解题思路:
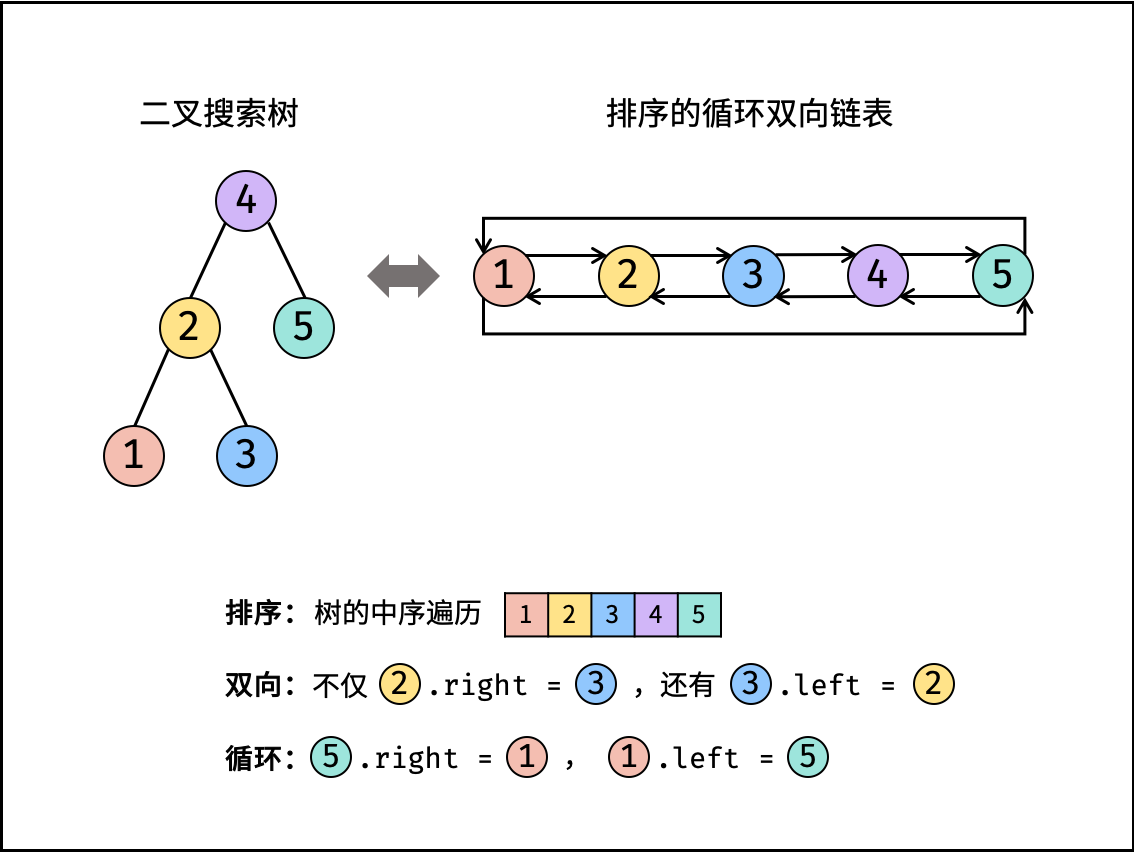
本文解法基于性质:二叉搜索树的中序遍历为 递增序列 。 将 二叉搜索树 转换成一个 “排序的循环双向链表” ,其中包含三个要素:
- 排序链表: 节点应从小到大排序,因此应使用 中序遍历 “从小到大”访问树的节点。
- 双向链表: 在构建相邻节点的引用关系时,设前驱节点
pre和当前节点cur,不仅应构建pre.right = cur,也应构建cur.left = pre。 - 循环链表: 设链表头节点
head和尾节点tail,则应构建head.left = tail和tail.right = head。
中序遍历 为对二叉树作 “左、根、右” 顺序遍历,递归实现如下:
Python
# 打印中序遍历
def dfs(root):
