方法一:递归法
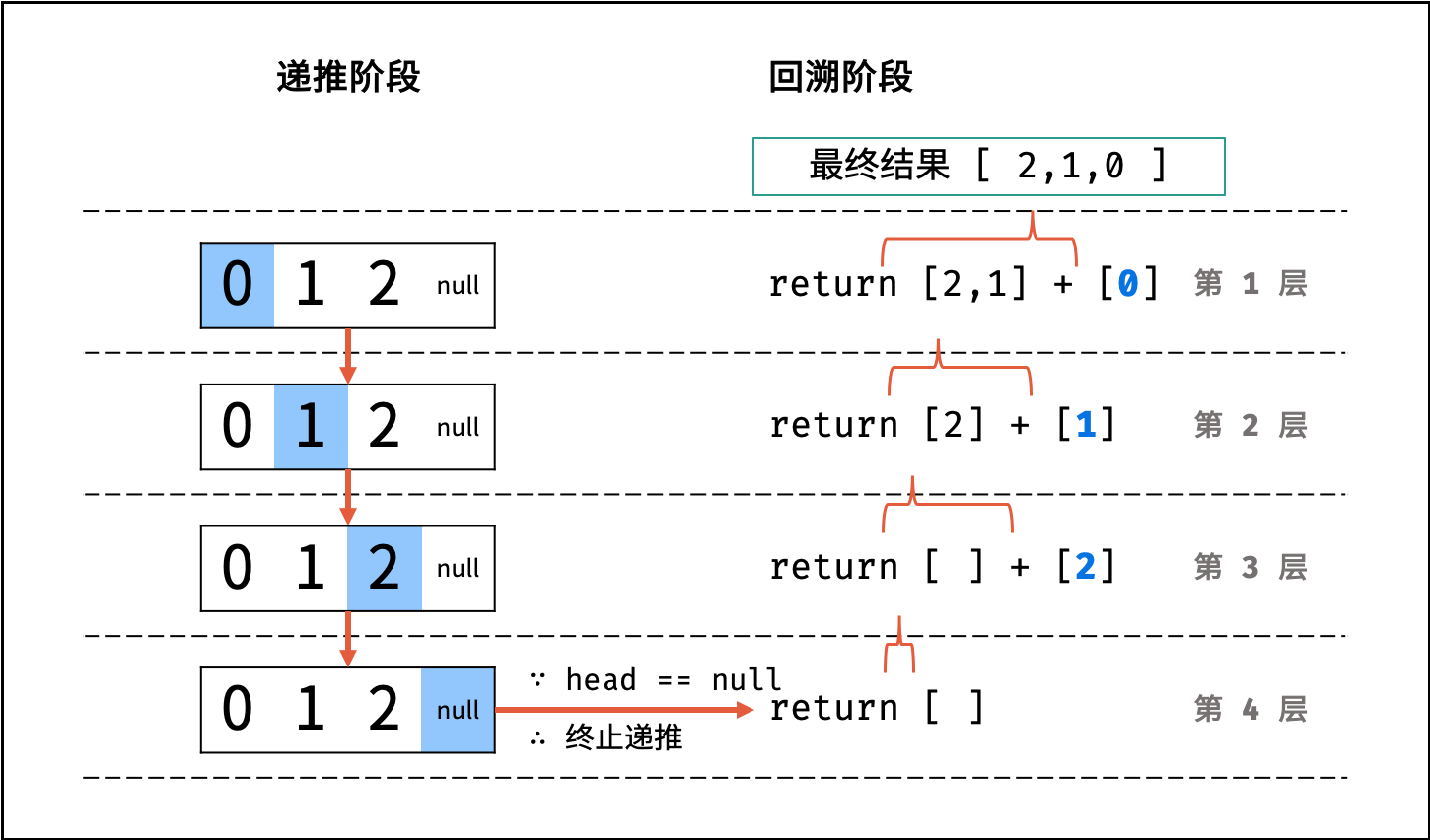
利用递归,先递推至链表末端;回溯时,依次将节点值加入列表,即可实现链表值的倒序输出。
递归解析:
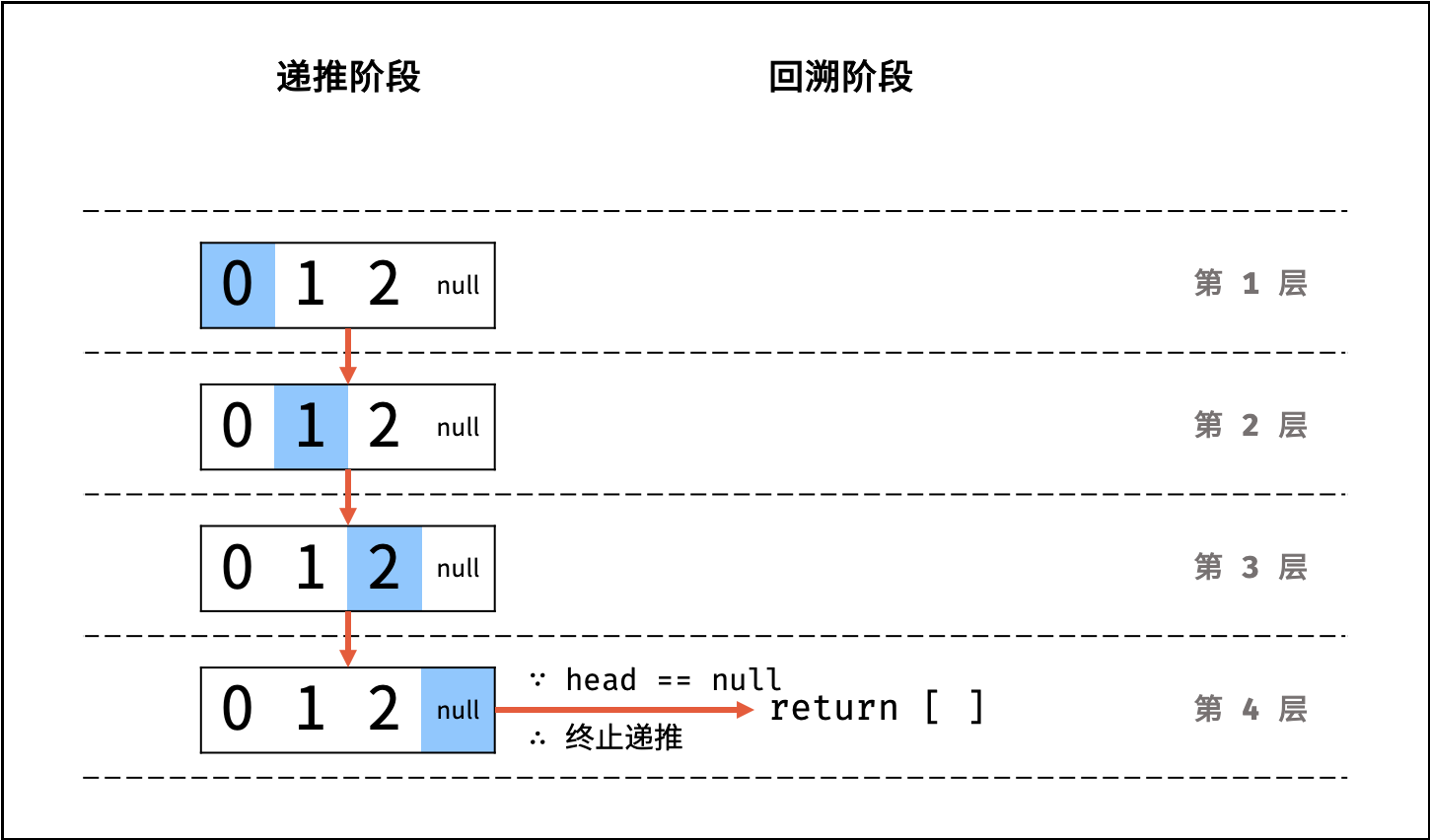
- 终止条件: 当
head == None时,代表越过了链表尾节点,则返回空列表; - 递推工作: 访问下一节点
head.next; - 回溯阶段:
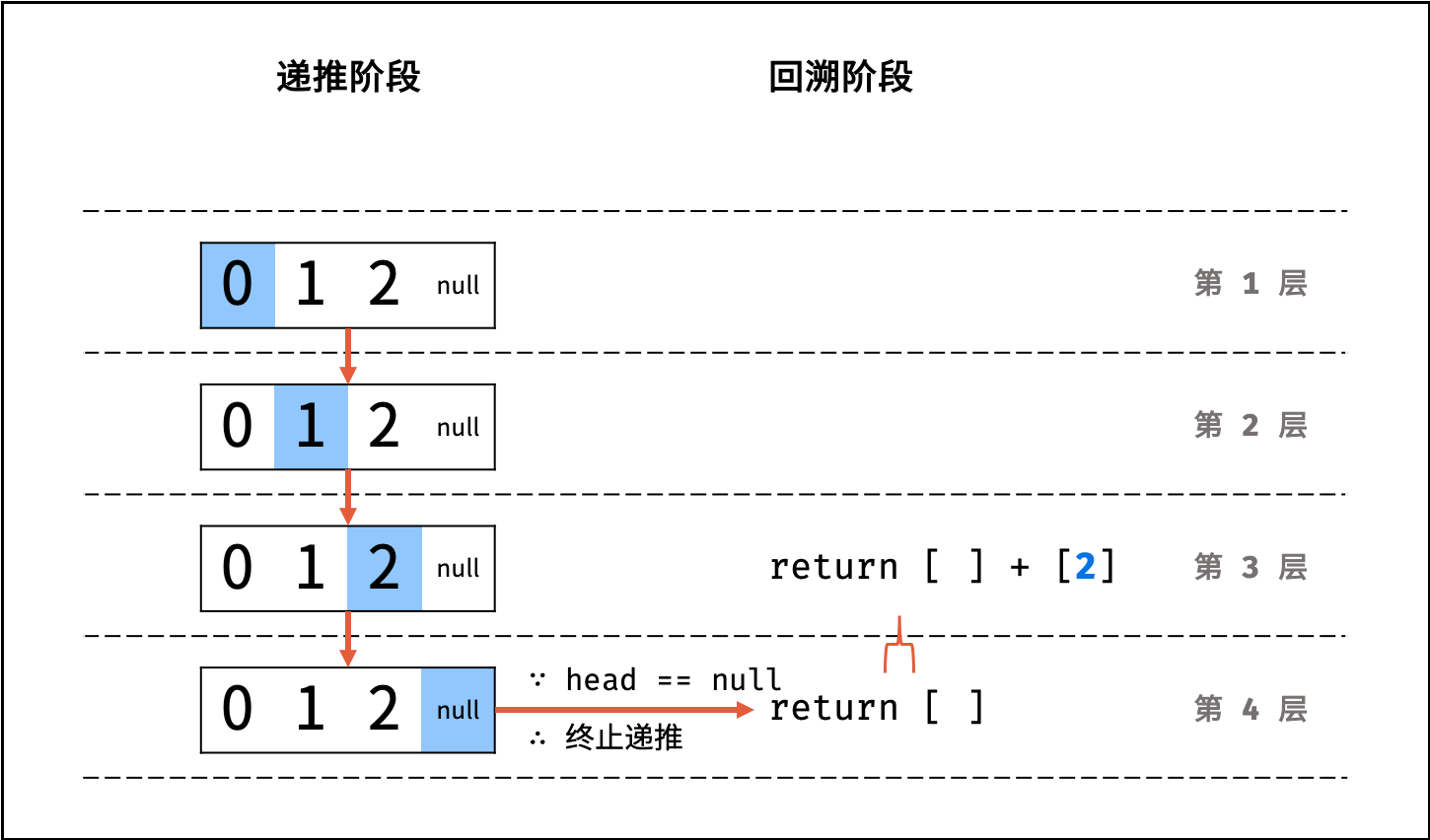
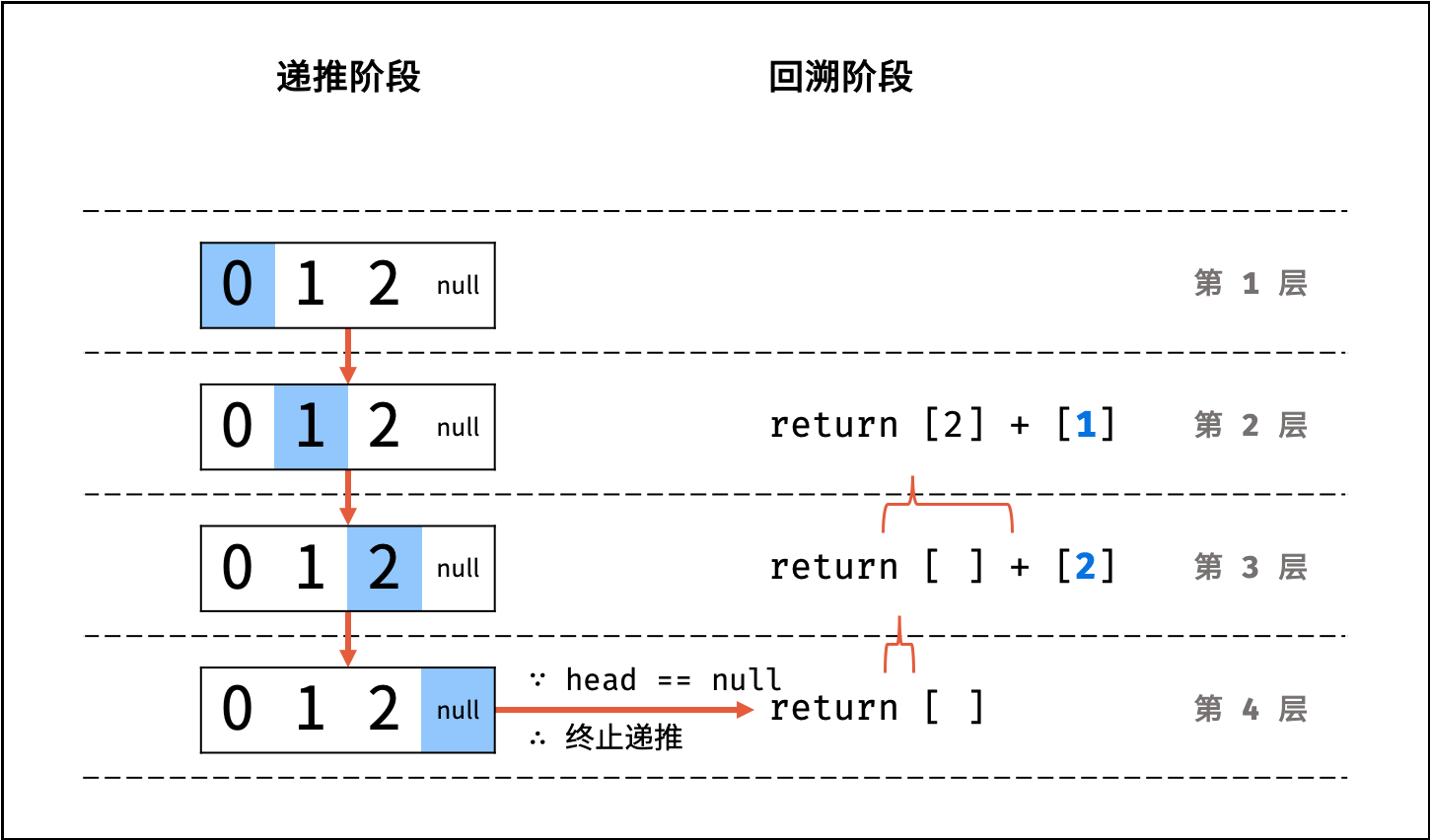
