解题思路:
本题解法较多,本文主要介绍 字符串切片 , 列表遍历拼接 , 字符串遍历拼接 三种方法,适用于 Python 和 Java 语言。同时,介绍了 三次翻转法 ,适用于 C++ 语言。
方法一:字符串切片
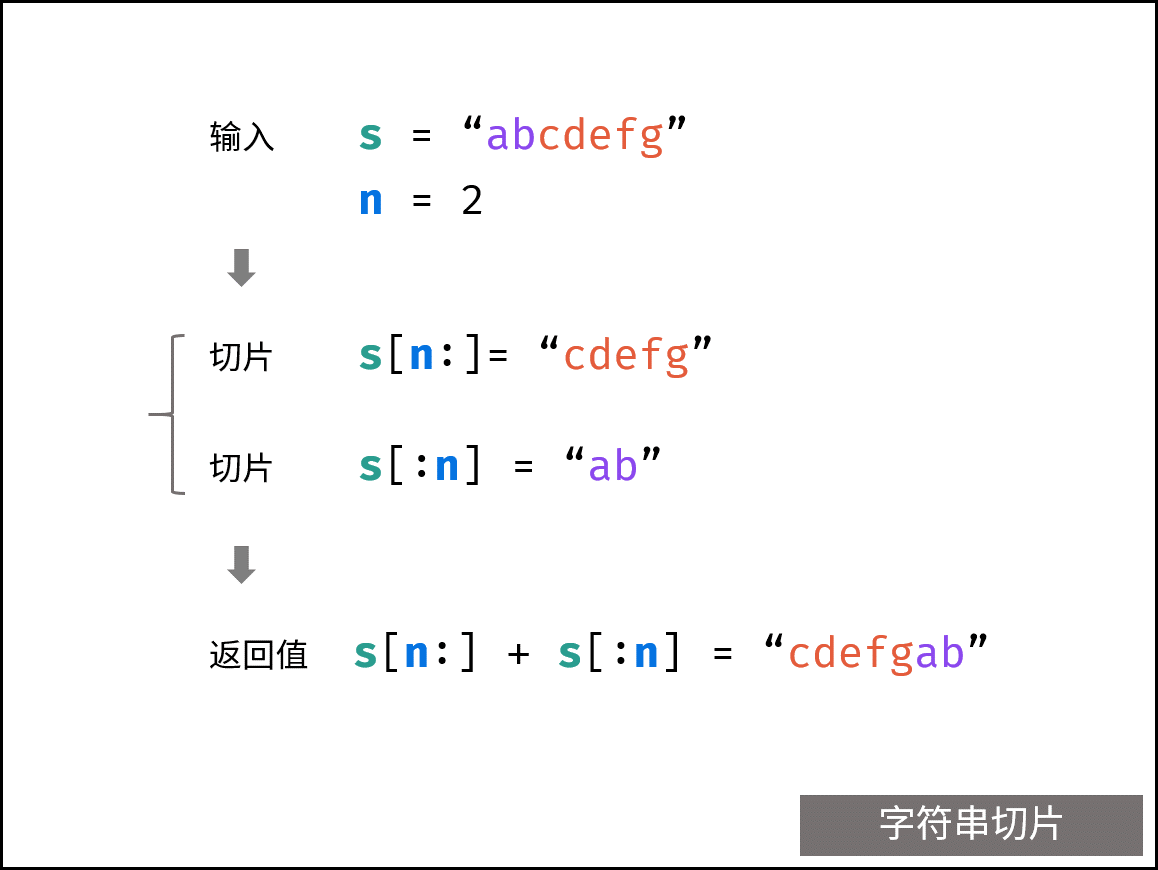
获取字符串 password[target:] 切片和 password[:target] 切片,使用 "$+$" 运算符拼接并返回即可。
下图中的
s对应本题的password。
代码:
class Solution:
def dynamicPassword(self, password: str, target: int) -> str:
return password[target:] + password[:target]class Solution {
public String dynamicPassword(String password, int target) {
return password.substring(target, password.length()) + password.substring(0, target);
}
}class Solution {
public:
string dynamicPassword(string password, int target) {
return password.substr(target, password.size()) + password.substr(0, target);
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 其中 $N$ 为字符串
password的长度,字符串切片函数为线性时间复杂度(参考资料)。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 两个字符串切片的总长度为 $N$ 。
方法二:列表遍历拼接
若面试规定不允许使用 切片函数 ,则使用此方法。
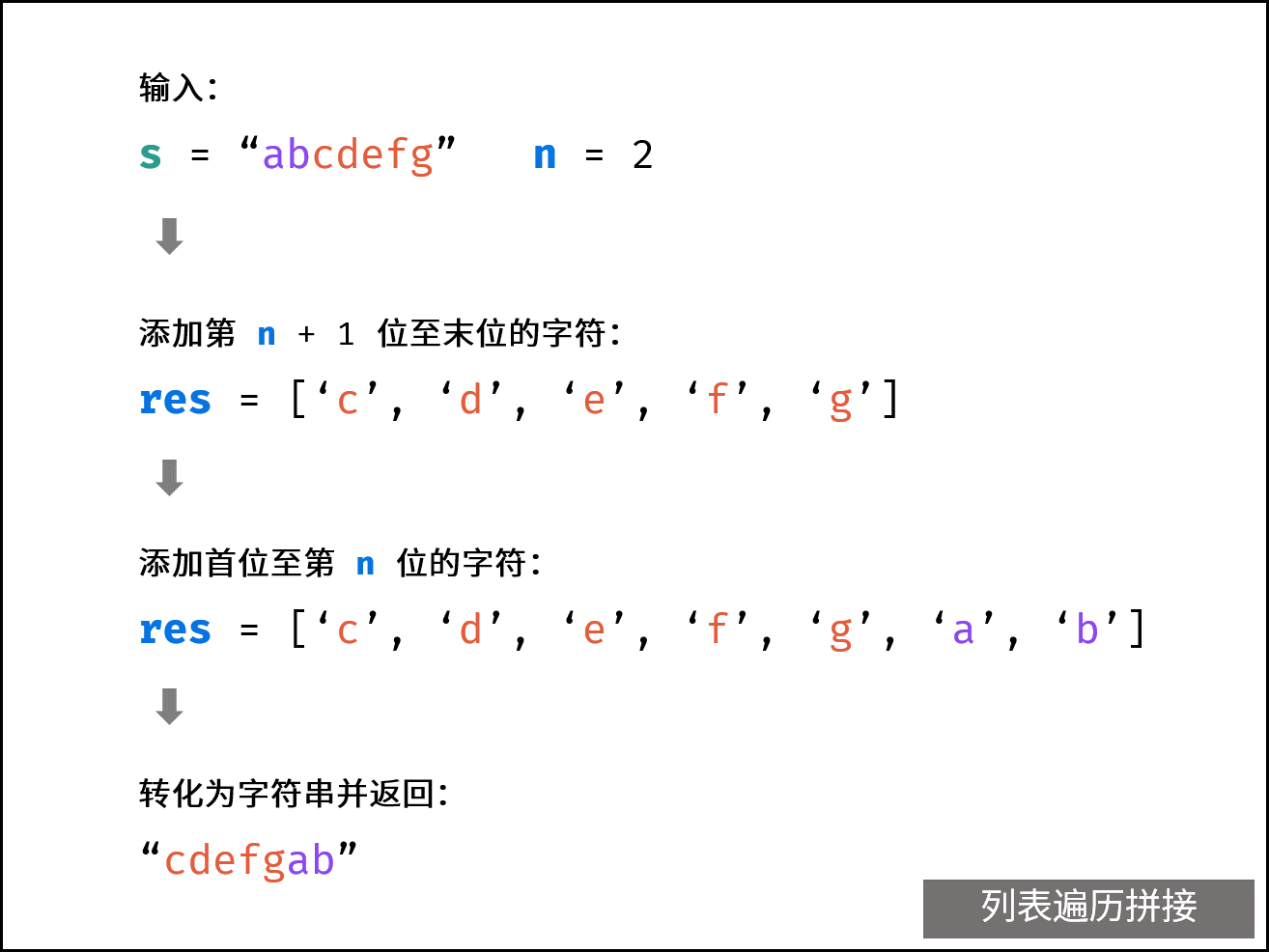
算法流程:
- 新建一个 list (Python) 、StringBuilder (Java) ,记为
res; - 先向
res添加 “第 $target + 1$ 位至末位的字符” ; - 再向
res添加 “首位至第 $target$ 位的字符” ; - 将
res转化为字符串并返回;
代码:
class Solution:
