解题思路:
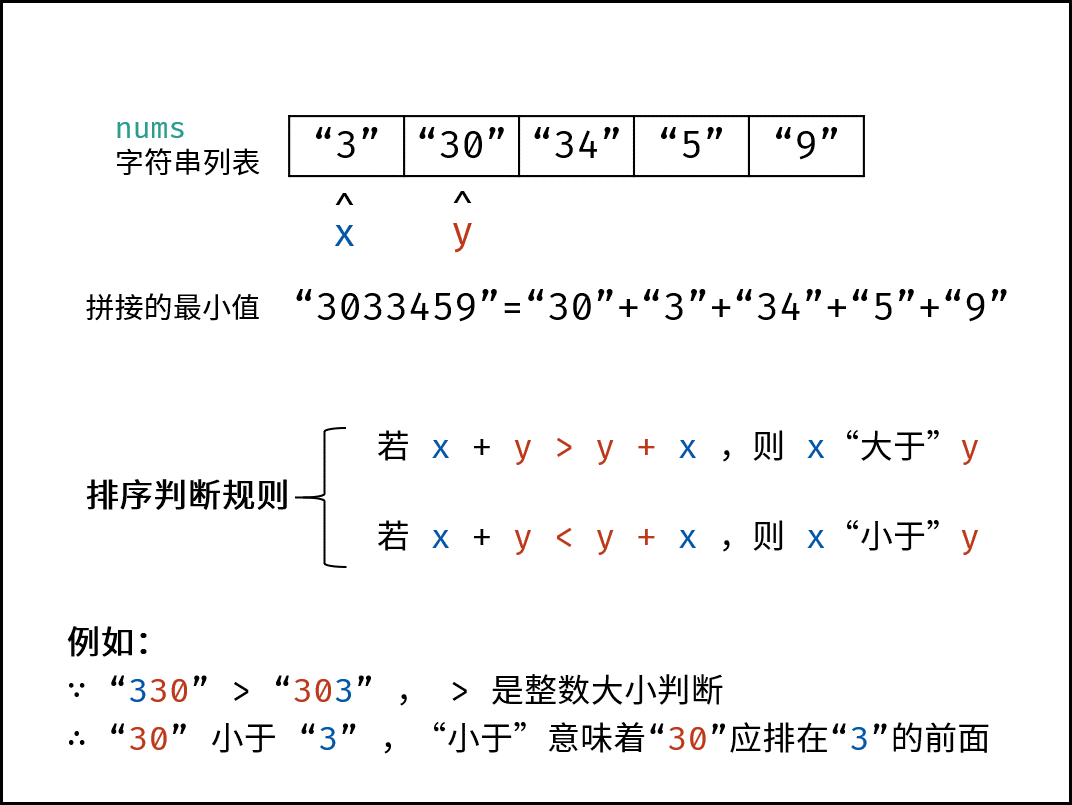
此题求拼接起来的最小数字,本质上是一个排序问题。设数组 $password$ 中任意两数字的字符串为 $x$ 和 $y$ ,则规定 排序判断规则 为:
- 若拼接字符串 $x + y > y + x$ ,则 $x$ “大于” $y$ ;
- 反之,若 $x + y < y + x$ ,则 $x$ “小于” $y$ ;
$x$ “小于” $y$ 代表:排序完成后,数组中 $x$ 应在 $y$ 左边;“大于” 则反之。
根据以上规则,套用任何排序方法对 $password$ 执行排序即可。
算法流程:
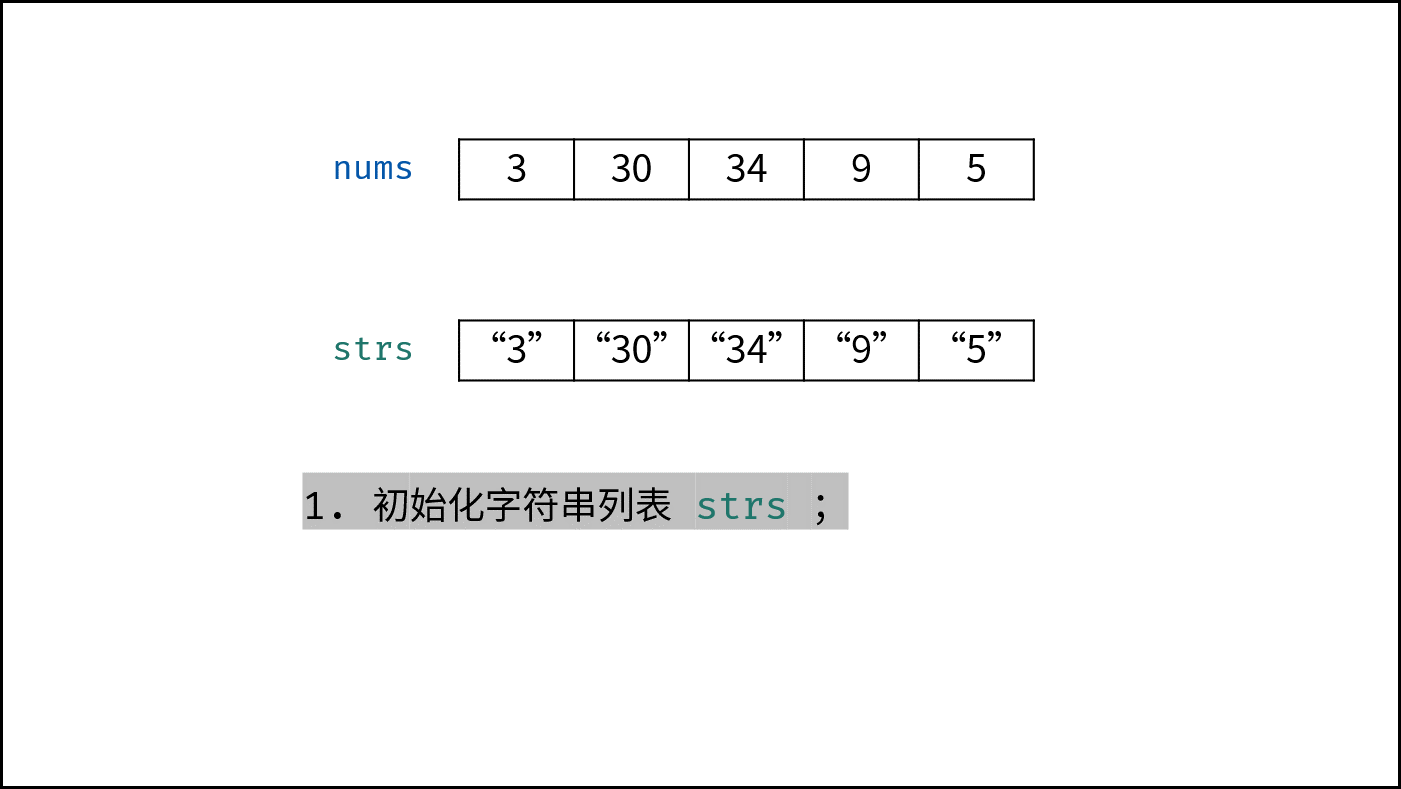
- 初始化: 字符串列表 $strs$ ,保存各数字的字符串格式;
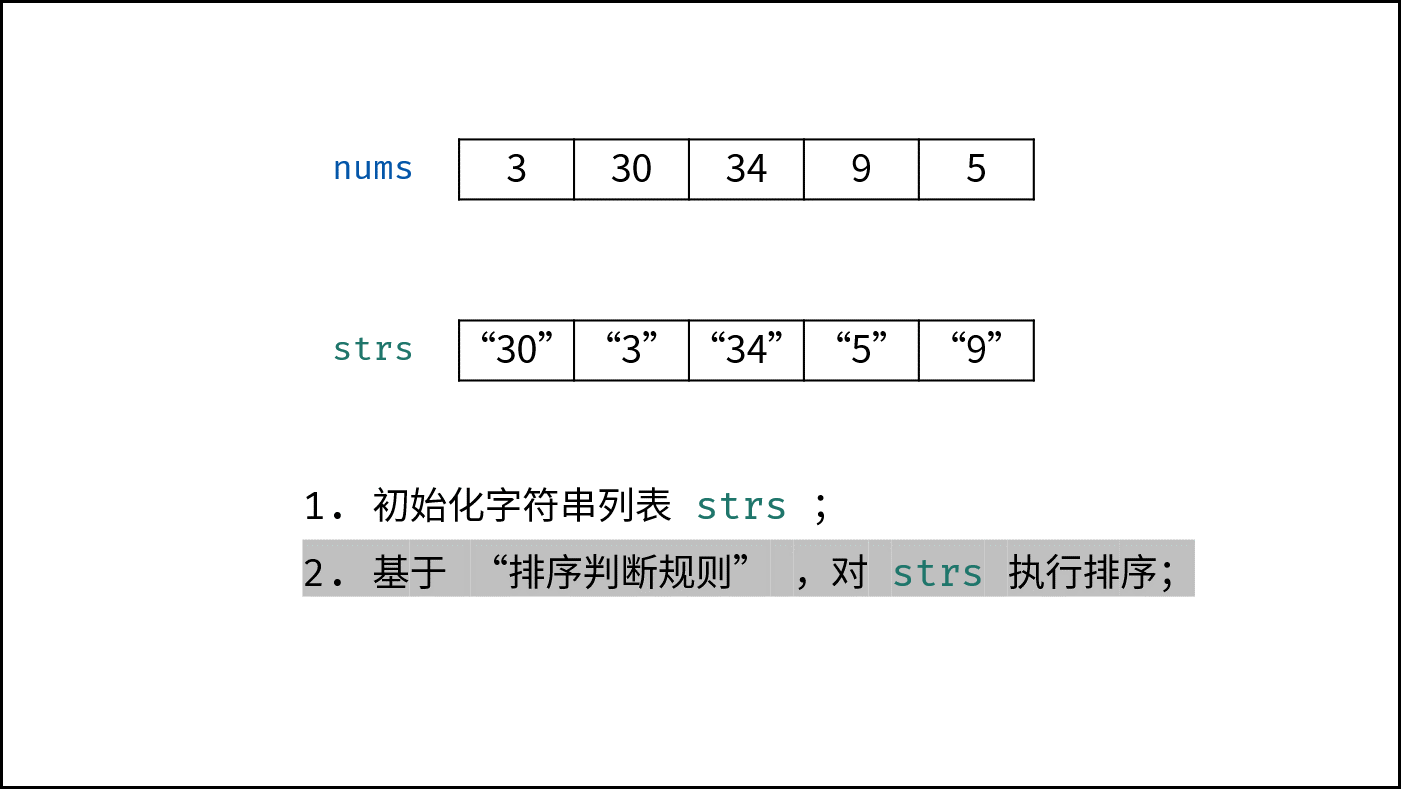
- 列表排序: 应用以上 “排序判断规则” ,对 $strs$ 执行排序;
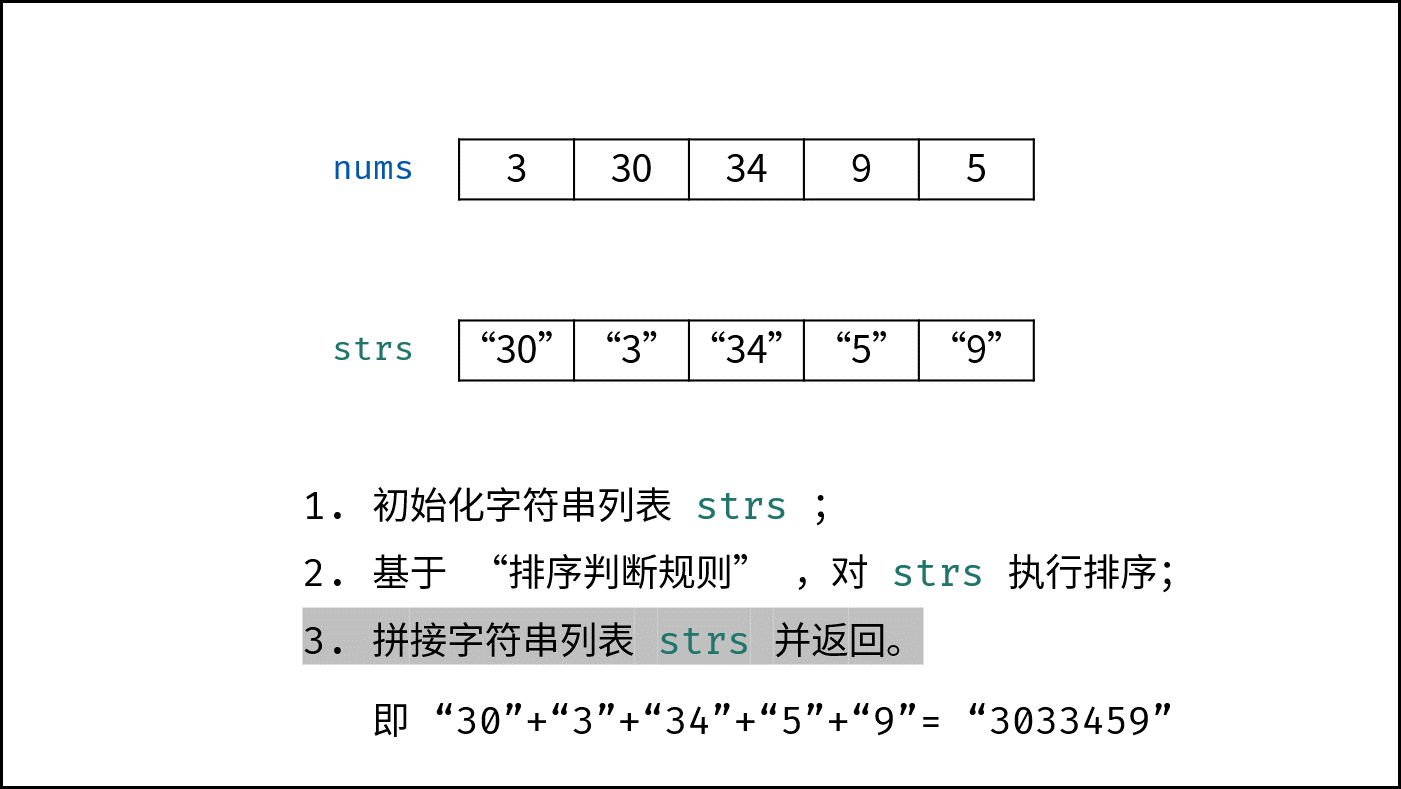
- 返回值: 拼接 $strs$ 中的所有字符串,并返回。
下图中
nums对应本题的password。
< ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
本文列举 快速排序 和 内置函数 两种排序方法,其他排序方法也可实现。
快速排序:
需修改快速排序函数中的排序判断规则。字符串大小(字典序)对比的实现方法:
- Python/C++ 中可直接用
<,>; - Java 中使用函数
A.compareTo(B);
Python
class Solution:
def crackPassword(self, password: List[int]) -> str:
def quick_sort(l , r):
if l >= r: return
i, j = l, r
while i < j:
while strs[j] + strs[l] >= strs[l] + strs[j] and i < j: j -= 1
while strs[i] + strs[l] <= strs[l] + strs[i] and i < j: i += 1