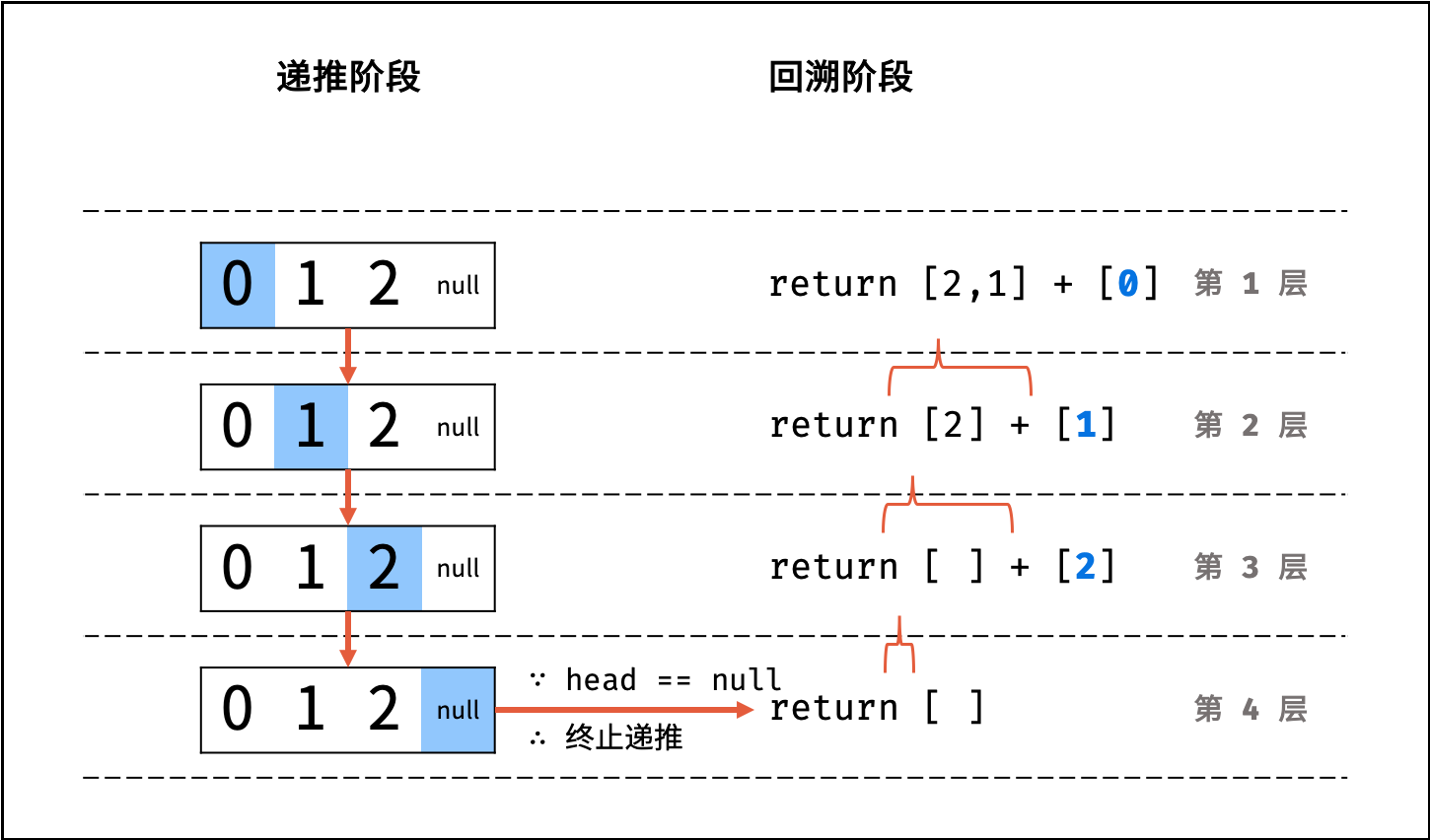
- Python: 返回
当前 list + 当前节点值 [head.val]; - Java / C++: 将当前节点值
head.val加入列表tmp;
- Python: 返回
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$: 遍历链表,递归 $N$ 次。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$: 系统递归需要使用 $O(N)$ 的栈空间。
图解以 Python 代码为例。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Python