def dynamicPassword(self, password: str, target: int) -> str:
res = []
for i in range(target, len(password)):
res.append(password[i])
for i in range(target):
res.append(password[i])
return ''.join(res)class Solution {
public String dynamicPassword(String password, int target) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = target; i < password.length(); i++)
res.append(password.charAt(i));
for(int i = 0; i < target; i++)
res.append(password.charAt(i));
return res.toString();
}
}利用求余运算,可以简化代码。
class Solution:
def dynamicPassword(self, password: str, target: int) -> str:
res = []
for i in range(target, target + len(password)):
res.append(password[i % len(password)])
return ''.join(res)class Solution {
public String dynamicPassword(String password, int target) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = target; i < target + password.length(); i++)
res.append(password.charAt(i % password.length()));
return res.toString();
}
}复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 线性遍历
password并添加,使用线性时间。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 新建的辅助
res使用 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间。
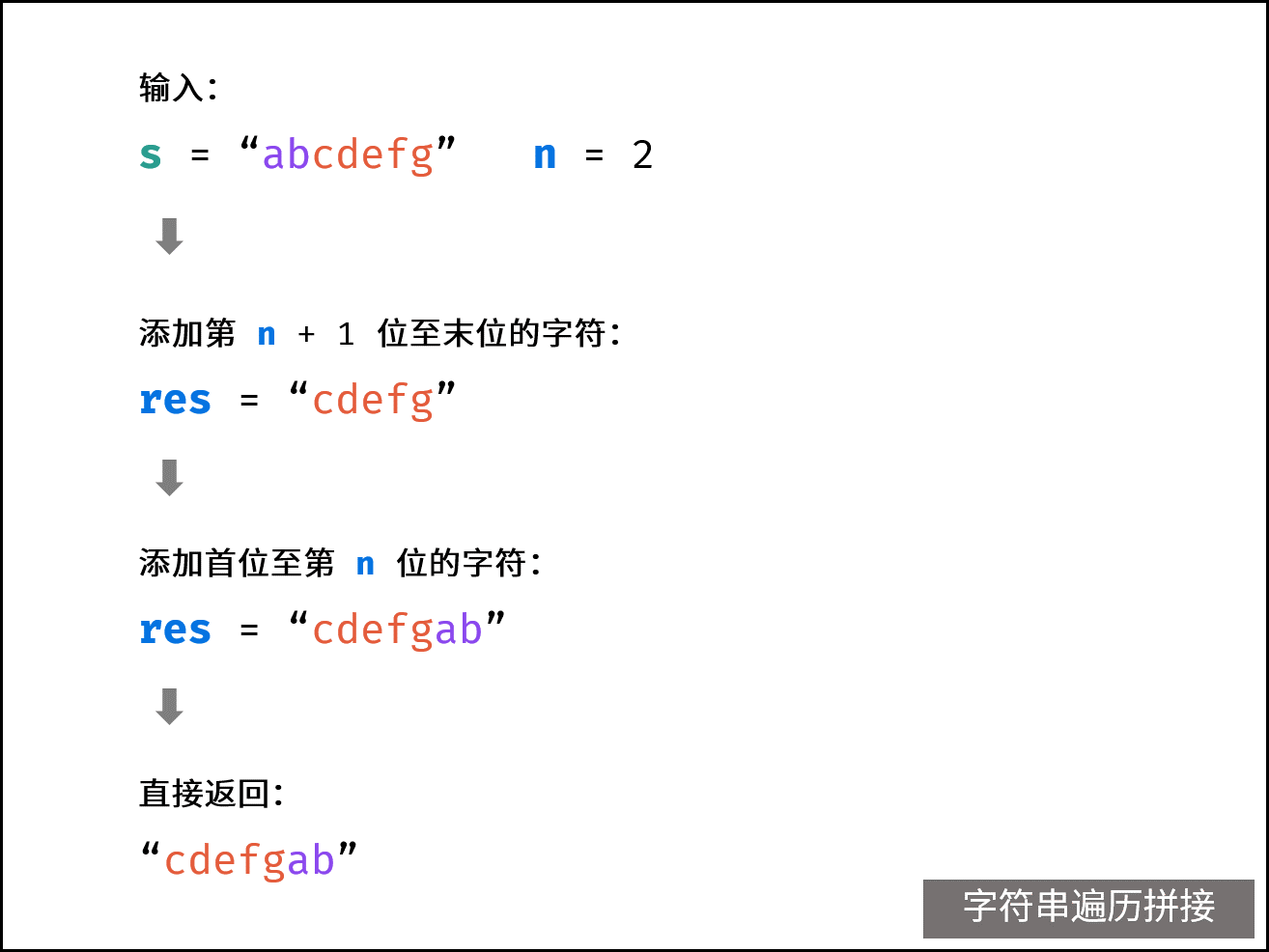
方法三:字符串遍历拼接
若规定 Python 不能使用
join()函数,或规定 Java 只能用 String ,则使用此方法。
此方法与 方法二 思路一致,区别是使用字符串代替列表。
class Solution:
def dynamicPassword(self, password: str, target: int) -> str:
res = ""
for i in range(target, len(password)):
res += password[i]
for i in range(target):
res += password[i]
return resclass Solution {
public String dynamicPassword(String password, int target) {
String res = "";
for(int i = target; i < password.length(); i++)
res += password.charAt(i);
for(int i = 0; i < target; i++)
res += password.charAt(i);
return res;
}
}同理,利用求余运算,可以简化代码。
class Solution:
def dynamicPassword(self, password: str, target: int) -> str:
res = ""
for i in range(target, target + len(password)):
res += password[i % len(password)]
return resclass Solution {
public String dynamicPassword(String password, int target) {
String res = "";
for(int i = target; i < target + password.length(); i++)
res += password.charAt(i % password.length());
return res;
}
}复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 线性遍历
