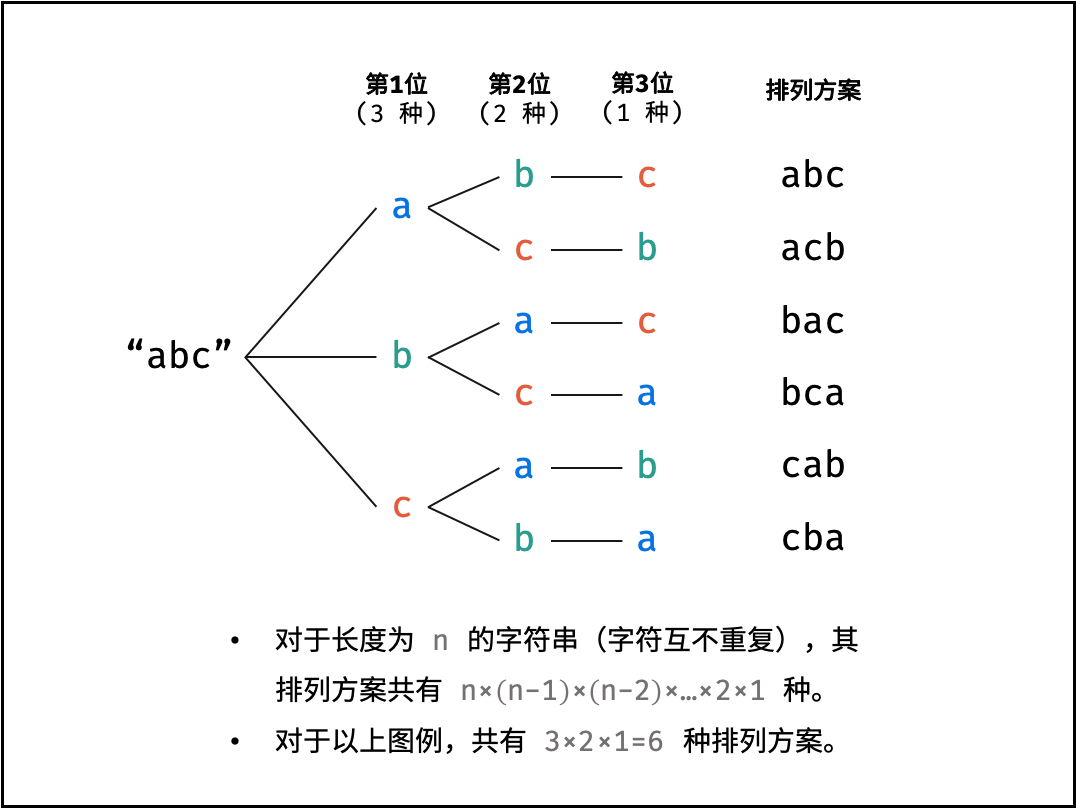
解题思路:
对于一个长度为 $n$ 的字符串(假设字符互不重复),其排列方案数共有:
$$ n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) … \times 2 \times 1 $$
排列方案的生成:
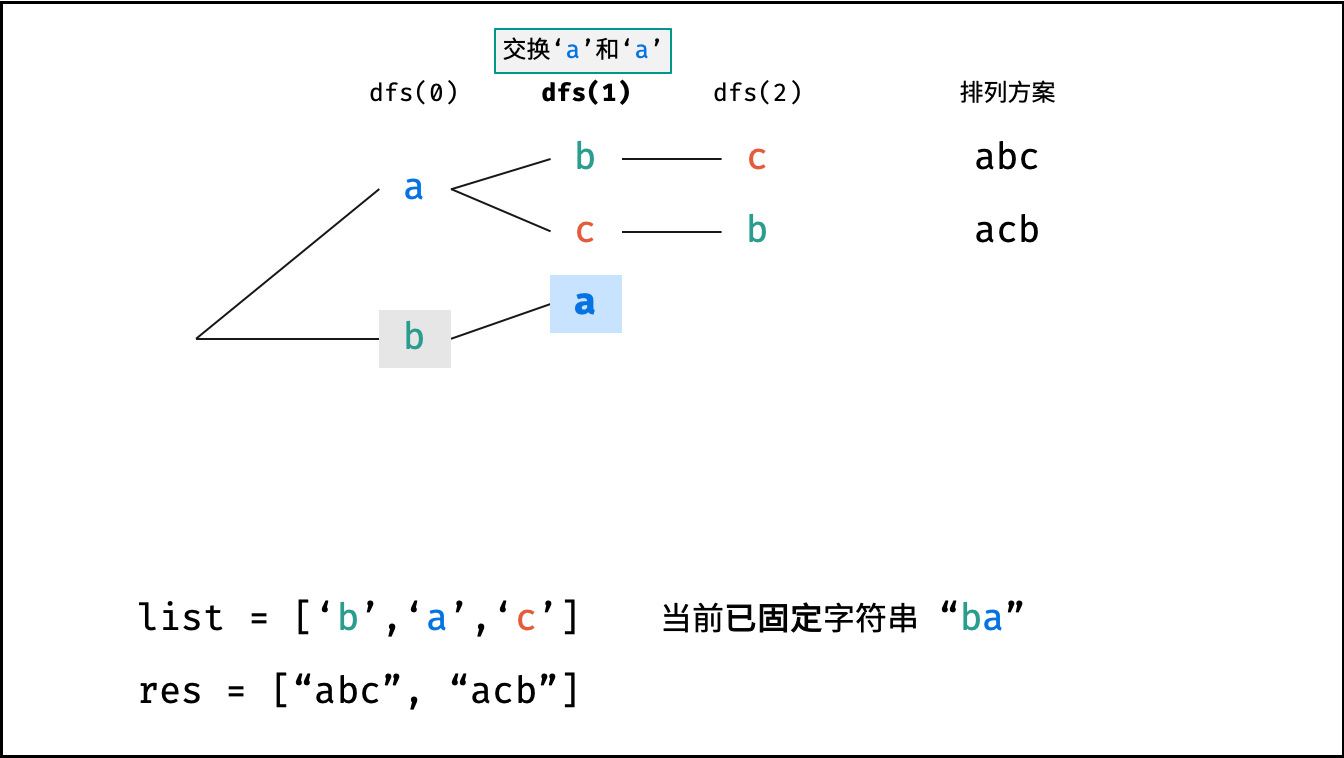
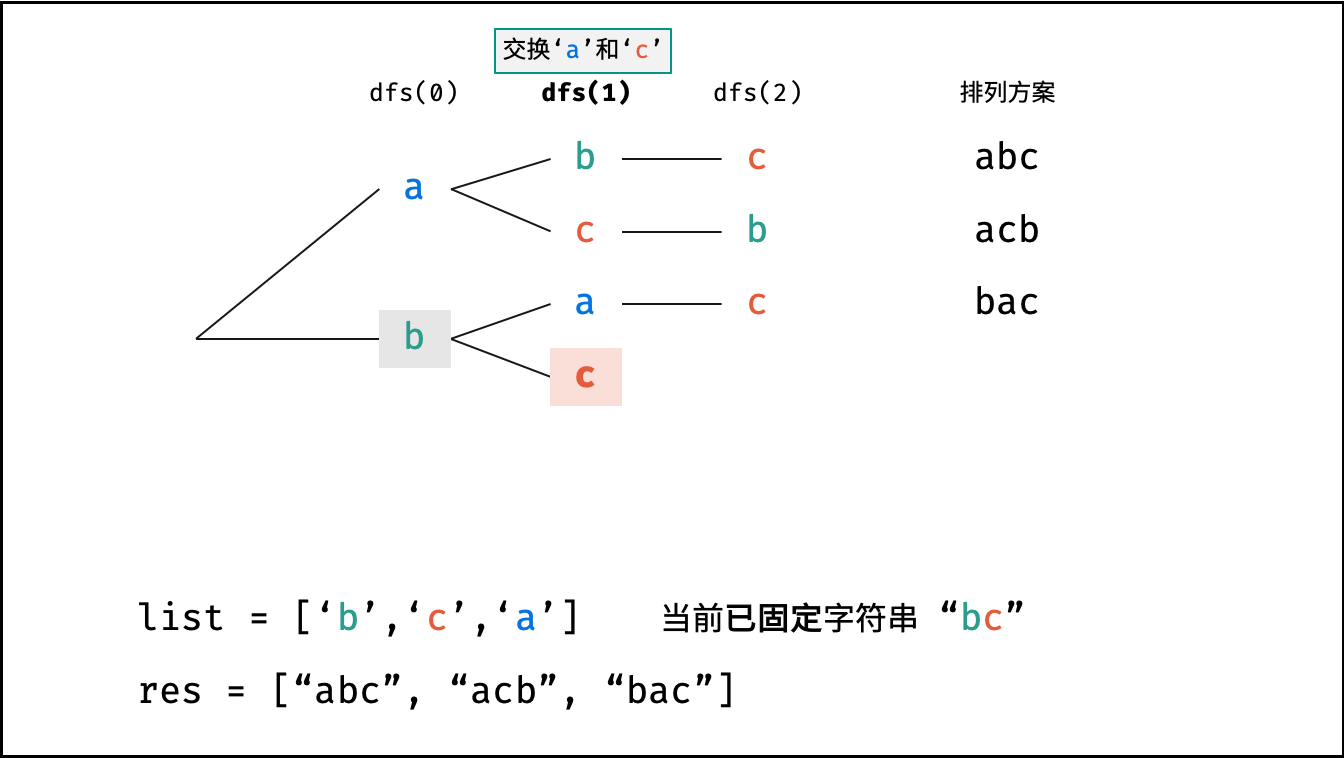
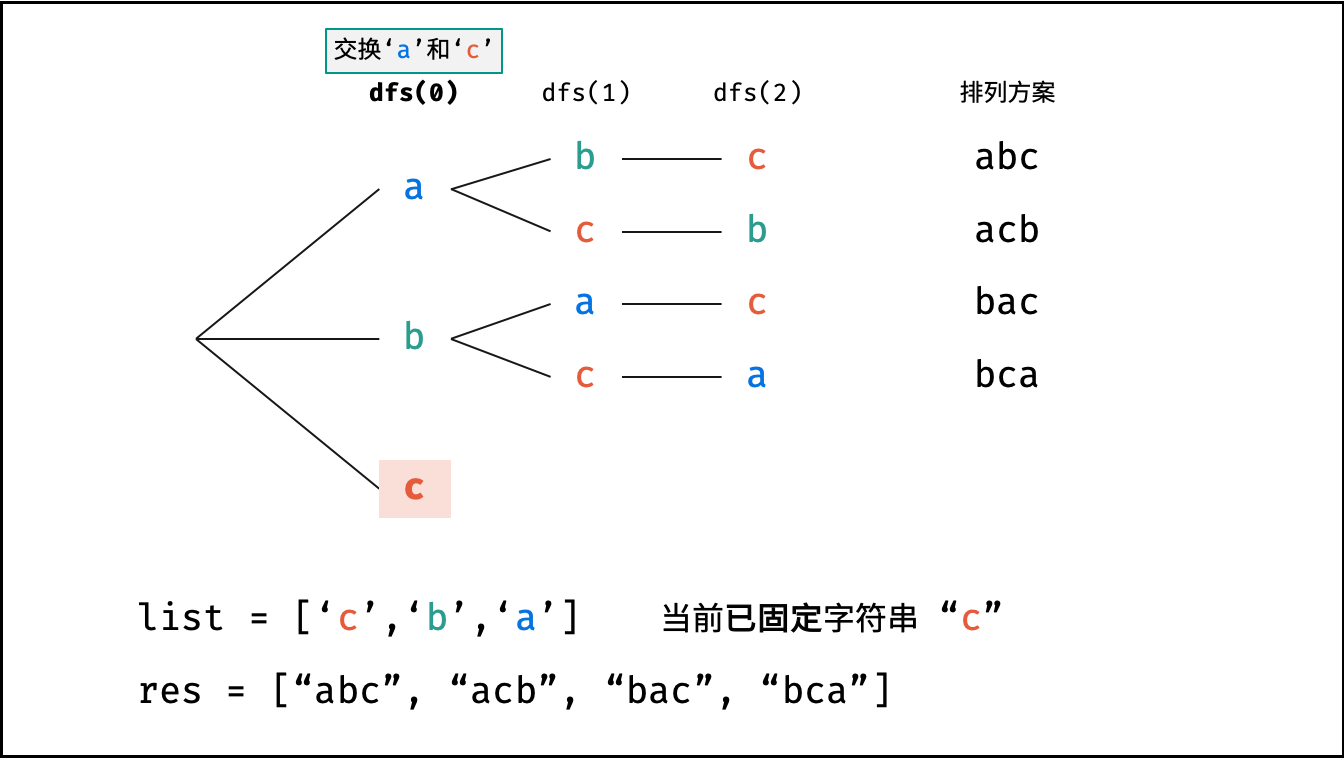
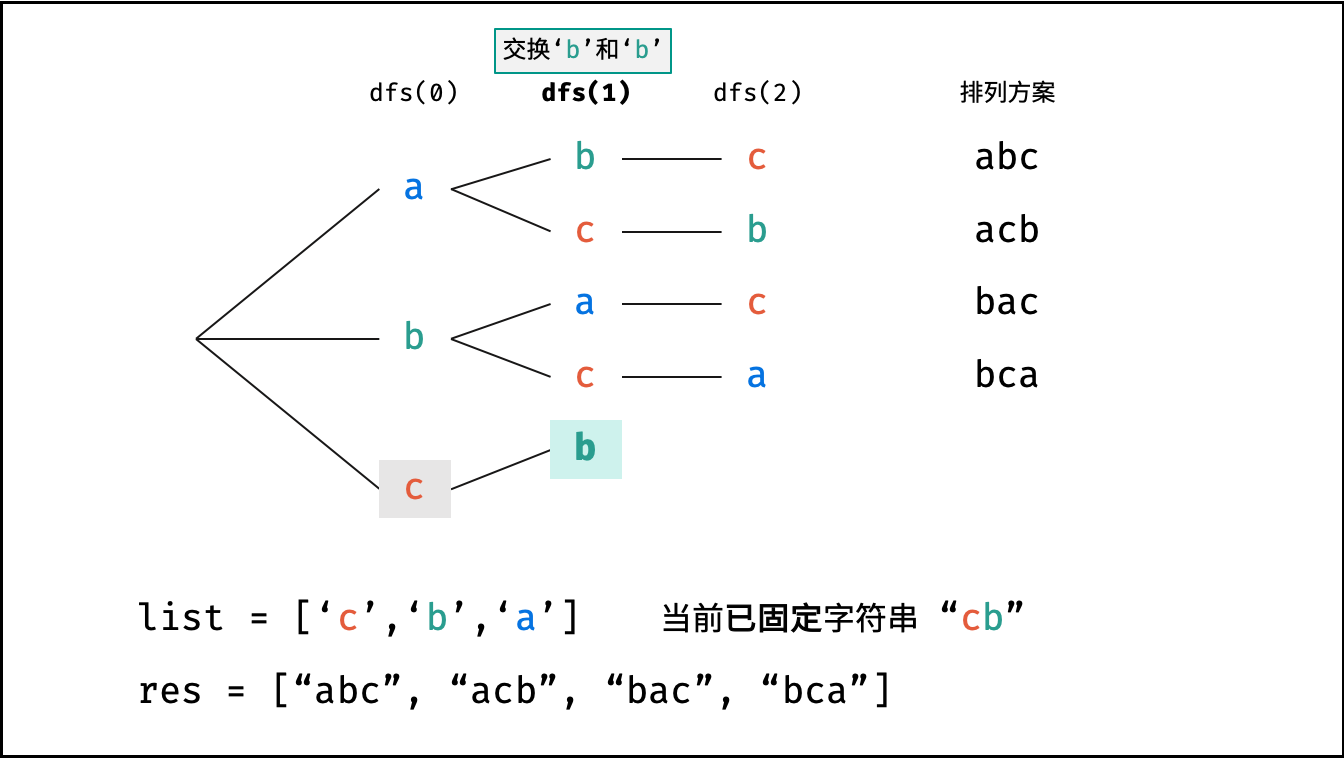
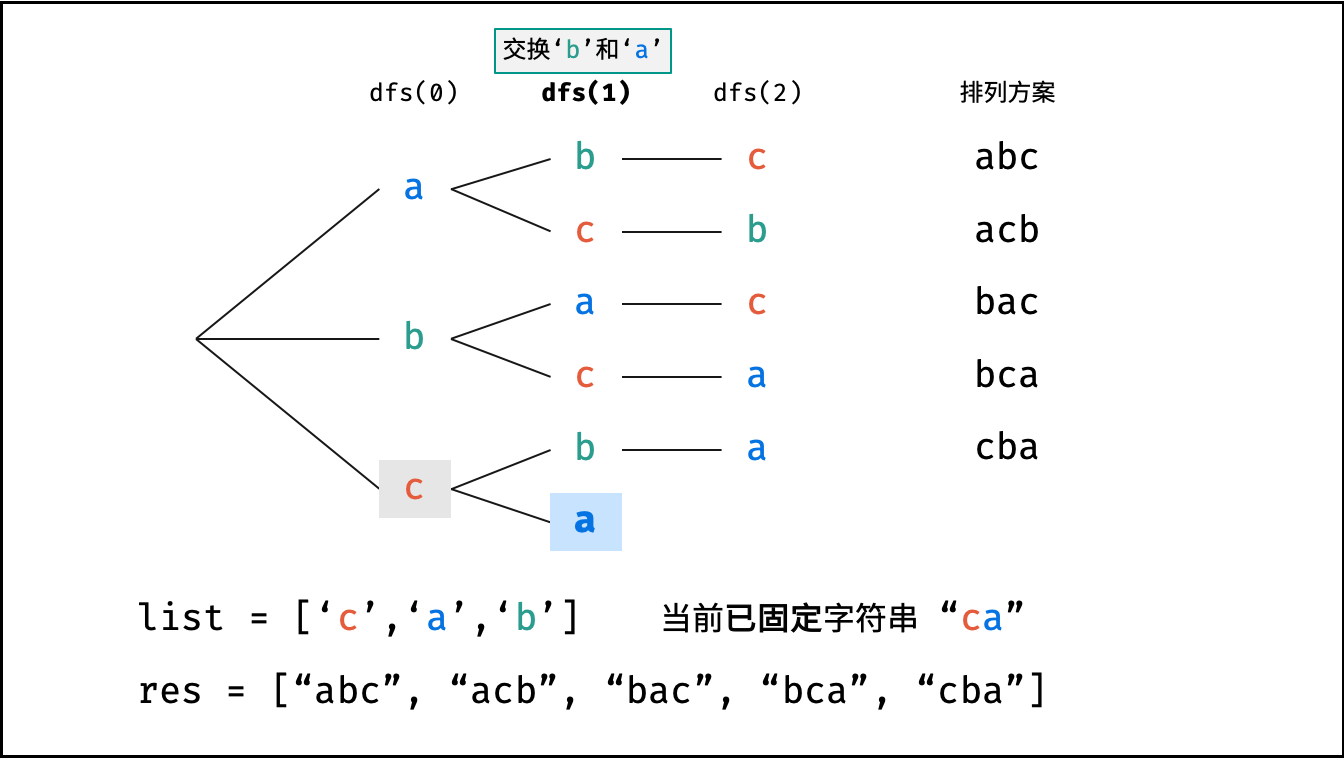