strs[i], strs[j] = strs[j], strs[i]
strs[i], strs[l] = strs[l], strs[i]
quick_sort(l, i - 1)
quick_sort(i + 1, r)
strs = [str(num) for num in password]
quick_sort(0, len(strs) - 1)
return ''.join(strs)Java
class Solution {
public String crackPassword(int[] password) {
String[] strs = new String[password.length];
for(int i = 0; i < password.length; i++)
strs[i] = String.valueOf(password[i]);
quickSort(strs, 0, strs.length - 1);
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : strs)
res.append(s);
return res.toString();
}
void quickSort(String[] strs, int l, int r) {
if(l >= r) return;
int i = l, j = r;
String tmp = strs[i];
while(i < j) {
while((strs[j] + strs[l]).compareTo(strs[l] + strs[j]) >= 0 && i < j) j--;
while((strs[i] + strs[l]).compareTo(strs[l] + strs[i]) <= 0 && i < j) i++;
tmp = strs[i];
strs[i] = strs[j];
strs[j] = tmp;
}
strs[i] = strs[l];
strs[l] = tmp;
quickSort(strs, l, i - 1);
quickSort(strs, i + 1, r);
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
string crackPassword(vector<int>& password) {
vector<string> strs;
for(int i = 0; i < password.size(); i++)
strs.push_back(to_string(password[i]));
quickSort(strs, 0, strs.size() - 1);
string res;
for(string s : strs)
res.append(s);
return res;
}
private:
void quickSort(vector<string>& strs, int l, int r) {
if(l >= r) return;
int i = l, j = r;
while(i < j) {
while(strs[j] + strs[l] >= strs[l] + strs[j] && i < j) j--;
while(strs[i] + strs[l] <= strs[l] + strs[i] && i < j) i++;
swap(strs[i], strs[j]);
}
swap(strs[i], strs[l]);
quickSort(strs, l, i - 1);
quickSort(strs, i + 1, r);
}
};内置函数:
需定义排序规则:
- Python 定义在函数
sort_rule(x, y)中; - Java 定义为
(x, y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x); - C++ 定义为
(string& x, string& y){ return x + y < y + x; };
Python
class Solution:
def crackPassword(self, password: List[int]) -> str:
def sort_rule(x, y):
a, b = x + y, y + x
if a > b: return 1
elif a < b: return -1
else: return 0
strs = [str(num) for num in password]
strs.sort(key = functools.cmp_to_key(sort_rule))
return ''.join(strs)Java
class Solution {
public String crackPassword(int[] password) {
String[] strs = new String[password.length];
for(int i = 0; i < password.length; i++)
strs[i] = String.valueOf(password[i]);
Arrays.sort(strs, (x, y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x));
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : strs)
res.append(s);
return res.toString();
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
string crackPassword(vector<int>& password) {
vector<string> strs;
string res;
for(int i = 0; i < password.size(); i++)
strs.push_back(to_string(password[i]));
sort(strs.begin(), strs.end(), [](string& x, string& y){ return x + y < y + x; });
for(int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++)
res.append(strs[i]);
return res;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N \log N)$ : $N$ 为最终返回值的字符数量( $strs$ 列表的长度 $\leq N$ );使用快排或内置函数的平均时间复杂度为 $O(N \log N)$ ,最差为 $O(N^2)$ 。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 字符串列表 $strs$ 占用线性大小的额外空间。