if not root: return
dfs(root.left) # 左
print(root.val) # 根
dfs(root.right) # 右Java
// 打印中序遍历
void dfs(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.left); // 左
System.out.println(root.val); // 根
dfs(root.right); // 右
}C++
// 打印中序遍历
void dfs(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left); // 左
cout << root->val << endl; // 根
dfs(root->right); // 右
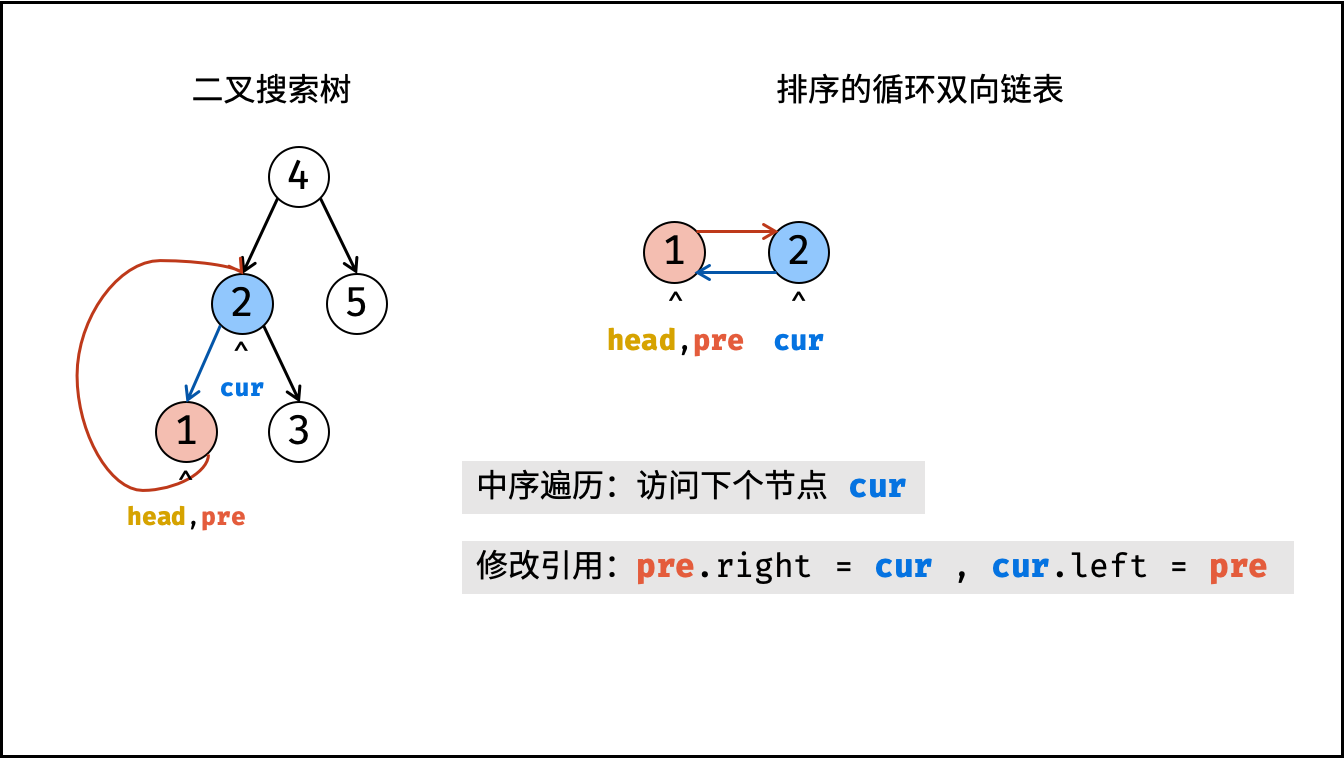
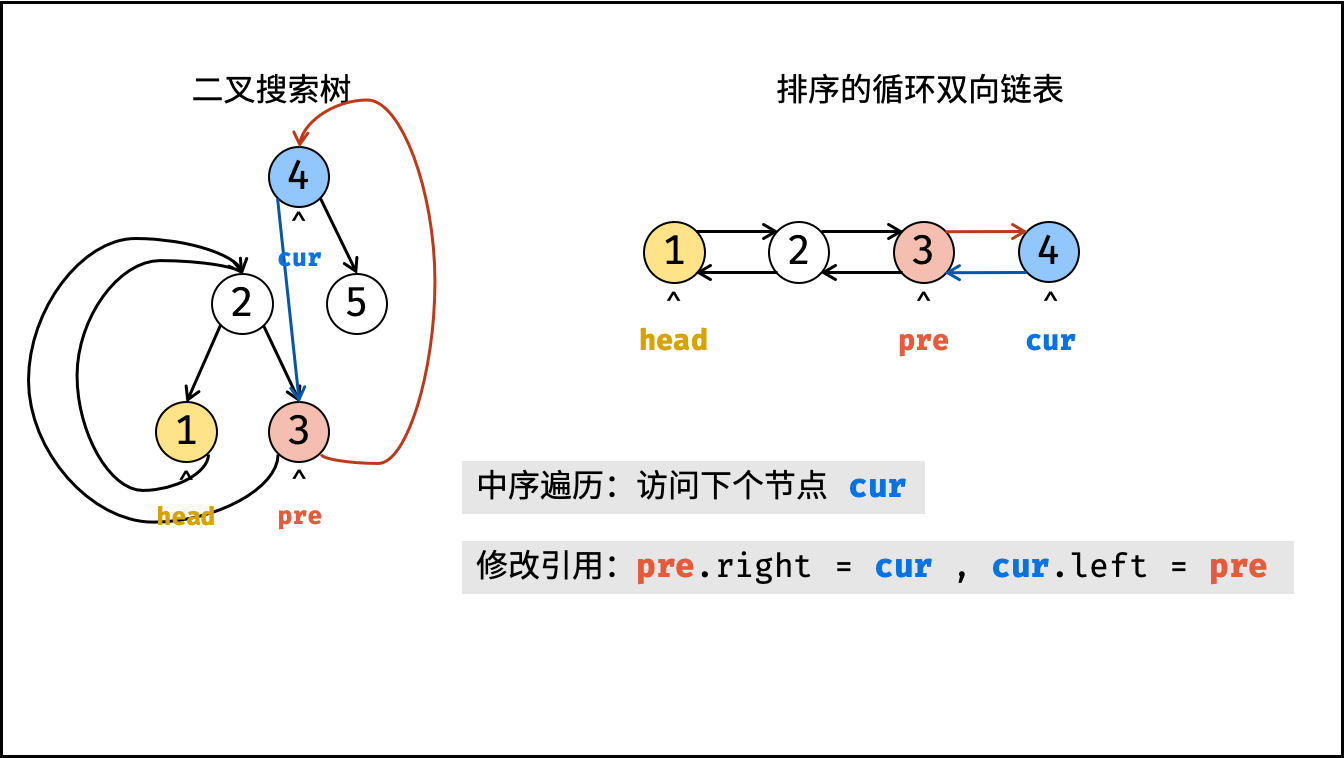
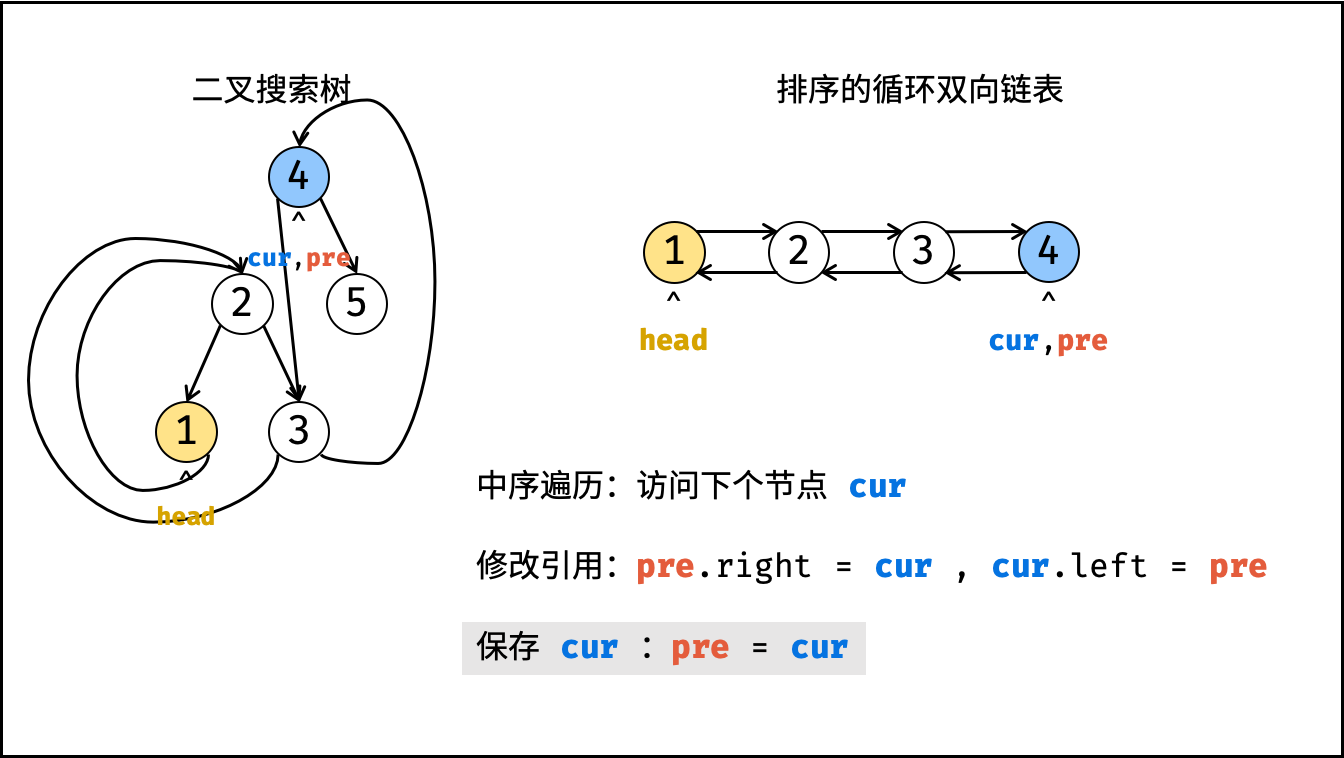
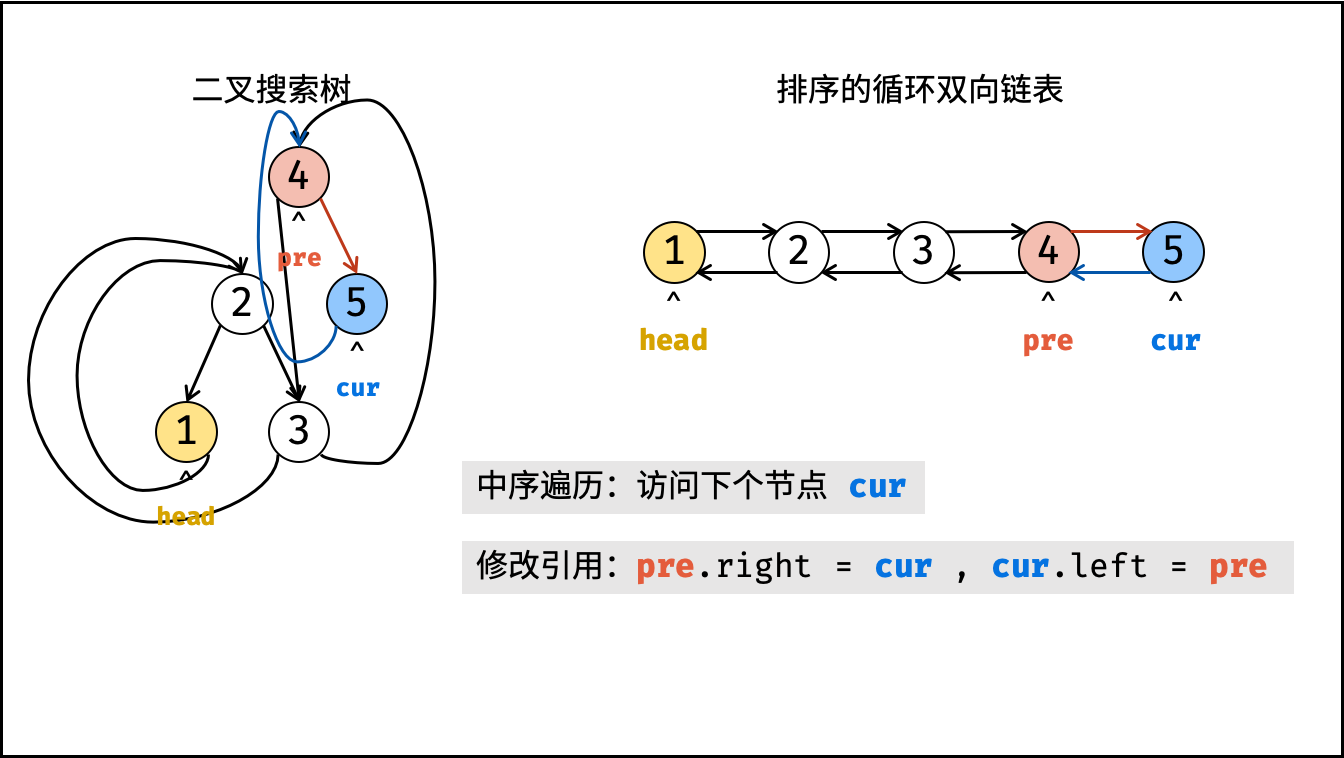
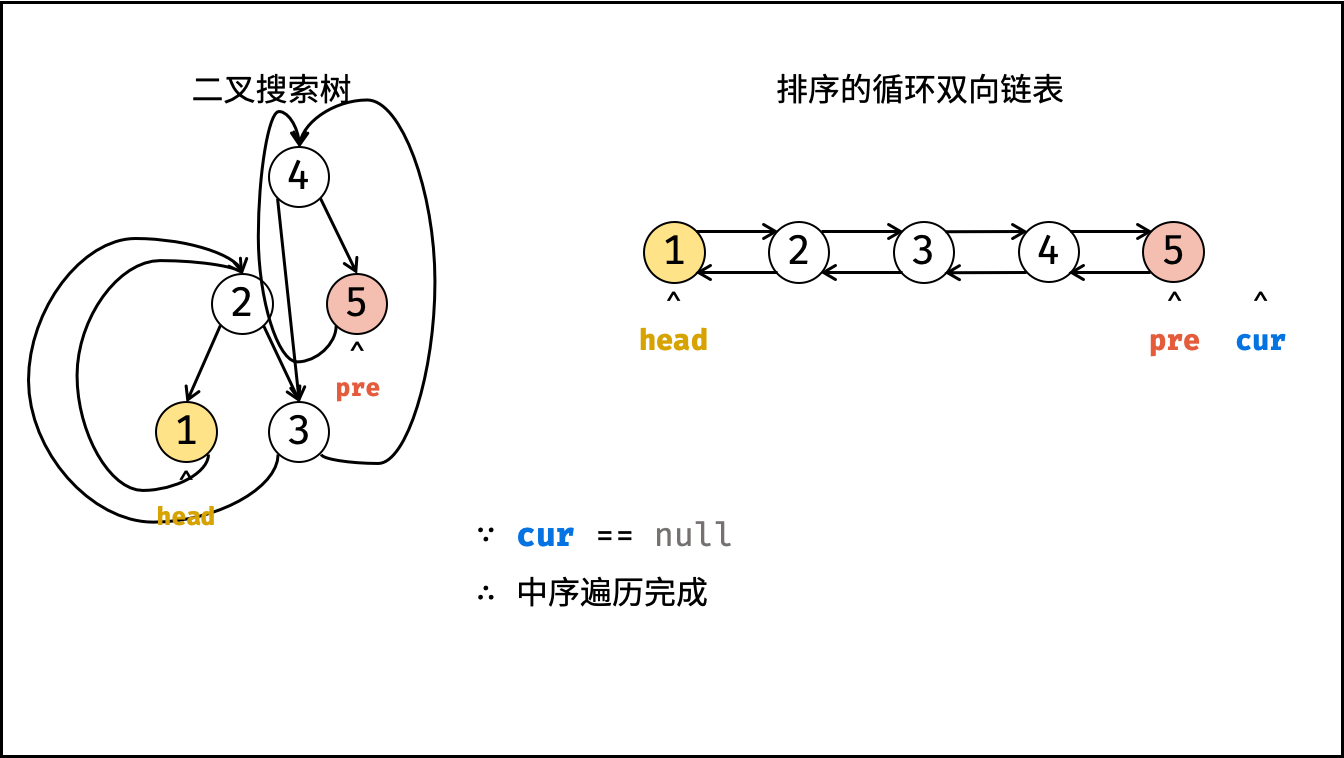
}根据以上分析,考虑使用中序遍历访问树的各节点 cur ;并在访问每个节点时构建 cur 和前驱节点 pre 的引用指向;中序遍历完成后,最后构建头节点和尾节点的引用指向即可。
算法流程:
dfs(cur): 递归中序遍历;
- 终止条件: 当节点
cur为空,代表越过叶节点,直接返回; - 递归左子树,即
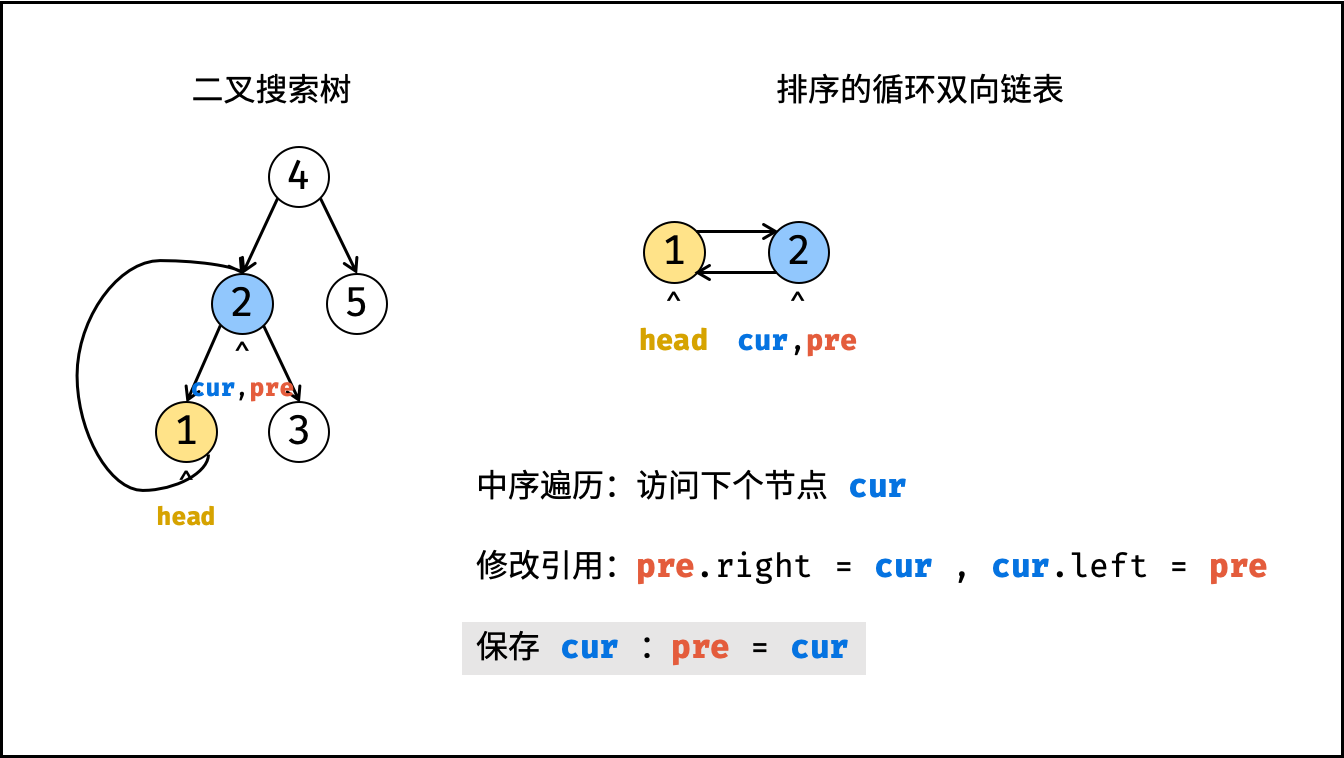