根据字符串排列的特点,考虑深度优先搜索所有排列方案。即通过字符交换,先固定第 $1$ 位字符( $n$ 种情况)、再固定第 $2$ 位字符( $n-1$ 种情况)、... 、最后固定第 $n$ 位字符( $1$ 种情况)。
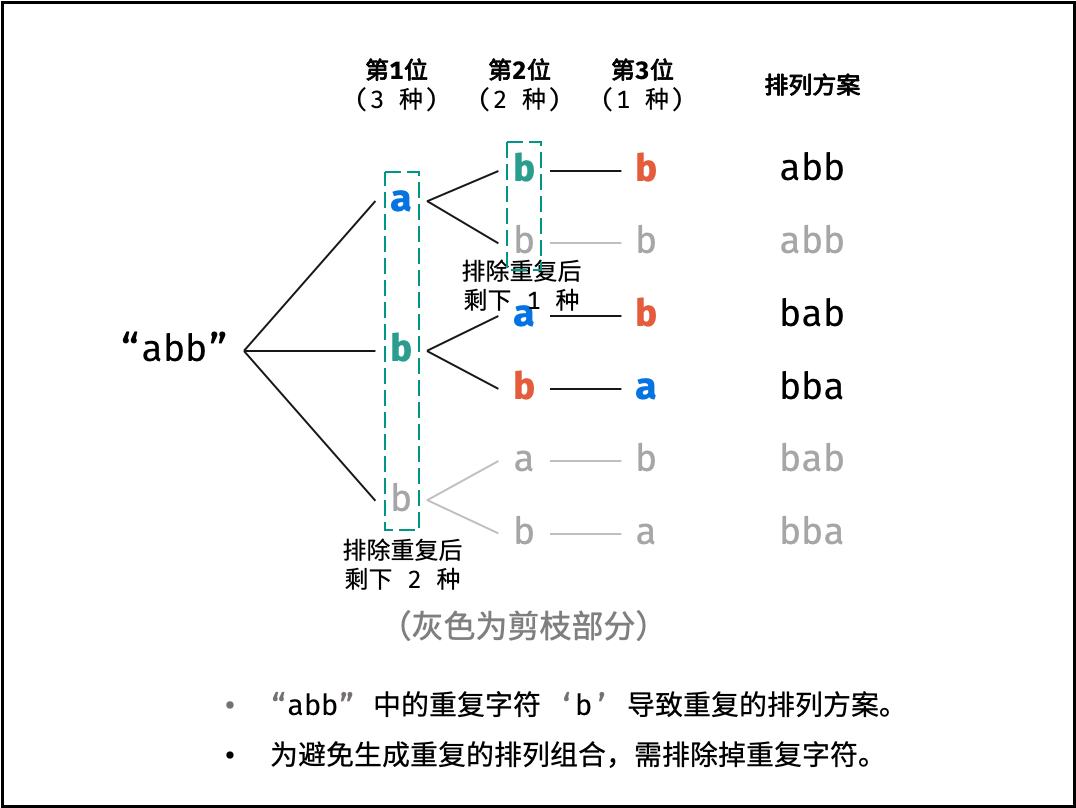
重复排列方案与剪枝:
当字符串存在重复字符时,排列方案中也存在重复的排列方案。为排除重复方案,需在固定某位字符时,保证 “每种字符只在此位固定一次” ,即遇到重复字符时不交换,直接跳过。从 DFS 角度看,此操作称为 “剪枝” 。
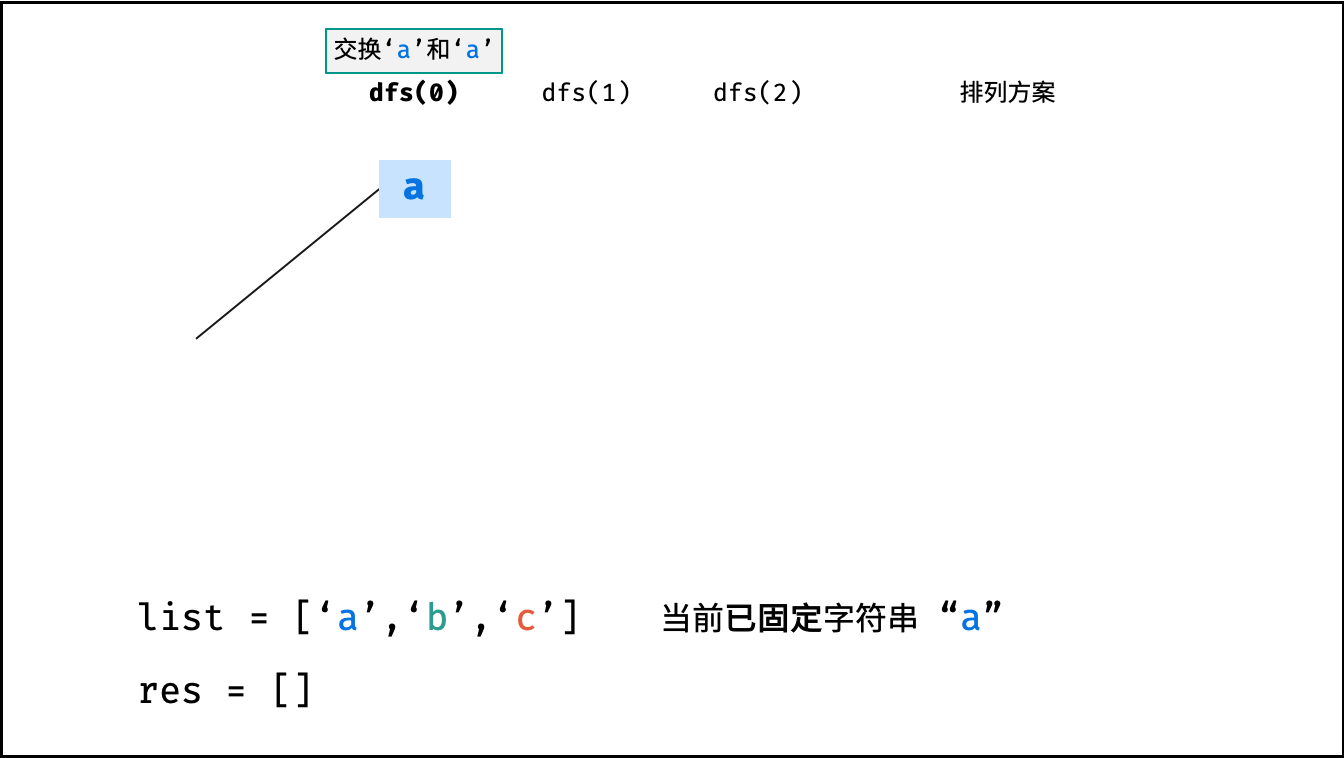
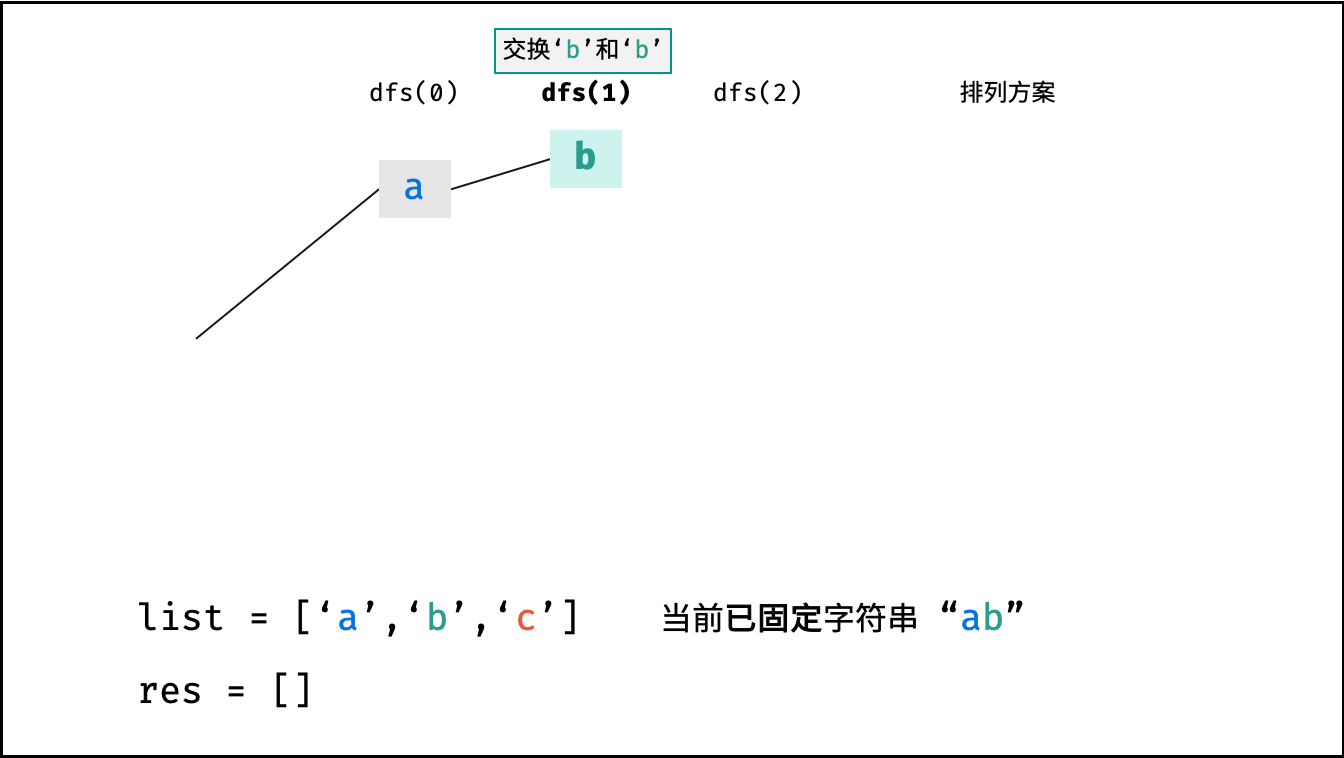
递归解析:
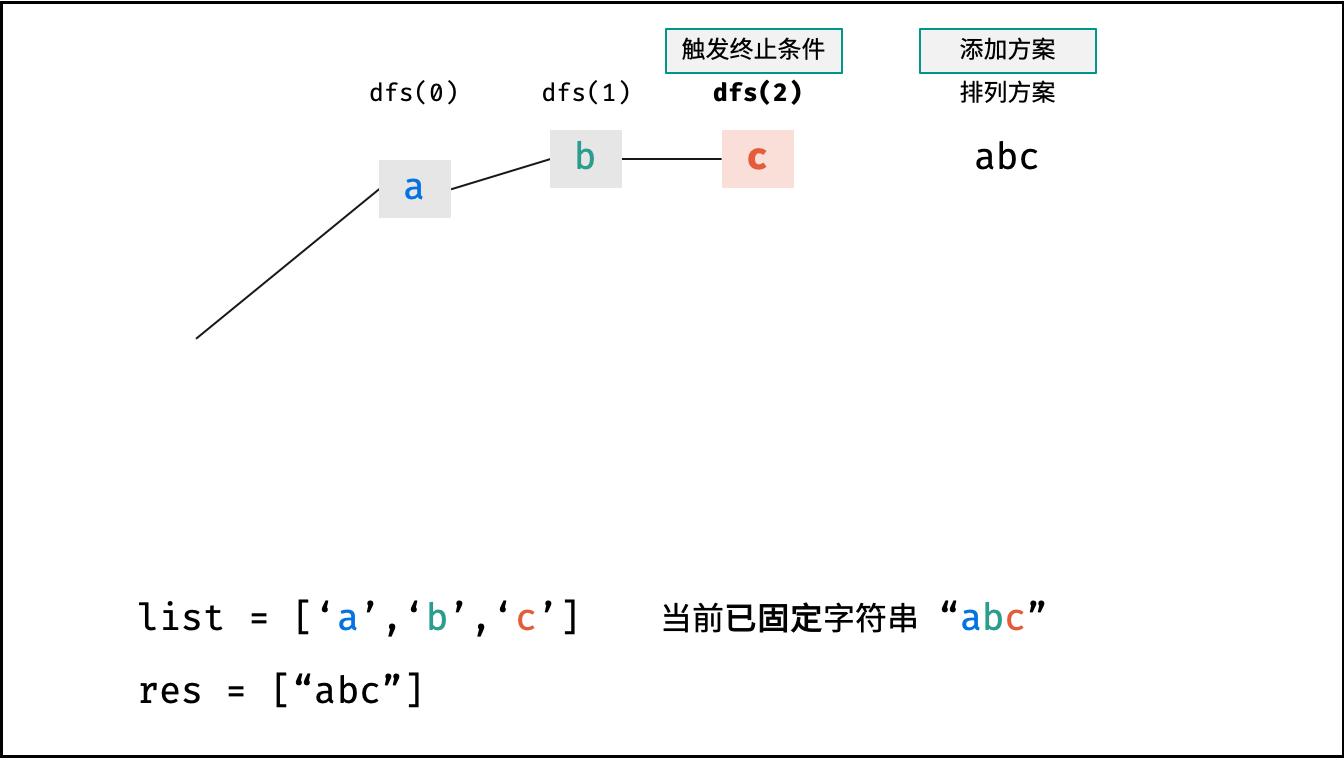
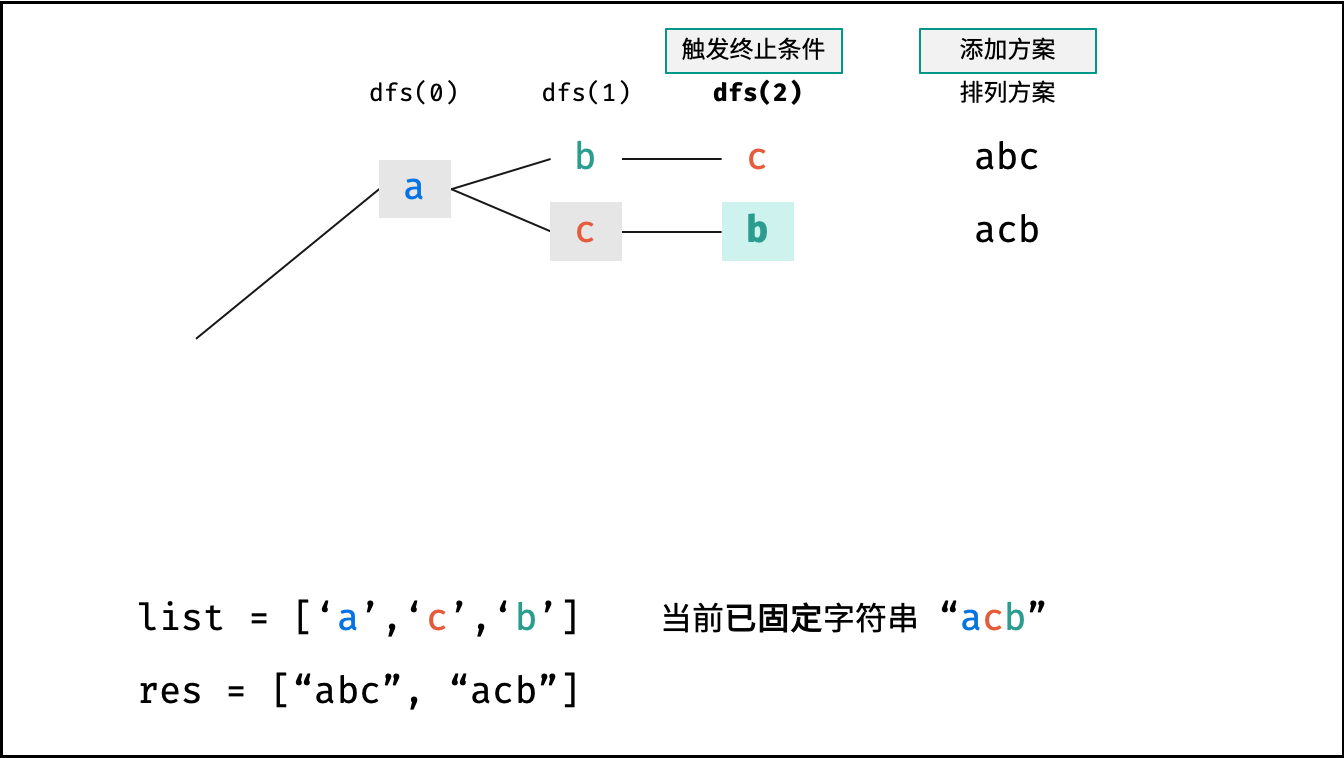
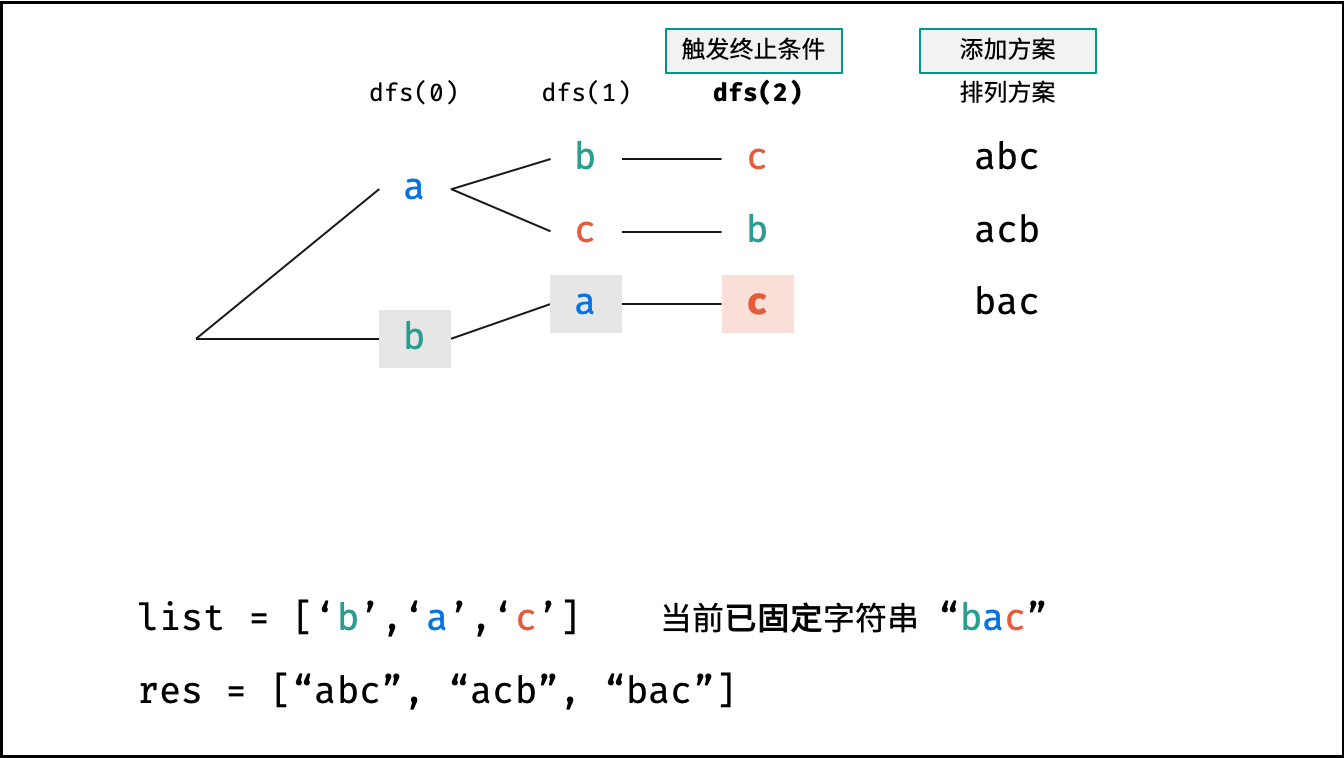
