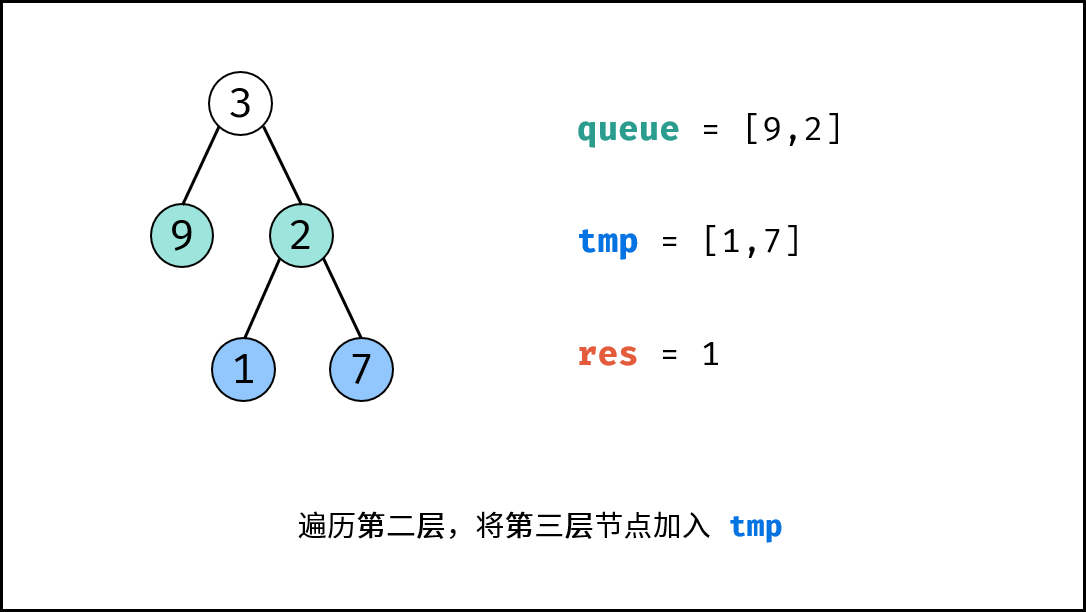
tmp,用于临时存储下一层节点; - 遍历队列: 遍历
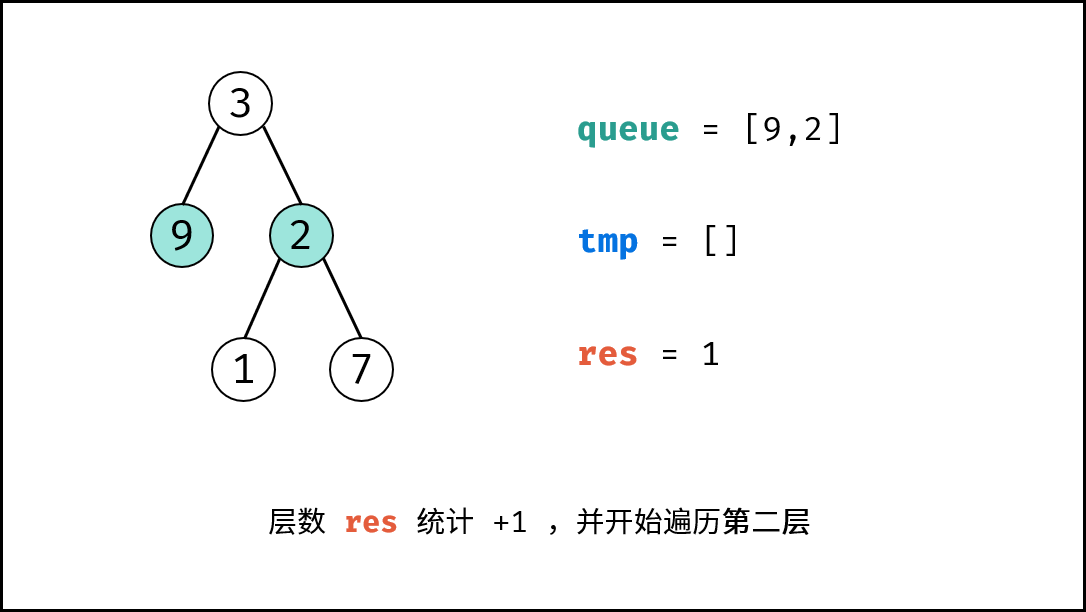
queue中的各节点node,并将其左子节点和右子节点加入tmp; - 更新队列: 执行
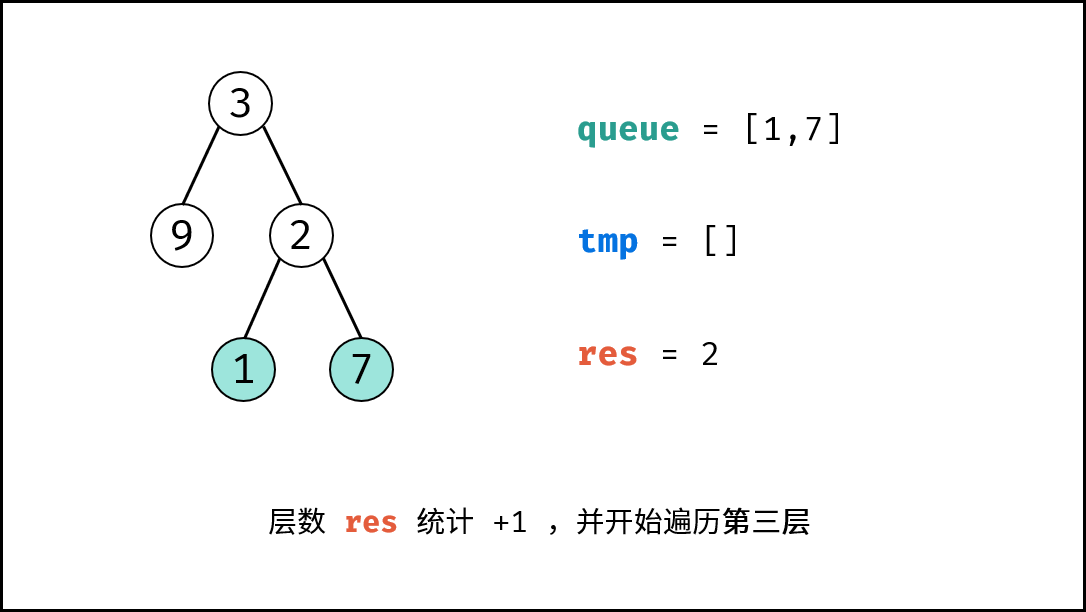
queue = tmp,将下一层节点赋值给queue; - 统计层数: 执行
res += 1,代表层数加 $1$;
- 初始化一个空列表
- 返回值: 返回
res即可。
<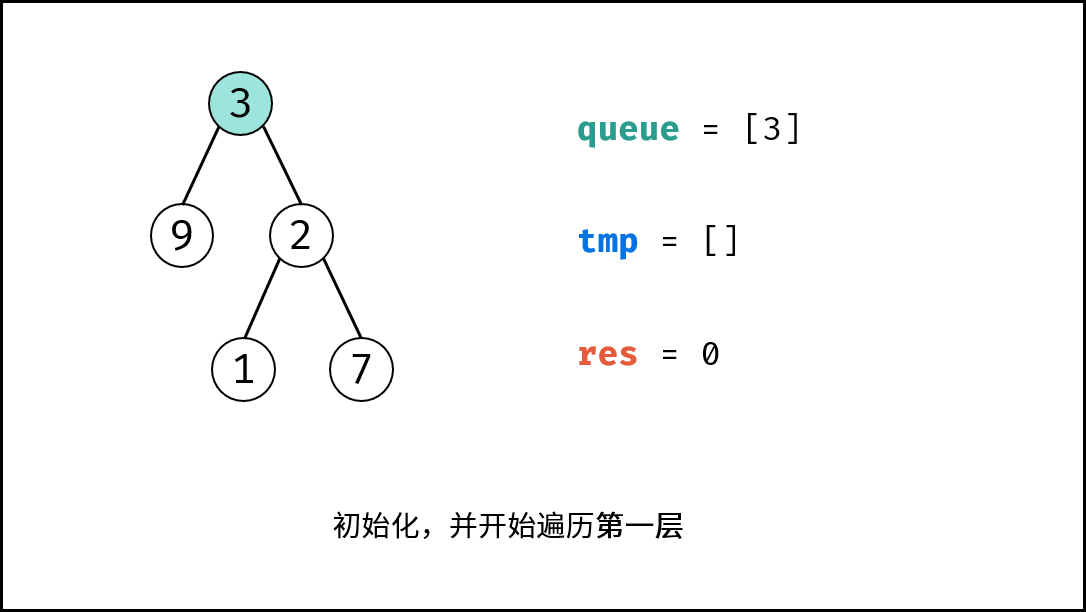 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def calculateDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root: return 0
queue, res = [root], 0
while queue:
tmp = []
for node in queue:
if node.left: tmp.append(node.left)
if node.right: tmp.append(node.right)
queue = tmp
res += 1
return resJava
class Solution {
public int calculateDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
List<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }}, tmp;
int res = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(TreeNode node : queue) {
if(node.left != null) tmp.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) tmp.add(node.right);
}
queue = tmp;
res++;
}
return res;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
int calculateDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
vector<TreeNode*> que;
que.push_back(root);
int res = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
vector<TreeNode*> tmp;
for(TreeNode* node : que) {
if(node->left != nullptr) tmp.push_back(node->left);
if(node->right != nullptr) tmp.push_back(node->right);
}
que = tmp;
res++;
}
return res;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : $N$ 为树的节点数量,计算树的深度需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下(当树平衡时),队列
queue同时存储 $N/2$ 个节点。