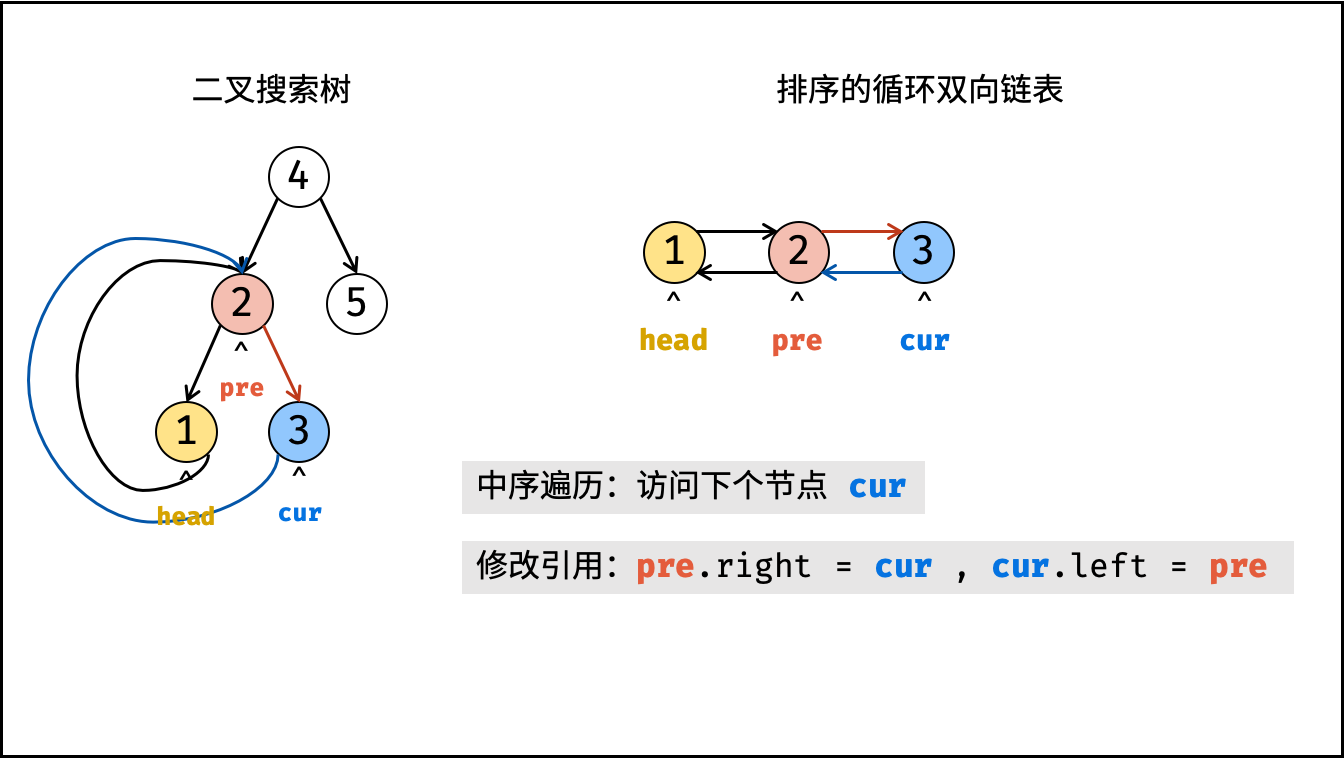
dfs(cur.left); - 构建链表:
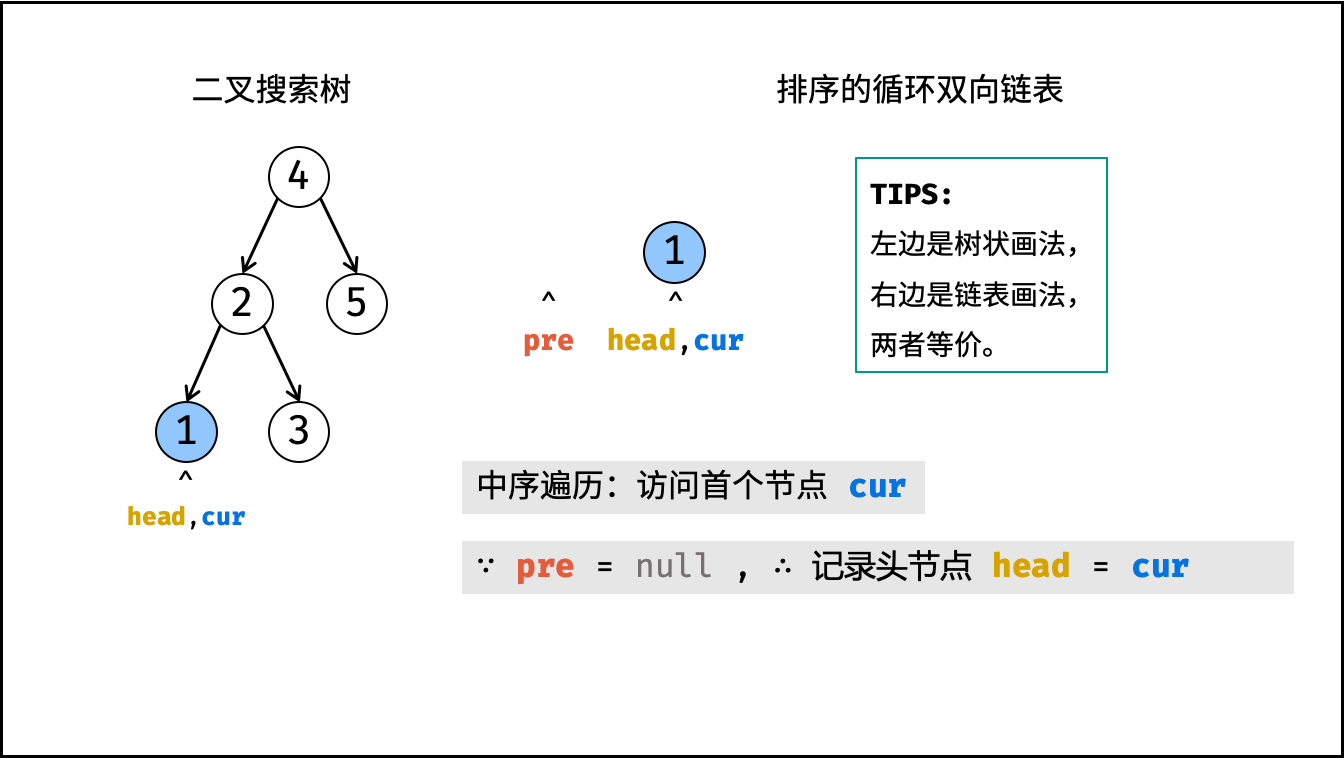
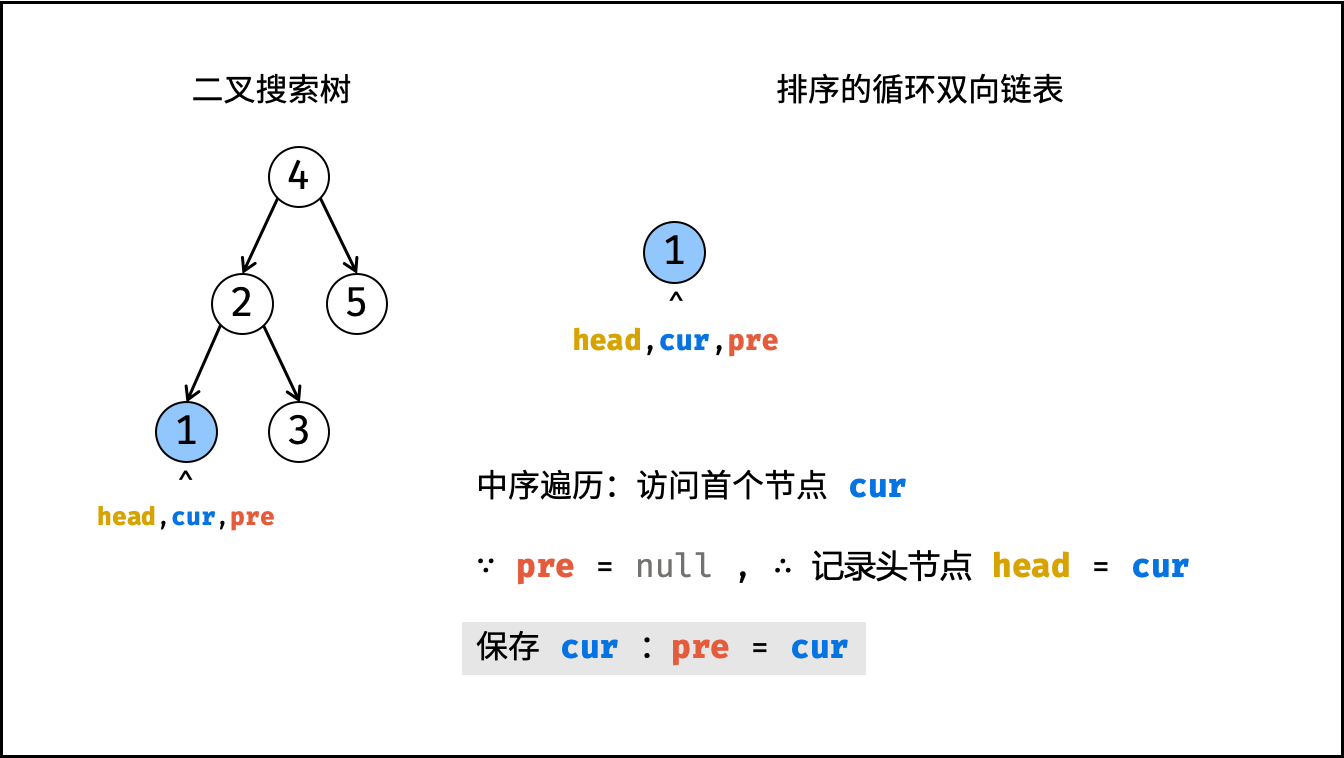
- 当
pre为空时: 代表正在访问链表头节点,记为head; - 当
pre不为空时: 修改双向节点引用,即pre.right = cur,cur.left = pre; - 保存
cur: 更新pre = cur,即节点cur是后继节点的pre;
- 当
- 递归右子树,即
dfs(cur.right);
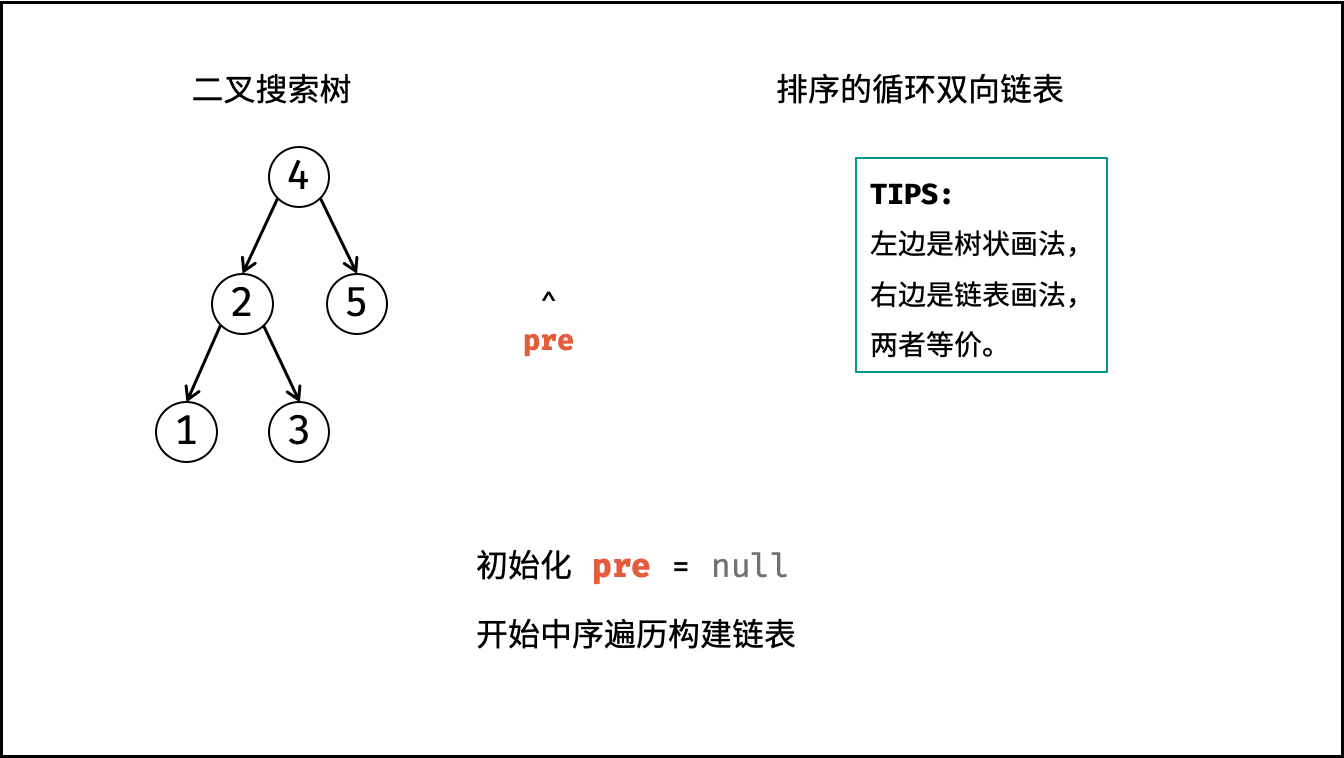
treeToDoublyList(root):