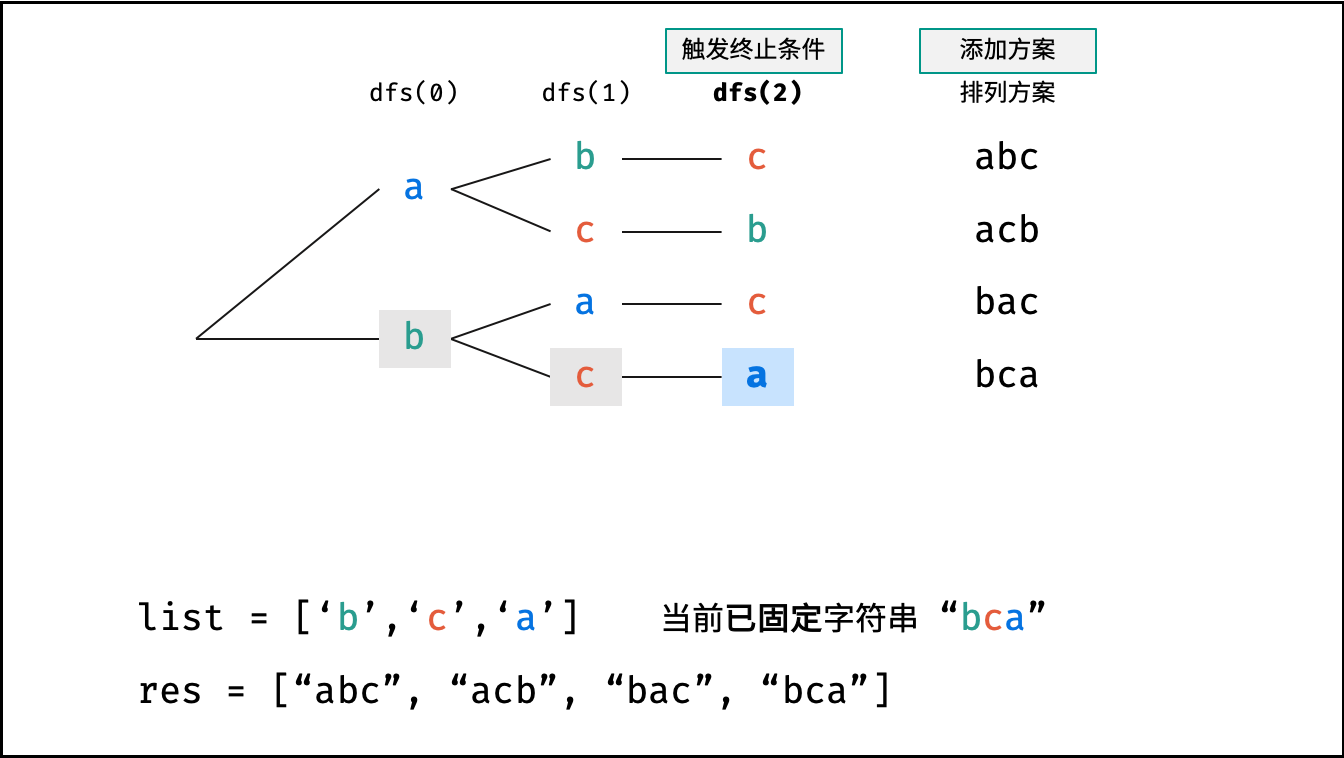
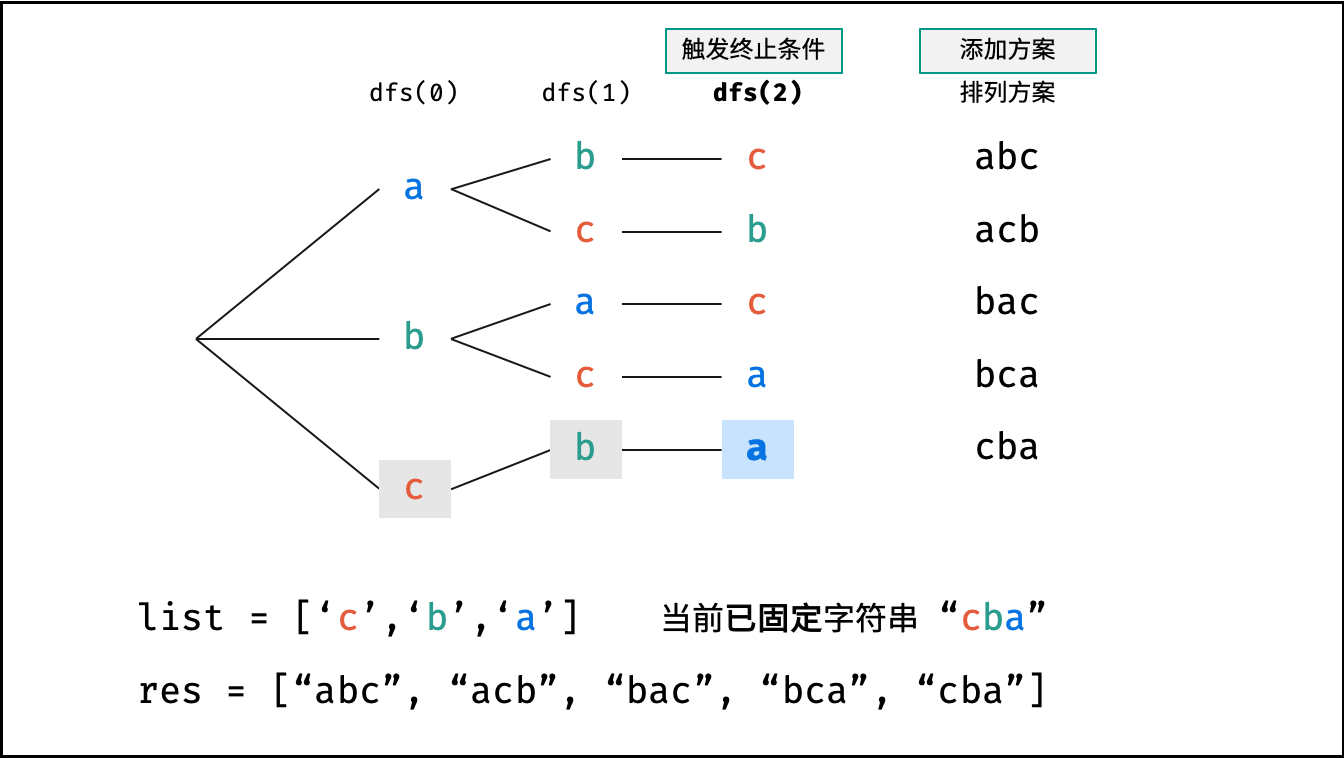
- 终止条件: 当
x = len(c) - 1时,代表所有位已固定(最后一位只有 $1$ 种情况),则将当前组合c转化为字符串并加入res,并返回; - 递推参数: 当前固定位
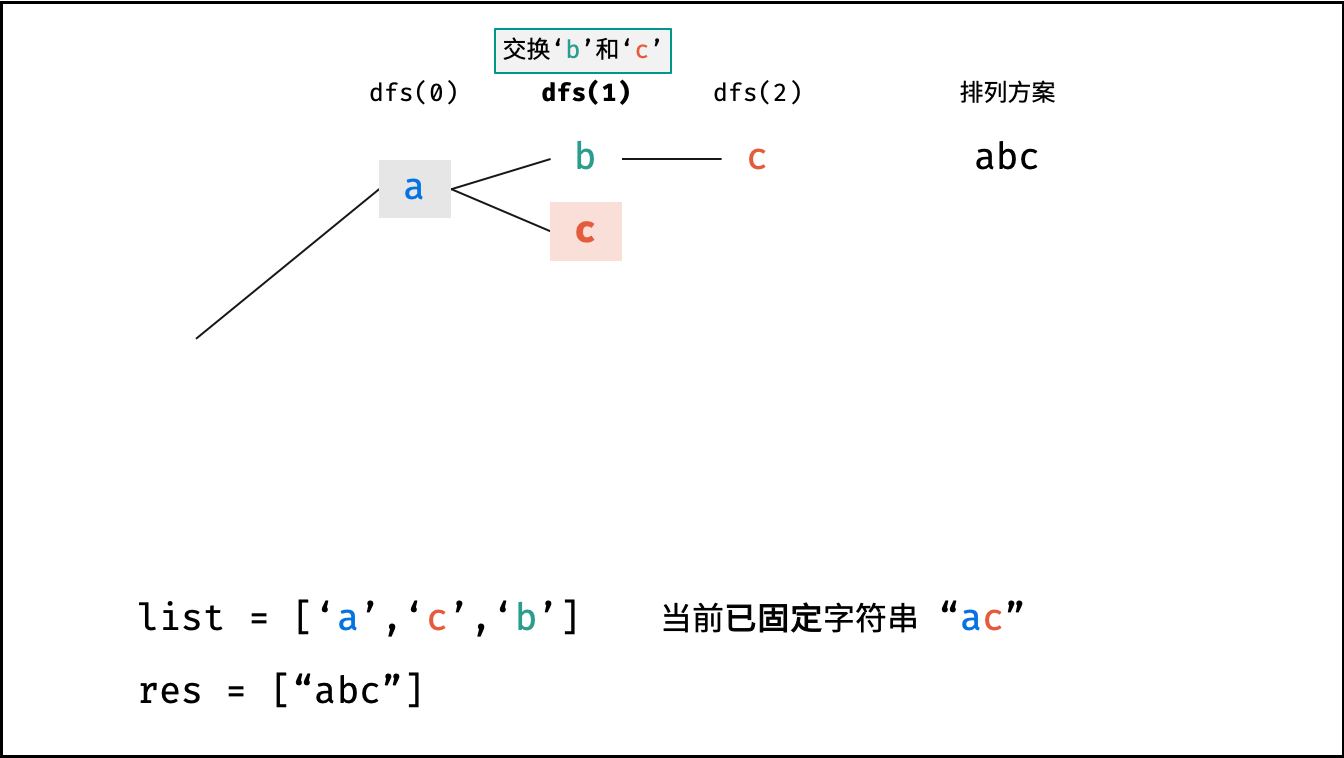
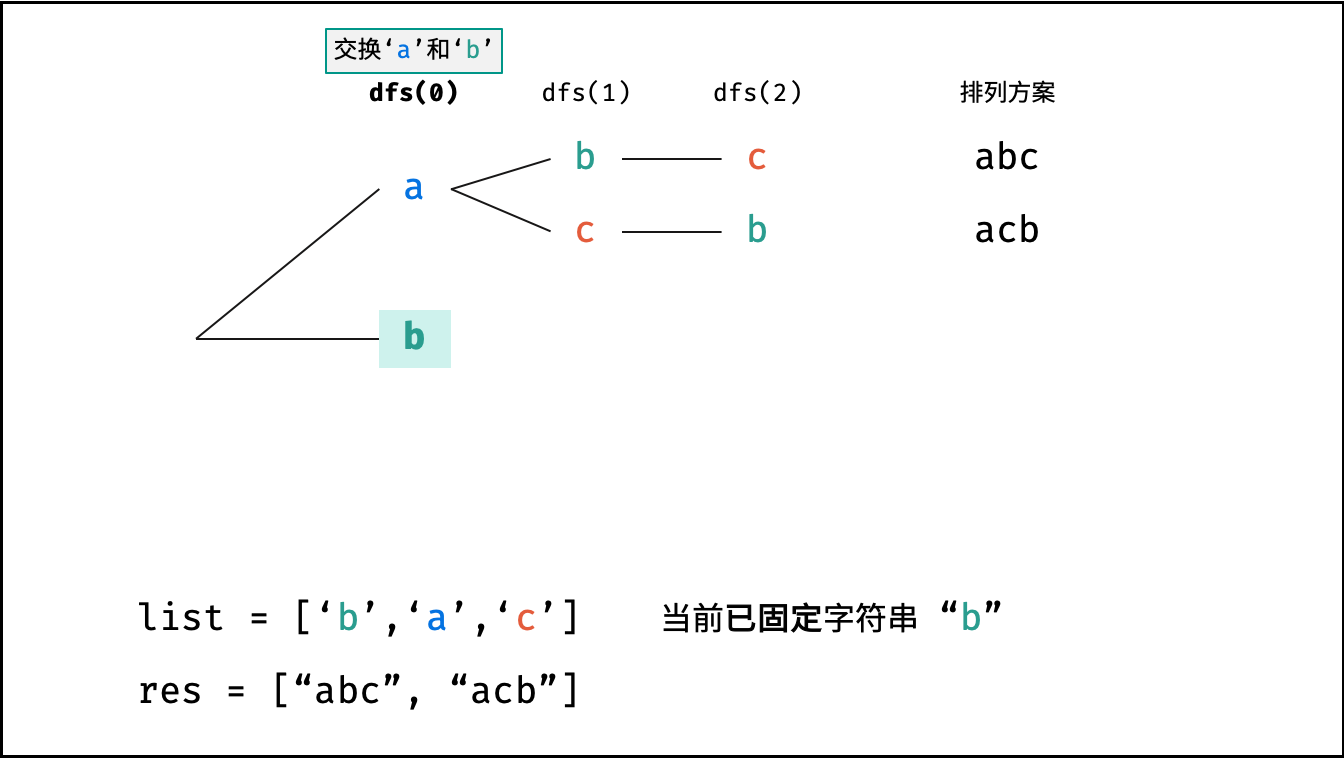
x; - 递推工作: 初始化一个 Set ,用于排除重复的字符;将第
x位字符与i$\in$[x, len(c)]字符分别交换,并进入下层递归;- 剪枝: 若
c[i]在 Set 中,代表其是重复字符,因此 “剪枝” ; - 将
c[i]加入 Set ,以便之后遇到重复字符时剪枝; - 固定字符: 将字符