class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:
return self.reversePrint(head.next) + [head.val] if head else []Java
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
recur(head);
int[] res = new int[tmp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = tmp.get(i);
return res;
}
void recur(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return;
recur(head.next);
tmp.add(head.val);
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
recur(head);
return res;
}
private:
vector<int> res;
void recur(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return;
recur(head->next);
res.push_back(head->val);
}
};方法二:辅助栈法
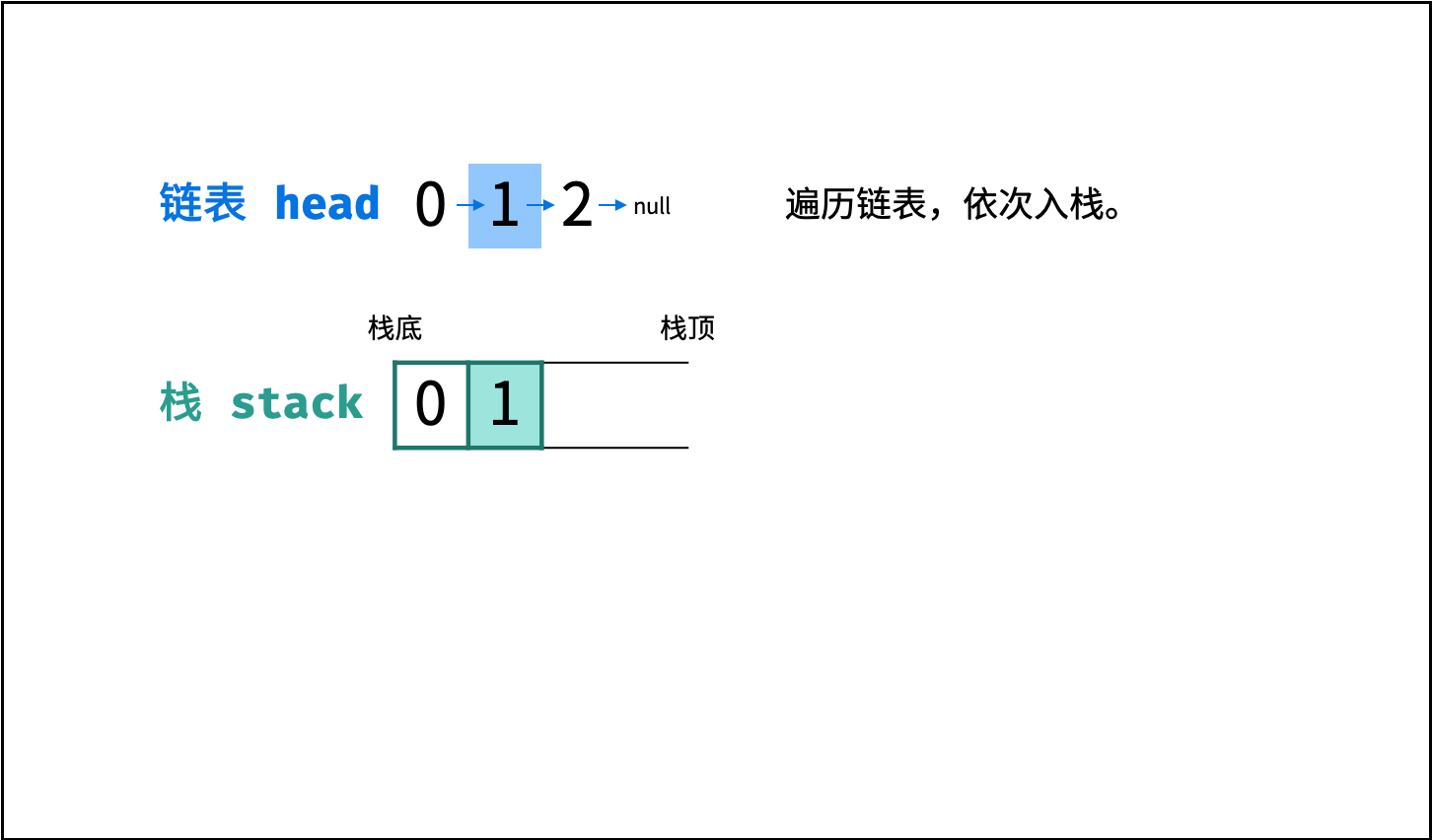
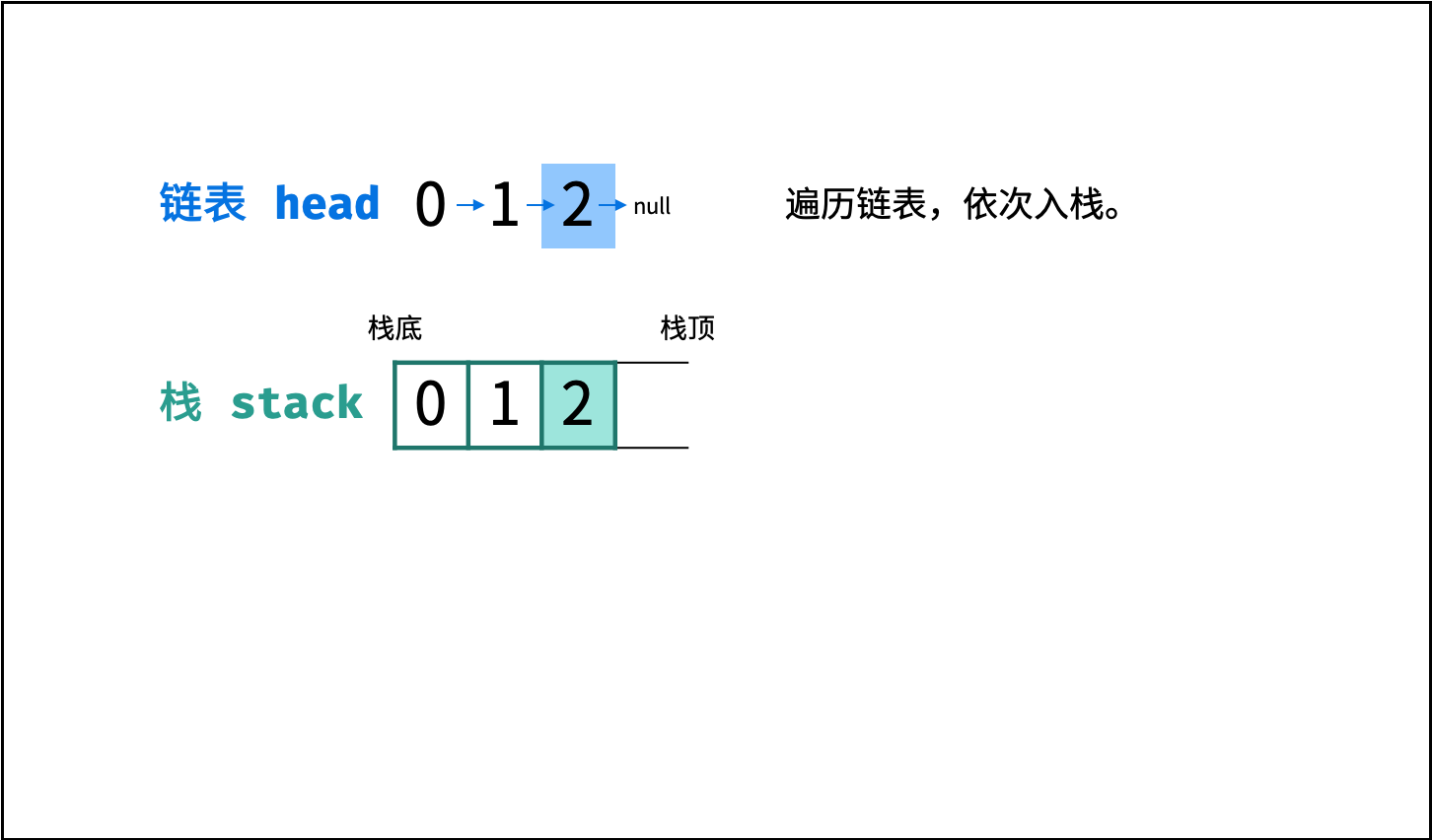
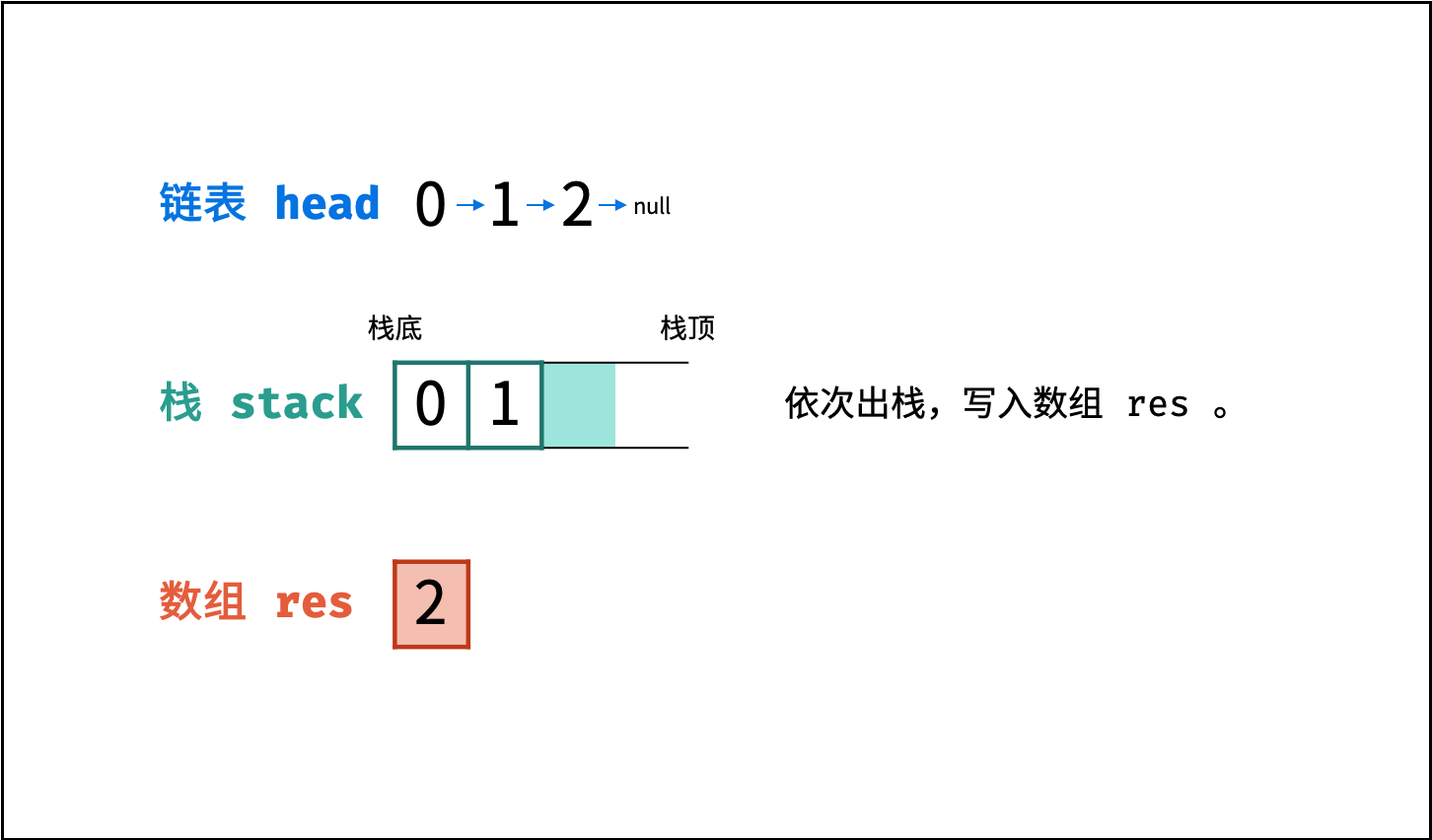
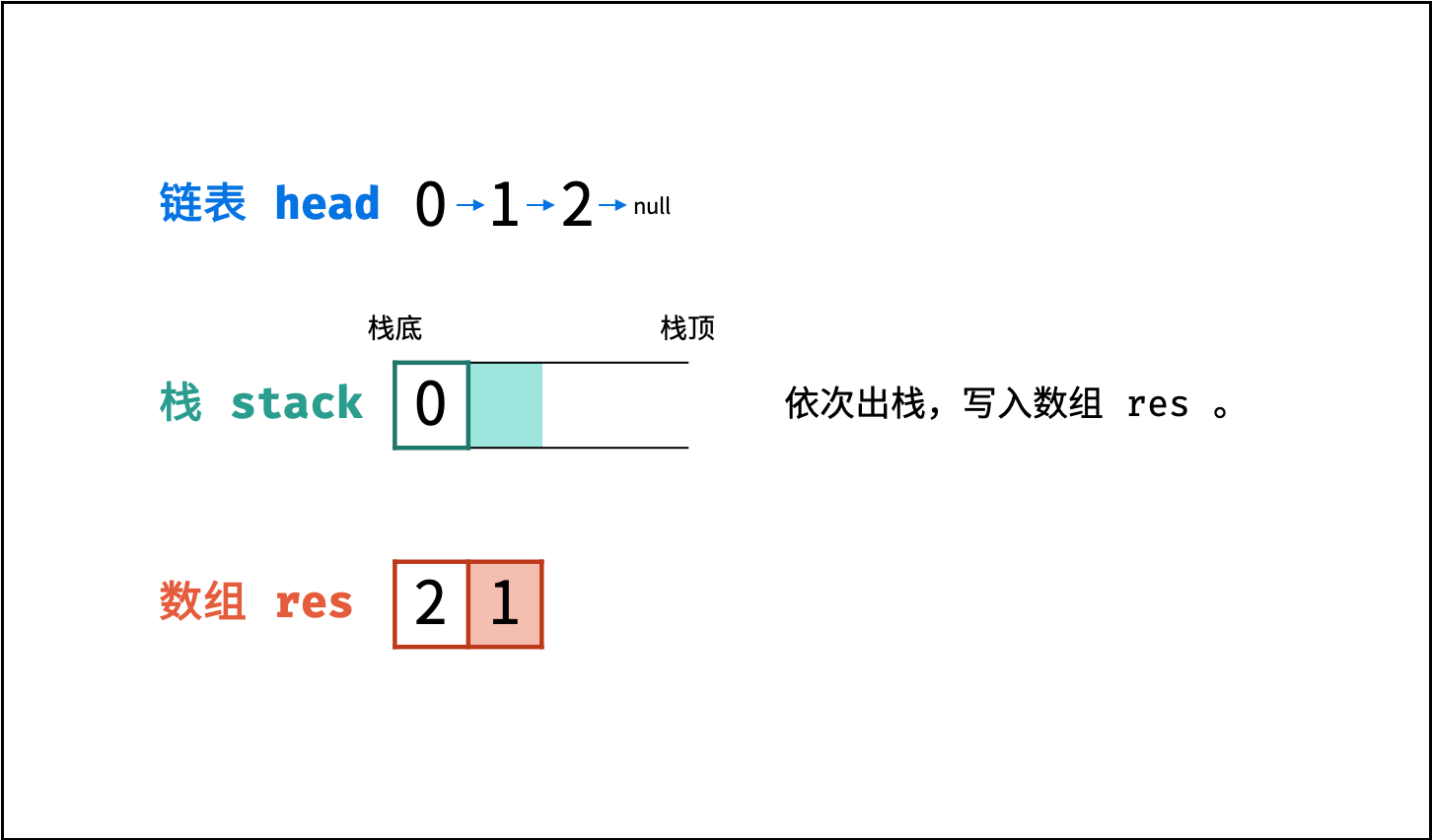
链表只能 从前至后 访问每个节点,而题目要求 倒序输出 各节点值,这种 先入后出 的需求可以借助 栈 来实现。
算法流程:
- 入栈: 遍历链表,将各节点值
push入栈。 - 出栈: 将各节点值
pop出栈,存储于数组并返回。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$: 入栈和出栈共使用 $O(N)$ 时间。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$: 辅助栈
stack和数组res共使用 $O(N)$ 的额外空间。
图解以 Java 代码为例,Python 无需将
stack转移至res,而是直接返回倒序数组。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
代码:
Java 数组长度不可变,因此使用 List 先存储,再转为数组并返回。
Python
class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:
stack = []
while head:
stack.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return stack[::-1]Java
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while(head != null) {
stack.addLast(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = stack.removeLast();
return res;
}
}C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
stack<int> stk;
while(head != nullptr) {
stk.push(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
vector<int> res;
while(!stk.empty()) {
res.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
return res;
}
};