- 特例处理: 若节点
root为空,则直接返回; - 初始化: 空节点
pre; - 转化为双向链表: 调用
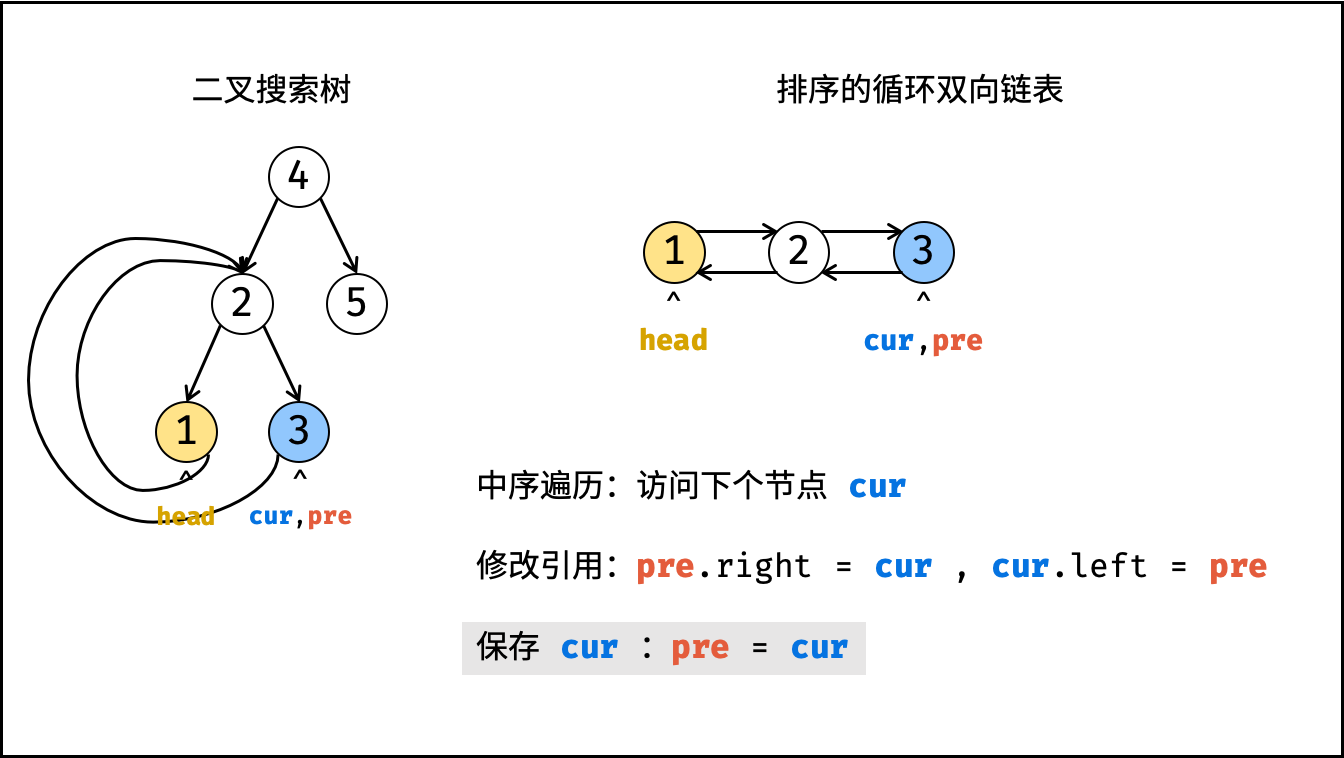
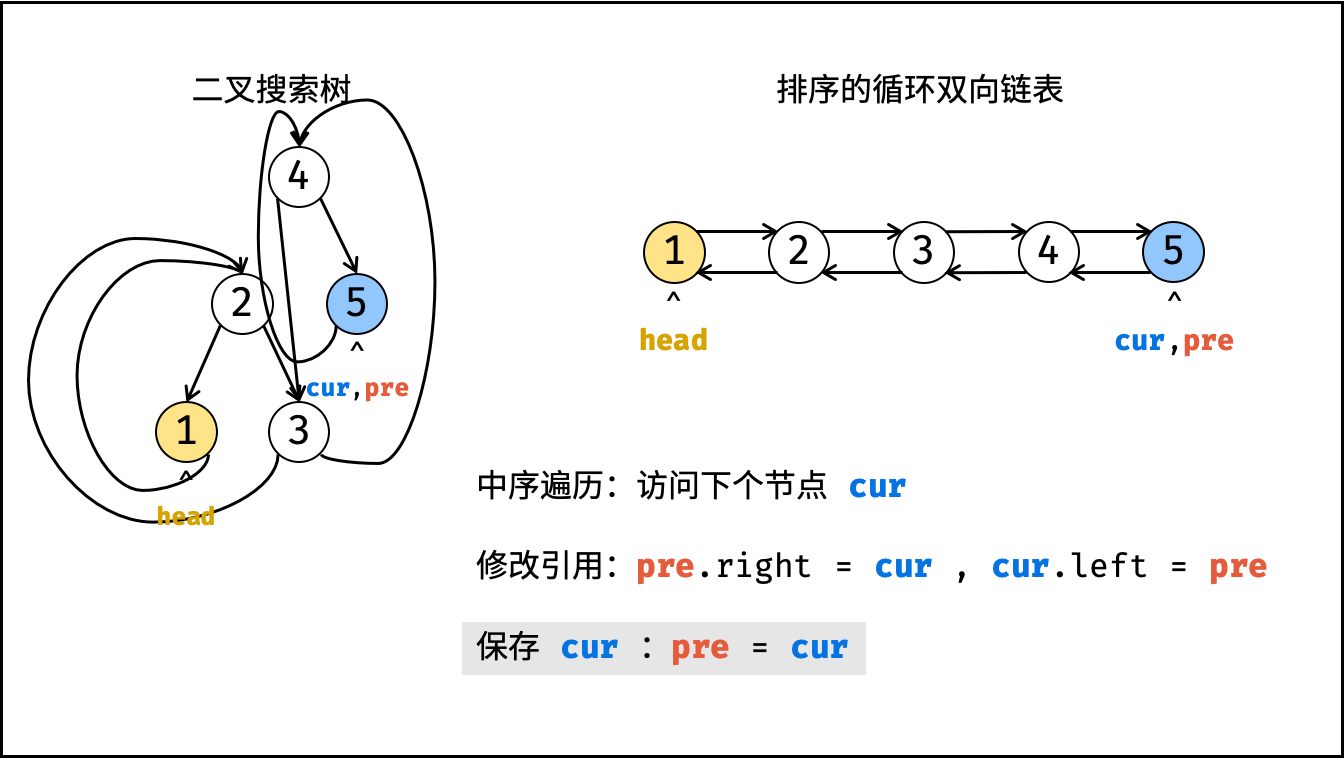
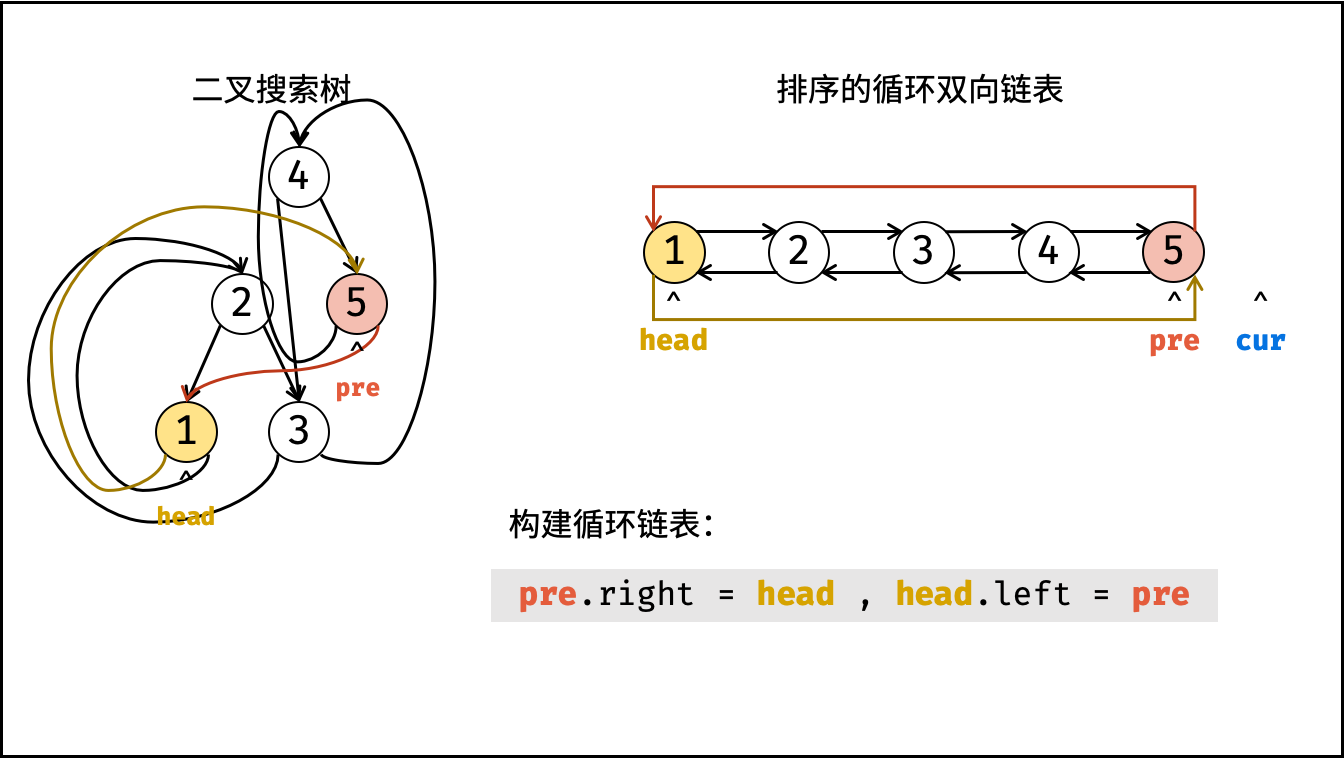
dfs(root); - 构建循环链表: 中序遍历完成后,
head指向头节点,pre指向尾节点,因此修改head和pre的双向节点引用即可; - 返回值: 返回链表的头节点
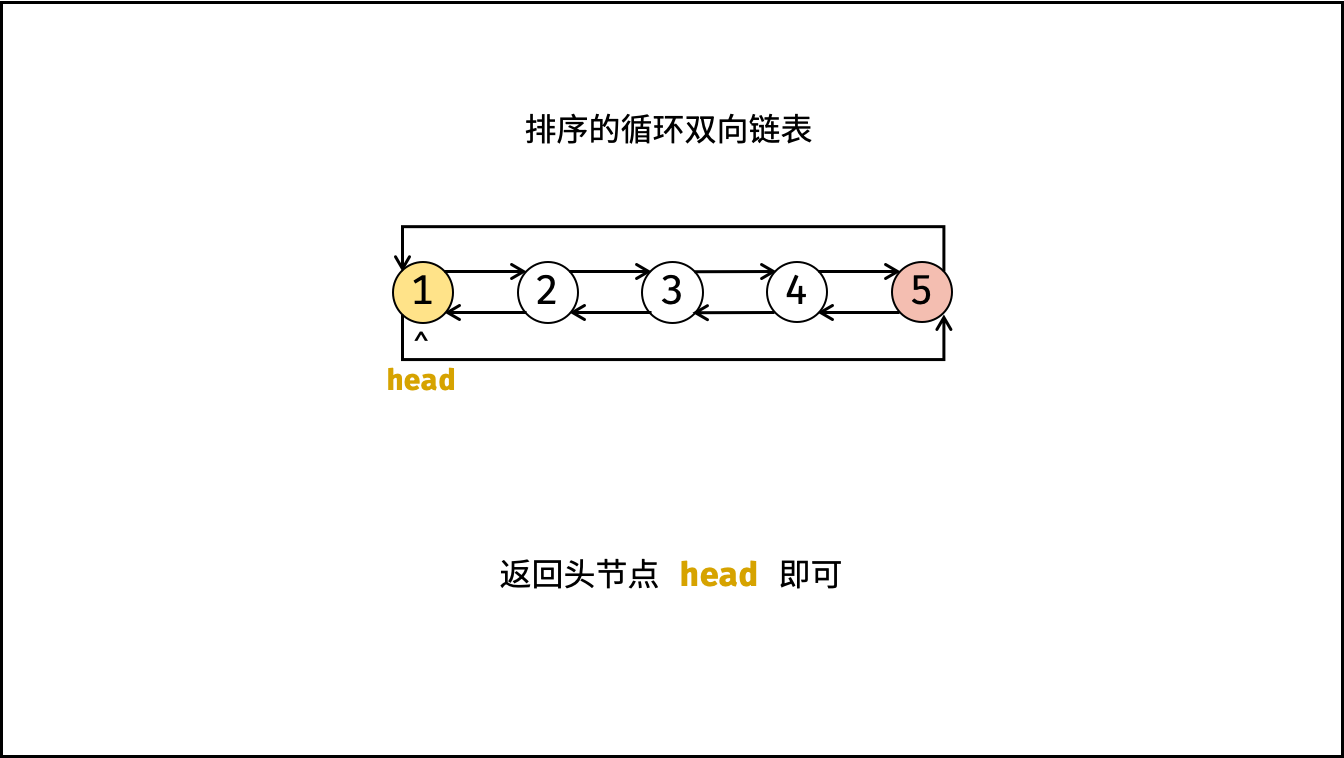
head即可;
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def dfs(cur):
if not cur: return
dfs(cur.left) # 递归左子树
if self.pre: # 修改节点引用
self.pre.right, cur.left = cur, self.pre
else: # 记录头节点
self.head = cur
self.pre = cur # 保存 cur
dfs(cur.right) # 递归右子树
if not root: return
self.pre = None
dfs(root)
self.head.left, self.pre.right = self.pre, self.head
return self.headJava
class Solution {
Node pre, head;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
dfs(root);
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node cur) {
if(cur == null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
if(pre != null) pre.right = cur;
else head = cur;
cur.left = pre;
pre = cur;
dfs(cur.right);
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
dfs(root);
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
private:
Node *pre, *head;
void dfs(Node* cur) {
if(cur == nullptr) return;
dfs(cur->left);
if(pre != nullptr) pre->right = cur;
else head = cur;
cur->left = pre;
pre = cur;
dfs(cur->right);
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : $N$ 为二叉树的节点数,中序遍历需要访问所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 最差情况下,即树退化为链表时,递归深度达到 $N$,系统使用 $O(N)$ 栈空间。