c[i]和c[x]交换,即固定c[i]为当前位字符; - 开启下层递归: 调用
dfs(x + 1),即开始固定第x + 1个字符; - 还原交换: 将字符
c[i]和c[x]交换(还原之前的交换);
- 剪枝: 若
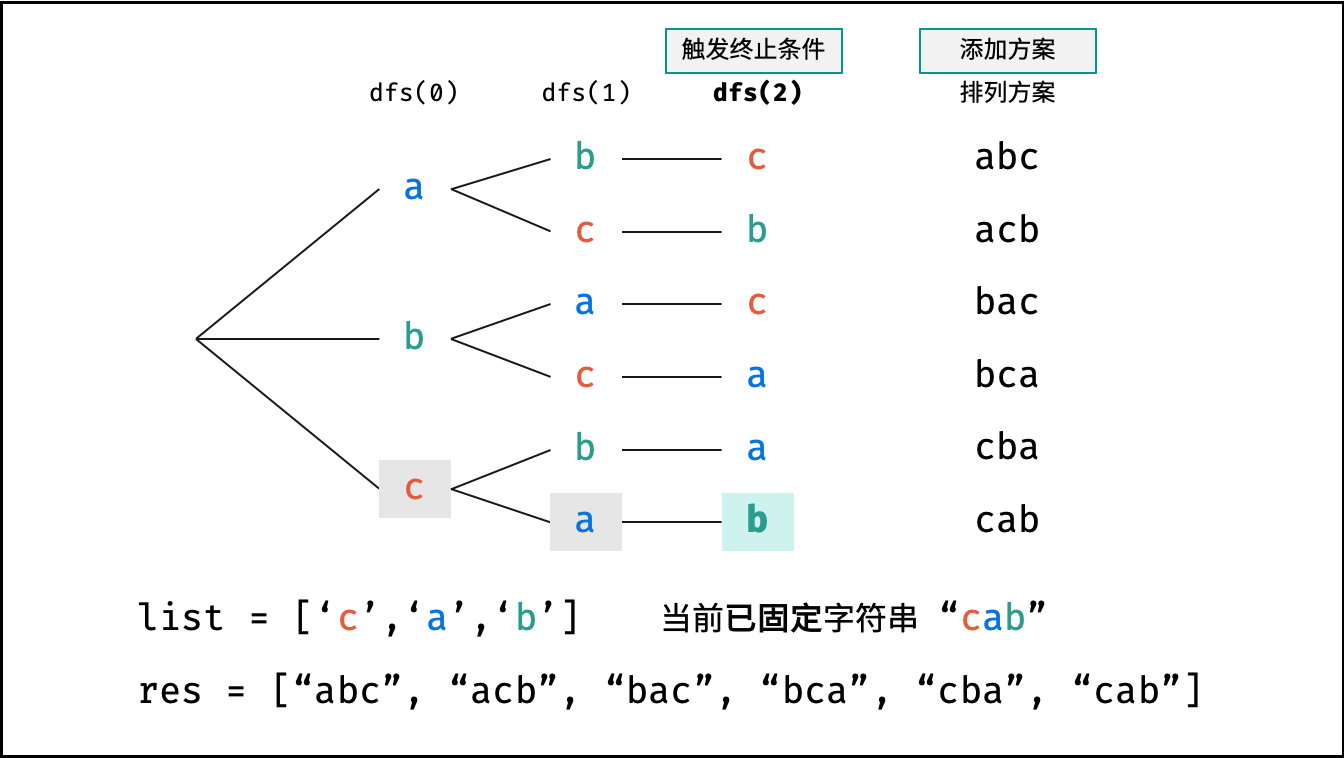
下图中
list对应文中的列表c。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N!N)$ : $N$ 为字符串
s的长度;时间复杂度和字符串排列的方案数成线性关系,方案数为 $N \times (N-1) \times (N-2) … \times 2 \times 1$ ,即复杂度为 $O(N!)$ ;字符串拼接操作join()使用 $O(N)$ ;因此总体时间复杂度为 $O(N!N)$ 。