password并添加,使用线性时间。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 假设循环过程中内存会被及时回收,内存中至少同时存在长度为 $N$ 和 $N-1$ 的两个字符串(新建长度为 $N$ 的
res需要使用前一个长度 $N-1$ 的res),因此至少使用 $O(N)$ 的额外空间。
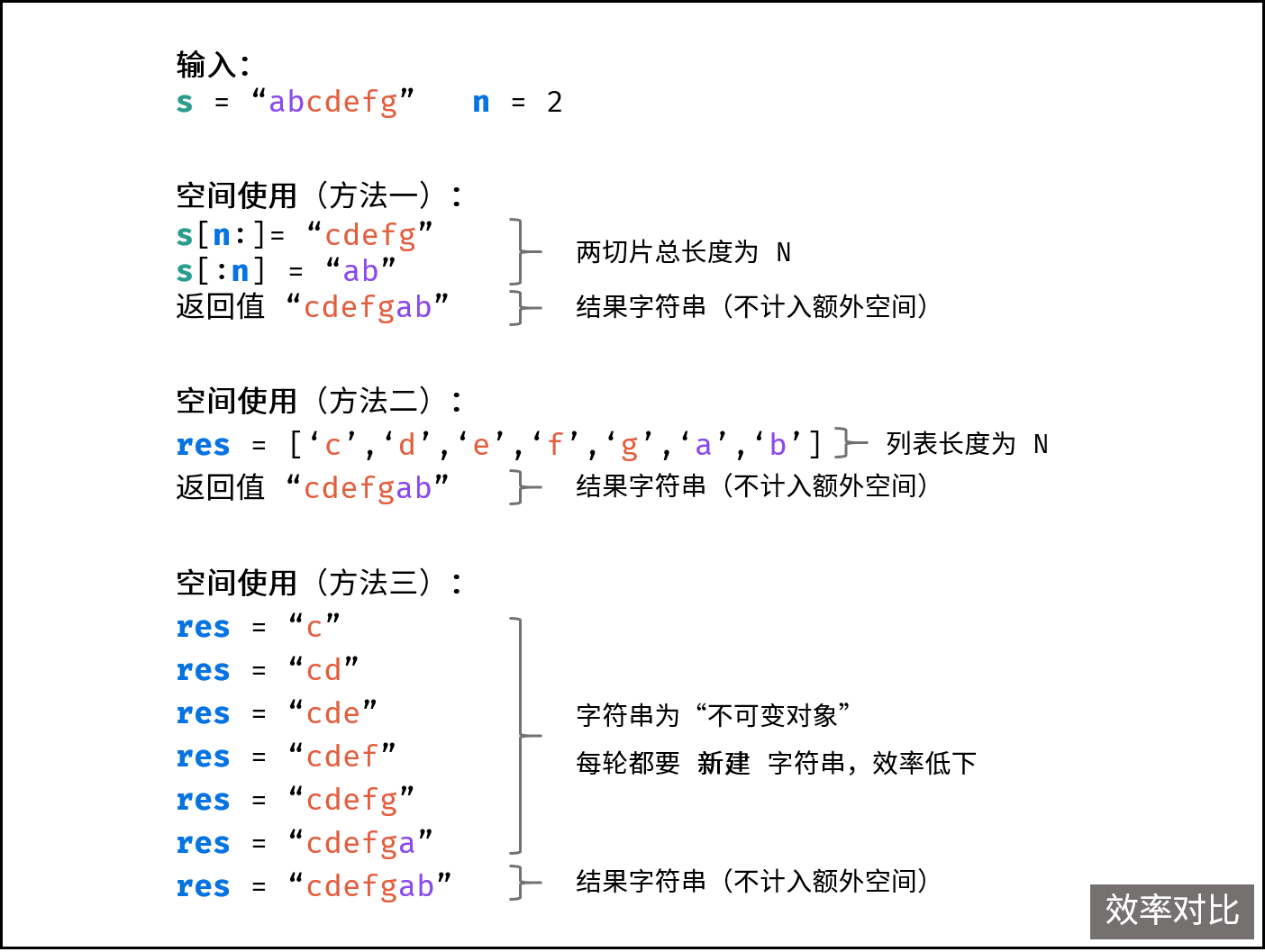
效率对比:
由于本题的多解法涉及到了 字符串为不可变对象 的相关概念,导致效率区别较大。以上三种方法的空间使用如下图所示。
详细分析请参考 Efficient String Concatenation in Python 。
以 Python 为例开展三种方法的效率测试,结论同样适用于 Java 语言。
测试数据:
长度为 $10000000$ 的全为 '1' 的字符串。
password = "1" * 10000000方法一测试:
新建两切片字符串,并将两切片拼接为结果字符串,无冗余操作,效率最高。
# 运行时间: 0.01 秒
def func1(password):
cut = len(password) // 3
return password[:cut] + password[cut:]方法二测试:
列表(Python) 和 StringBuilder(Java) 都是可变对象,每轮遍历拼接字符时,只是向列表尾部添加一个新的字符元素。最终拼接转化为字符串时,系统 仅申请一次内存 。
# 运行时间: 1.86 秒
def func2(password):
res = []
for i in range(len(password)):
res.append(password[i]) # 仅需在列表尾部添加元素
return ''.join(res)方法三测试:
在 Python 和 Java 中,字符串是 “不可变对象” 。因此,每轮遍历拼接字符时,都需要新建一个字符串;因此,系统 需申请 $N$ 次内存 ,数据量较大时效率低下。
# 运行时间: 6.31 秒
def func3(password):
res = ""
for i in range(len(password)):
res += password[i] # 每次拼接都需要新建一个字符串
return res方法四:三次翻转(C++)
由于 C++ 中的字符串是 可变类型 ,因此可在原字符串上直接操作实现字符串旋转,实现 $O(1)$ 的空间复杂度。
设字符串 $password = s_1 s_2$ ,字符串 $password$ 的反转字符串为 $\hat password$ ,则左旋转字符串 $s_2 s_1$ 计算方法为:
$$ s_2 s_1 = \hat{\hat{s_1} \hat{s_2}} $$
例如,$password = "abcdefg"$ , $s_1 = "ab"$ , $s_2 = "cdefg"$ ,则有: $$ \hat{s_1} = "ba" \ \hat{s_2} = "gfedc" \ \hat{\hat{s_1} \hat{s_2}} = \hat{"bagfedc"} = "cdefgba" $$ 即 $"cdefgba"$ 为所求字符串 $password$ 的左旋转结果。
代码:
自行实现字符串翻转函数 reverseString() ,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
string dynamicPassword(string password, int target) {
reverseString(password, 0, target - 1);
reverseString(password, target, password.size() - 1);
reverseString(password, 0, password.size() - 1);
return password;
}
private:
void reverseString(string& password, int i, int j) {
while(i < j) swap(password[i++], password[j--]);
}
};也可使用库函数实现,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
string dynamicPassword(string password, int target) {
reverse(password.begin(), password.begin() + target);
reverse(password.begin() + target, password.end());
reverse(password.begin(), password.end());
return password;
}
};复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$ : 共线性遍历两轮
password。 - 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : C++ 原地字符串操作,使用常数大小额外空间。