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N^2)$ : 全排列的递归深度为 $N$ ,系统累计使用栈空间大小为 $O(N)$ ;递归中辅助 Set 累计存储的字符数量最多为 $N + (N-1) + ... + 2 + 1 = (N+1)N/2$ ,即占用 $O(N^2)$ 的额外空间。
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def permutation(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
c, res = list(s), []
def dfs(x):
if x == len(c) - 1:
res.append(''.join(c)) # 添加排列方案
return
dic = set()
for i in range(x, len(c)):
if c[i] in dic: continue # 重复,因此剪枝
dic.add(c[i])
c[i], c[x] = c[x], c[i] # 交换,将 c[i] 固定在第 x 位
dfs(x + 1) # 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
c[i], c[x] = c[x], c[i] # 恢复交换
dfs(0)
return resJava
class Solution {
List<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
char[] c;
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();
dfs(0);
return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
}
void dfs(int x) {
if(x == c.length - 1) {
res.add(String.valueOf(c)); // 添加排列方案
return;
}
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = x; i < c.length; i++) {
if(set.contains(c[i])) continue; // 重复,因此剪枝
set.add(c[i]);
swap(i, x); // 交换,将 c[i] 固定在第 x 位
dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
swap(i, x); // 恢复交换
}
}
void swap(int a, int b) {
char tmp = c[a];
c[a] = c[b];
c[b] = tmp;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
dfs(s, 0);
return res;
}
private:
vector<string> res;
void dfs(string s, int x) {
if(x == s.size() - 1) {
res.push_back(s); // 添加排列方案
return;
}
set<int> st;
for(int i = x; i < s.size(); i++) {
if(st.find(s[i]) != st.end()) continue; // 重复,因此剪枝
st.insert(s[i]);
swap(s[i], s[x]); // 交换,将 s[i] 固定在第 x 位
dfs(s, x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
swap(s[i], s[x]); // 恢复交换
}
}
};